在本节中,我们将介绍 wxPython 中的基本小部件。 每个小部件都有一个小的代码示例。 小部件是应用的基本构建块。 wxPython 有各种各样的小部件,包括按钮,复选框,滑块和列表框。
wx.Buttonwx.ToggleButtonwx.StaticTextwx.StaticLinewx.StaticBoxwx.ComboBoxwx.CheckBoxwx.StatusBarwx.RadioButtonwx.Gaugewx.Sliderwx.SpinCtrl
wx.Button
wx.Button是一个简单的小部件。 它包含一个文本字符串。 用于触发动作。
button_wid.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode wxPython tutorialIn this code example, we create abutton widget.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: www.zetcode.comlast modified: April 2018"""import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)closeButton = wx.Button(pnl, label='Close', pos=(20, 20))closeButton.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose)self.SetSize((350, 250))self.SetTitle('wx.Button')self.Centre()def OnClose(self, e):self.Close(True)def main():app = wx.App()ex = Example(None)ex.Show()app.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
在代码示例中,我们创建一个“关闭”按钮,当按下该按钮时,它将终止应用。
cbtn = wx.Button(pnl, label='Close', pos=(20, 20))
wx.Button小部件已创建。 在小部件的构造器中,我们提供按钮的标签和面板上的位置。
cbtn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose)
当我们单击按钮时,将触发wx.EVT_BUTTON事件。 我们为事件指定事件处理器。
def OnClose(self, e):self.Close(True)
在OnClose()方法中,我们使用Close()方法终止应用。
图:wx.Button
wx.ToggleButton
wx.ToggleButton是具有两种状态的按钮:已按下和未按下。 通过单击可以在这两种状态之间切换。 在某些情况下此功能非常合适。
toggle_buttons.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode wxPython tutorialIn this code example, we create threetoggle button widgets.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: www.zetcode.comlast modified: April 2018"""import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)self.col = wx.Colour(0, 0, 0)rtb = wx.ToggleButton(pnl, label='red', pos=(20, 25))gtb = wx.ToggleButton(pnl, label='green', pos=(20, 60))btb = wx.ToggleButton(pnl, label='blue', pos=(20, 100))self.cpnl = wx.Panel(pnl, pos=(150, 20), size=(110, 110))self.cpnl.SetBackgroundColour(self.col)rtb.Bind(wx.EVT_TOGGLEBUTTON, self.ToggleRed)gtb.Bind(wx.EVT_TOGGLEBUTTON, self.ToggleGreen)btb.Bind(wx.EVT_TOGGLEBUTTON, self.ToggleBlue)self.SetSize((350, 250))self.SetTitle('Toggle buttons')self.Centre()def ToggleRed(self, e):obj = e.GetEventObject()isPressed = obj.GetValue()green = self.col.Green()blue = self.col.Blue()if isPressed:self.col.Set(255, green, blue)else:self.col.Set(0, green, blue)self.cpnl.SetBackgroundColour(self.col)self.cpnl.Refresh()def ToggleGreen(self, e):obj = e.GetEventObject()isPressed = obj.GetValue()red = self.col.Red()blue = self.col.Blue()if isPressed:self.col.Set(red, 255, blue)else:self.col.Set(red, 0, blue)self.cpnl.SetBackgroundColour(self.col)self.cpnl.Refresh()def ToggleBlue(self, e):obj = e.GetEventObject()isPressed = obj.GetValue()red = self.col.Red()green = self.col.Green()if isPressed:self.col.Set(red, green, 255)else:self.col.Set(red, green, 0)self.cpnl.SetBackgroundColour(self.col)self.cpnl.Refresh()def main():app = wx.App()ex = Example(None)ex.Show()app.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
我们有红色,绿色和蓝色的切换按钮和一个面板。 我们通过单击切换按钮来更改面板的颜色。
rtb = wx.ToggleButton(pnl, label='red', pos=(20, 25))
wx.ToggleButton小部件已创建。
self.cpnl = wx.Panel(pnl, pos=(150, 20), size=(110, 110))self.cpnl.SetBackgroundColour(self.col)
这是一个面板的颜色,我们将使用切换按钮对其进行修改。
rtb.Bind(wx.EVT_TOGGLEBUTTON, self.ToggleRed)
当我们单击rtb切换按钮时,将调用ToggleRed()事件处理器。
def ToggleRed(self, e):obj = e.GetEventObject()isPressed = obj.GetValue()green = self.col.Green()blue = self.col.Blue()if isPressed:self.col.Set(255, green, blue)else:self.col.Set(0, green, blue)self.cpnl.SetBackgroundColour(self.col)
在ToggleRed()方法中,我们对按下rtb按钮这一事实作出反应。 我们找出颜色部分并更新颜色面板的颜色。
图:开关按钮
wx.StaticText
wx.StaticText小部件显示一行或多行只读文本。
static_text.py
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode wxPython tutorialIn this code example, we create a static text.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: www.zetcode.comlast modified: April 2018"""import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):txt1 = '''I'm giving up the ghost of lovein the shadows cast on devotionShe is the one that I adorecreed of my silent suffocationBreak this bittersweet spell on melost in the arms of destiny'''txt2 = '''There is something in the wayYou're always somewhere elseFeelings have deserted meTo a point of no returnI don't believe in GodBut I pray for you'''pnl = wx.Panel(self)vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)font = wx.Font(13, wx.DEFAULT, wx.NORMAL, wx.DEFAULT)st1 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label=txt1, style=wx.ALIGN_LEFT)st2 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label=txt2, style=wx.ALIGN_LEFT)st1.SetFont(font)st2.SetFont(font)vbox.Add(st1, flag=wx.ALL, border=15)vbox.Add(st2, flag=wx.ALL, border=15)pnl.SetSizer(vbox)self.SetTitle('Bittersweet')self.Centre()def main():app = wx.App()ex = Example(None)ex.Show()app.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
在示例中,我们使用wx.StaticText小部件显示了两首 Bittersweet 歌曲的节奏。
font = wx.Font(13, wx.DEFAULT, wx.NORMAL, wx.DEFAULT)
我们为文本创建一个字体对象。
txt1 = '''I'm giving up the ghost of lovein the shadows cast on devotionShe is the one that I adorecreed of my silent suffocationBreak this bittersweet spell on melost in the arms of destiny'''
这是要在wx.StaticText小部件中显示的字符串。
st1 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label=txt1, style=wx.ALIGN_LEFT)
我们创建wx.StaticText小部件。 文本将向左对齐。
st1.SetFont(font)st2.SetFont(font)
我们使用SetFont()将字体设置为静态文本小部件。
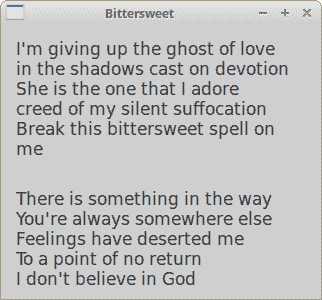
图:wx.StaticText
wx.StaticLine
此小部件在窗口上显示一条简单的线。 它可以是水平或垂直的。
static_line.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode wxPython tutorialIn this code example, we create a static line.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: www.zetcode.comlast modified: April 2018"""import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)font = wx.Font(10, wx.DEFAULT, wx.NORMAL, wx.BOLD)heading = wx.StaticText(self, label='The Central Europe',pos=(25, 15), size=(200, -1))heading.SetFont(font)wx.StaticLine(self, pos=(25, 50), size=(300,1))wx.StaticText(self, label='Slovakia', pos=(25, 80))wx.StaticText(self, label='Hungary', pos=(25, 100))wx.StaticText(self, label='Poland', pos=(25, 120))wx.StaticText(self, label='Czech Republic', pos=(25, 140))wx.StaticText(self, label='Germany', pos=(25, 160))wx.StaticText(self, label='Slovenia', pos=(25, 180))wx.StaticText(self, label='Austria', pos=(25, 200))wx.StaticText(self, label='Switzerland', pos=(25, 220))wx.StaticText(self, label='5 445 000', pos=(250, 80))wx.StaticText(self, label='10 014 000', pos=(250, 100))wx.StaticText(self, label='38 186 000', pos=(250, 120))wx.StaticText(self, label='10 562 000', pos=(250, 140))wx.StaticText(self, label='81 799 000', pos=(250, 160))wx.StaticText(self, label='2 050 000', pos=(250, 180))wx.StaticText(self, label='8 414 000', pos=(250, 200))wx.StaticText(self, label='7 866 000', pos=(250, 220))wx.StaticLine(self, pos=(25, 260), size=(300,1))tsum = wx.StaticText(self, label='164 336 000', pos=(240, 280))sum_font = tsum.GetFont()sum_font.SetWeight(wx.BOLD)tsum.SetFont(sum_font)btn = wx.Button(self, label='Close', pos=(140, 310))btn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose)self.SetSize((360, 380))self.SetTitle('wx.StaticLine')self.Centre()def OnClose(self, e):self.Close(True)def main():app = wx.App()ex = Example(None)ex.Show()app.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
该脚本显示了中欧国家及其人口。 wx.StatLine使它看起来更具视觉吸引力。
wx.StaticLine(self, pos=(25, 50), size=(300,1))
这是wx.StaticLine的构造器
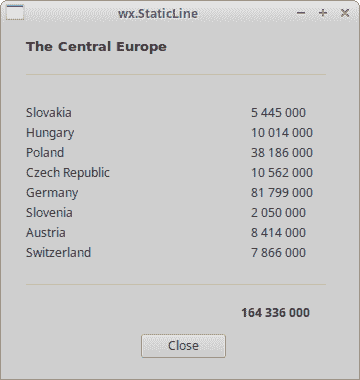
图:wx.StaticLine
wx.StaticBox
这是一种装饰器小部件。 它用于对各种小部件进行逻辑分组。 请注意,必须在其包含的窗口小部件之前创建此窗口小部件,并且这些窗口小部件应该是静态框的同级,而不是子级。
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)wx.StaticBox(pnl, label='Personal Info', pos=(5, 5), size=(240, 170))wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='Male', pos=(15, 30))wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='Married', pos=(15, 55))wx.StaticText(pnl, label='Age', pos=(15, 95))wx.SpinCtrl(pnl, value='1', pos=(55, 90), size=(60, -1), min=1, max=120)btn = wx.Button(pnl, label='Ok', pos=(90, 185), size=(60, -1))btn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose)self.SetSize((270, 250))self.SetTitle('Static box')self.Centre()self.Show(True)def OnClose(self, e):self.Close(True)def main():ex = wx.App()Example(None)ex.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
我们有一个wx.StaticBox来装饰其他四个小部件。
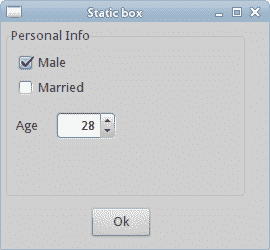
图:静态框
wx.ComboBox
wx.ComboBox是单行文本字段,带有向下箭头图像的按钮和列表框的组合。 当您按下按钮时,将出现一个列表框。 用户只能从提供的字符串列表中选择一个选项。
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)distros = ['Ubuntu', 'Arch', 'Fedora', 'Debian', 'Mint']cb = wx.ComboBox(pnl, pos=(50, 30), choices=distros,style=wx.CB_READONLY)self.st = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='', pos=(50, 140))cb.Bind(wx.EVT_COMBOBOX, self.OnSelect)self.SetSize((250, 230))self.SetTitle('wx.ComboBox')self.Centre()self.Show(True)def OnSelect(self, e):i = e.GetString()self.st.SetLabel(i)def main():ex = wx.App()Example(None)ex.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
从组合框中选择的选项显示在下面的标签中。
distros = ['Ubuntu', 'Arch', 'Fedora', 'Debian', 'Mint']
组合框将包含此字符串列表。
cb = wx.ComboBox(pnl, pos=(50, 30), choices=distros,style=wx.CB_READONLY)
wx.ComboBox小部件已创建。 choices参数采用要在组合框显示的字符串列表。 wx.CB_READONLY样式使列表的字符串为只读。
cb.Bind(wx.EVT_COMBOBOX, self.OnSelect)
当我们从组合框中选择一个选项时,将触发wx.EVT_COMBOBOX事件。 我们将OnSelect()事件处理器插入此事件。
def OnSelect(self, e):i = e.GetString()self.st.SetLabel(i)
我们从组合框中获取选定的项目并将其设置为标签。
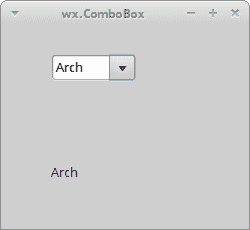
图:wx.ComboBox
wx.CheckBox
wx.CheckBox是具有两种状态的窗口小部件:开和关。 这是一个带有标签的盒子。 标签可以设置在框的右侧或左侧。 如果选中wx.CheckBox,则在方框中用勾号表示。
checkbox.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode wxPython tutorialIn this example we create a checkbox widget.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: www.zetcode.comlast modified: April 2018"""import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)cb = wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='Show title')cb.SetValue(True)cb.Bind(wx.EVT_CHECKBOX, self.ShowOrHideTitle)vbox.Add(cb, flag=wx.TOP|wx.LEFT, border=30)pnl.SetSizer(vbox)self.SetTitle('wx.CheckBox')self.Centre()def ShowOrHideTitle(self, e):sender = e.GetEventObject()isChecked = sender.GetValue()if isChecked:self.SetTitle('wx.CheckBox')else:self.SetTitle('')def main():app = wx.App()ex = Example(None)ex.Show()app.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
在上面的示例中,我们使用wx.CheckBox小部件显示或隐藏窗口标题。
cb = wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='Show title')
这是wx.CheckBox小部件的构造器。
cb.SetValue(True)
默认情况下显示框架窗口的标题,因此我们使用SetValue()方法检查wx.CheckBox小部件。
cb.Bind(wx.EVT_CHECKBOX, self.ShowOrHideTitle)
当我们单击wx.CheckBox小部件时,将触发wx.EVT_CHECKBOX事件。 在此事件上调用ShowOrHideTitle()事件处理器。
def ShowOrHideTitle(self, e):sender = e.GetEventObject()isChecked = sender.GetValue()if isChecked:self.SetTitle('wx.CheckBox')else:self.SetTitle('')
在ShowOrHideTitle()方法中,我们根据wx.CheckBox小部件的状态显示或隐藏标题。
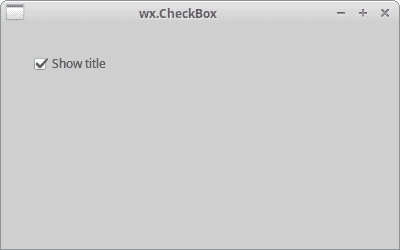
图:wx.CheckBox
wx.StatusBar
wx.StatusBar小部件用于显示应用状态信息。 它可以分为几个部分以显示不同类型的信息。 我们可以在wx.StatusBar中插入其他小部件。 它可以用作对话框的替代方法,因为对话框经常被滥用,并且大多数用户不喜欢它们。 我们可以通过两种方式创建wx.StatusBar。 我们可以手动创建自己的wx.StatusBar并调用SetStatusBar()方法,也可以简单地调用CreateStatusBar()方法。 后一种方法为我们创建了默认的wx.StatusBar。
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)button = wx.Button(pnl, label='Button', pos=(20, 20))text = wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='CheckBox', pos=(20, 90))combo = wx.ComboBox(pnl, pos=(120, 22), choices=['Python', 'Ruby'])slider = wx.Slider(pnl, 5, 6, 1, 10, (120, 90), (110, -1))pnl.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter)button.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter)text.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter)combo.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter)slider.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter)self.sb = self.CreateStatusBar()self.SetSize((250, 230))self.SetTitle('wx.Statusbar')self.Centre()self.Show(True)def OnWidgetEnter(self, e):name = e.GetEventObject().GetClassName()self.sb.SetStatusText(name + ' widget')e.Skip()def main():ex = wx.App()Example(None)ex.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
在我们的示例中,我们有一个wx.Frame小部件以及其他五个小部件。 如果将鼠标指针悬停在窗口小部件上,则其名称将显示在wx.StatusBar中。
pnl.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter)
如果我们输入小部件的区域,则会生成EVT_ENTER_WINDOW事件。
self.sb = self.CreateStatusBar()
使用CreateStatusBar()方法创建状态栏。
def OnWidgetEnter(self, e):name = e.GetEventObject().GetClassName()self.sb.SetStatusText(name + ' widget')e.Skip()
在OnWidgetEnter()方法内部,我们找出使用鼠标指针输入的小部件的名称。 我们使用SetStatusText()方法设置状态文本。
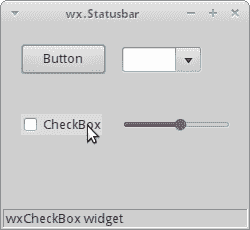
图:wx.StatusBar
wx.RadioButton
wx.RadioButton是一个小部件,允许用户从一组选项中选择一个唯一选项。 通过使组中的第一个单选按钮包含wx.RB_GROUP样式来定义单选按钮组。 在第一个带有此样式标记的单选按钮之后定义的所有其他单选按钮将添加到第一个单选按钮的功能组中。 用wx.RB_GROUP标志声明另一个单选按钮将启动一个新的单选按钮组。
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)self.rb1 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value A', pos=(10, 10),style=wx.RB_GROUP)self.rb2 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value B', pos=(10, 30))self.rb3 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value C', pos=(10, 50))self.rb1.Bind(wx.EVT_RADIOBUTTON, self.SetVal)self.rb2.Bind(wx.EVT_RADIOBUTTON, self.SetVal)self.rb3.Bind(wx.EVT_RADIOBUTTON, self.SetVal)self.sb = self.CreateStatusBar(3)self.sb.SetStatusText("True", 0)self.sb.SetStatusText("False", 1)self.sb.SetStatusText("False", 2)self.SetSize((210, 210))self.SetTitle('wx.RadioButton')self.Centre()self.Show(True)def SetVal(self, e):state1 = str(self.rb1.GetValue())state2 = str(self.rb2.GetValue())state3 = str(self.rb3.GetValue())self.sb.SetStatusText(state1, 0)self.sb.SetStatusText(state2, 1)self.sb.SetStatusText(state3, 2)def main():ex = wx.App()Example(None)ex.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
我们有一组三个单选按钮。 每个单选按钮的状态显示在状态栏中。
self.rb1 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value A', pos=(10, 10),style=wx.RB_GROUP)self.rb2 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value B', pos=(10, 30))self.rb3 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value C', pos=(10, 50))
我们创建三个单选按钮。 第一个单选按钮设置为wx.RB_GROUP样式。 它将启动一个新的广播组。
self.rb1.Bind(wx.EVT_RADIOBUTTON, self.SetVal)
我们将wx.EVT_RADIOBUTTON事件绑定到SetVal()事件处理器。
self.sb = self.CreateStatusBar(3)self.sb.SetStatusText("True", 0)self.sb.SetStatusText("False", 1)self.sb.SetStatusText("False", 2)
我们创建一个带有三个字段的状态栏。 我们将初始文本设置为与单选按钮状态相对应的状态栏。
def SetVal(self, e):state1 = str(self.rb1.GetValue())state2 = str(self.rb2.GetValue())state3 = str(self.rb3.GetValue())self.sb.SetStatusText(state1, 0)self.sb.SetStatusText(state2, 1)self.sb.SetStatusText(state3, 2)
在SetVal()方法内,我们找出单选按钮的状态。 我们将状态栏字段更新为当前的单选按钮值。
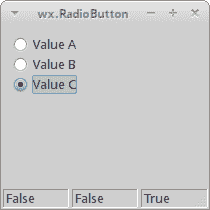
图:wx.RadioButton
wx.Gauge
wx.Gauge是在处理冗长的任务时使用的小部件。 它具有一个指示器以显示任务的当前状态。
gauge_wid.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode wxPython tutorialIn this example we create gauge widget.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: www.zetcode.comlast modified: April 2018"""import wxTASK_RANGE = 50class Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):self.timer = wx.Timer(self, 1)self.count = 0self.Bind(wx.EVT_TIMER, self.OnTimer, self.timer)pnl = wx.Panel(self)vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)hbox1 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)hbox2 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)hbox3 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)self.gauge = wx.Gauge(pnl, range=TASK_RANGE, size=(250, -1))self.btn1 = wx.Button(pnl, wx.ID_OK)self.btn2 = wx.Button(pnl, wx.ID_STOP)self.text = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='Task to be done')self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnOk, self.btn1)self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnStop, self.btn2)hbox1.Add(self.gauge, proportion=1, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE)hbox2.Add(self.btn1, proportion=1, flag=wx.RIGHT, border=10)hbox2.Add(self.btn2, proportion=1)hbox3.Add(self.text, proportion=1)vbox.Add((0, 30))vbox.Add(hbox1, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE)vbox.Add((0, 20))vbox.Add(hbox2, proportion=1, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE)vbox.Add(hbox3, proportion=1, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE)pnl.SetSizer(vbox)self.SetTitle('wx.Gauge')self.Centre()def OnOk(self, e):if self.count >= TASK_RANGE:returnself.timer.Start(100)self.text.SetLabel('Task in Progress')def OnStop(self, e):if self.count == 0 or self.count >= TASK_RANGE or not self.timer.IsRunning():returnself.timer.Stop()self.text.SetLabel('Task Interrupted')def OnTimer(self, e):self.count = self.count + 1self.gauge.SetValue(self.count)if self.count == TASK_RANGE:self.timer.Stop()self.text.SetLabel('Task Completed')def main():app = wx.App()ex = Example(None)ex.Show()app.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
我们有一个压力表和两个按钮。 一个按钮启动压力表,另一按钮停止压力表。
self.timer = wx.Timer(self, 1)self.count = 0
我们使用wx.Timer在特定间隔执行代码。 届时我们将更新量规。 count变量用于确定已完成任务的一部分。
self.gauge = wx.Gauge(pnl, range=TASK_RANGE, size=(250, -1))
这是wx.Gauge小部件的构造器。 range参数设置窗口小部件的最大整数值。
def OnOk(self, e):if self.count >= TASK_RANGE:returnself.timer.Start(100)self.text.SetLabel('Task in Progress')
当我们单击确定按钮时,将调用OnOk()方法。 我们首先检查count变量是否在任务范围内。 如果没有,我们从方法中返回。 如果任务尚未完成,我们将启动计时器并更新静态文本。
def OnStop(self, e):if self.count == 0 or self.count >= TASK_RANGE or not self.timer.IsRunning():returnself.timer.Stop()self.text.SetLabel('Task Interrupted')
当我们单击停止按钮时,将调用OnStop()方法。 我们检查停止任务的条件。 如果遇到他们,我们将停止计时器并更新静态文本。
def OnTimer(self, e):self.count = self.count + 1self.gauge.SetValue(self.count)if self.count == TASK_RANGE:self.timer.Stop()self.text.SetLabel('Task Completed')
启动计时器后,会定期调用OnTimer()方法。 在该方法中,我们更新了count变量和gauge控件。 如果count变量等于TASK_RANGE,我们将停止计时器并更新静态文本。
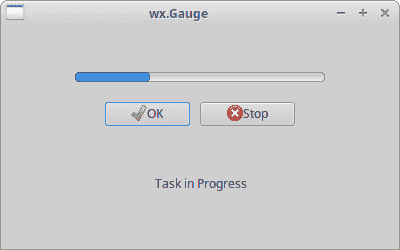
图:wx.Gauge
wx.Slider
wx.Slider是具有简单句柄的小部件。 该手柄可以前后拉动。 这样,我们可以选择特定任务。
slider_wid.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode wxPython tutorialIn this example we create slider control.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: www.zetcode.comlast modified: April 2018"""import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)sizer = wx.GridBagSizer(5, 5)sld = wx.Slider(pnl, value=200, minValue=150, maxValue=500,style=wx.SL_HORIZONTAL)sld.Bind(wx.EVT_SCROLL, self.OnSliderScroll)sizer.Add(sld, pos=(0, 0), flag=wx.ALL|wx.EXPAND, border=25)self.txt = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='200')sizer.Add(self.txt, pos=(0, 1), flag=wx.TOP|wx.RIGHT, border=25)sizer.AddGrowableCol(0)pnl.SetSizer(sizer)self.SetTitle('wx.Slider')self.Centre()def OnSliderScroll(self, e):obj = e.GetEventObject()val = obj.GetValue()self.txt.SetLabel(str(val))def main():app = wx.App()ex = Example(None)ex.Show()app.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
静态文本中显示了在滑块中选择的值。
sld = wx.Slider(pnl, value=200, minValue=150, maxValue=500,style=wx.SL_HORIZONTAL)
创建了wx.Slider。 我们使用值参数提供滑块的初始位置,并使用minValue和maxValue参数提供最小和最大滑块位置。 wx.SL_HORIZONTAL使滑块变为水平。
sld.Bind(wx.EVT_SCROLL, self.OnSliderScroll)
遇到wx.EVT_SCROLL事件时,将调用OnSliderScroll()方法。
self.txt = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='200')
当前选择的滑块值显示在静态文本中,该文本位于滑块下方。
def OnSliderScroll(self, e):obj = e.GetEventObject()val = obj.GetValue()self.txt.SetLabel(str(val))
在OnSliderScroll()方法中,我们获取事件的发送者。 我们获取滑块的当前值并将其设置为静态文本。
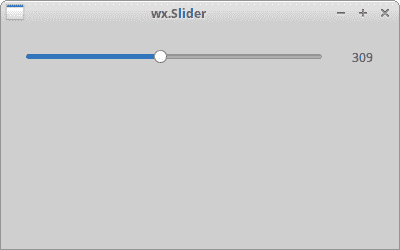
图:wx.Slider
wx.SpinCtrl
wx.SpinCtrl小部件使我们可以增加和减少值。
spin_ctrl.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode wxPython tutorialIn this example we create spin control.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: www.zetcode.comlast modified: April 2018"""import wxclass Example(wx.Frame):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)self.InitUI()def InitUI(self):pnl = wx.Panel(self)sizer = wx.GridBagSizer(5, 5)st1 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='Convert Fahrenheit temperature to Celsius')sizer.Add(st1, pos=(0, 0), span=(1, 2), flag=wx.ALL, border=15)st2 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='Fahrenheit:')sizer.Add(st2, pos=(1, 0), flag=wx.ALL | wx.ALIGN_CENTER, border=15)self.sc = wx.SpinCtrl(pnl, value='0')self.sc.SetRange(-459, 1000)sizer.Add(self.sc, pos=(1, 1), flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTER)st3 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='Celsius:')sizer.Add(st3, pos=(2, 0), flag=wx.ALL|wx.ALIGN_RIGHT, border=15)self.celsius = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='')sizer.Add(self.celsius, pos=(2, 1), flag=wx.ALL, border=15)computeButton = wx.Button(pnl, label='Compute')computeButton.SetFocus()sizer.Add(computeButton, pos=(3, 0), flag=wx.ALIGN_RIGHT|wx.TOP, border=30)closeButton = wx.Button(pnl, label='Close')sizer.Add(closeButton, pos=(3, 1), flag=wx.ALIGN_LEFT|wx.TOP, border=30)computeButton.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnCompute)closeButton.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose)pnl.SetSizer(sizer)self.SetTitle('wx.SpinCtrl')self.Centre()def OnClose(self, e):self.Close(True)def OnCompute(self, e):fahr = self.sc.GetValue()cels = round((fahr - 32) * 5 / 9.0, 2)self.celsius.SetLabel(str(cels))def main():app = wx.App()ex = Example(None)ex.Show()app.MainLoop()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
该脚本将华氏温度转换为摄氏温度。 我们使用wx.SpinCtrl小部件为华氏温度选择一个值。
self.sc = wx.SpinCtrl(pnl, value='0')self.sc.SetRange(-459, 1000)
我们创建一个初始值为 0 的wx.SpinCtrl小部件。SetRange()设置该小部件的值范围。
def OnCompute(self, e):fahr = self.sc.GetValue()cels = round((fahr - 32) * 5 / 9.0, 2)self.celsius.SetLabel(str(cels))
当我们单击计算按钮时,将调用OnCompute()方法。 在方法的主体中,我们从旋转控件中获取当前值。 我们计算摄氏温度并将计算的温度设置为静态文本小部件。
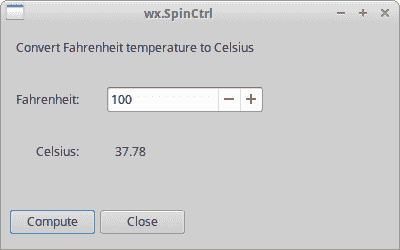
图:wx.SpinCtrl
wxPython 教程的这一部分专用于核心 wxPython 小部件。

