在 Java SWT 教程的这一部分中,我们介绍Table小部件。 Table是细胞的二维网格。 可以将数据写入这些单元中的每一个中。 该小部件由电子表格应用引入。
Table可以显示列标题,并且当单元格很多时,Table可以显示滚动条。
空表
第一个示例创建一个简单的空表。
TableEx.java
package com.zetcode;import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridData;import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridLayout;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableItem;/*** ZetCode Java SWT tutorial** In this program, we create a simple, empty* table widget.** Author: Jan Bodnar* Website: zetcode.com* Last modified: June 2015*/public class TableEx {public TableEx(Display display) {initUI(display);}@SuppressWarnings("unused")private void initUI(Display display) {Shell shell = new Shell(display);shell.setLayout(new GridLayout());Table table = new Table(shell, SWT.BORDER);table.setHeaderVisible(true);table.setLinesVisible(true);GridData data = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);data.heightHint = 300;data.widthHint = 350;table.setLayoutData(data);String[] titles = { "A", "B", "C" };for (int i = 0; i < titles.length; i++) {TableColumn column = new TableColumn(table, SWT.CENTER);column.setWidth(120);column.setText(titles[i]);}for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {TableItem item = new TableItem(table, SWT.NONE);}shell.setText("Empty table");shell.pack();shell.open();while (!shell.isDisposed()) {if (!display.readAndDispatch())display.sleep();}}@SuppressWarnings("unused")public static void main(String[] args) {Display display = new Display();TableEx ex = new TableEx(display);display.dispose();}}
该代码示例创建一个具有三列和十五行的表小部件。 表单元为空。
Table table = new Table(shell, SWT.BORDER);
创建Table小部件的实例。
table.setHeaderVisible(true);
setHeaderVisible()使表格标题可见。 标题由表列名称组成。
table.setLinesVisible(true);
setLinesVisible()显示表格单元格的边框。 默认情况下,单元格不可见。
String[] titles = { "A", "B", "C" };
这些是列标题。
for (int i = 0; i < titles.length; i++) {TableColumn column = new TableColumn(table, SWT.CENTER);column.setWidth(120);column.setText(titles[i]);}
在此for循环中,我们创建表列。 TableColumn的实例表示表窗口小部件中的一列。 setWidth()设置列的宽度,setText()方法设置列的名称。
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {TableItem item = new TableItem(table, SWT.NONE);}
TableItem代表表中的一行。 这段代码创建了十五个空单元格。
图:空表
用数据填充单元格
在第二个示例中,表格单元格显示一些数据。
TableEx2.java
package com.zetcode;import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableItem;/*** ZetCode Java SWT tutorial** In this program, we fill table cells* with data.** Author: Jan Bodnar* Website: zetcode.com* Last modified: June 2015*/public class TableEx2 {public TableEx2(Display display) {initUI(display);}private void initUI(Display display) {Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);shell.setLayout(new FillLayout());Table table = new Table(shell, SWT.BORDER);table.setHeaderVisible(true);table.setLinesVisible(true);TableColumn tc1 = new TableColumn(table, SWT.CENTER);TableColumn tc2 = new TableColumn(table, SWT.CENTER);TableColumn tc3 = new TableColumn(table, SWT.CENTER);tc1.setText("First Name");tc2.setText("Last Name");tc3.setText("Profession");tc1.setWidth(70);tc2.setWidth(70);tc3.setWidth(80);TableItem item1 = new TableItem(table, SWT.NONE);item1.setText(new String[] { "Jane", "Brown", "Accountant" });TableItem item2 = new TableItem(table, SWT.NONE);item2.setText(new String[] { "Tim", "Warner", "Lawyer" });TableItem item3 = new TableItem(table, SWT.NONE);item3.setText(new String[] { "Bob", "Milton", "Police officer" });shell.setText("Table widget");shell.pack();shell.open();while (!shell.isDisposed()) {if (!display.readAndDispatch())display.sleep();}}@SuppressWarnings("unused")public static void main(String[] args) {Display display = new Display();TableEx2 ex = new TableEx2(display);display.dispose();}}
该示例显示了具有三列三行的表格小部件。 单元格充满数据。
TableItem item1 = new TableItem(table, SWT.NONE);item1.setText(new String[] { "Jane", "Brown", "Accountant" });
setText()方法用数据填充一行的所有三个单元格。
图:带有数据的表格单元
选择表格行
以下示例介绍了表格项目的选择。
TableEx3.java
package com.zetcode;import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridData;import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridLayout;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Label;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableItem;/*** ZetCode Java SWT tutorial** In this program, we show the data from* the selected row in the statusbar.** Author: Jan Bodnar* Website: zetcode.com* Last modified: June 2015*/public class TableEx3 {private Label label;private final String data[][] = { { "Ferarri", "33333" },{ "Skoda", "22000" }, { "Volvo", "18000" }, { "Mazda", "15000" },{ "Mercedes", "38000" } };public TableEx3(Display display) {initUI(display);}private void initUI(Display display) {Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);shell.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, true));Table table = new Table(shell, SWT.BORDER);table.setHeaderVisible(true);table.setLinesVisible(true);String[] titles = { "Car", "Price" };for (int i = 0; i & titles.length; i++) {TableColumn column = new TableColumn(table, SWT.NULL);column.setText(titles[i]);column.setWidth(130);}for (int i = 0; i & data.length; i++) {TableItem item = new TableItem(table, SWT.NULL);item.setText(0, data[i][0]);item.setText(1, data[i][1]);}label = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);table.addListener(SWT.Selection, event -> onTableItemSelected(table));GridData gd = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);gd.widthHint = 360;gd.heightHint = 300;table.setLayoutData(gd);label.setLayoutData(new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.CENTER, true, false));shell.setText("Table widget");shell.pack();shell.open();while (!shell.isDisposed()) {if (!display.readAndDispatch())display.sleep();}}private void onTableItemSelected(Table table) {TableItem[] sel = table.getSelection();String msg = String.format("%s: %s", sel[0].getText(0),sel[0].getText(1));label.setText(msg);}@SuppressWarnings("unused")public static void main(String[] args) {Display display = new Display();TableEx3 ex = new TableEx3(display);display.dispose();}}
在示例中,所选行中的数据显示在状态栏中。
table.addListener(SWT.Selection, event -> onTableItemSelected(table));
选择监听器将添加到表中。 每当选择表格项目时,都会调用onTableItemSelected()。
private void onTableItemSelected(Table table) {TableItem[] sel = table.getSelection();String msg = String.format("%s: %s", sel[0].getText(0),sel[0].getText(1));label.setText(msg);}
getSelection()方法返回一个选定表项的数组。 (由于我们使用默认选择模式(即单选模式),因此仅返回一个表项。)我们使用getText()方法从该行的单元格中检索数据。 我们构建消息并使用其setText()方法将其显示在标签中。
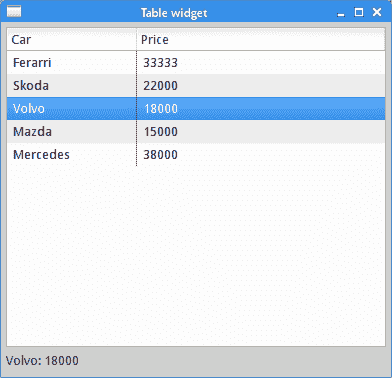
图:选择表项
添加新表项
在以下示例中,新表项被动态添加到表中。
TableEx4.java
package com.zetcode;import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridData;import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridLayout;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Event;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Label;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Table;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableColumn;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TableItem;import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text;/*** ZetCode Java SWT tutorial** In this program, we add new table items* to the table.** Author: Jan Bodnar* Website: zetcode.com* Last modified: June 2015*/public class TableEx4 {private Text text1;private Text text2;private Table table;private final String data[][] = { { "Ferarri", "33333" },{ "Skoda", "22000" }, { "Volvo", "18000" }, { "Mazda", "15000" },{ "Mercedes", "38000" } };public TableEx4(Display display) {initUI(display);}private void initUI(Display display) {Shell shell = new Shell(display, SWT.SHELL_TRIM | SWT.CENTER);shell.setLayout(new GridLayout(5, false));table = new Table(shell, SWT.BORDER | SWT.MULTI);table.setHeaderVisible(true);// table.setLinesVisible(true);String[] titles = { "Car", "Price" };for (int i = 0; i < titles.length; i++) {TableColumn column = new TableColumn(table, SWT.NULL);column.setText(titles[i]);column.setWidth(130);}for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {TableItem item = new TableItem(table, SWT.NULL);item.setText(0, data[i][0]);item.setText(1, data[i][1]);}GridData gd = new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.FILL, true, true);gd.horizontalSpan = 5;gd.widthHint = 360;gd.heightHint = 300;table.setLayoutData(gd);Label carName = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);carName.setText("Car:");text1 = new Text(shell, SWT.BORDER);Label priceOfCar = new Label(shell, SWT.NONE);priceOfCar.setText("Price:");text2 = new Text(shell, SWT.BORDER);text1.setLayoutData(new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.CENTER, true, false));text2.setLayoutData(new GridData(SWT.FILL, SWT.CENTER, true, false));Button addBtn = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH);addBtn.setText("Insert");addBtn.addListener(SWT.Selection, event -> onInsertButtonSelected(event));shell.setText("Table widget");shell.pack();shell.open();while (!shell.isDisposed()) {if (!display.readAndDispatch())display.sleep();}}private void onInsertButtonSelected(Event event) {String val1 = text1.getText();String val2 = text2.getText();if (val1.isEmpty() || val2.isEmpty()) {return;}TableItem item = new TableItem(table, SWT.NULL);item.setText(0, val1);item.setText(1, val2);text1.setText("");text2.setText("");}@SuppressWarnings("unused")public static void main(String[] args) {Display display = new Display();TableEx4 ex = new TableEx4(display);display.dispose();}}
在底部,有两个文本小部件和一个按钮。 插入到文本小部件中的数据将插入到新表项的单元格中。
private void onInsertButtonSelected(Event event) {String val1 = text1.getText();String val2 = text2.getText();...}
在onInsertButtonSelected()方法中,我们从文本小部件中获取插入的文本。
if (val1.isEmpty() || val2.isEmpty()) {return;}
我们确保文本小部件不为空。
TableItem item = new TableItem(table, SWT.NULL);item.setText(0, val1);item.setText(1, val2);
构造新表项,并获取插入的数据。
text1.setText("");text2.setText("");
最后,将清除文本小部件。

图:添加新表项
在 Java SWT 教程的这一部分中,我们介绍了Table小部件。

