在 Vaadin ComboBox教程中,我们学习 Vaadin ComboBox组件的基础知识。 Vaadin ComboBox示例在标签组件中显示选定的值。
Vaadin
Vaadin 是一种流行的 Java Web 开发框架,用于构建单页 Web 应用。
Vaadin ComboBox
ComboBox是允许从下拉列表中选择项目的选择组件。 在可编辑模式下,可以输入新值。
Vaadin ComboBox示例
以下程序演示了 Vaadin ComboBox组件的用法。 从ComboBox中选择的值显示在标签组件中。
NetBeans IDE 可用于轻松创建 Vaadin Web 应用。 我们需要安装 NetBeans Vaadin 插件,然后创建一个新的 Vaadin Web 应用项目。
MyUI.java
package com.zetcode.ui;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;import com.vaadin.annotations.Theme;import com.vaadin.annotations.Title;import com.vaadin.annotations.VaadinServletConfiguration;import com.vaadin.data.HasValue;import com.vaadin.server.VaadinRequest;import com.vaadin.server.VaadinServlet;import com.vaadin.ui.Alignment;import com.vaadin.ui.ComboBox;import com.vaadin.ui.HorizontalLayout;import com.vaadin.ui.Label;import com.vaadin.ui.UI;@Theme("mytheme")@Title("Vaadin ComboBox")public class MyUI extends UI {@Overrideprotected void init(VaadinRequest vaadinRequest) {HorizontalLayout layout = new HorizontalLayout();Label lbl = new Label();ComboBox<String> cb = new ComboBox<>();cb.setTextInputAllowed(false);cb.setItems("Ubuntu", "Debian", "Arch", "Mint");cb.setEmptySelectionAllowed(false);cb.addValueChangeListener((HasValue.ValueChangeEvent<String> event) -> {String item = event.getValue();lbl.setValue(item);});layout.addComponents(cb, lbl);layout.setComponentAlignment(lbl, Alignment.MIDDLE_CENTER);layout.setMargin(true);setContent(layout);}@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/*", name = "MyUIServlet", asyncSupported = true)@VaadinServletConfiguration(ui = MyUI.class, productionMode = false)public static class MyUIServlet extends VaadinServlet {}}
这是MyUI类。
HorizontalLayout layout = new HorizontalLayout();
在我们的示例中,我们使用HorizontalLayout连续显示两个组件。
Label lbl = new Label("");
Label组件不显示从组合框中选择的值。
ComboBox<String> cb = new ComboBox<>();
创建一个ComboBox组件。
cb.setTextInputAllowed(false);
使用setTextInputAllowed()方法,可以禁用ComboBox的可编辑模式。
cb.setItems("Ubuntu", "Debian", "Arch", "Mint");
使用setItems(),我们将四个字符串元素添加到ComboBox中。
cb.setEmptySelectionAllowed(false);
默认情况下,ComboBox显示一个空项目,允许用户不选择任何项目。 我们使用setEmptySelectionAllowed()禁用此选项。
cb.addValueChangeListener((HasValue.ValueChangeEvent<String> event) -> {String item = event.getValue();lbl.setValue(item);});
使用addValueChangeListener(),我们为ComboBox中的值更改添加了一个监听器。 我们用getValue()方法获得ComboBox当前选择的项目。 使用setValue()方法将检索到的值设置为标签。
layout.addComponents(cb, lbl);
通过addComponents()方法将这两个组件添加到HorizontalLayout。
layout.setComponentAlignment(lbl, Alignment.MIDDLE_CENTER);
我们将标签放置在setComponentAlignment()和Alignment.MIDDLE_CENTER对齐的行中间。
layout.setMargin(true);
我们在HorizontalLayout周围留了一些余量。
mytheme.scss
@import "../valo/valo.scss";@mixin mytheme {@include valo;.v-horizontal > .v-spacing {width: 2em;}}
我们增加了HorizontalLayout中组件之间的间距。
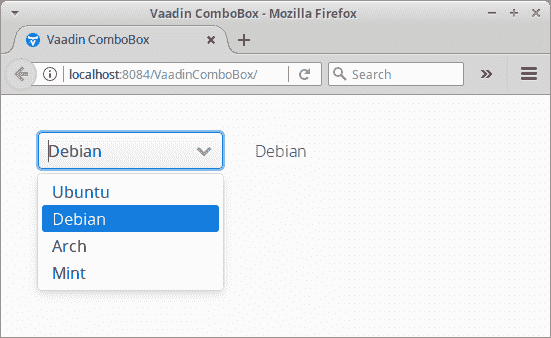
图:Vaadin ComboBox
Vaadin ComboBox示例 II
在第二个示例中,ComboBox填充了从服务方法中检索到的城市对象的列表。 使用setItemCaptionGenerator()产生ComboBox中显示的字符串。
City.java
package com.zetcode.bean;import java.io.Serializable;public class City implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;private Long id;private String name;private int population;public City() {}public City(Long id, String name, int population) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.population = population;}public Long getId() {return id;}public void setId(Long id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getPopulation() {return population;}public void setPopulation(int population) {this.population = population;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "City{" + "id=" + id + ", name=" + name +", population=" + population + '}';}}
这是City bean; 它包含id,name和population属性。
ICityService.java
package com.zetcode.service;import com.zetcode.bean.City;import java.util.List;public interface ICityService {public List<City> findAll();}
ICityService定义findAll()合约方法。
CityService.java
package com.zetcode.service;import com.zetcode.bean.City;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class CityService implements ICityService {@Overridepublic List<City> findAll() {List<City> cities = new ArrayList<>();cities.add(new City(1L, "Bratislava", 432000));cities.add(new City(2L, "Budapest", 1759000));cities.add(new City(3L, "Prague", 1280000));cities.add(new City(4L, "Warsaw", 1748000));cities.add(new City(5L, "Los Angeles", 3971000));cities.add(new City(6L, "New York", 8550000));cities.add(new City(7L, "Edinburgh", 464000));cities.add(new City(8L, "Berlin", 3671000));return cities;}}
CityService返回City对象的列表。
MyUI.java
package com.zetcode.ui;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;import com.vaadin.annotations.Theme;import com.vaadin.annotations.Title;import com.vaadin.annotations.VaadinServletConfiguration;import com.vaadin.data.HasValue;import com.vaadin.server.VaadinRequest;import com.vaadin.server.VaadinServlet;import com.vaadin.ui.Alignment;import com.vaadin.ui.ComboBox;import com.vaadin.ui.HorizontalLayout;import com.vaadin.ui.Label;import com.vaadin.ui.UI;import com.zetcode.bean.City;import com.zetcode.service.CityService;@Theme("mytheme")@Title("Vaadin ComboBox")public class MyUI extends UI {@Overrideprotected void init(VaadinRequest vaadinRequest) {CityService cityService = new CityService();HorizontalLayout layout = new HorizontalLayout();Label lbl = new Label();ComboBox<City> cb = new ComboBox<>();cb.setTextInputAllowed(false);cb.setItems(cityService.findAll());cb.setEmptySelectionAllowed(false);cb.setItemCaptionGenerator(City::getName);cb.addValueChangeListener((HasValue.ValueChangeEvent<City> event) -> {City city = event.getValue();String item = String.format("%s: %s", city.getName(),city.getPopulation());lbl.setValue(item);});layout.addComponents(cb, lbl);layout.setComponentAlignment(lbl, Alignment.MIDDLE_CENTER);layout.setMargin(true);setContent(layout);}@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/*", name = "MyUIServlet", asyncSupported = true)@VaadinServletConfiguration(ui = MyUI.class, productionMode = false)public static class MyUIServlet extends VaadinServlet {}}
这是MyUI类。
ComboBox<City> cb = new ComboBox<>();
创建参数化的ComboBox。
cb.setItems(cityService.findAll());
ComboBox中填充了服务方法中的数据。
cb.setItemCaptionGenerator(City::getName);
使用setItemCaptionGenerator(),我们选择要在ComboBox中显示为项目标签的城市名称。
cb.addValueChangeListener((HasValue.ValueChangeEvent<City> event) -> {City city = event.getValue();String item = String.format("%s: %s", city.getName(),city.getPopulation());lbl.setValue(item);});
在标签中,我们显示城市名称及其人口,并用冒号分隔。
在本教程中,我们展示了 Vaadin ComboBox组件的基础知识。 您可能也对相关教程感兴趣: Vaadin 网格教程, Vaadin Button教程, Vaadin 滑块教程, Vaadin CheckBox教程, Java 教程。

