在 PyQt5 编程教程的这一部分中,我们将探讨应用中发生的事件和信号。
事件
GUI 应用是事件驱动的。 事件主要由应用的用户生成。 但是它们也可以通过其他方式生成。 例如互联网连接,窗口管理器或计时器。 当我们调用应用的exec_()方法时,应用进入主循环。 主循环获取事件并将其发送到对象。
在事件模型中,有三个参与者:
- 事件来源
- 事件对象
- 事件目标
事件源是状态更改的对象。 它生成事件。事件对象(事件)将状态更改封装在事件源中。事件目标是要通知的对象。 事件源对象将处理事件的任务委托给事件目标。
PyQt5 具有独特的信号和槽机制来处理事件。 信号和槽用于对象之间的通信。 当发生特定事件时,会发出信号。槽可以是任何 Python 可调用的。 发出连接信号时,将调用槽。
信号和槽
这是一个简单的示例,展示了 PyQt5 中的信号和槽。
sigslot.py
#!/usr/bin/python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode PyQt5 tutorialIn this example, we connect a signalof a QSlider to a slot of a QLCDNumber.Author: Jan BodnarWebsite: zetcode.comLast edited: January 2017"""import sysfrom PyQt5.QtCore import Qtfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QLCDNumber, QSlider,QVBoxLayout, QApplication)class Example(QWidget):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.initUI()def initUI(self):lcd = QLCDNumber(self)sld = QSlider(Qt.Horizontal, self)vbox = QVBoxLayout()vbox.addWidget(lcd)vbox.addWidget(sld)self.setLayout(vbox)sld.valueChanged.connect(lcd.display)self.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 150)self.setWindowTitle('Signal and slot')self.show()if __name__ == '__main__':app = QApplication(sys.argv)ex = Example()sys.exit(app.exec_())
在我们的示例中,我们显示QtGui.QLCDNumber和QtGui.QSlider。 我们通过拖动滑块来更改lcd编号。
sld.valueChanged.connect(lcd.display)
在这里,我们将滑块的valueChanged信号连接到lcd号的display槽。
发送器是发送信号的对象。接收器是接收信号的对象。槽是对信号做出反应的方法。
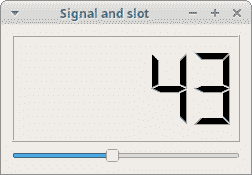
图:信号和槽
重新实现事件处理器
PyQt5 中的事件通常通过重新实现事件处理器来处理。
escape.py
#!/usr/bin/python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode PyQt5 tutorialIn this example, we reimplement anevent handler.Author: Jan BodnarWebsite: zetcode.comLast edited: August 2017"""import sysfrom PyQt5.QtCore import Qtfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget, QApplicationclass Example(QWidget):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.initUI()def initUI(self):self.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 150)self.setWindowTitle('Event handler')self.show()def keyPressEvent(self, e):if e.key() == Qt.Key_Escape:self.close()if __name__ == '__main__':app = QApplication(sys.argv)ex = Example()sys.exit(app.exec_())
在我们的示例中,我们重新实现了keyPressEvent()事件处理器。
def keyPressEvent(self, e):if e.key() == Qt.Key_Escape:self.close()
如果单击“退出”按钮,则应用终止。
事件对象
事件对象是一个 Python 对象,其中包含许多描述事件的属性。 事件对象特定于生成的事件类型。
eventobject.py
#!/usr/bin/python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode PyQt5 tutorialIn this example, we display the x and ycoordinates of a mouse pointer in a label widget.Author: Jan BodnarWebsite: zetcode.comLast edited: August 2017"""import sysfrom PyQt5.QtCore import Qtfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget, QApplication, QGridLayout, QLabelclass Example(QWidget):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.initUI()def initUI(self):grid = QGridLayout()x = 0y = 0self.text = "x: {0}, y: {1}".format(x, y)self.label = QLabel(self.text, self)grid.addWidget(self.label, 0, 0, Qt.AlignTop)self.setMouseTracking(True)self.setLayout(grid)self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 200)self.setWindowTitle('Event object')self.show()def mouseMoveEvent(self, e):x = e.x()y = e.y()text = "x: {0}, y: {1}".format(x, y)self.label.setText(text)if __name__ == '__main__':app = QApplication(sys.argv)ex = Example()sys.exit(app.exec_())
在此示例中,我们在标签小部件中显示了鼠标指针的 x 和 y 坐标。
self.text = "x: {0}, y: {1}".format(x, y)self.label = QLabel(self.text, self)
x 和 y 坐标显示在QLabel小部件中。
self.setMouseTracking(True)
默认情况下,鼠标跟踪是禁用的,因此,仅在移动鼠标时按下至少一个鼠标按钮时,窗口小部件才会接收鼠标移动事件。 如果启用了鼠标跟踪,则即使未按任何按钮,窗口小部件也会接收鼠标移动事件。
def mouseMoveEvent(self, e):x = e.x()y = e.y()text = "x: {0}, y: {1}".format(x, y)self.label.setText(text)
e是事件对象; 它包含有关已触发事件的数据; 在我们的例子中,是一个鼠标移动事件。 使用x()和y()方法,我们可以确定鼠标指针的 x 和 y 坐标。 我们构建字符串并将其设置为标签小部件。
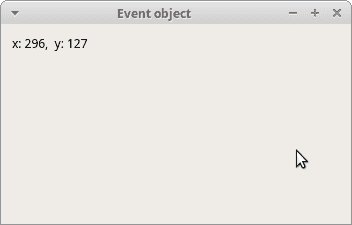
图:事件对象
事件发送者
有时很方便地知道哪个窗口小部件是信号的发送者。 为此,PyQt5 具有sender()方法。
eventsource.py
#!/usr/bin/python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode PyQt5 tutorialIn this example, we determine the event senderobject.Author: Jan BodnarWebsite: zetcode.comLast edited: August 2017"""import sysfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QPushButton, QApplicationclass Example(QMainWindow):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.initUI()def initUI(self):btn1 = QPushButton("Button 1", self)btn1.move(30, 50)btn2 = QPushButton("Button 2", self)btn2.move(150, 50)btn1.clicked.connect(self.buttonClicked)btn2.clicked.connect(self.buttonClicked)self.statusBar()self.setGeometry(300, 300, 290, 150)self.setWindowTitle('Event sender')self.show()def buttonClicked(self):sender = self.sender()self.statusBar().showMessage(sender.text() + ' was pressed')if __name__ == '__main__':app = QApplication(sys.argv)ex = Example()sys.exit(app.exec_())
我们的示例中有两个按钮。 在buttonClicked()方法中,我们通过调用sender()方法来确定单击了哪个按钮。
btn1.clicked.connect(self.buttonClicked)btn2.clicked.connect(self.buttonClicked)
两个按钮都连接到同一槽。
def buttonClicked(self):sender = self.sender()self.statusBar().showMessage(sender.text() + ' was pressed')
我们通过调用sender()方法来确定信号源。 在应用的状态栏中,我们显示了被按下的按钮的标签。
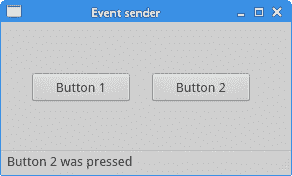
图:事件发送者
发射信号
从QObject创建的对象可以发出信号。 以下示例说明了如何发出自定义信号。
customsignal.py
#!/usr/bin/python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode PyQt5 tutorialIn this example, we show how toemit a custom signal.Author: Jan BodnarWebsite: zetcode.comLast edited: August 2017"""import sysfrom PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSignal, QObjectfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplicationclass Communicate(QObject):closeApp = pyqtSignal()class Example(QMainWindow):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.initUI()def initUI(self):self.c = Communicate()self.c.closeApp.connect(self.close)self.setGeometry(300, 300, 290, 150)self.setWindowTitle('Emit signal')self.show()def mousePressEvent(self, event):self.c.closeApp.emit()if __name__ == '__main__':app = QApplication(sys.argv)ex = Example()sys.exit(app.exec_())
我们创建一个名为closeApp的新信号。 在鼠标按下事件期间发出此信号。 信号连接到QMainWindow的close()槽。
class Communicate(QObject):closeApp = pyqtSignal()
使用pyqtSignal()作为外部Communicate类的类属性创建信号。
self.c = Communicate()self.c.closeApp.connect(self.close)
定制的closeApp信号连接到QMainWindow的close()槽。
def mousePressEvent(self, event):self.c.closeApp.emit()
当我们用鼠标指针单击窗口时,会发出closeApp信号。 该应用终止。
在 PyQt5 教程的这一部分中,我们介绍了信号和槽。

