- 1、[CL] GLUCOSE: GeneraLized and COntextualized Story Explanations
- 2、[AI] Spot The Bot: A Robust and Efficient Framework for the Evaluation of Conversational Dialogue Systems
- 3、[CL] Visually Grounded Compound PCFGs
- 4、[CL] Identifying Necessary Elements for BERT’s Multilinguality
- 5、[LG] What Makes Instance Discrimination Good for Transfer Learning?
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
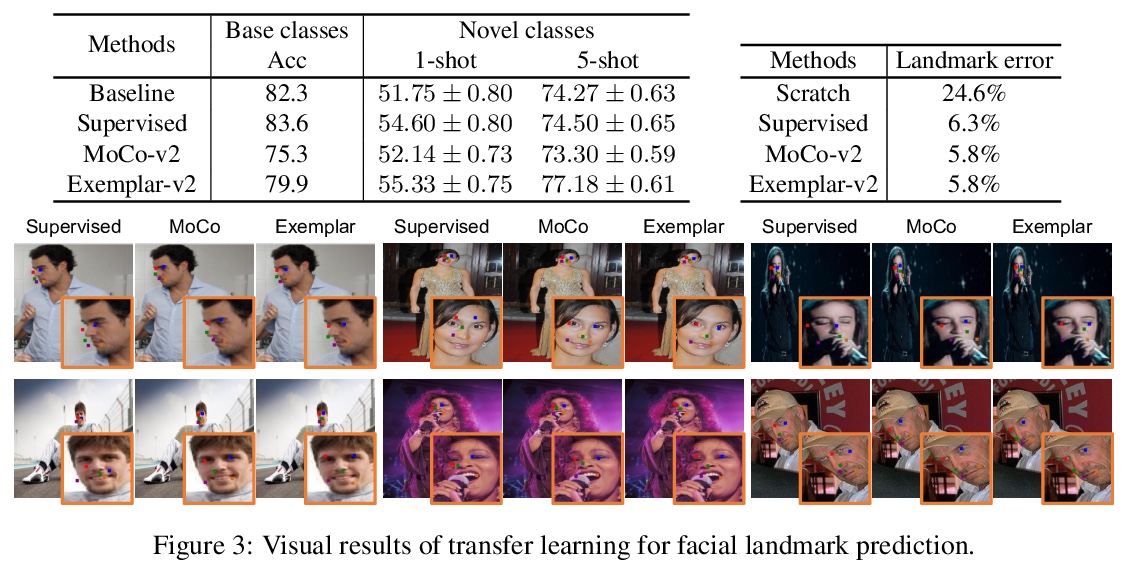
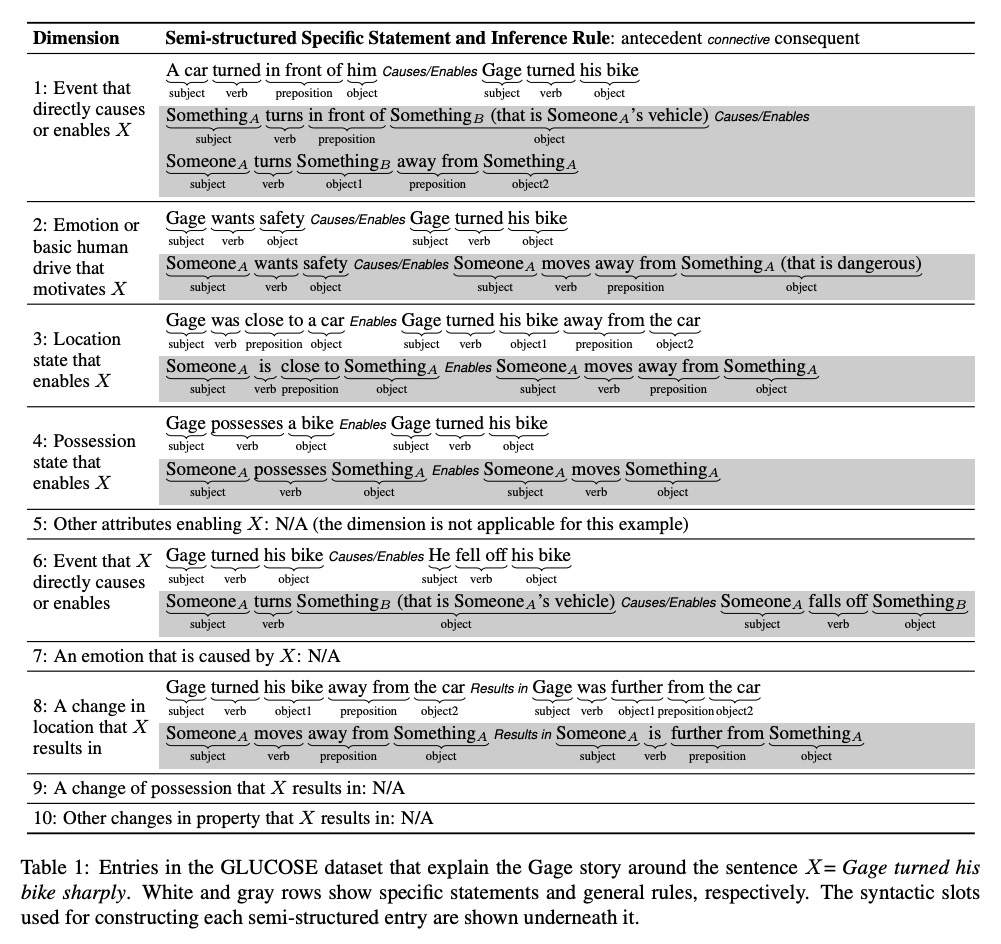
1、[CL] GLUCOSE: GeneraLized and COntextualized Story Explanations
N Mostafazadeh, A Kalyanpur, L Moon, D Buchanan, L Berkowitz, O Biran, J Chu-Carroll
[Elemental Cognition]
GLUCOSE:广义和语境化的故事解释。介绍了大规模隐性常识知识数据集GLUCOSE,编码了基于叙事背景的解释性描述,这些描述被分为受认知心理学启发的十个因果维度,重点关注事件、状态、动机和情绪,其中每个条目包括一个特定于故事的因果陈述,与从该陈述中归纳出的推理规则相对应。提出了多阶段pipeline,由众包人员提供半结构化因果解释,最终得到了基于日常儿童故事的670K个标记,这些语句和规则包含了关于日常情况的隐性常识知识。
When humans read or listen, they make implicit commonsense inferences that frame their understanding of what happened and why. As a step toward AI systems that can build similar mental models, we introduce GLUCOSE, a large-scale dataset of implicit commonsense causal knowledge, encoded as causal mini-theories about the world, each grounded in a narrative context. To construct GLUCOSE, we drew on cognitive psychology to identify ten dimensions of causal explanation, focusing on events, states, motivations, and emotions. Each GLUCOSE entry includes a story-specific causal statement paired with an inference rule generalized from the statement. This paper details two concrete contributions. First, we present our platform for effectively crowdsourcing GLUCOSE data at scale, which uses semi-structured templates to elicit causal explanations. Using this platform, we collected a total of ~670K specific statements and general rules that capture implicit commonsense knowledge about everyday situations. Second, we show that existing knowledge resources and pretrained language models do not include or readily predict GLUCOSE’s rich inferential content. However, when state-of-the-art neural models are trained on this knowledge, they can start to make commonsense inferences on unseen stories that match humans’ mental models.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JB6AroePC
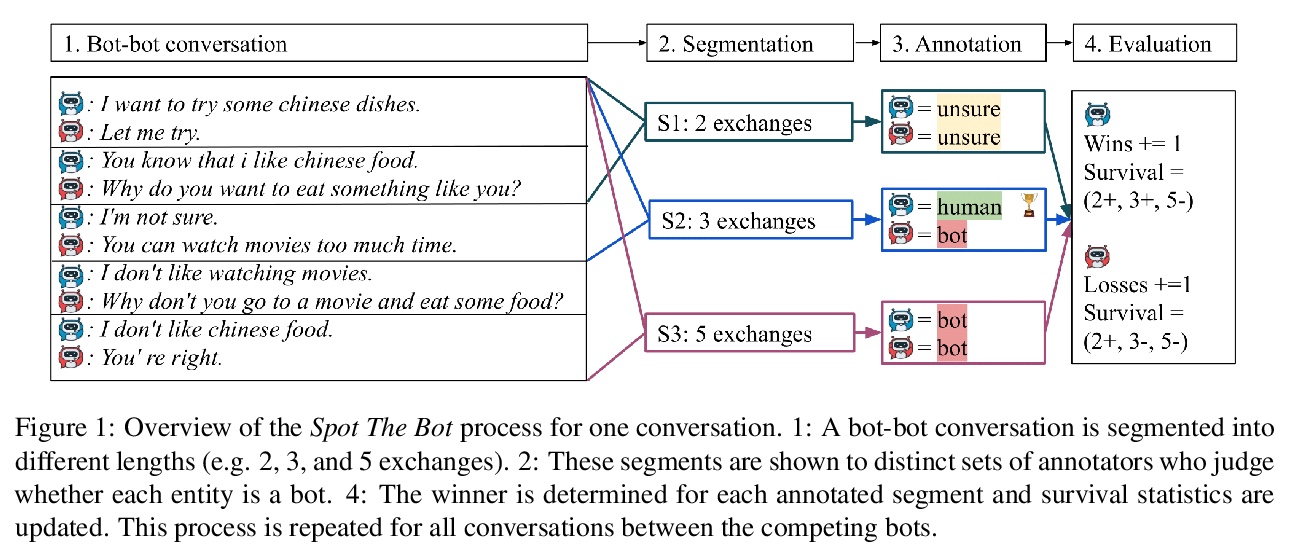
2、[AI] Spot The Bot: A Robust and Efficient Framework for the Evaluation of Conversational Dialogue Systems
J Deriu, D Tuggener, P v Däniken, J A Campos, A Rodrigo, T Belkacem, A Soroa, E Agirre, M Cieliebak
[Zurich University of Applied Sciences (ZHAW) & University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU)]
Spot The Bot:鲁棒且高效的会话对话系统评价方法。基于机器人之间的对话,由人工对机器人模仿人类行为的能力进行评价。加入了一个指标,用来衡量哪些聊天机器人能最长时间地维持类人行为,这个指标能将机器人的表现与某些特性(如流畅度、敏感度)相关联,产生可解释的结果。与其他评价框架相比,Spot The Bot产生了鲁棒和显著的结果,同时减少了评价时间。
The lack of time-efficient and reliable evaluation methods hamper the development of conversational dialogue systems (chatbots). Evaluations requiring humans to converse with chatbots are time and cost-intensive, put high cognitive demands on the human judges, and yield low-quality results. In this work, we introduce Spot The Bot, a cost-efficient and robust evaluation framework that replaces human-bot conversations with conversations between bots. Human judges then only annotate for each entity in a conversation whether they think it is human or not (assuming there are humans participants in these conversations). These annotations then allow us to rank chatbots regarding their ability to mimic the conversational behavior of humans. Since we expect that all bots are eventually recognized as such, we incorporate a metric that measures which chatbot can uphold human-like behavior the longest, i.e., Survival Analysis. This metric has the ability to correlate a bot’s performance to certain of its characteristics (e.g., fluency or sensibleness), yielding interpretable results. The comparably low cost of our framework allows for frequent evaluations of chatbots during their evaluation cycle. We empirically validate our claims by applying Spot The Bot to three domains, evaluating several state-of-the-art chatbots, and drawing comparisons to related work. The framework is released as a ready-to-use tool.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JB6Qi8jd9
3、[CL] Visually Grounded Compound PCFGs
Y Zhao, I Titov
[University of Edinburgh & University of Amsterdam]
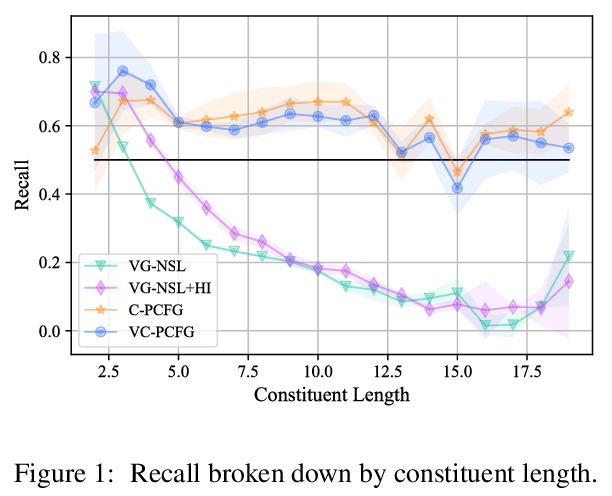
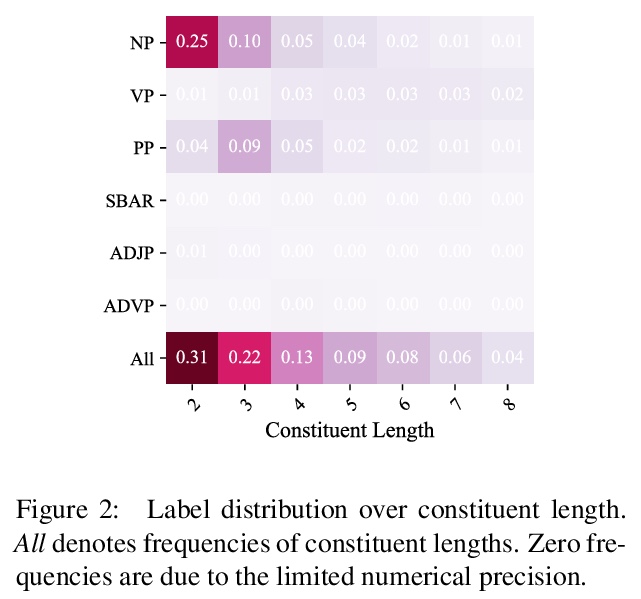
视觉信号辅助的自然语言文法学习。提出了视觉信号辅助下的概率文法的通用学习框架VC-PCFG,依赖于概率文法模型(Probabilistic Context-Free Grammars),具有端到端学习、完全可微的优点。针对视觉辅助学习中视觉信号不足的问题,提出在语言模型上对概率文法模型进行额外优化。通过实验,验证了视觉信号以及语言模型的优化目标有助于概率文法学习。
Exploiting visual groundings for language understanding has recently been drawing much attention. In this work, we study visually grounded grammar induction and learn a constituency parser from both unlabeled text and its visual groundings. Existing work on this task (Shi et al., 2019) optimizes a parser via Reinforce and derives the learning signal only from the alignment of images and sentences. While their model is relatively accurate overall, its error distribution is very uneven, with low performance on certain constituents types (e.g., 26.2% recall on verb phrases, VPs) and high on others (e.g., 79.6% recall on noun phrases, NPs). This is not surprising as the learning signal is likely insufficient for deriving all aspects of phrase-structure syntax and gradient estimates are noisy. We show that using an extension of probabilistic context-free grammar model we can do fully-differentiable end-to-end visually grounded learning. Additionally, this enables us to complement the image-text alignment loss with a language modeling objective. On the MSCOCO test captions, our model establishes a new state of the art, outperforming its non-grounded version and, thus, confirming the effectiveness of visual groundings in constituency grammar induction. It also substantially outperforms the previous grounded model, with largest improvements on more `abstract’ categories (e.g., +55.1% recall on VPs).
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JB6WMFdKf
4、[CL] Identifying Necessary Elements for BERT’s Multilinguality
P Dufter, H Schütze
[LMU Munich]
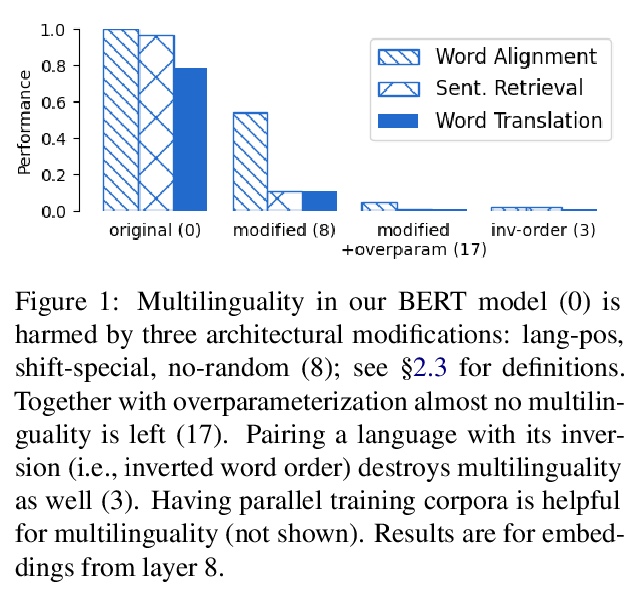
BERT多语言性的要素。研究了架构方面和语言方面哪些特性对BERT生成跨语言表示是必不可少的。主要结论包括:i)共享位置嵌入、共享特殊词条、用随机词条替换屏蔽词条、有限数量参数是多语言的必要元素。ii)多语言性和词序有关 iii) 训练语料库的可比性有助于多语言性。
It has been shown that multilingual BERT (mBERT) yields high quality multilingual representations and enables effective zero-shot transfer. This is surprising given that mBERT does not use any crosslingual signal during training. While recent literature has studied this phenomenon, the reasons for the multilinguality are still somewhat obscure. We aim to identify architectural properties of BERT and linguistic properties of languages that are necessary for BERT to become multilingual. To allow for fast experimentation we propose an efficient setup with small BERT models trained on a mix of synthetic and natural data. Overall, we identify four architectural and two linguistic elements that influence multilinguality. Based on our insights, we experiment with a multilingual pretraining setup that modifies the masking strategy using VecMap, i.e., unsupervised embedding alignment. Experiments on XNLI with three languages indicate that our findings transfer from our small setup to larger scale settings.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JB7eRq6r3
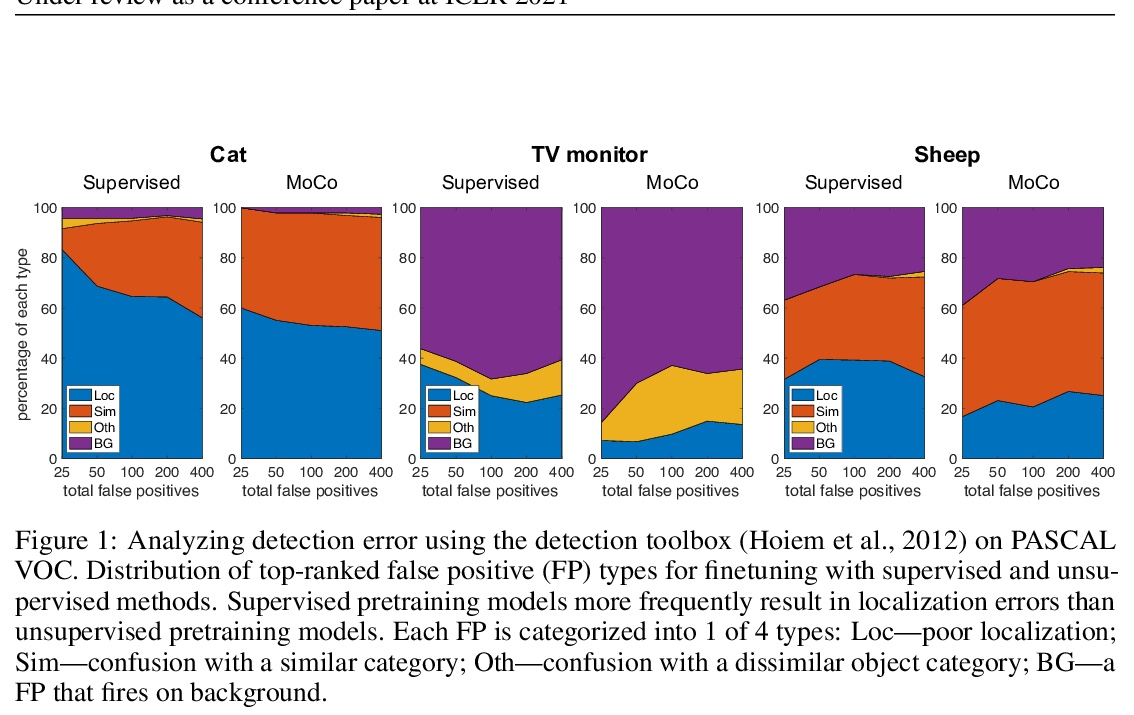
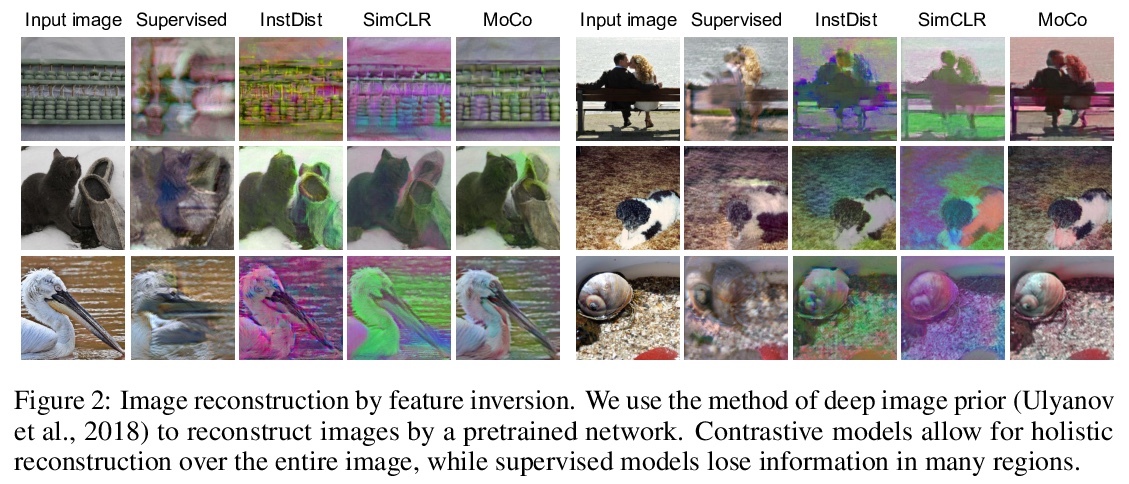
5、[LG] What Makes Instance Discrimination Good for Transfer Learning?
是什么让实例识别预训练有利于转移学习?从这些模型中究竟学习和迁移了哪些知识?如何更好地利用人工标记标签进行预训练?本文研究有三个方面的发现:对迁移真正重要的是低级和中级表示,而不是高级表示;传统监督模型所强制的类内不变性,会通过增加任务错位来削弱迁移性;有监督预训练可以通过遵循一个基于范例的方法来加强,无需同类别实例间的明确约束。
Contrastive visual pretraining based on the instance discrimination pretext task has made significant progress. Notably, recent work on unsupervised pretraining has shown to surpass the supervised counterpart for finetuning downstream applications such as object detection and segmentation. It comes as a surprise that image annotations would be better left unused for transfer learning. In this work, we investigate the following problems: What makes instance discrimination pretraining good for transfer learning? What knowledge is actually learned and transferred from these models? From this understanding of instance discrimination, how can we better exploit human annotation labels for pretraining? Our findings are threefold. First, what truly matters for the transfer is low-level and mid-level representations, not high-level representations. Second, the intra-category invariance enforced by the traditional supervised model weakens transferability by increasing task misalignment. Finally, supervised pretraining can be strengthened by following an exemplar-based approach without explicit constraints among the instances within the same category.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JB7wBfrPx