制作计算机游戏具有挑战性。 程序员迟早会希望有一天创建一个计算机游戏。 实际上,许多人对编程很感兴趣,因为他们玩游戏并想创建自己的游戏。 制作计算机游戏将有助于提高您的编程技能。
俄罗斯方块
俄罗斯方块游戏是有史以来最受欢迎的计算机游戏之一。 原始游戏是由俄罗斯程序员 Alexey Pajitnov 于 1985 年设计和编程的。此后,几乎所有版本的几乎所有计算机平台上都可以使用俄罗斯方块。 甚至我的手机都有俄罗斯方块游戏的修改版。
俄罗斯方块被称为下降块益智游戏。 在这个游戏中,我们有七个不同的形状,称为tetrominoes。 S 形,Z 形,T 形,L 形,线形,镜像 L 形和正方形。 这些形状中的每一个都形成有四个正方形。 形状从板上掉下来。 俄罗斯方块游戏的目的是移动和旋转形状,以便它们尽可能地适合。 如果我们设法形成一行,则该行将被破坏并得分。 我们玩俄罗斯方块游戏,直到达到顶峰。
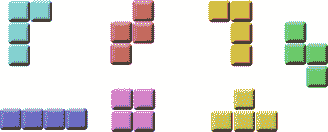
图:Tetrominoes
PySide 是旨在创建应用的工具包。 还有其他一些旨在创建计算机游戏的库。 但是,可以使用 PySide 和其他应用工具包来创建游戏。
开发
我们的俄罗斯方块游戏没有图像,我们使用 PySide 编程工具包中提供的绘图 API 绘制四面体。 每个计算机游戏的背后都有一个数学模型。 俄罗斯方块也是如此。
游戏背后的一些想法:
- 我们使用
QtCore.QBasicTimer()创建游戏周期。 - 绘制四方块。
- 形状以正方形为单位移动(而不是逐个像素移动)。
- 从数学上讲,棋盘是一个简单的数字列表。
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""ZetCode PySide tutorialThis is a simple Tetris clonein PySide.author: Jan Bodnarwebsite: zetcode.comlast edited: August 2011"""import sys, randomfrom PySide import QtCore, QtGuiclass Communicate(QtCore.QObject):msgToSB = QtCore.Signal(str)class Tetris(QtGui.QMainWindow):def __init__(self):super(Tetris, self).__init__()self.setGeometry(300, 300, 180, 380)self.setWindowTitle('Tetris')self.Tetrisboard = Board(self)self.setCentralWidget(self.Tetrisboard)self.statusbar = self.statusBar()self.Tetrisboard.c.msgToSB[str].connect(self.statusbar.showMessage)self.Tetrisboard.start()self.center()def center(self):screen = QtGui.QDesktopWidget().screenGeometry()size = self.geometry()self.move((screen.width()-size.width())/2,(screen.height()-size.height())/2)class Board(QtGui.QFrame):BoardWidth = 10BoardHeight = 22Speed = 300def __init__(self, parent):super(Board, self).__init__()self.timer = QtCore.QBasicTimer()self.isWaitingAfterLine = Falseself.curPiece = Shape()self.nextPiece = Shape()self.curX = 0self.curY = 0self.numLinesRemoved = 0self.board = []self.setFocusPolicy(QtCore.Qt.StrongFocus)self.isStarted = Falseself.isPaused = Falseself.clearBoard()self.c = Communicate()self.nextPiece.setRandomShape()def shapeAt(self, x, y):return self.board[(y * Board.BoardWidth) + x]def setShapeAt(self, x, y, shape):self.board[(y * Board.BoardWidth) + x] = shapedef squareWidth(self):return self.contentsRect().width() / Board.BoardWidthdef squareHeight(self):return self.contentsRect().height() / Board.BoardHeightdef start(self):if self.isPaused:returnself.isStarted = Trueself.isWaitingAfterLine = Falseself.numLinesRemoved = 0self.clearBoard()self.c.msgToSB.emit(str(self.numLinesRemoved))self.newPiece()self.timer.start(Board.Speed, self)def pause(self):if not self.isStarted:returnself.isPaused = not self.isPausedif self.isPaused:self.timer.stop()self.c.msgToSB.emit("paused")else:self.timer.start(Board.Speed, self)self.c.msgToSB.emit(str(self.numLinesRemoved))self.update()def paintEvent(self, event):painter = QtGui.QPainter(self)rect = self.contentsRect()boardTop = rect.bottom() - Board.BoardHeight * self.squareHeight()for i in range(Board.BoardHeight):for j in range(Board.BoardWidth):shape = self.shapeAt(j, Board.BoardHeight - i - 1)if shape != Tetrominoes.NoShape:self.drawSquare(painter,rect.left() + j * self.squareWidth(),boardTop + i * self.squareHeight(), shape)if self.curPiece.shape() != Tetrominoes.NoShape:for i in range(4):x = self.curX + self.curPiece.x(i)y = self.curY - self.curPiece.y(i)self.drawSquare(painter, rect.left() + x * self.squareWidth(),boardTop + (Board.BoardHeight - y - 1) * self.squareHeight(),self.curPiece.shape())def keyPressEvent(self, event):if not self.isStarted or self.curPiece.shape() == Tetrominoes.NoShape:QtGui.QWidget.keyPressEvent(self, event)returnkey = event.key()if key == QtCore.Qt.Key_P:self.pause()returnif self.isPaused:returnelif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Left:self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX - 1, self.curY)elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Right:self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX + 1, self.curY)elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Down:self.tryMove(self.curPiece.rotatedRight(), self.curX, self.curY)elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Up:self.tryMove(self.curPiece.rotatedLeft(), self.curX, self.curY)elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Space:self.dropDown()elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_D:self.oneLineDown()else:QtGui.QWidget.keyPressEvent(self, event)def timerEvent(self, event):if event.timerId() == self.timer.timerId():if self.isWaitingAfterLine:self.isWaitingAfterLine = Falseself.newPiece()else:self.oneLineDown()else:QtGui.QFrame.timerEvent(self, event)def clearBoard(self):for i in range(Board.BoardHeight * Board.BoardWidth):self.board.append(Tetrominoes.NoShape)def dropDown(self):newY = self.curYwhile newY > 0:if not self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX, newY - 1):breaknewY -= 1self.pieceDropped()def oneLineDown(self):if not self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX, self.curY - 1):self.pieceDropped()def pieceDropped(self):for i in range(4):x = self.curX + self.curPiece.x(i)y = self.curY - self.curPiece.y(i)self.setShapeAt(x, y, self.curPiece.shape())self.removeFullLines()if not self.isWaitingAfterLine:self.newPiece()def removeFullLines(self):numFullLines = 0rowsToRemove = []for i in range(Board.BoardHeight):n = 0for j in range(Board.BoardWidth):if not self.shapeAt(j, i) == Tetrominoes.NoShape:n = n + 1if n == 10:rowsToRemove.append(i)rowsToRemove.reverse()for m in rowsToRemove:for k in range(m, Board.BoardHeight):for l in range(Board.BoardWidth):self.setShapeAt(l, k, self.shapeAt(l, k + 1))numFullLines = numFullLines + len(rowsToRemove)if numFullLines > 0:self.numLinesRemoved = self.numLinesRemoved + numFullLinesprint self.numLinesRemovedself.c.msgToSB.emit(str(self.numLinesRemoved))self.isWaitingAfterLine = Trueself.curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoes.NoShape)self.update()def newPiece(self):self.curPiece = self.nextPieceself.nextPiece.setRandomShape()self.curX = Board.BoardWidth / 2 + 1self.curY = Board.BoardHeight - 1 + self.curPiece.minY()if not self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX, self.curY):self.curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoes.NoShape)self.timer.stop()self.isStarted = Falseself.c.msgToSB.emit("Game over")def tryMove(self, newPiece, newX, newY):for i in range(4):x = newX + newPiece.x(i)y = newY - newPiece.y(i)if x < 0 or x >= Board.BoardWidth or y < 0 or y >= Board.BoardHeight:return Falseif self.shapeAt(x, y) != Tetrominoes.NoShape:return Falseself.curPiece = newPieceself.curX = newXself.curY = newYself.update()return Truedef drawSquare(self, painter, x, y, shape):colorTable = [0x000000, 0xCC6666, 0x66CC66, 0x6666CC,0xCCCC66, 0xCC66CC, 0x66CCCC, 0xDAAA00]color = QtGui.QColor(colorTable[shape])painter.fillRect(x + 1, y + 1, self.squareWidth() - 2,self.squareHeight() - 2, color)painter.setPen(color.lighter())painter.drawLine(x, y + self.squareHeight() - 1, x, y)painter.drawLine(x, y, x + self.squareWidth() - 1, y)painter.setPen(color.darker())painter.drawLine(x + 1, y + self.squareHeight() - 1,x + self.squareWidth() - 1, y + self.squareHeight() - 1)painter.drawLine(x + self.squareWidth() - 1,y + self.squareHeight() - 1, x + self.squareWidth() - 1, y + 1)class Tetrominoes(object):NoShape = 0ZShape = 1SShape = 2LineShape = 3TShape = 4SquareShape = 5LShape = 6MirroredLShape = 7class Shape(object):coordsTable = (((0, 0), (0, 0), (0, 0), (0, 0)),((0, -1), (0, 0), (-1, 0), (-1, 1)),((0, -1), (0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1)),((0, -1), (0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2)),((-1, 0), (0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1)),((0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)),((-1, -1), (0, -1), (0, 0), (0, 1)),((1, -1), (0, -1), (0, 0), (0, 1)))def __init__(self):self.coords = [[0,0] for i in range(4)]self.pieceShape = Tetrominoes.NoShapeself.setShape(Tetrominoes.NoShape)def shape(self):return self.pieceShapedef setShape(self, shape):table = Shape.coordsTable[shape]for i in range(4):for j in range(2):self.coords[i][j] = table[i][j]self.pieceShape = shapedef setRandomShape(self):self.setShape(random.randint(1, 7))def x(self, index):return self.coords[index][0]def y(self, index):return self.coords[index][1]def setX(self, index, x):self.coords[index][0] = xdef setY(self, index, y):self.coords[index][1] = ydef minX(self):m = self.coords[0][0]for i in range(4):m = min(m, self.coords[i][0])return mdef maxX(self):m = self.coords[0][0]for i in range(4):m = max(m, self.coords[i][0])return mdef minY(self):m = self.coords[0][1]for i in range(4):m = min(m, self.coords[i][1])return mdef maxY(self):m = self.coords[0][1]for i in range(4):m = max(m, self.coords[i][1])return mdef rotatedLeft(self):if self.pieceShape == Tetrominoes.SquareShape:return selfresult = Shape()result.pieceShape = self.pieceShapefor i in range(4):result.setX(i, self.y(i))result.setY(i, -self.x(i))return resultdef rotatedRight(self):if self.pieceShape == Tetrominoes.SquareShape:return selfresult = Shape()result.pieceShape = self.pieceShapefor i in range(4):result.setX(i, -self.y(i))result.setY(i, self.x(i))return resultdef main():app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)t = Tetris()t.show()sys.exit(app.exec_())if __name__ == '__main__':main()
我对游戏做了一些简化,以便于理解。 游戏启动后立即开始。 我们可以通过按 p 键暂停游戏。 空格键将把俄罗斯方块放在底部。 游戏以恒定速度进行,没有实现加速。 分数是我们已删除的行数。
self.statusbar = self.statusBar()self.Tetrisboard.c.msgToSB[str].connect(self.statusbar.showMessage)
我们创建一个状态栏,在其中显示消息。 我们将显示三种可能的消息。 已删除的行数。 暂停的消息和游戏结束消息。
...self.curX = 0self.curY = 0self.numLinesRemoved = 0self.board = []...
在开始游戏周期之前,我们先初始化一些重要的变量。 self.board变量是一个从 0 到 7 的数字的列表。它表示各种形状的位置以及板上形状的其余部分。
for j in range(Board.BoardWidth):shape = self.shapeAt(j, Board.BoardHeight - i - 1)if shape != Tetrominoes.NoShape:self.drawSquare(painter,rect.left() + j * self.squareWidth(),boardTop + i * self.squareHeight(), shape)
游戏的绘图分为两个步骤。 在第一步中,我们绘制所有形状或已放置到板底部的形状的其余部分。 所有正方形都记在self.board列表变量中。 我们使用shapeAt()方法访问它。
if self.curPiece.shape() != Tetrominoes.NoShape:for i in range(4):x = self.curX + self.curPiece.x(i)y = self.curY - self.curPiece.y(i)self.drawSquare(painter, rect.left() + x * self.squareWidth(),boardTop + (Board.BoardHeight - y - 1) * self.squareHeight(),self.curPiece.shape())
下一步是绘制掉落的实际零件。
elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Left:self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX - 1, self.curY)elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Right:self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX + 1, self.curY)
在keyPressEvent中,我们检查是否有按下的键。 如果按向右箭头键,我们将尝试将棋子向右移动。 我们说尝试,因为这片可能无法移动。
def tryMove(self, newPiece, newX, newY):for i in range(4):x = newX + newPiece.x(i)y = newY - newPiece.y(i)if x < 0 or x >= Board.BoardWidth or y < 0 or y >= Board.BoardHeight:return Falseif self.shapeAt(x, y) != Tetrominoes.NoShape:return Falseself.curPiece = newPieceself.curX = newXself.curY = newYself.update()return True
在tryMove()方法中,我们尝试移动形状。 如果形状在板的边缘或与其他零件相邻,则返回false。 否则,我们将当前的下降片放到新位置。
def timerEvent(self, event):if event.timerId() == self.timer.timerId():if self.isWaitingAfterLine:self.isWaitingAfterLine = Falseself.newPiece()else:self.oneLineDown()else:QtGui.QFrame.timerEvent(self, event)
在计时器事件中,我们可以在上一个下降到底部之后创建一个新的片断,或者将下降的片断向下移动一行。
def removeFullLines(self):numFullLines = 0rowsToRemove = []for i in range(Board.BoardHeight):n = 0for j in range(Board.BoardWidth):if not self.shapeAt(j, i) == Tetrominoes.NoShape:n = n + 1if n == 10:rowsToRemove.append(i)rowsToRemove.reverse()for m in rowsToRemove:for k in range(m, Board.BoardHeight):for l in range(Board.BoardWidth):self.setShapeAt(l, k, self.shapeAt(l, k + 1))...
如果片段触底,我们将调用removeFullLines()方法。 首先,我们找出所有实线。 然后我们将其删除。 通过将所有行移动到当前全行上方来将其向下移动一行来实现。 注意,我们颠倒了要删除的行的顺序。 否则,它将无法正常工作。 在我们的情况下,我们使用天真重力。 这意味着碎片可能会漂浮在空的间隙上方。
def newPiece(self):self.curPiece = self.nextPieceself.nextPiece.setRandomShape()self.curX = Board.BoardWidth / 2 + 1self.curY = Board.BoardHeight - 1 + self.curPiece.minY()if not self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX, self.curY):self.curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoes.NoShape)self.timer.stop()self.isStarted = Falseself.c.msgToSB.emit("Game over")
newPiece()方法随机创建一个新的俄罗斯方块。 如果棋子无法进入其初始位置,则游戏结束。
Shape类保存有关俄罗斯方块的信息。
self.coords = [[0,0] for i in range(4)]
创建后,我们将创建一个空坐标列表。 该列表将保存俄罗斯方块的坐标。 例如,这些元组(0,-1),(0,0),(1,0),(1,1)表示旋转的 S 形。 下图说明了形状。
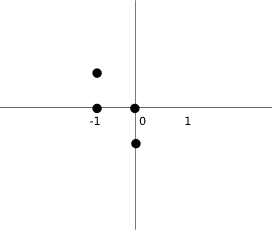
图:坐标
当绘制当前下降片时,将其绘制在self.curX,self.curY position处。 然后,我们查看坐标表并绘制所有四个正方形。
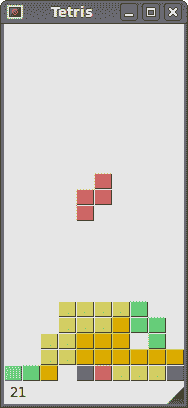
图:俄罗斯方块
这是 PySide 中的俄罗斯方块游戏。

