{% raw %}
俄罗斯方块
http://zetcode.com/tutorials/javaswingtutorial/thetetrisgame/
在本章中,我们将在 Java Swing 中创建一个俄罗斯方块游戏克隆。
俄罗斯方块
俄罗斯方块游戏是有史以来最受欢迎的计算机游戏之一。 原始游戏是由俄罗斯程序员 Alexey Pajitnov 于 1985 年设计和编程的。此后,几乎所有版本的几乎所有计算机平台上都可以使用俄罗斯方块。
俄罗斯方块被称为下降块益智游戏。 在这个游戏中,我们有七个不同的形状,称为 tetrominoes:S 形,Z 形,T 形,L 形,线形,MirroredL 形和方形。 这些形状中的每一个都形成有四个正方形。 形状从板上掉下来。 俄罗斯方块游戏的目的是移动和旋转形状,以使其尽可能地适合。 如果我们设法形成一行,则该行将被破坏并得分。 我们玩俄罗斯方块游戏,直到达到顶峰。
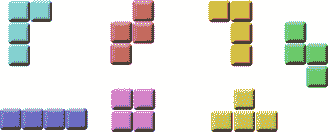
图:Tetrominoes
开发
我们的俄罗斯方块游戏没有图像,我们使用 Swing 绘图 API 绘制四面体。 每个计算机游戏的背后都有一个数学模型。 俄罗斯方块也是如此。
游戏背后的一些想法。
- 我们使用
Timer类创建游戏周期 - 绘制四方块
- 形状以正方形为单位移动(不是逐个像素移动)
- 从数学上讲,棋盘是简单的数字列表
游戏经过简化,因此更易于理解。 游戏启动后立即开始。 我们可以通过按 p 键暂停游戏。 空格键将俄罗斯方块放到底部。 d 键将棋子下降一行。 (它可以用来加快下降速度。)游戏以恒定速度运行,没有实现加速。 分数是我们已删除的行数。
com/zetcode/Tetris.java
package com.zetcode;import java.awt.BorderLayout;import java.awt.EventQueue;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JLabel;/*Java Tetris game cloneAuthor: Jan BodnarWebsite: http://zetcode.com*/public class Tetris extends JFrame {private JLabel statusbar;public Tetris() {initUI();}private void initUI() {statusbar = new JLabel(" 0");add(statusbar, BorderLayout.SOUTH);var board = new Board(this);add(board);board.start();setTitle("Tetris");setSize(200, 400);setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);setLocationRelativeTo(null);}JLabel getStatusBar() {return statusbar;}public static void main(String[] args) {EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {var game = new Tetris();game.setVisible(true);});}}
在Tetris中,我们设置了游戏。 我们创建一个玩游戏的棋盘。 我们创建一个状态栏。
board.start();
start()方法启动俄罗斯方块游戏。
com/zetcode/Shape.java
package com.zetcode;import java.util.Random;public class Shape {protected enum Tetrominoe {NoShape, ZShape, SShape, LineShape,TShape, SquareShape, LShape, MirroredLShape}private Tetrominoe pieceShape;private int coords[][];private int[][][] coordsTable;public Shape() {coords = new int[4][2];setShape(Tetrominoe.NoShape);}void setShape(Tetrominoe shape) {coordsTable = new int[][][]{{{0, 0}, {0, 0}, {0, 0}, {0, 0}},{{0, -1}, {0, 0}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}},{{0, -1}, {0, 0}, {1, 0}, {1, 1}},{{0, -1}, {0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, 2}},{{-1, 0}, {0, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}},{{0, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 1}},{{-1, -1}, {0, -1}, {0, 0}, {0, 1}},{{1, -1}, {0, -1}, {0, 0}, {0, 1}}};for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {System.arraycopy(coordsTable[shape.ordinal()], 0, coords, 0, 4);}pieceShape = shape;}private void setX(int index, int x) {coords[index][0] = x;}private void setY(int index, int y) {coords[index][1] = y;}int x(int index) {return coords[index][0];}int y(int index) {return coords[index][1];}Tetrominoe getShape() {return pieceShape;}void setRandomShape() {var r = new Random();int x = Math.abs(r.nextInt()) % 7 + 1;Tetrominoe[] values = Tetrominoe.values();setShape(values[x]);}public int minX() {int m = coords[0][0];for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {m = Math.min(m, coords[i][0]);}return m;}int minY() {int m = coords[0][1];for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {m = Math.min(m, coords[i][1]);}return m;}Shape rotateLeft() {if (pieceShape == Tetrominoe.SquareShape) {return this;}var result = new Shape();result.pieceShape = pieceShape;for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {result.setX(i, y(i));result.setY(i, -x(i));}return result;}Shape rotateRight() {if (pieceShape == Tetrominoe.SquareShape) {return this;}var result = new Shape();result.pieceShape = pieceShape;for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {result.setX(i, -y(i));result.setY(i, x(i));}return result;}}
Shape提供有关俄罗斯方块的信息。
protected enum Tetrominoe {NoShape, ZShape, SShape, LineShape,TShape, SquareShape, LShape, MirroredLShape}
Tetrominoe拥有七个俄罗斯方块形状名称,而空的形状称为NoShape。
public Shape() {coords = new int[4][2];setShape(Tetrominoe.NoShape);}
这是Shape类的构造器。 coords数组保存俄罗斯方块的实际坐标。
coordsTable = new int[][][] {{ { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 } },{ { 0, -1 }, { 0, 0 }, { -1, 0 }, { -1, 1 } },{ { 0, -1 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, 1 } },{ { 0, -1 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 } },{ { -1, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, 1 } },{ { 0, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, 1 }, { 1, 1 } },{ { -1, -1 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 1 } },{ { 1, -1 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 1 } }};
coordsTable数组保存我们的俄罗斯方块的所有可能的坐标值。 这是一个模板,所有零件均从该模板获取其坐标值。
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {System.arraycopy(coordsTable[shape.ordinal()], 0, coords, 0, 4);}
在这里,我们将一行坐标值从coordsTable复制到俄罗斯方块的coords数组。 请注意ordinal()方法的使用。 在 C++ 中,枚举类型本质上是一个整数。 与 C++ 不同,Java 枚举是完整类,ordinal()方法返回枚举类型在枚举对象中的当前位置。
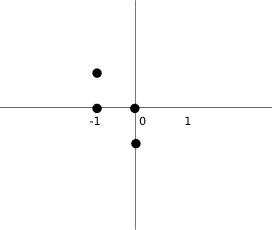
图:坐标
该图像有助于进一步了解坐标值。 coords数组保存俄罗斯方块的坐标。 下图说明了旋转的 S 形。 它具有以下坐标:(-1,1),(-1,0),(0,0)和(0,-1)。
Shape rotateRight() {if (pieceShape == Tetrominoe.SquareShape) {return this;}var result = new Shape();result.pieceShape = pieceShape;for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {result.setX(i, -y(i));result.setY(i, x(i));}return result;}
此代码将棋子向右旋转。 正方形不必旋转。 这就是为什么在Tetrominoe.SquareShape的情况下我们仅将引用返回给当前对象的原因。 查看上一张图片将有助于进一步了解旋转情况。
com/zetcode/Board.java
package com.zetcode;import com.zetcode.Shape.Tetrominoe;import javax.swing.JLabel;import javax.swing.JPanel;import javax.swing.Timer;import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.Graphics;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;public class Board extends JPanel implements ActionListener {private final int BOARD_WIDTH = 10;private final int BOARD_HEIGHT = 22;private Timer timer;private boolean isFallingFinished = false;private boolean isStarted = false;private boolean isPaused = false;private int numLinesRemoved = 0;private int curX = 0;private int curY = 0;private JLabel statusbar;private Shape curPiece;private Tetrominoe[] board;public Board(Tetris parent) {initBoard(parent);}private void initBoard(Tetris parent) {setFocusable(true);curPiece = new Shape();int DELAY = 400;timer = new Timer(DELAY, this);timer.start();statusbar = parent.getStatusBar();board = new Tetrominoe[BOARD_WIDTH * BOARD_HEIGHT];addKeyListener(new TAdapter());clearBoard();}@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {if (isFallingFinished) {isFallingFinished = false;newPiece();} else {oneLineDown();}}private int squareWidth() { return (int) getSize().getWidth() / BOARD_WIDTH; }private int squareHeight() { return (int) getSize().getHeight() / BOARD_HEIGHT; }private Tetrominoe shapeAt(int x, int y) { return board[(y * BOARD_WIDTH) + x]; }void start() {if (isPaused) {return;}isStarted = true;isFallingFinished = false;numLinesRemoved = 0;clearBoard();newPiece();timer.start();}private void pause() {if (!isStarted) {return;}isPaused = !isPaused;if (isPaused) {timer.stop();statusbar.setText("paused");} else {timer.start();statusbar.setText(String.valueOf(numLinesRemoved));}repaint();}private void doDrawing(Graphics g) {var size = getSize();int boardTop = (int) size.getHeight() - BOARD_HEIGHT * squareHeight();for (int i = 0; i < BOARD_HEIGHT; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < BOARD_WIDTH; ++j) {Tetrominoe shape = shapeAt(j, BOARD_HEIGHT - i - 1);if (shape != Tetrominoe.NoShape)drawSquare(g, j * squareWidth(),boardTop + i * squareHeight(), shape);}}if (curPiece.getShape() != Tetrominoe.NoShape) {for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {int x = curX + curPiece.x(i);int y = curY - curPiece.y(i);drawSquare(g, x * squareWidth(),boardTop + (BOARD_HEIGHT - y - 1) * squareHeight(),curPiece.getShape());}}}@Overridepublic void paintComponent(Graphics g) {super.paintComponent(g);doDrawing(g);}private void dropDown() {int newY = curY;while (newY > 0) {if (!tryMove(curPiece, curX, newY - 1)) {break;}--newY;}pieceDropped();}private void oneLineDown() {if (!tryMove(curPiece, curX, curY - 1)) {pieceDropped();}}private void clearBoard() {for (int i = 0; i < BOARD_HEIGHT * BOARD_WIDTH; ++i) {board[i] = Tetrominoe.NoShape;}}private void pieceDropped() {for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {int x = curX + curPiece.x(i);int y = curY - curPiece.y(i);board[(y * BOARD_WIDTH) + x] = curPiece.getShape();}removeFullLines();if (!isFallingFinished) {newPiece();}}private void newPiece() {curPiece.setRandomShape();curX = BOARD_WIDTH / 2 + 1;curY = BOARD_HEIGHT - 1 + curPiece.minY();if (!tryMove(curPiece, curX, curY)) {curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoe.NoShape);timer.stop();isStarted = false;statusbar.setText("game over");}}private boolean tryMove(Shape newPiece, int newX, int newY) {for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {int x = newX + newPiece.x(i);int y = newY - newPiece.y(i);if (x < 0 || x >= BOARD_WIDTH || y < 0 || y >= BOARD_HEIGHT)return false;if (shapeAt(x, y) != Tetrominoe.NoShape)return false;}curPiece = newPiece;curX = newX;curY = newY;repaint();return true;}private void removeFullLines() {int numFullLines = 0;for (int i = BOARD_HEIGHT - 1; i >= 0; --i) {boolean lineIsFull = true;for (int j = 0; j < BOARD_WIDTH; ++j) {if (shapeAt(j, i) == Tetrominoe.NoShape) {lineIsFull = false;break;}}if (lineIsFull) {++numFullLines;for (int k = i; k < BOARD_HEIGHT - 1; ++k) {for (int j = 0; j < BOARD_WIDTH; ++j)board[(k * BOARD_WIDTH) + j] = shapeAt(j, k + 1);}}}if (numFullLines > 0) {numLinesRemoved += numFullLines;statusbar.setText(String.valueOf(numLinesRemoved));isFallingFinished = true;curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoe.NoShape);repaint();}}private void drawSquare(Graphics g, int x, int y, Tetrominoe shape) {Color colors[] = { new Color(0, 0, 0), new Color(204, 102, 102),new Color(102, 204, 102), new Color(102, 102, 204),new Color(204, 204, 102), new Color(204, 102, 204),new Color(102, 204, 204), new Color(218, 170, 0)};var color = colors[shape.ordinal()];g.setColor(color);g.fillRect(x + 1, y + 1, squareWidth() - 2, squareHeight() - 2);g.setColor(color.brighter());g.drawLine(x, y + squareHeight() - 1, x, y);g.drawLine(x, y, x + squareWidth() - 1, y);g.setColor(color.darker());g.drawLine(x + 1, y + squareHeight() - 1,x + squareWidth() - 1, y + squareHeight() - 1);g.drawLine(x + squareWidth() - 1, y + squareHeight() - 1,x + squareWidth() - 1, y + 1);}class TAdapter extends KeyAdapter {@Overridepublic void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {if (!isStarted || curPiece.getShape() == Tetrominoe.NoShape) {return;}int keycode = e.getKeyCode();if (keycode == 'P') {pause();return;}if (isPaused) {return;}switch (keycode) {case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT:tryMove(curPiece, curX - 1, curY);break;case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT:tryMove(curPiece, curX + 1, curY);break;case KeyEvent.VK_DOWN:tryMove(curPiece.rotateRight(), curX, curY);break;case KeyEvent.VK_UP:tryMove(curPiece.rotateLeft(), curX, curY);break;case KeyEvent.VK_SPACE:dropDown();break;case KeyEvent.VK_D:oneLineDown();break;}}}}
游戏逻辑位于Board中。
private final int BOARD_WIDTH = 10;private final int BOARD_HEIGHT = 22;
BOARD_WIDTH和BOARD_HEIGHT常数定义电路板的大小。
...private boolean isFallingFinished = false;private boolean isStarted = false;private boolean isPaused = false;private int numLinesRemoved = 0;private int curX = 0;private int curY = 0;...
我们初始化一些重要的变量。 isFallingFinished变量确定俄罗斯方块形状是否已完成下降,然后我们需要创建一个新形状。 numLinesRemoved计算行数,到目前为止我们已经删除了行数。 curX和curY变量确定下降的俄罗斯方块形状的实际位置。
setFocusable(true);
我们必须显式调用setFocusable()方法。 从现在开始,开发板具有键盘输入。
int DELAY = 400;
DELAY常数定义游戏的速度。
timer = new Timer(DELAY, this);timer.start();
在指定的延迟后,Timer对象将触发一个或多个操作事件。 在我们的情况下,计时器每DELAY ms 调用一次actionPerformed()方法。
@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {if (isFallingFinished) {isFallingFinished = false;newPiece();} else {oneLineDown();}}
actionPerformed()方法检查下降是否已完成。 如果是这样,将创建一个新作品。 如果不是,下降的俄罗斯方块下降了一行。
在doDrawing()方法内部,我们在板上绘制了所有对象。 这幅画有两个步骤。
for (int i = 0; i < BOARD_HEIGHT; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < BOARD_WIDTH; ++j) {Tetrominoe shape = shapeAt(j, BOARD_HEIGHT - i - 1);if (shape != Tetrominoe.NoShape)drawSquare(g, j * squareWidth(),boardTop + i * squareHeight(), shape);}}
在第一步中,我们绘制掉落到板底部的所有形状或形状的其余部分。 所有正方形都记在板数组中。 我们使用shapeAt()方法访问它。
if (curPiece.getShape() != Tetrominoe.NoShape) {for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {int x = curX + curPiece.x(i);int y = curY - curPiece.y(i);drawSquare(g, 0 + x * squareWidth(),boardTop + (BOARD_HEIGHT - y - 1) * squareHeight(),curPiece.getShape());}}
在第二步中,我们绘制实际的下降部分。
private void dropDown() {int newY = curY;while (newY > 0) {if (!tryMove(curPiece, curX, newY - 1)) {break;}--newY;}pieceDropped();}
如果我们按 Space 键,则该片段将落到底部。 我们只是简单地尝试将一块下降到另一条俄罗斯方块下降的底部或顶部。 当俄罗斯方块结束下降时,将调用pieceDropped()。
private void clearBoard() {for (int i = 0; i < BOARD_HEIGHT * BOARD_WIDTH; ++i) {board[i] = Tetrominoe.NoShape;}}
clearBoard()方法用空的NoShapes填充电路板。
private void pieceDropped() {for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {int x = curX + curPiece.x(i);int y = curY - curPiece.y(i);board[(y * BOARD_WIDTH) + x] = curPiece.getShape();}removeFullLines();if (!isFallingFinished) {newPiece();}}
pieceDropped()方法将下降的片段放入board数组。 棋盘再次保持了所有碎片的正方形和已经落下的碎片的剩余部分。 当一块完成落下时,就该检查是否可以去除板上的一些线了。 这是removeFullLines()方法的工作。 然后,我们尝试创建一个新作品。
private void newPiece() {curPiece.setRandomShape();curX = BOARD_WIDTH / 2 + 1;curY = BOARD_HEIGHT - 1 + curPiece.minY();if (!tryMove(curPiece, curX, curY)) {curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoe.NoShape);timer.stop();isStarted = false;statusbar.setText("game over");}}
newPiece()方法创建一个新的俄罗斯方块。 作品获得了新的随机形状。 然后,我们计算初始curX和curY值。 如果我们不能移动到初始位置,则游戏结束。 我们加油。 计时器停止。 我们将游戏放在状态栏上的字符串上方。
private boolean tryMove(Shape newPiece, int newX, int newY) {for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {int x = newX + newPiece.x(i);int y = newY - newPiece.y(i);if (x < 0 || x >= BOARD_WIDTH || y < 0 || y >= BOARD_HEIGHT) {return false;}if (shapeAt(x, y) != Tetrominoe.NoShape) {return false;}}curPiece = newPiece;curX = newX;curY = newY;repaint();return true;}
tryMove()方法尝试移动俄罗斯方块。 如果该方法已达到板边界或与已经跌落的俄罗斯方块相邻,则返回false。
int numFullLines = 0;for (int i = BOARD_HEIGHT - 1; i >= 0; --i) {boolean lineIsFull = true;for (int j = 0; j < BOARD_WIDTH; ++j) {if (shapeAt(j, i) == Tetrominoe.NoShape) {lineIsFull = false;break;}}if (lineIsFull) {++numFullLines;for (int k = i; k < BOARD_HEIGHT - 1; ++k) {for (int j = 0; j < BOARD_WIDTH; ++j)board[(k * BOARD_WIDTH) + j] = shapeAt(j, k + 1);}}}
在removeFullLines()方法内部,我们检查board的所有行中是否有完整的行。 如果至少有一条实线,则将其删除。 找到整条线后,我们增加计数器。 我们将整行上方的所有行向下移动一行。 这样我们就破坏了整个生产线。 注意,在我们的俄罗斯方块游戏中,我们使用了所谓的朴素重力。 这意味着正方形可能会漂浮在空白间隙上方。
每个俄罗斯方块都有四个正方形。 每个正方形都使用drawSquare()方法绘制。 俄罗斯方块有不同的颜色。
g.setColor(color.brighter());g.drawLine(x, y + squareHeight() - 1, x, y);g.drawLine(x, y, x + squareWidth() - 1, y);
正方形的左侧和顶部以较亮的颜色绘制。 类似地,底部和右侧用较深的颜色绘制。 这是为了模拟 3D 边缘。
我们使用键盘控制游戏。 控制机制通过KeyAdapter实现。 这是一个覆盖keyPressed()方法的内部类。
case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT:tryMove(curPiece, curX - 1, curY);break;
如果按向左箭头键,则尝试将下降片向左移动一个正方形。
图:俄罗斯方块
这是俄罗斯方块游戏。
{% endraw %}

