在 Java 2D 教程的这一部分中,我们将讨论裁剪。
剪裁
剪裁将图形限制在某个区域。 这样做是出于效率原因并产生各种效果。 使用剪裁时,我们必须使用Graphics对象的副本,或者恢复原始的剪裁属性。 更改剪裁不会影响现有像素; 它仅影响将来的渲染。
在以下示例中,我们将图像裁剪为圆形。
ClippingEx.java
package com.zetcode;import java.awt.Dimension;import java.awt.EventQueue;import java.awt.Graphics;import java.awt.Graphics2D;import java.awt.Image;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D;import javax.swing.ImageIcon;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JPanel;import javax.swing.Timer;class Surface extends JPanelimplements ActionListener {private int pos_x = 8;private int pos_y = 8;private final int RADIUS = 90;private final int DELAY = 35;private Timer timer;private Image image;private final double delta[] = { 3, 3 };public Surface() {loadImage();determineAndSetImageSize();initTimer();}private void loadImage() {image = new ImageIcon("mushrooms.jpg").getImage();}private void determineAndSetImageSize() {int h = image.getHeight(this);int w = image.getWidth(this);setPreferredSize(new Dimension(w, h));}private void initTimer() {timer = new Timer(DELAY, this);timer.start();}private void doDrawing(Graphics g) {Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) g.create();g2d.clip(new Ellipse2D.Double(pos_x, pos_y, RADIUS, RADIUS));g2d.drawImage(image, 0, 0, null);g2d.dispose();}@Overridepublic void paintComponent(Graphics g) {super.paintComponent(g);doDrawing(g);}@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {moveCircle();repaint();}private void moveCircle() {int w = getWidth();int h = getHeight();if (pos_x < 0) {delta[0] = Math.random() % 4 + 5;} else if (pos_x > w - RADIUS) {delta[0] = -(Math.random() % 4 + 5);}if (pos_y < 0 ) {delta[1] = Math.random() % 4 + 5;} else if (pos_y > h - RADIUS) {delta[1] = -(Math.random() % 4 + 5);}pos_x += delta[0];pos_y += delta[1];}}public class ClippingEx extends JFrame {public ClippingEx() {initUI();}private void initUI() {setTitle("Clipping");add(new Surface());pack();setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);setLocationRelativeTo(null);}public static void main(String[] args) {EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {ClippingEx cl = new ClippingEx();cl.setVisible(true);}});}}
屏幕上正在移动一个圆圈,并显示了一部分基础图像。 这就像我们从孔中看一样。
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) g.create();
我们创建Graphics2D对象的副本。 因此,更改剪裁不会影响其他在Graphics2D对象被重用的 Swing 零件。
g2d.clip(new Ellipse2D.Double(pos_x, pos_y, RADIUS, RADIUS));
clip()方法将现有剪裁与作为参数给出的形状结合在一起。 所得的相交设置为片段。 在我们的例子中,最终的剪裁是圆形。
if (pos_x < 0) {delta[0] = Math.random() % 4 + 5;} else if (pos_x > w - RADIUS) {delta[0] = -(Math.random() % 4 + 5);}
如果圆碰到窗口的左侧或右侧,则圆的移动方向会随机变化。 顶部和底部也一样。
g2d.dispose();
完成绘画后,我们必须释放Graphics2D对象的副本。
剪裁形状
在下面的示例中,我们将剪切到两个形状的交点:矩形和圆形。
ClippingShapesEx.java
package com.zetcode;import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.EventQueue;import java.awt.Graphics;import java.awt.Graphics2D;import java.awt.Rectangle;import java.awt.RenderingHints;import java.awt.Shape;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import java.awt.geom.AffineTransform;import java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D;import java.awt.geom.GeneralPath;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JPanel;import javax.swing.Timer;class Surface extends JPanelimplements ActionListener {private Timer timer;private double rotate = 1;private int pos_x = 8;private int pos_y = 8;private final double delta[] = {1, 1};private final int RADIUS = 60;public Surface() {initTimer();}private void initTimer() {timer = new Timer(10, this);timer.start();}private void doDrawing(Graphics g) {Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) g;g2d.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);g2d.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_RENDERING,RenderingHints.VALUE_RENDER_QUALITY);Shape oldClip = g2d.getClip();int w = getWidth();int h = getHeight();Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(0, 0, 200, 80);AffineTransform tx = new AffineTransform();tx.rotate(Math.toRadians(rotate), w / 2, h / 2);tx.translate(w / 2 - 100, h / 2 - 40);Ellipse2D circle = new Ellipse2D.Double(pos_x, pos_y,RADIUS, RADIUS);GeneralPath path = new GeneralPath();path.append(tx.createTransformedShape(rect), false);g2d.clip(circle);g2d.clip(path);g2d.setPaint(new Color(110, 110, 110));g2d.fill(circle);g2d.setClip(oldClip);g2d.draw(circle);g2d.draw(path);}@Overridepublic void paintComponent(Graphics g) {super.paintComponent(g);doDrawing(g);}public void step() {int w = getWidth();int h = getHeight();rotate += 1;if (pos_x < 0) {delta[0] = 1;} else if (pos_x > w - RADIUS) {delta[0] = -1;}if (pos_y < 0) {delta[1] = 1;} else if (pos_y > h - RADIUS) {delta[1] = -1;}pos_x += delta[0];pos_y += delta[1];}@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {step();repaint();}}public class ClippingShapesEx extends JFrame {public ClippingShapesEx() {initUI();}private void initUI() {setTitle("Clipping shapes");add(new Surface());setSize(350, 300);setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);setLocationRelativeTo(null);}public static void main(String[] args) {EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {ClippingShapesEx ex = new ClippingShapesEx();ex.setVisible(true);}});}}
在我们的示例中,我们有一个弹跳的圆和一个旋转的矩形。 当这些形状重叠时,结果区域将充满颜色。
Shape oldClip = g2d.getClip();
由于我们没有创建Graphics2D对象的副本,因此我们将存储旧剪裁以供以后使用。 最后,我们必须将剪裁重置为原始剪裁。
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(0, 0, 200, 80);AffineTransform tx = new AffineTransform();tx.rotate(Math.toRadians(rotate), w / 2, h / 2);tx.translate(w / 2 - 100, h / 2 - 40);
矩形正在旋转。 它始终位于面板的中间。
GeneralPath path = new GeneralPath();path.append(tx.createTransformedShape(rect), false);
在这里,我们得到了旋转矩形的形状。
g2d.clip(circle);g2d.clip(path);g2d.setPaint(new Color(110, 110, 110));g2d.fill(circle);
在这里,我们将绘图限制为两个形状的交点。 如果它们重叠,则结果形状的内部将充满颜色。 clip()方法将初始剪裁(组件的客户区域)与给定的两个形状组合在一起。
g2d.setClip(oldClip);
使用setClip()方法,我们在绘制形状之前将剪裁区域重置为旧剪裁。 与clip()方法不同,setClip()不合并剪切区域。 它将剪裁重置到新区域。 因此,此方法应专门用于还原旧剪裁。
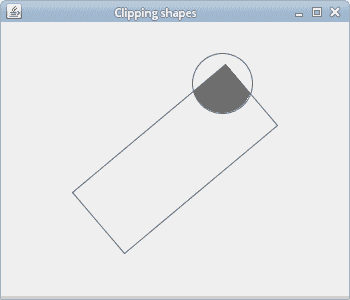
图:剪裁形状
在 Java 2D 教程的这一部分中,我们讨论了剪裁。

