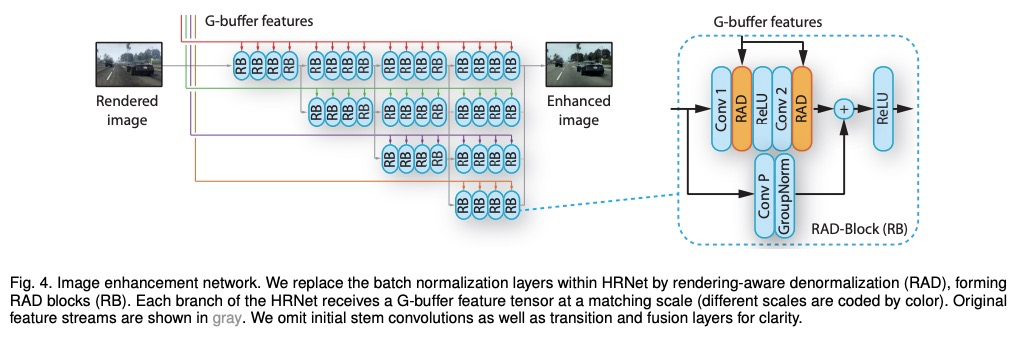
- 1、[CV] Enhancing Photorealism Enhancement
- 2、[LG] Diffusion Models Beat GANs on Image Synthesis
- 3、[LG] Deep Neural Networks as Point Estimates for Deep Gaussian Processes
- 4、[CV] VICReg: Variance-Invariance-Covariance Regularization for Self-Supervised Learning
- 5、[CV] NeRD: Neural 3D Reflection Symmetry Detector
- [CV] Measuring Model Biases in the Absence of Ground Truth
- [SI] COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy on Social Media: Building a Public Twitter Dataset of Anti-vaccine Content, Vaccine Misinformation and Conspiracies
- [LG] Leveraging Sparse Linear Layers for Debuggable Deep Networks
- [LG] Optimization of Graph Neural Networks: Implicit Acceleration by Skip Connections and More Depth
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] Enhancing Photorealism Enhancement
S R. Richter, H A AlHaija, V Koltun
[Intel Lab]
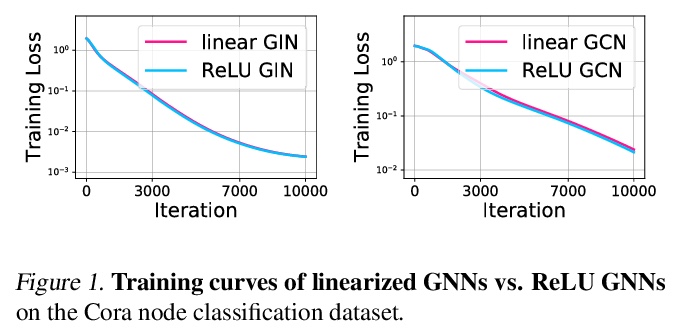
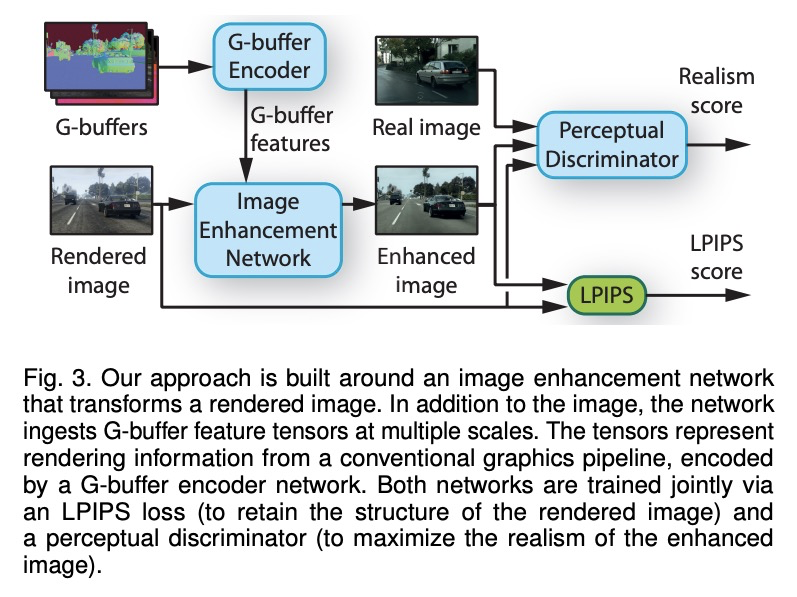
合成图像真实度提升。提出一种增强合成图像真实性的方法。图像由一个卷积网络进行增强,该网络利用传统渲染管道产生的中间表征,通过一种新的对抗性目标进行训练,在多个感知层次提供了有力的监督。分析了常用数据集的场景布局分布,发现它们在重要方面存在差异。假设这是导致在许多先前方法的结果中可以观察到的明显假象的原因之一。为解决该问题,提出一种新策略,在训练期间对图块进行采样,在用于逼真度提升的深度网络模块引入了多项架构改进,大大增强了渲染图像的真实性。总体上,该方法产生了高质量的增强效果,在几何和语义上与输入图像一致,同时与各自的数据集的风格相匹配。
We present an approach to enhancing the realism of synthetic images. The images are enhanced by a convolutional network that leverages intermediate representations produced by conventional rendering pipelines. The network is trained via a novel adversarial objective, which provides strong supervision at multiple perceptual levels. We analyze scene layout distributions in commonly used datasets and find that they differ in important ways. We hypothesize that this is one of the causes of strong artifacts that can be observed in the results of many prior methods. To address this we propose a new strategy for sampling image patches during training. We also introduce multiple architectural improvements in the deep network modules used for photorealism enhancement. We confirm the benefits of our contributions in controlled experiments and report substantial gains in stability and realism in comparison to recent image-to-image translation methods and a variety of other baselines.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfdfq54Hw


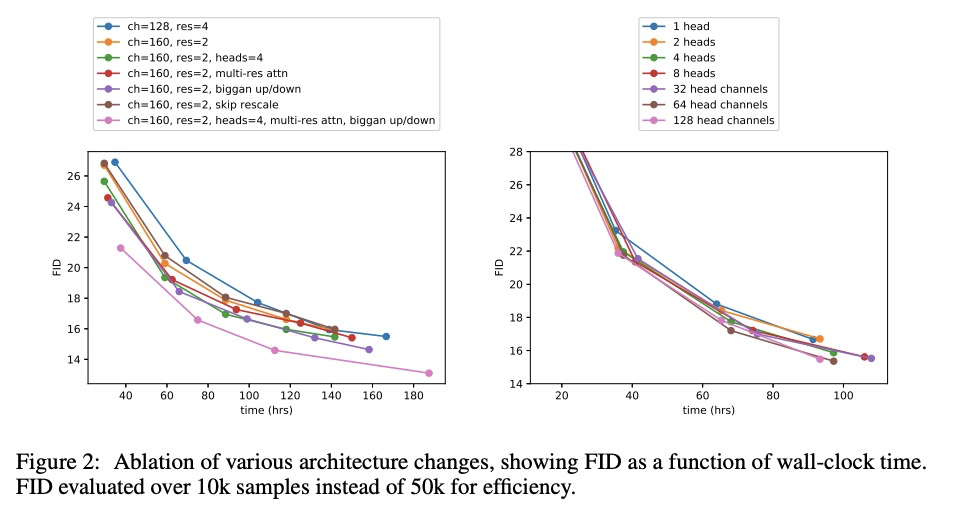
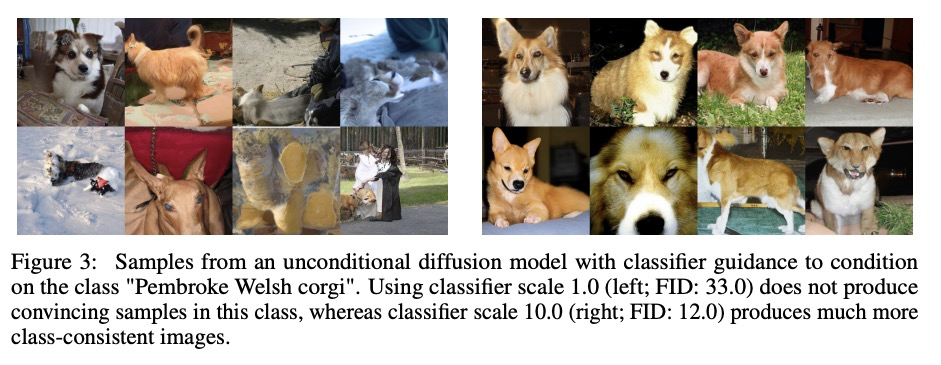
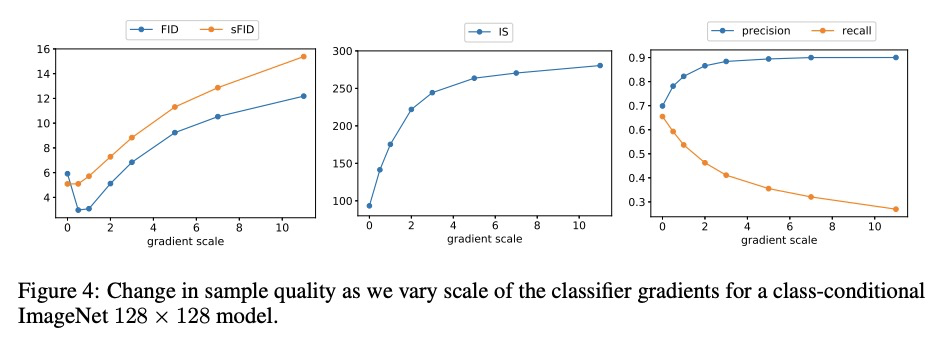
2、[LG] Diffusion Models Beat GANs on Image Synthesis
P Dhariwal, A Nichol
[OpenAI]
扩散模型在图像合成上击败GAN。本文表明,扩散模型可实现优于当前最先进的生成模型的图像样本质量,在无条件图像合成上实现了这一点,通过一系列消融找到了更好的架构。对于有条件的图像合成,通过分类器引导进一步提高样本质量:这是一种简单的、计算效率高的方法,利用分类器梯度来权衡多样性和样本质量。在ImageNet 128×128上实现了2.97的FID,在ImageNet 256×256上实现了4.59的FID,在ImageNet 512×512上实现了7.72的FID,在每个样本只有25次前向传播的情况下就能与BigGAN-deep相匹配,同时保持更好的分布覆盖。同时,分类器指导与上采样扩散模型结合得很好,在ImageNet 512×512上的FID进一步提高到3.85。
We show that diffusion models can achieve image sample quality superior to the current state-of-the-art generative models. We achieve this on unconditional image synthesis by finding a better architecture through a series of ablations. For conditional image synthesis, we further improve sample quality with classifier guidance: a simple, compute-efficient method for trading off diversity for sample quality using gradients from a classifier. We achieve an FID of 2.97 on ImageNet 128× 128, 4.59 on ImageNet 256× 256, and 7.72 on ImageNet 512× 512, and we match BigGAN-deep even with as few as 25 forward passes per sample, all while maintaining better coverage of the distribution. Finally, we find that classifier guidance combines well with upsampling diffusion models, further improving FID to 3.85 on ImageNet 512× 512. We release our code at https://github.com/ openai/guided-diffusion.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfdlwAmpK

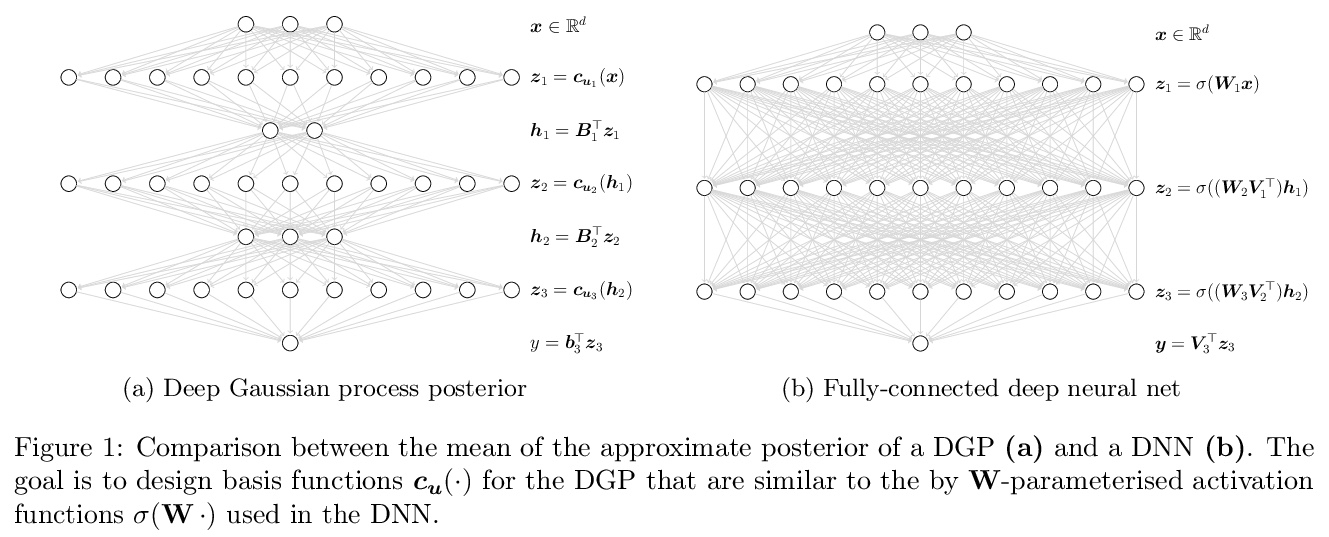
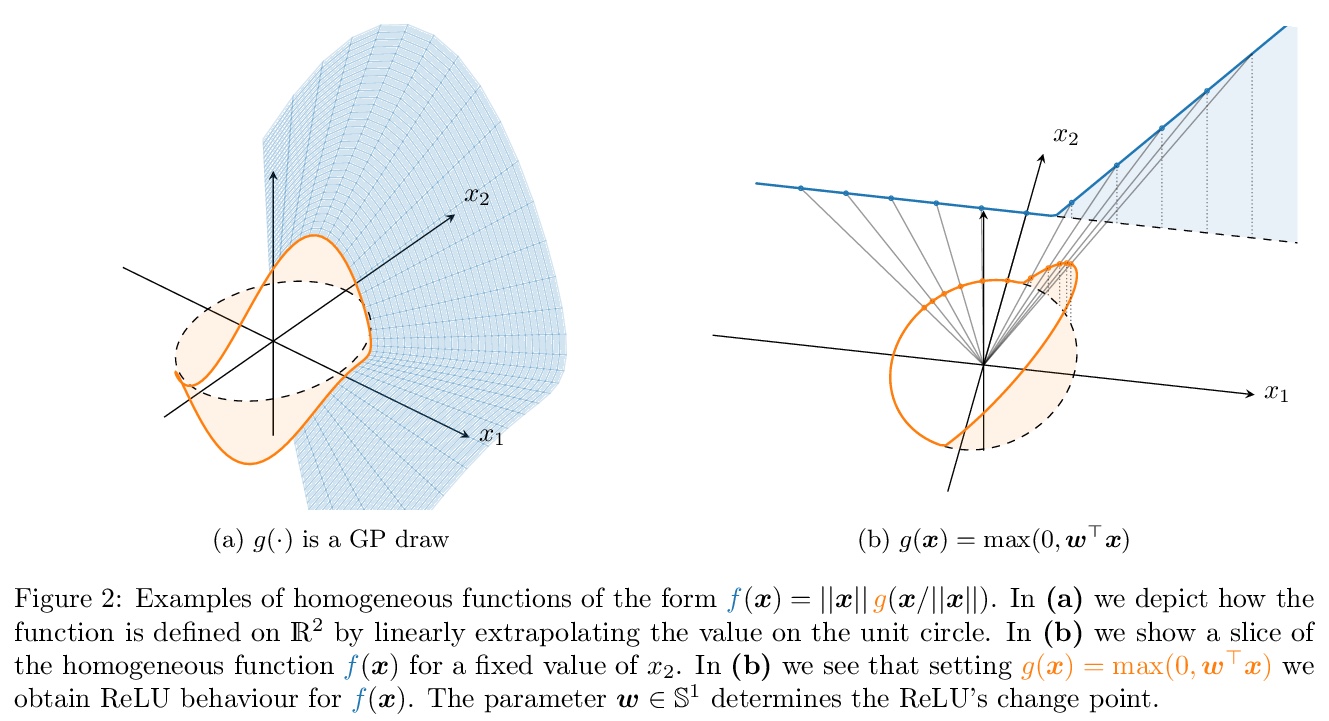
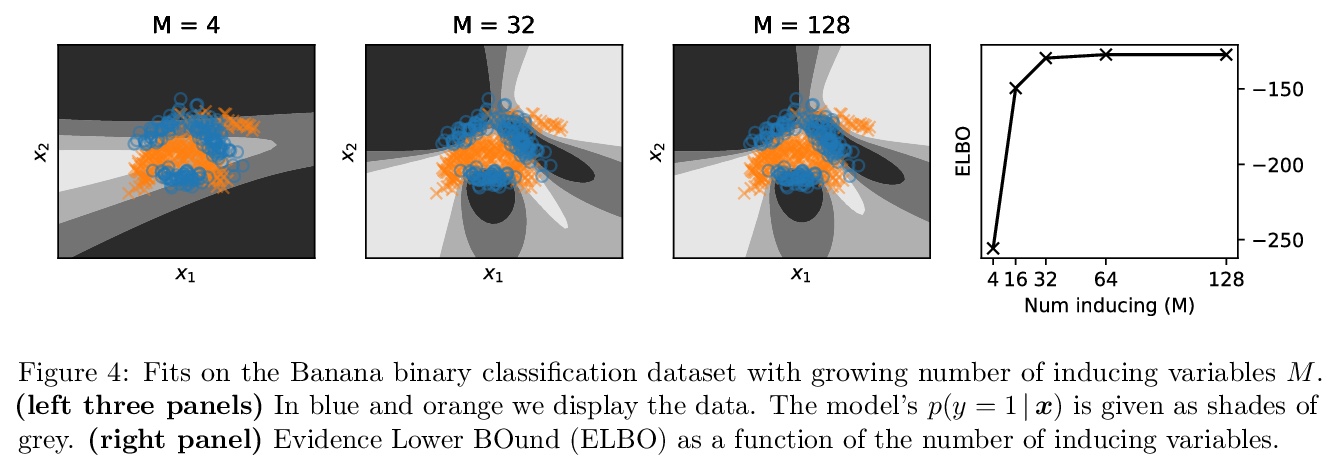
3、[LG] Deep Neural Networks as Point Estimates for Deep Gaussian Processes
V Dutordoir, J Hensman, M v d Wilk, C H Ek, Z Ghahramani, N Durrande
[University of Cambridge & Amazon & Imperial College London]
用深度神经网络作为深度高斯过程的点估计。由于与贝叶斯推理相关的挑战和成本,深高斯过程(DGP)在应用中一直在努力寻求相关性。本文为DGP提出一种稀疏的变种近似方法,其近似的后验平均值具有与深度神经网络相同的数学结构。通过找到一种域间变换,将GP后验均值表示为ReLU基函数的总和,使DGP的前向传递与ReLU DNN相当。这种统一使DGP作为一个神经网络进行初始化和训练,利用了深度学习社区的成熟做法,极大地帮助了推理任务。实验表明,与目前的DGP方法相比,精度提高了,训练速度加快了,同时保留了有利的预测不确定性。
Deep Gaussian processes (DGPs) have struggled for relevance in applications due to the challenges and cost associated with Bayesian inference. In this paper we propose a sparse variational approximation for DGPs for which the approximate posterior mean has the same mathematical structure as a Deep Neural Network (DNN). We make the forward pass through a DGP equivalent to a ReLU DNN by finding an interdomain transformation that represents the GP posterior mean as a sum of ReLU basis functions. This unification enables the initialisation and training of the DGP as a neural network, leveraging the well established practice in the deep learning community, and so greatly aiding the inference task. The experiments demonstrate improved accuracy and faster training compared to current DGP methods, while retaining favourable predictive uncertainties.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfdp0j2FZ

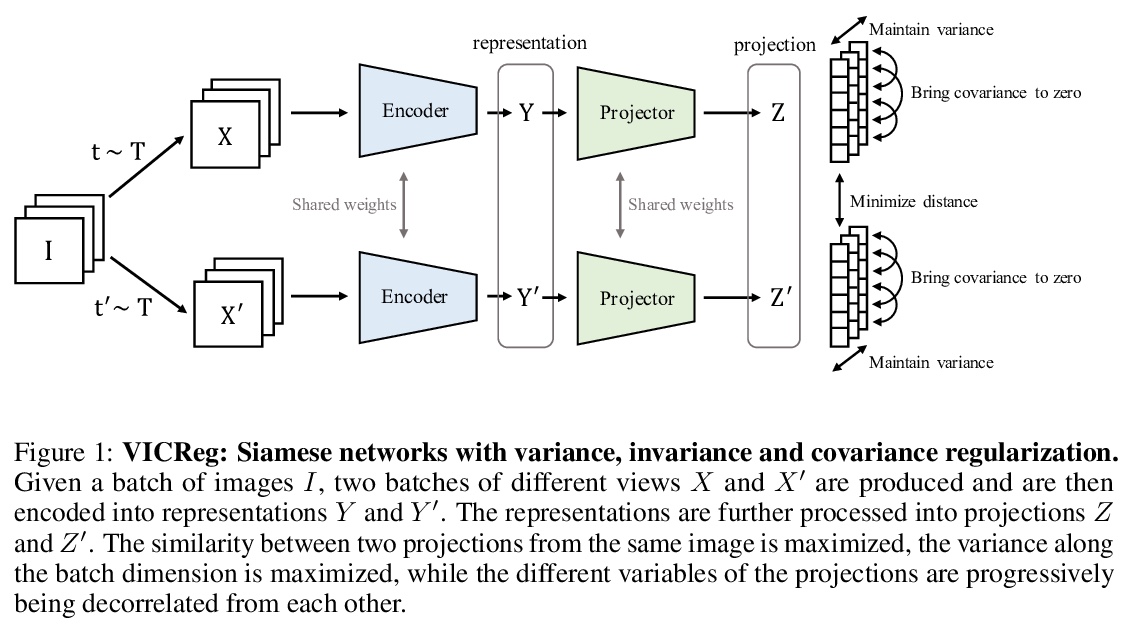
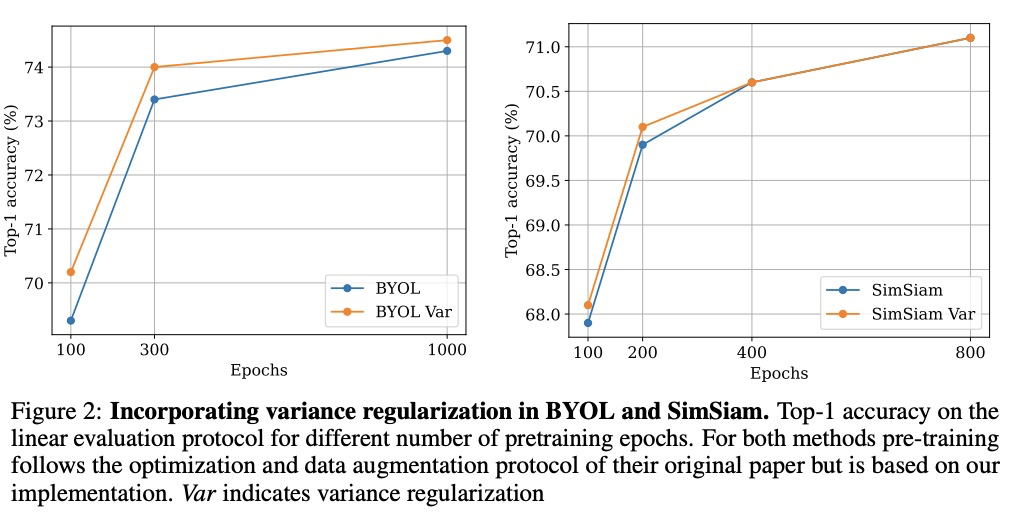
4、[CV] VICReg: Variance-Invariance-Covariance Regularization for Self-Supervised Learning
A Bardes, J Ponce, Y LeCun
[Facebook AI Research & PSL Research University]
VICReg:自监督学习的方差-协方差正则化。最近用于图像表示学习的自监督方法,是基于最大化同一图像不同视图的嵌入向量之间的一致性。当编码器输出常数向量时,会得到一个平凡解。这个崩溃问题往往通过学习架构中的隐性偏差来避免,这些偏差往往缺乏明确的理由或解释。本文提出VICReg,即方差-不变-协方差正则化,一种简单而有效、可解释的方法,通过在每个维度的嵌入方差上设置一个简单的正则化项,可以防止自监督的联合嵌入学习中的崩溃。VICReg将方差项与基于减少冗余和协方差正则化的去相关机制结合起来,在几个下游任务上取得了与目前技术水平相当的结果。实验表明,将新方差项纳入其他方法还有助于稳定训练并提高性能。
Recent self-supervised methods for image representation learning are based on maximizing the agreement between embedding vectors from different views of the same image. A trivial solution is obtained when the encoder outputs constant vectors. This collapse problem is often avoided through implicit biases in the learning architecture, that often lack a clear justification or interpretation. In this paper, we introduce VICReg (Variance-Invariance-Covariance Regularization), a method that explicitly avoids the collapse problem with a simple regularization term on the variance of the embeddings along each dimension individually. VICReg combines the variance term with a decorrelation mechanism based on redundancy reduction and covariance regularization, and achieves results on par with the state of the art on several downstream tasks. In addition, we show that incorporating our new variance term into other methods helps stabilize the training and leads to performance improvements.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfdrJ3OS1
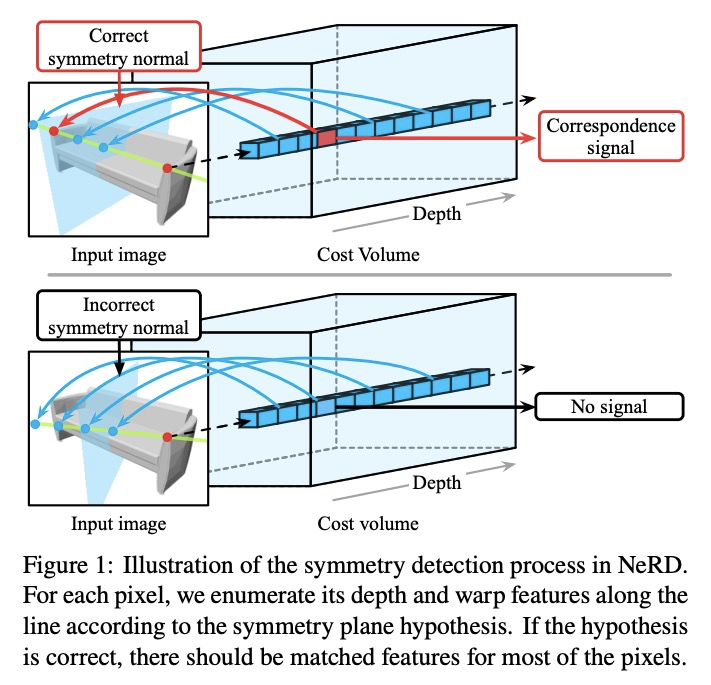
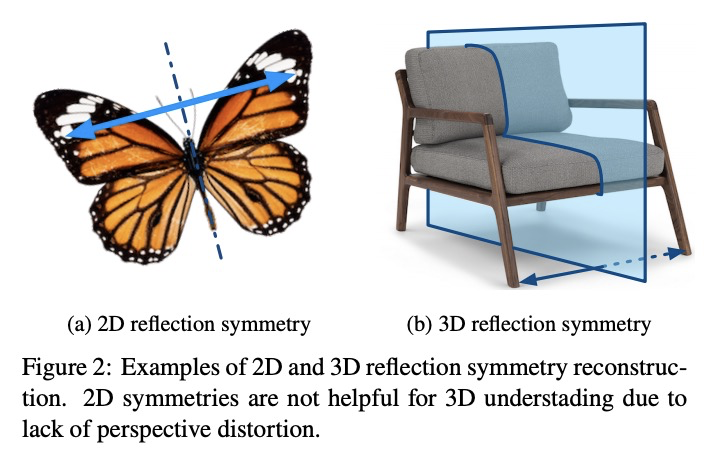
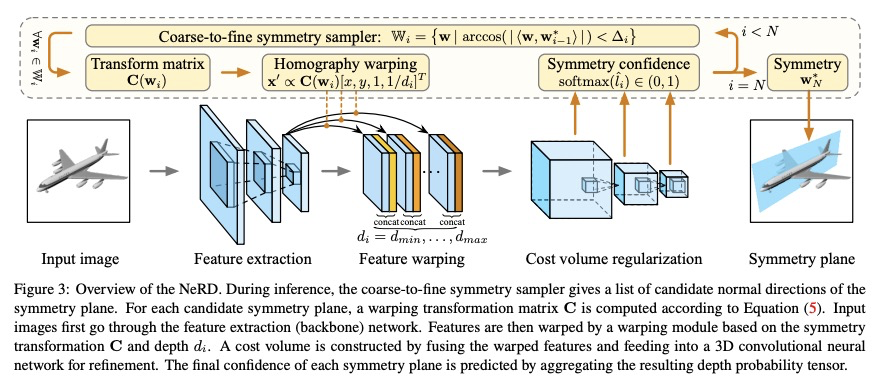
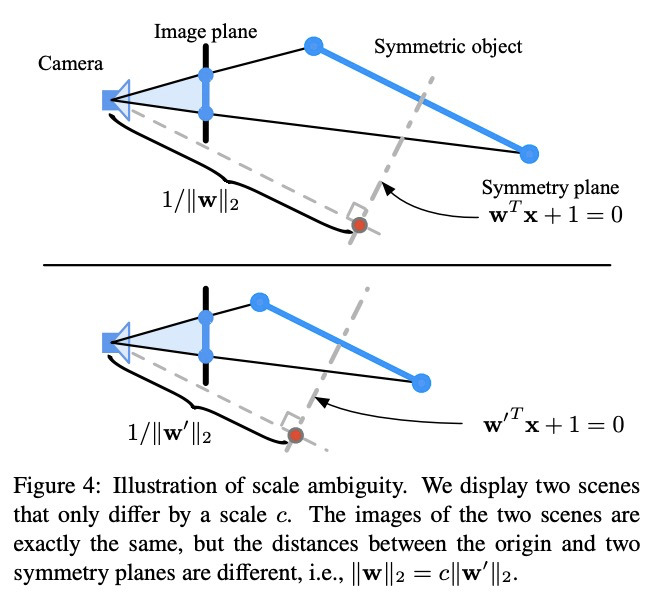
5、[CV] NeRD: Neural 3D Reflection Symmetry Detector
Y Zhou, S Liu, Y Ma
[UC Berkeley & Univ. of Southern California]
NeRD:神经3D反射对称性检测器。最近的进展表明,对称性是大多数物体表现出的结构性先验,可支持各种单视角的3D理解任务。然而,从图像中检测3D对称性仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。之前的工作要么假设对称性是给定的,要么用基于启发式的方法检测对称性。本文提出NeRD,一种神经3D反射对称性检测器,结合了基于学习的识别和基于几何的重建的优势,以准确恢复物体镜像平面的法线方向。先用从粗到细的策略列举出对称平面,通过建立3D损失体来检查图像内像素的对称性,从而找到最佳的对称平面。实验表明,在合成和真实世界的数据集上,用该方法检测到的对称平面明显比直接用CNN回归的平面更准确,检测到的对称性可以用来提高下游任务的性能,如姿态估计和深度图回归。
Recent advances have shown that symmetry, a structural prior that most objects exhibit, can support a variety of single-view 3D understanding tasks. However, detecting 3D symmetry from an image remains a challenging task. Previous works either assume that the symmetry is given or detect the symmetry with a heuristic-based method. In this paper, we present NeRD, a Neural 3D Reflection Symmetry Detector, which combines the strength of learning-based recognition and geometry-based reconstruction to accurately recover the normal direction of objects’ mirror planes. Specifically, we first enumerate the symmetry planes with a coarse-to-fine strategy and then find the best ones by building 3D cost volumes to examine the intra-image pixel correspondence from the symmetry. Our experiments show that the symmetry planes detected with our method are significantly more accurate than the planes from direct CNN regression on both synthetic and real-world datasets. We also demonstrate that the detected symmetry can be used to improve the performance of downstream tasks such as pose estimation and depth map regression. The code of this paper has been made public at https://github.com/zhou13/nerd .
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfdwy655J
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CV] Measuring Model Biases in the Absence of Ground Truth
缺少真值情况下模型偏差的测定
O Aka, K Burke, A Bäuerle, C Greer, M Mitchell
[Google & Ulm University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfdzgxV3m
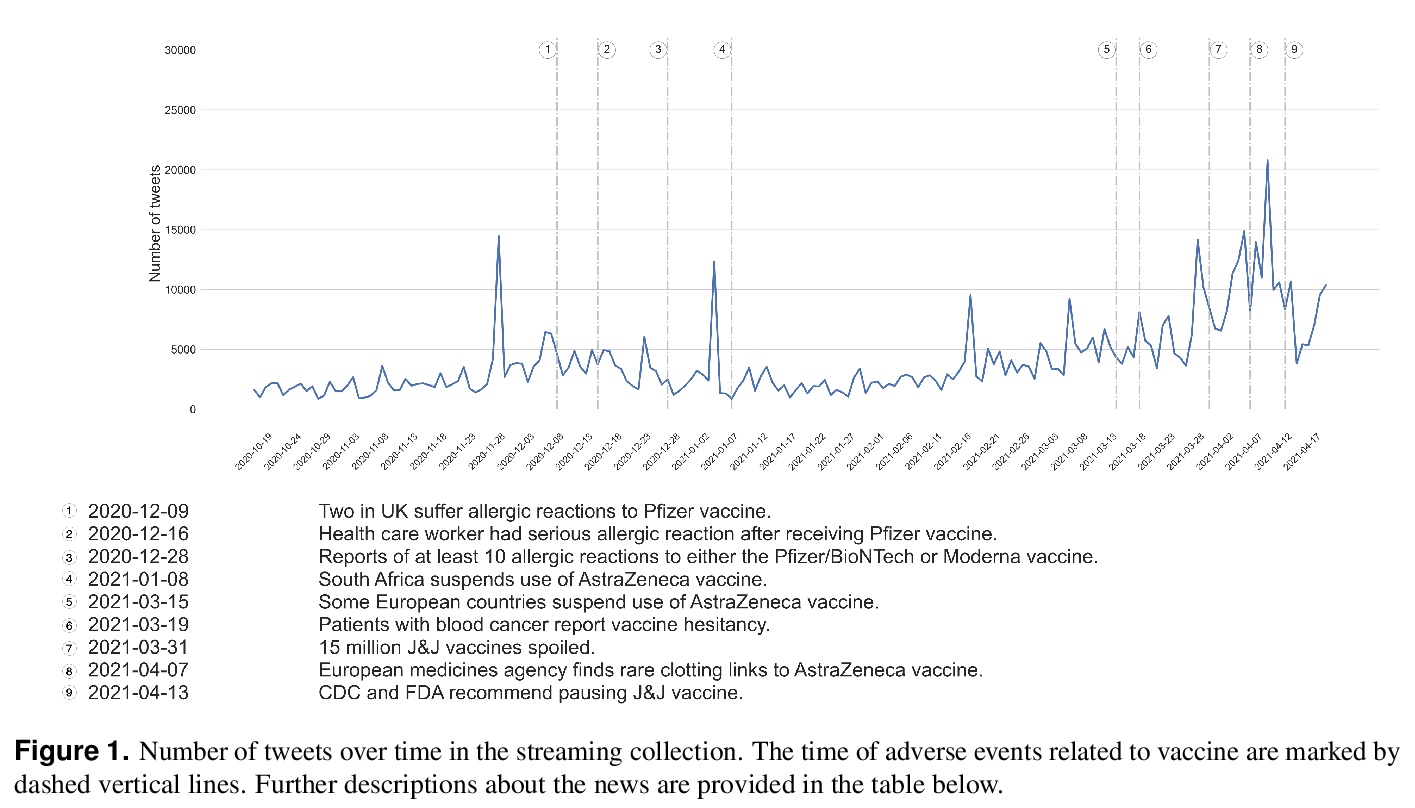
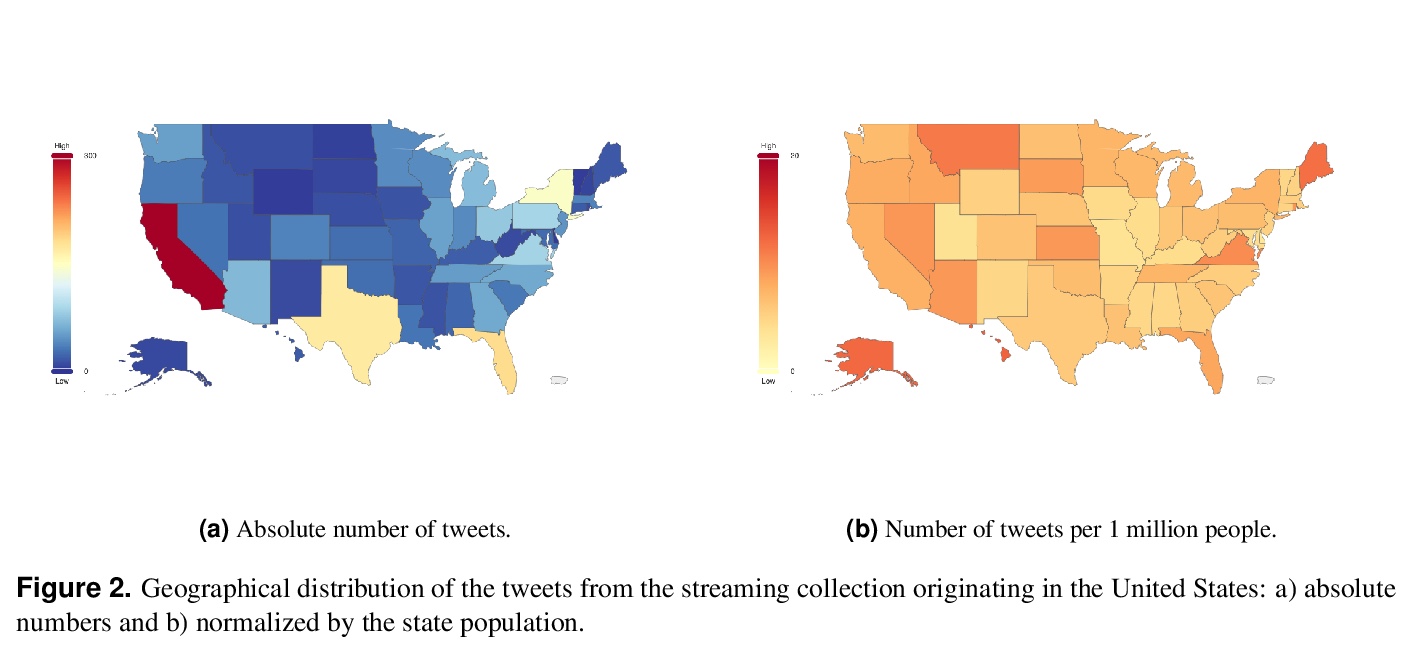
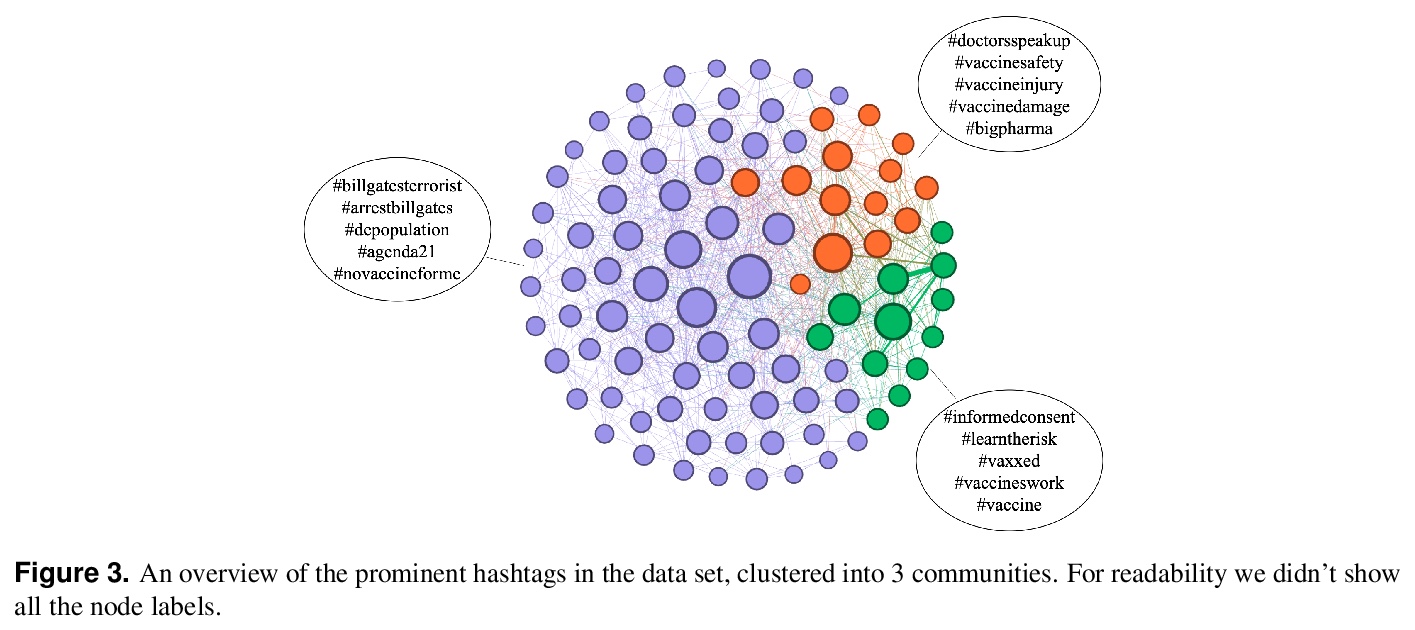
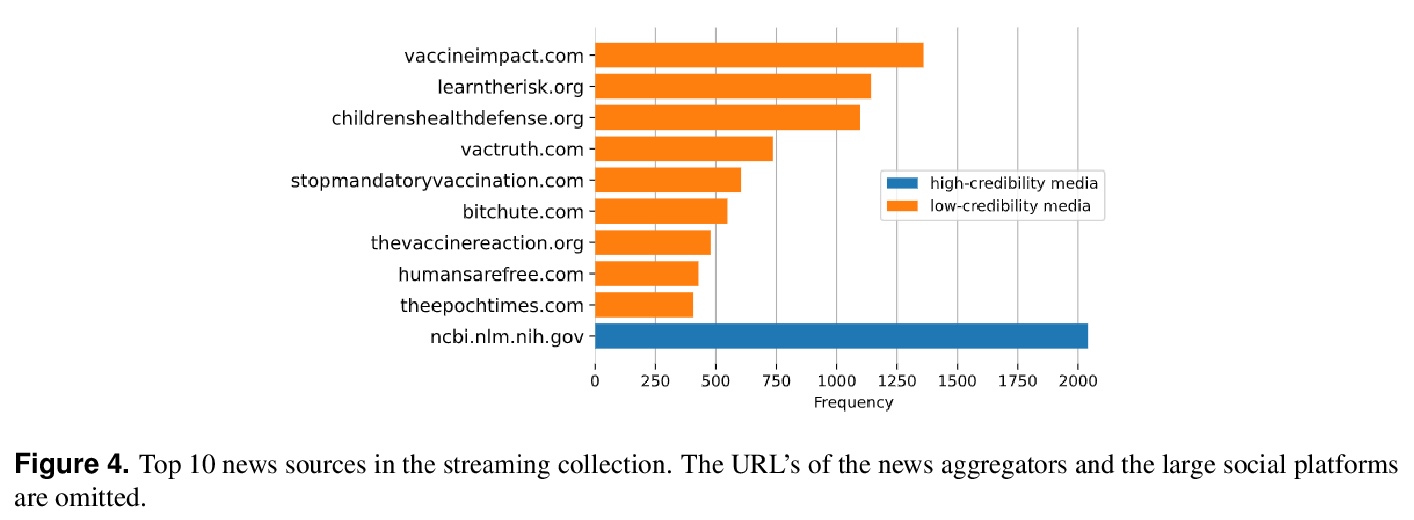
[SI] COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy on Social Media: Building a Public Twitter Dataset of Anti-vaccine Content, Vaccine Misinformation and Conspiracies
社交媒体上关于新冠疫苗的犹豫:建立反疫苗内容、疫苗错误信息和阴谋的公共推特数据集
G Muric, Y Wu, E Ferrara
[University of Southern California]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfdBF7Dr5
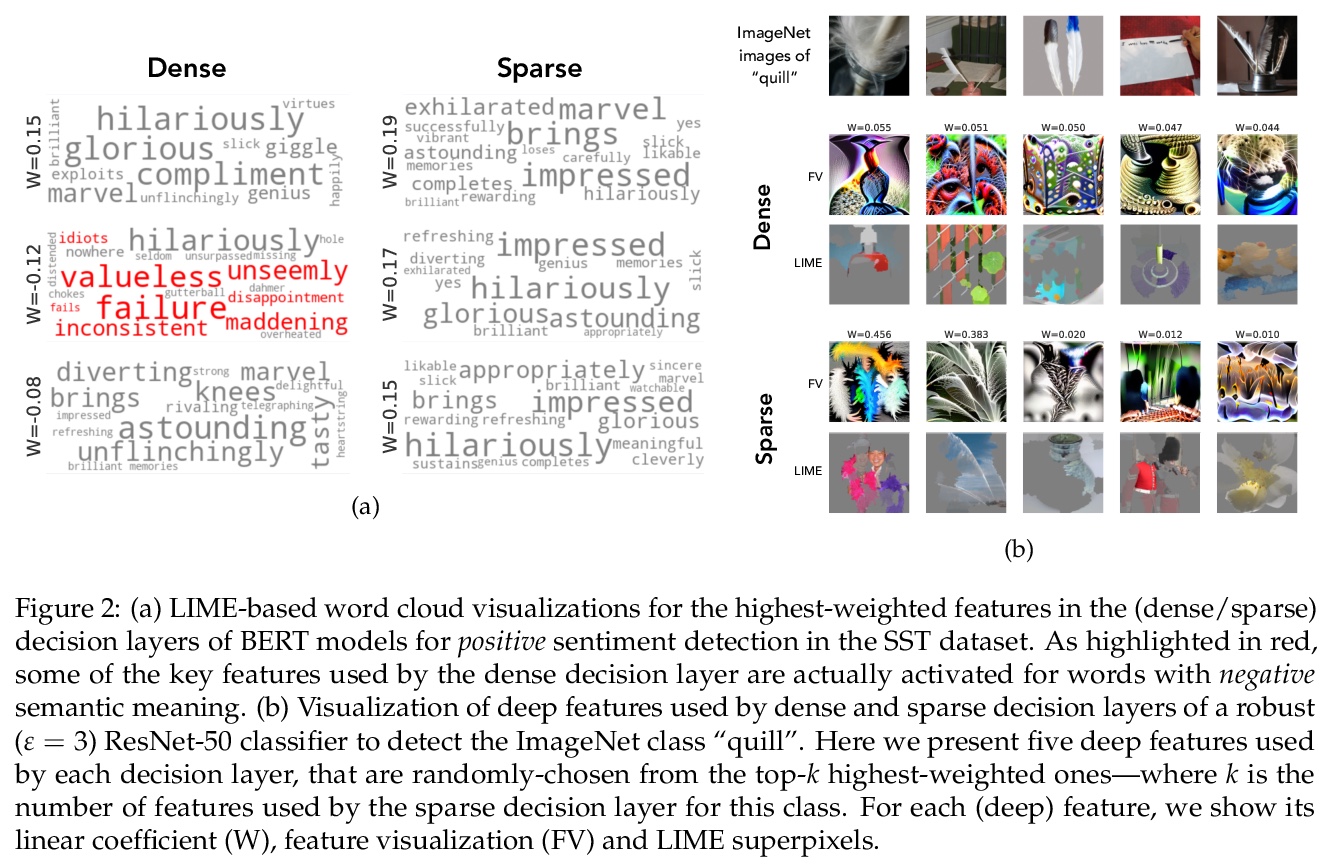
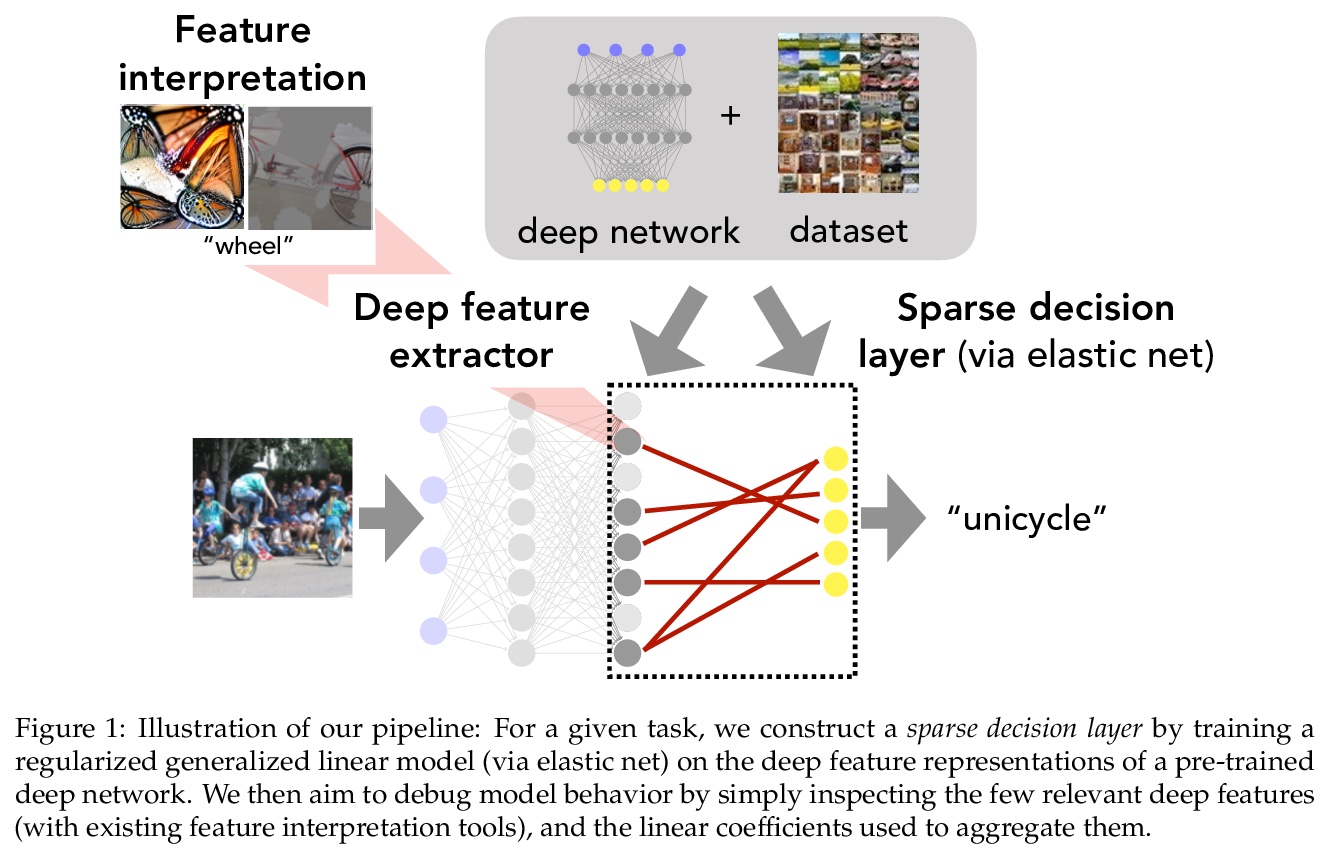
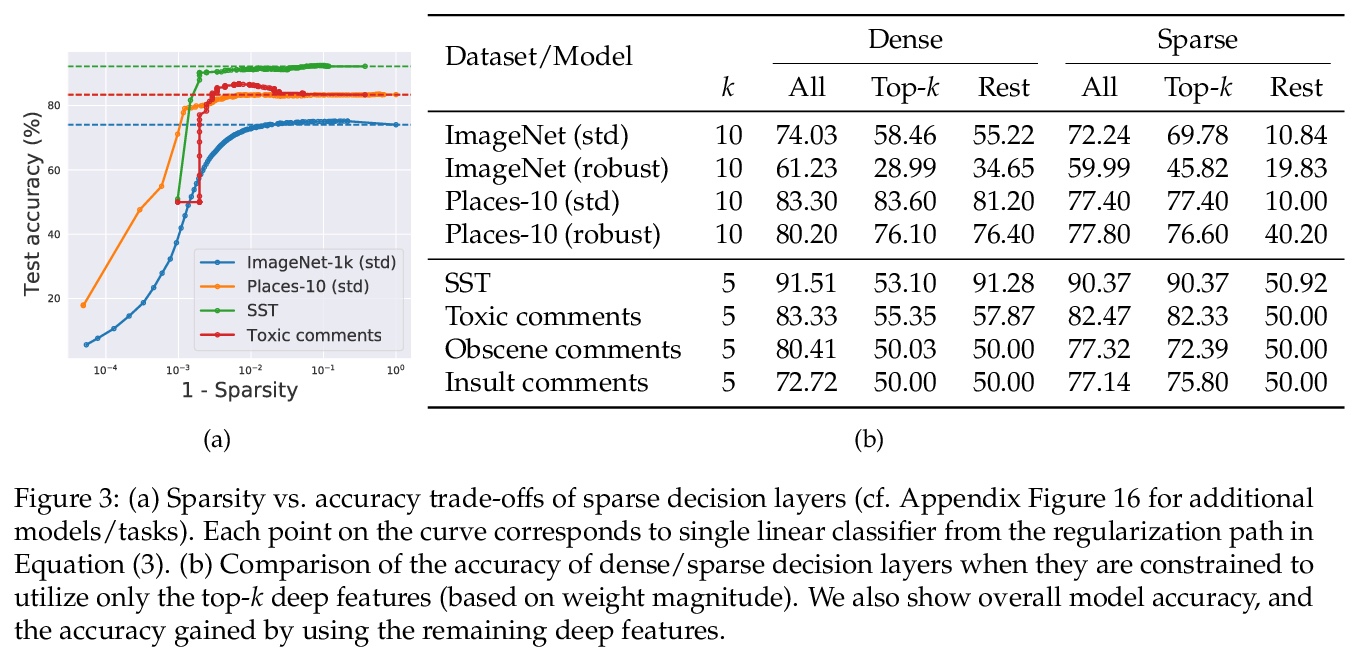
[LG] Leveraging Sparse Linear Layers for Debuggable Deep Networks
利用稀疏线性层构建可调试深度网络
E Wong, S Santurkar, A Mądry
[MIT]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfdEN3LCY

[LG] Optimization of Graph Neural Networks: Implicit Acceleration by Skip Connections and More Depth
图神经网络优化:基于跳接和加深的隐式加速
K Xu, M Zhang, S Jegelka, K Kawaguchi
[MIT & The University of Maryland & Harvard University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfdGp9BsZ