Hair Material
A new hair material has been implemented in OctaneRender® 2020 series that improves hair rendering realism. The difference between hair material and traditional diffuse/specular materials is that hair material assumes the geometry it’s assigned to is strictly a hair spline, allowing pre-integration for multi-scattering effects that occur in hair geometry. The Octane Hair material works in connection with the Cinema 4D hair material (see the Cinema 4D hair material documentation here), as the C4D hair material specifies certain physical hair characteristics, such as frizz and kink (its use with the Octane hair material is discussed here) and the W Coordinate node, which allows for color changes along the length of the hair strand, as discussed here.
The Hair material has its unique set of parameters, allowing different coloring modes for hair, and also multiple roughness parameters for different scattering behavior along a hair strand. The illustration below shows the Hair material node.
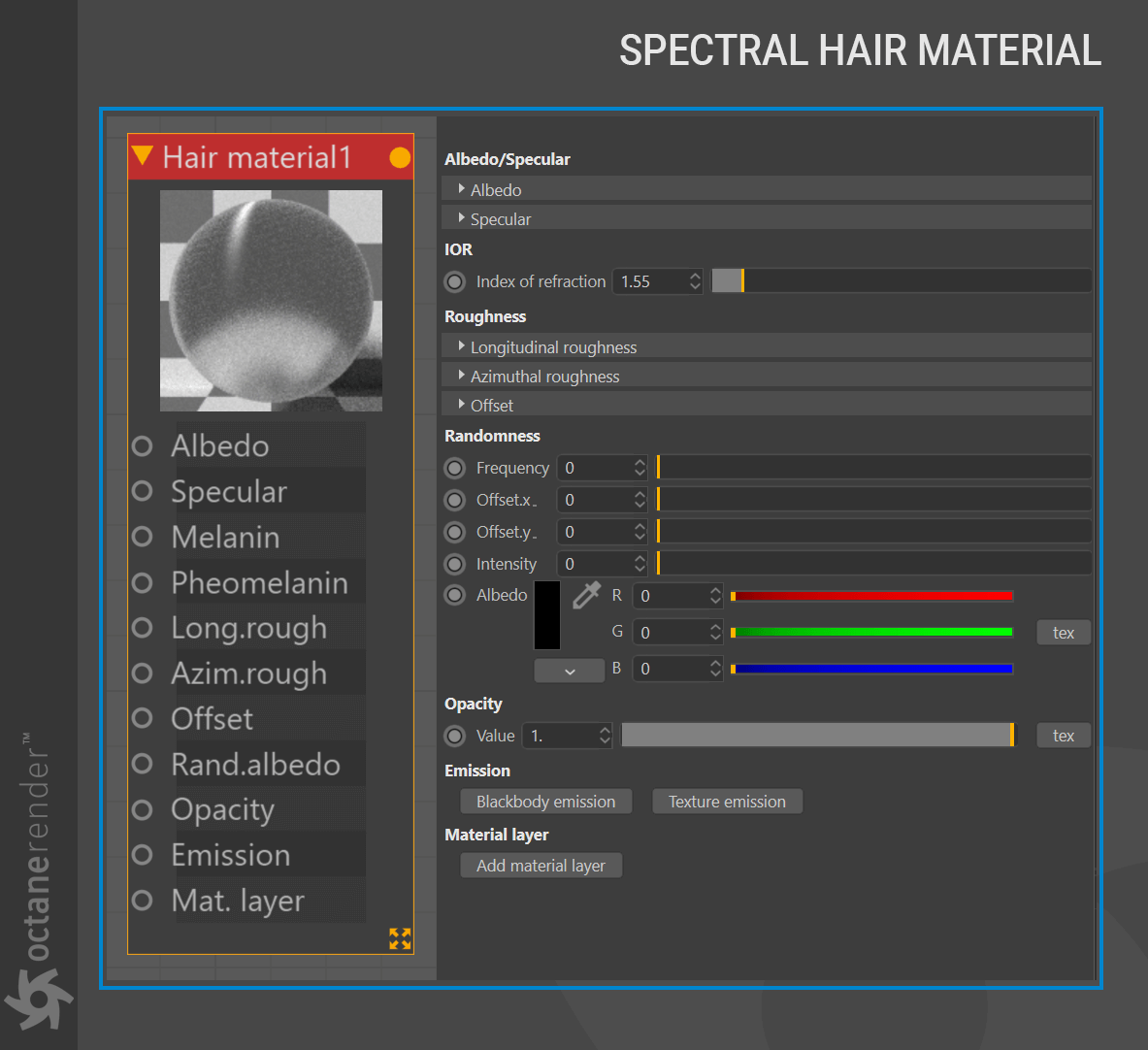
Melanin:
The pigmentation component that gives the hair strand its main color. The higher the value assigned, the higher the concentration of melanin and the darker the hair strands are.
Pheomelanin:
The redness (pheomelanin content) of the hair strand as a fraction of all melanin. 1.0 makes the hair redder. The ratio of melanin to pheomelanin determines how red the hair is. The pheomelanin amount will have no effect if the melanin is set to 0.
Opacity:
Controls the transparency of the hair. A value of 0.0 is transparent, while 1.0 is fully opaque.
IOR:
Hair index of refraction. The typical value for human hair is 1.55. The higher the value, the more reflective the hair strands.
**
Mode:
Mode allows you to specify whether you want the color of the hair to be defined by either the melanin+pheomelanin option or the albedo+specular option.
Albedo:
Albedo is used only in albedo+specular mode, and defines the base color of the hair strand directly (everything that is not specularly reflected).
Specular:
Specular is used only in albedo+specular mode, and defines the specular reflection color.
Longitudinal Roughness:
Longitudinal roughness defines the roughness along a strand of hair, the higher this value is, the more scattering along the strand (this is called longitudinal scattering) and the rougher the strand of hair would look. On the other hand, the lower this value is, the shinier a strand of hair would look, as seen in the image below with varying longitudinal roughness from low (left) to high (right):

**
Azimuthal Roughness:
Azimuthal roughness defines the roughness for the cross section of a hair strand at the intersection, the higher this value, the more multiple scattered light exits the hair strand, and overall hair volume lightens. The image below shows the effect with varying azimuthal roughness from low (left) to high (right):

**
Offset:
Offest adds a series of small scales of angles along the cylindrical hair strand, so it appears less uniform.
Random frequency:
Random frequency specifies a value from 0 to 1 to control the frequency of randomness applied on the hair color.
Randomness offset:
Random offset specifies a 2-dimensional value from 0 to 1 to shift the randomness applied on the hair color.
Randomness intensity:
Random intensity specifies the intensity of the random albedo is being applied over the base color.
Random albedo:
Random albedo is limited to the albedo + specular mode, it allows a random color to be applied over the base albedo of the hair model.
Emission:
Emission allows the connection of an emission node type to allow a hair strand to emit color.

