- 1、[CV] Scaling Vision Transformers
- 2、[CL] Evolutionary velocity with protein language models
- 3、[LG] HoroPCA: Hyperbolic Dimensionality Reduction via Horospherical Projections
- 4、[LG] Meta-Learning with Fewer Tasks through Task Interpolation
- 5、[CV] DETReg: Unsupervised Pretraining with Region Priors for Object Detection
- [LG] A Survey of Transformers
- [CL] Swords: A Benchmark for Lexical Substitution with Improved Data Coverage and Quality
- [AI] Differentiable Quality Diversity
- [CV] Demystifying Local Vision Transformer: Sparse Connectivity, Weight Sharing, and Dynamic Weight
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
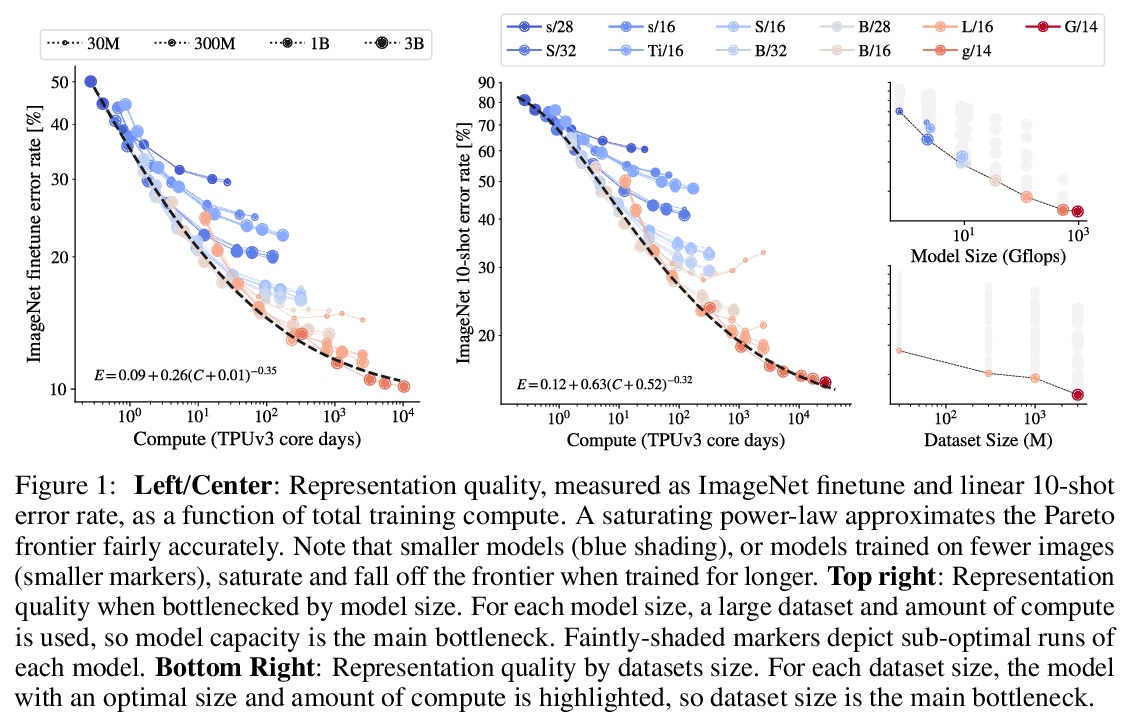
1、[CV] Scaling Vision Transformers
X Zhai, A Kolesnikov, N Houlsby, L Beyer
[Google Research]
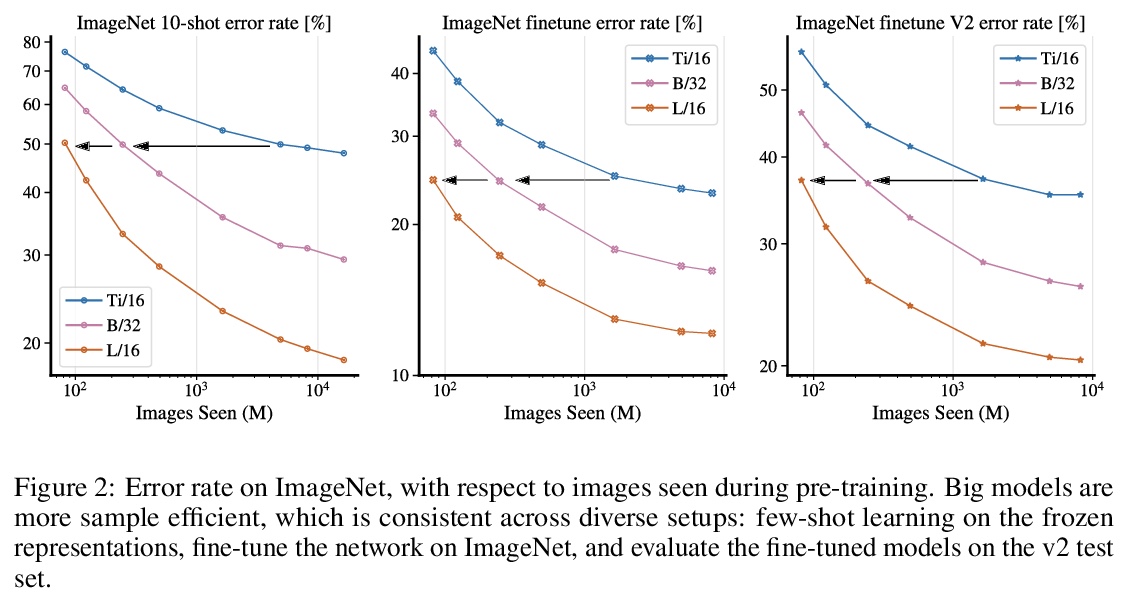
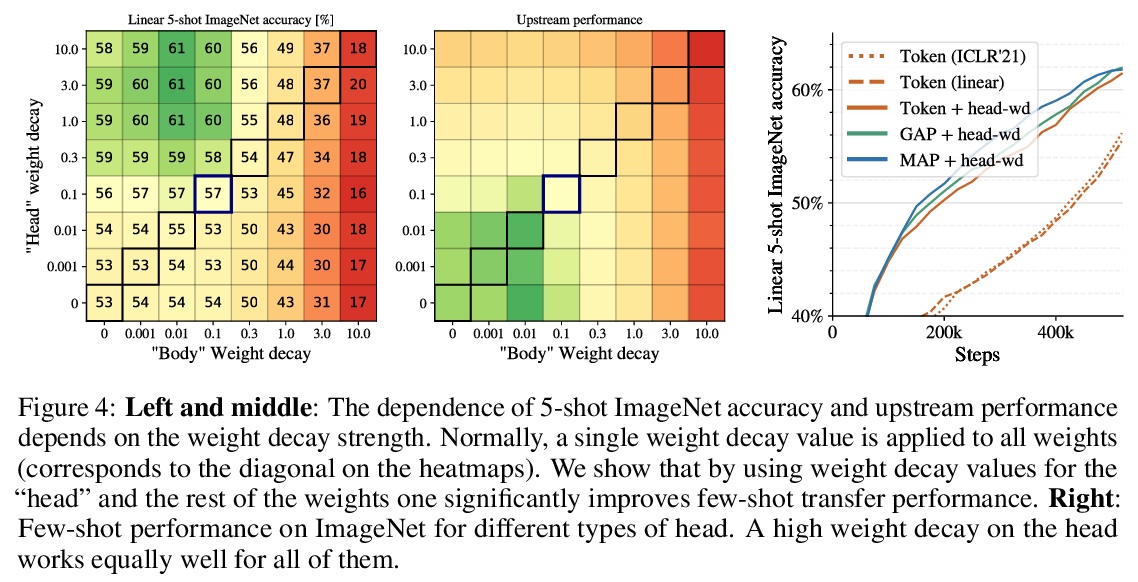
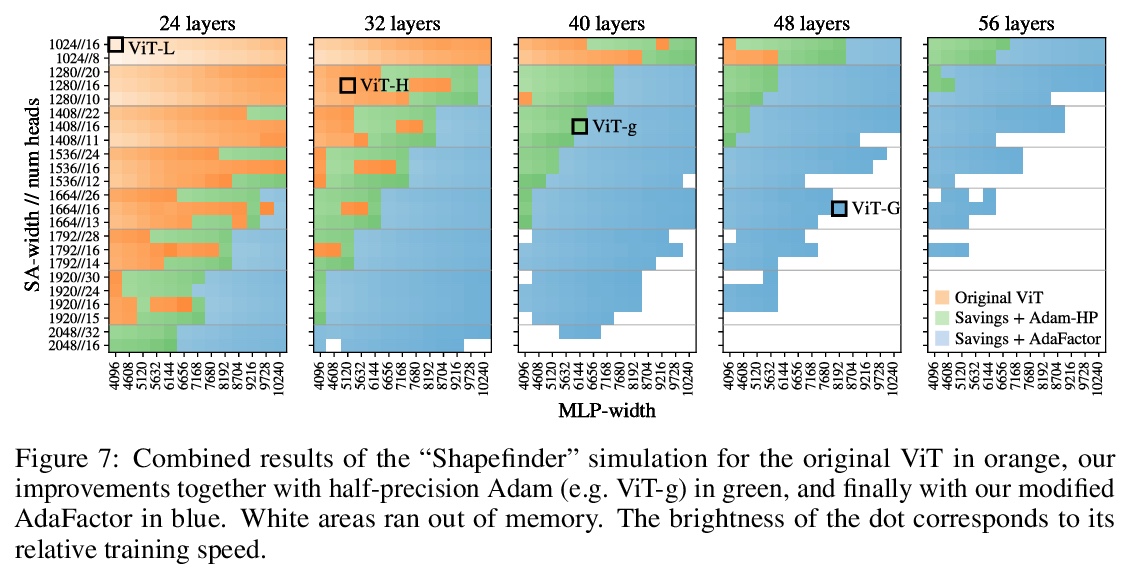
扩展视觉Transformer。基于注意力的神经网络,如视觉Transformers(ViT),最近在许多计算机视觉基准上取得了最先进的结果。规模是取得优异成绩的主要因素,因此,了解一个模型的扩展特性是有效设计未来一代的关键。虽然对Transformer语言模型的扩展规律已经进行了一些研究,但对视觉Transformer的扩展方式却一无所知。为解决该问题,将ViT模型和数据向上/向下扩展,描述错误率、数据和计算之间的关系。在此过程中,完善了ViT的架构和训练,减少了内存消耗,提高了所产生的模型的准确性。成功训练了一个具有20亿参数的ViT模型,在ImageNet上达到了90.45%的最高准确率的新水平。在少样本学习中也表现良好,在ImageNet上,每类只有10个样本,也达到了84.86%的最高准确率。
Attention-based neural networks such as the Vision Transformer (ViT) have recently attained state-of-the-art results on many computer vision benchmarks. Scale is a primary ingredient in attaining excellent results, therefore, understanding a model’s scaling properties is a key to designing future generations effectively. While the laws for scaling Transformer language models have been studied, it is unknown how Vision Transformers scale. To address this, we scale ViT models and data, both up and down, and characterize the relationships between error rate, data, and compute. Along the way, we refine the architecture and training of ViT, reducing memory consumption and increasing accuracy of the resulting models. As a result, we successfully train a ViT model with two billion parameters, which attains a new state-of-the-art on ImageNet of 90.45% top-1 accuracy. The model also performs well on few-shot learning, for example, reaching 84.86% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet with only 10 examples per class.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kjtimuqnr
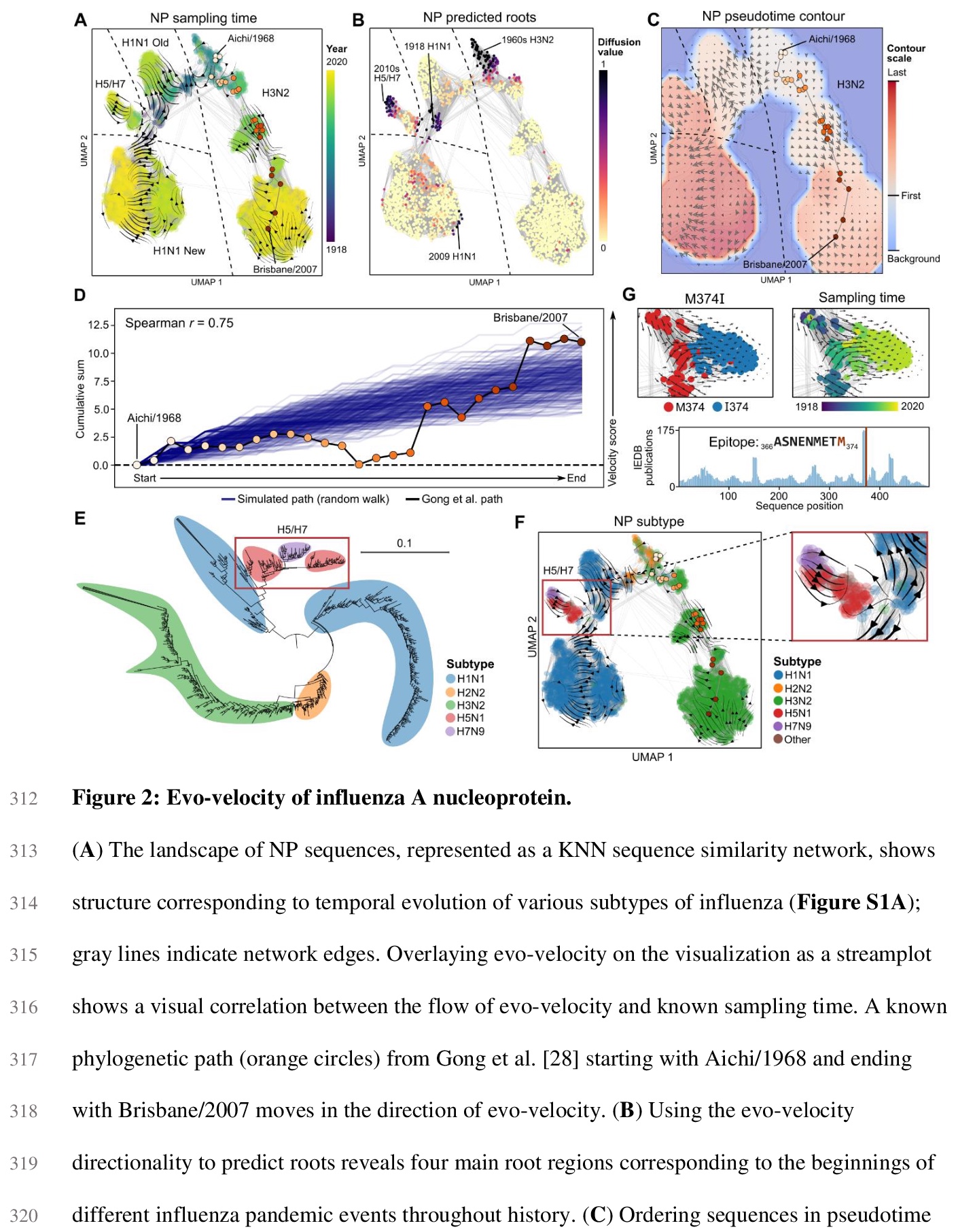
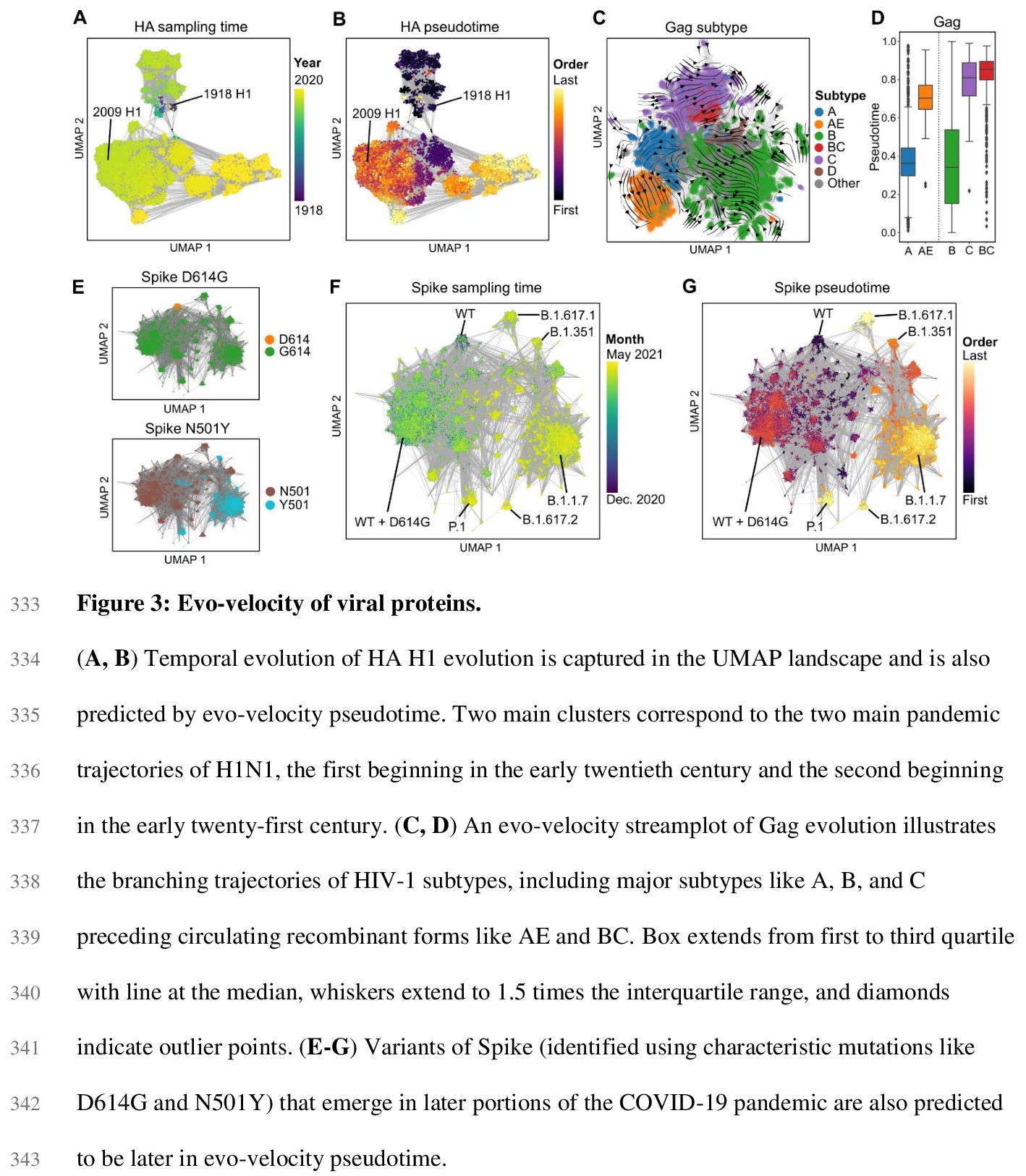
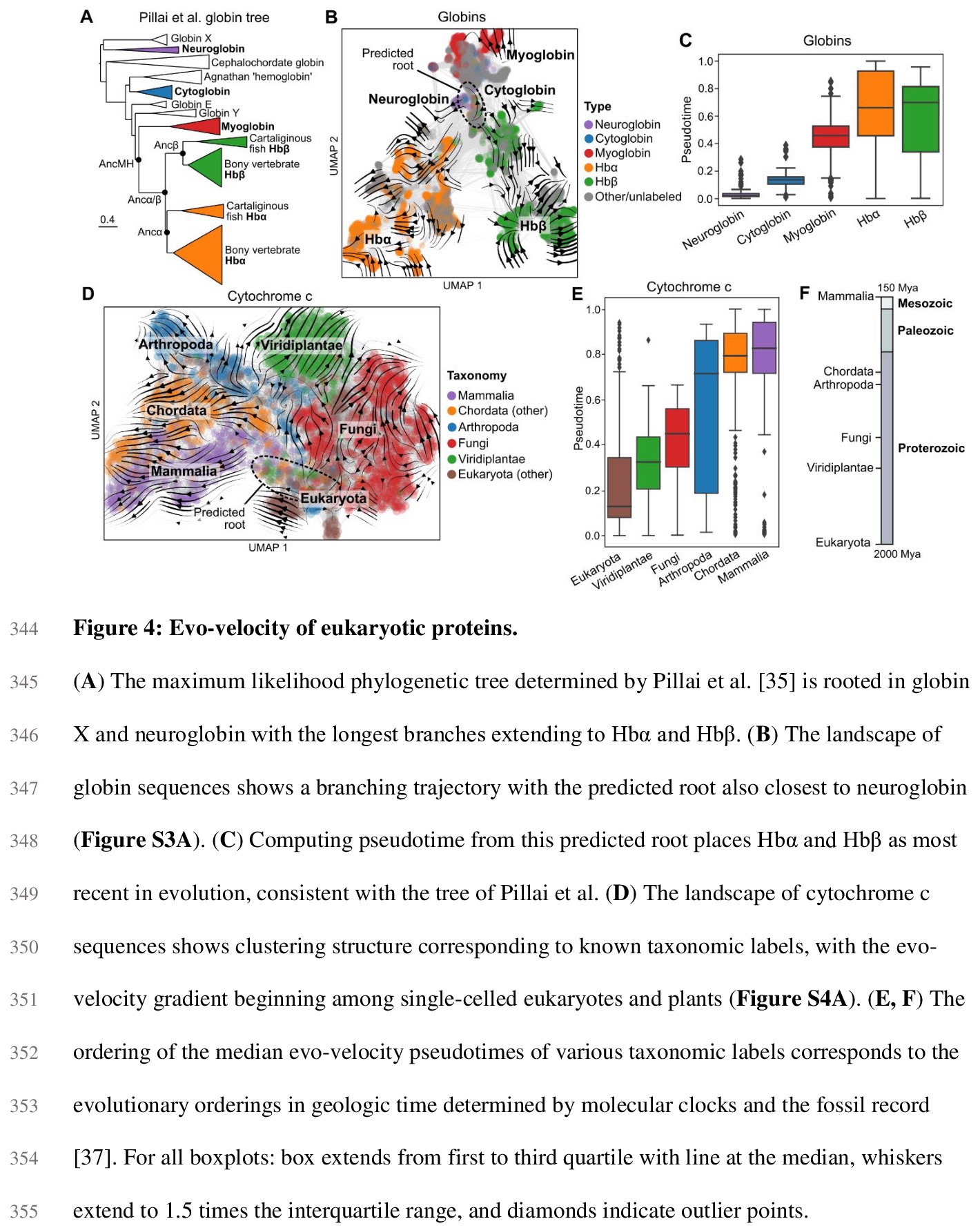
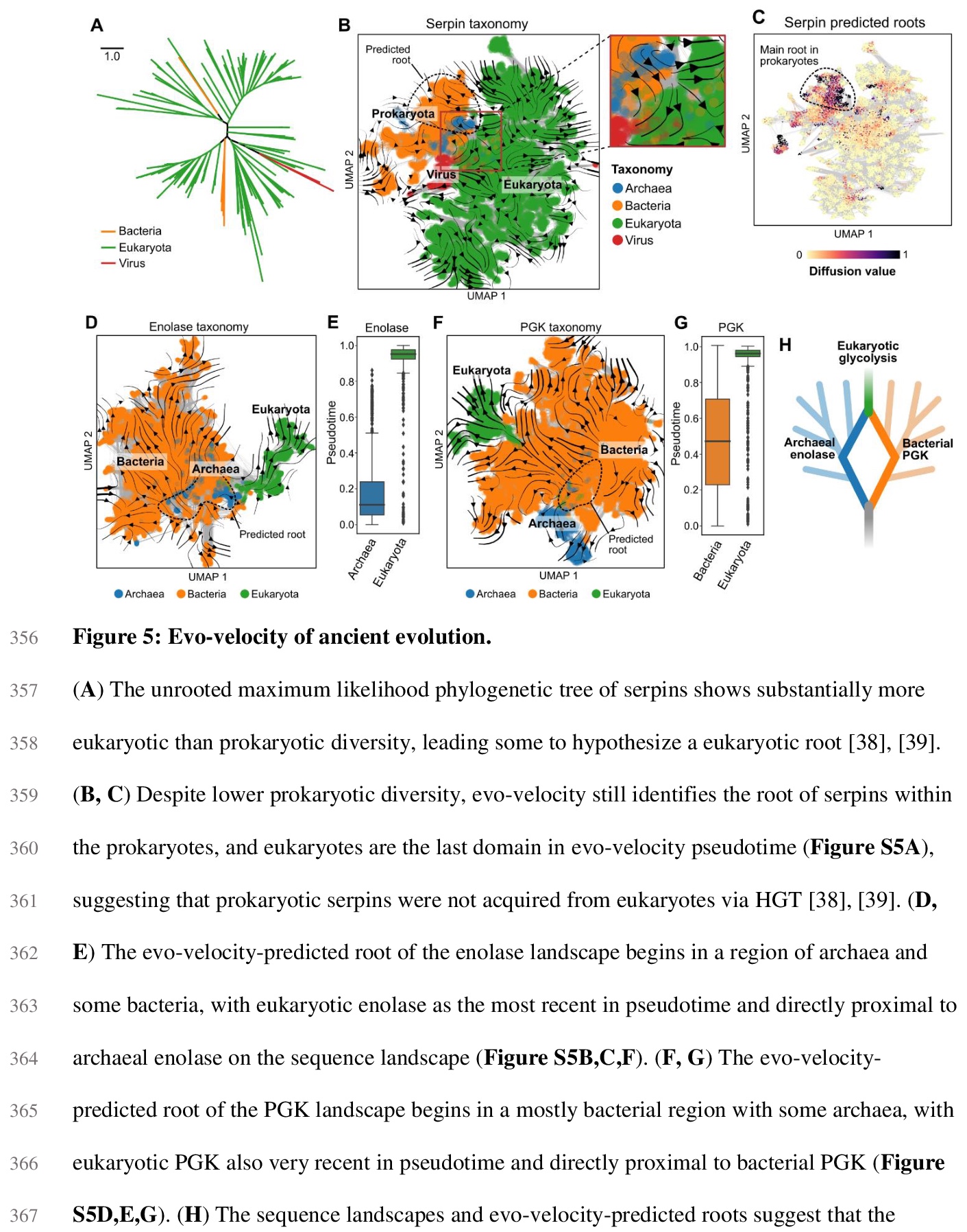
2、[CL] Evolutionary velocity with protein language models
B L. Hie, K K. Yang, P S. Kim
[Stanford University & Microsoft Research New England]
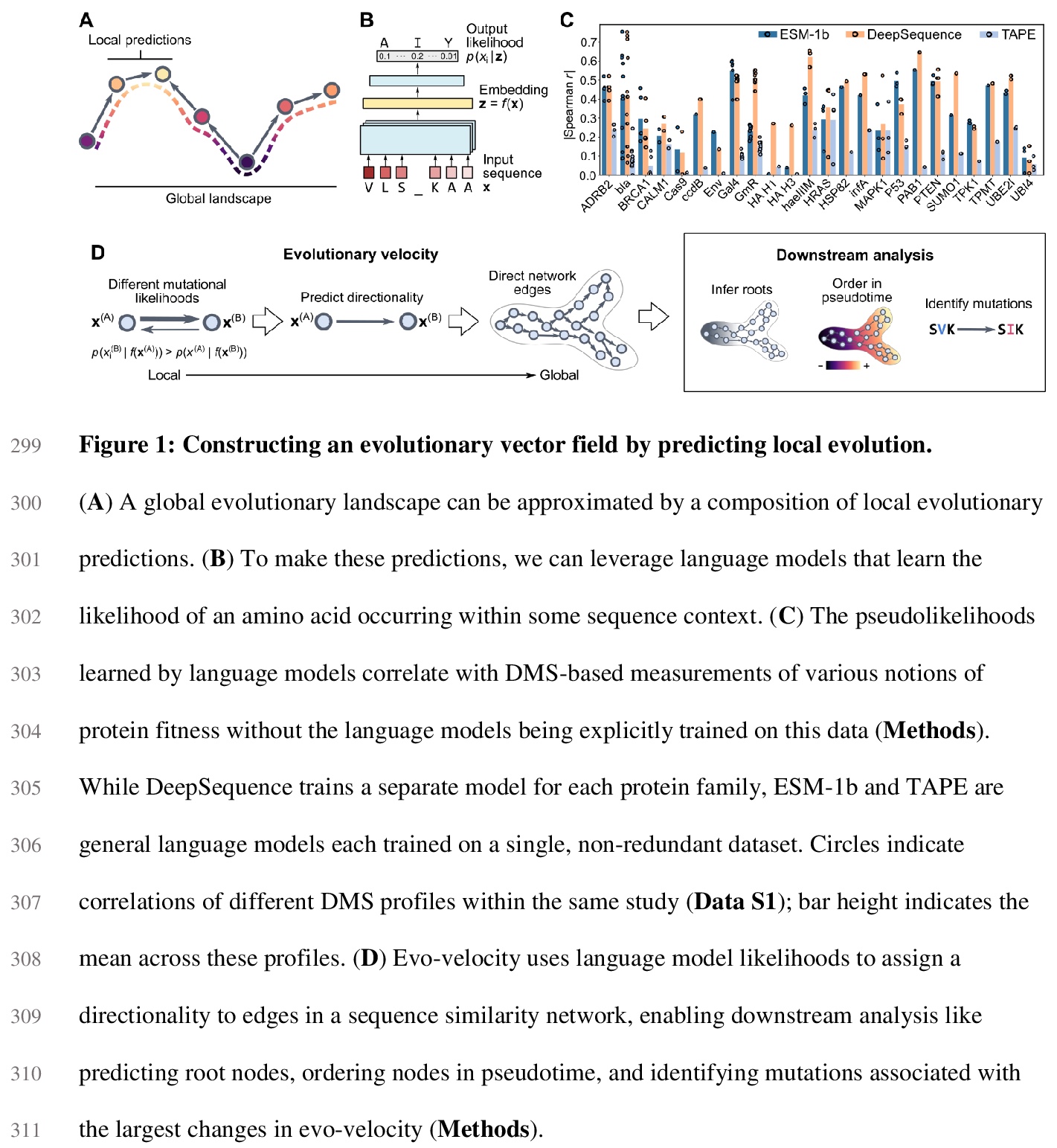
蛋白质语言模型的进化速度。预测生物同源顺序,是进化生物学的一项基本任务。对蛋白质进化来说,这种顺序通常是通过先将序列排列成系统发育树来确定的,存在限制性假设,可能造成大量的模糊性。本文展示了被称为语言模型的机器学习算法,如何学习预测进化方向性的突变可能性,从而实现遗传进化分析,解决现有方法的关键性限制。主要概念进展是通过局部进化预测,构建一个蛋白质进化的”矢量场”,称之为进化速度(evo-velocity)。进化速度可成功预测不同时间尺度的进化秩序,从病毒蛋白在几年内的进化,到真核生物蛋白在地质年代的进化。进化速度还产生了新的进化见解,预测了病毒-宿主免疫逃逸的策略,解决了关于蛇蛋白进化的冲突理论,揭示了水平基因转移在真核生物糖酵解进化中的关键作用。在此过程中,语言模型可以学习足够的天然蛋白质进化规则,实现进化的可预测性。
Predicting the order of biological homologs is a fundamental task in evolutionary biology. For protein evolution, this order is often determined by first arranging sequences into a phylogenetic tree, which has limiting assumptions and can suffer from substantial ambiguity. Here, we demonstrate how machine learning algorithms called language models can learn mutational likelihoods that predict the directionality of evolution, thereby enabling phylogenetic analysis that addresses key limitations of existing methods. Our main conceptual advance is to construct a “vector field” of protein evolution through local evolutionary predictions that we refer to as evolutionary velocity (evo-velocity). We show that evo-velocity can successfully predict evolutionary order at vastly different timescales, from viral proteins evolving over years to eukaryotic proteins evolving over geologic eons. Evo-velocity also yields new evolutionary insights, predicting strategies of viral-host immune escape, resolving conflicting theories on the evolution of serpins, and revealing a key role of horizontal gene transfer in the evolution of eukaryotic glycolysis. In doing so, our work suggests that language models can learn sufficient rules of natural protein evolution to enable evolutionary predictability.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjtmE3Vjs
3、[LG] HoroPCA: Hyperbolic Dimensionality Reduction via Horospherical Projections
I Chami, A Gu, D Nguyen, C Ré
[Stanford University]
HoroPCA:基于球面投影的双曲降维。研究了双曲空间数据的主成分分析(PCA)。给定方向,PCA依赖: (1)这些方向所跨越的子空间的参数化,(2)保留这些方向信息的子空间的投影方法,以及(3)优化目标,即投影所解释的方差。将这些概念中的每一个,推广到双曲空间,提出HOROPCA,一种用于双曲空间降维的方法。通过聚焦主方向提取这一核心问题,HOROPCA在理论上比之前的PCA归纳更好地保留了距离等原始数据信息。实验验证了HOROPCA优于现有的降维方法,大大减少了距离保存的误差。作为一种数据白化方法,与不使用白化的方法相比,可将下游分类提高3.9%。HOROPCA还可用于可视化二维双曲线数据。
This paper studies Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for data lying in hyperbolic spaces. Given directions, PCA relies on: (1) a parameterization of subspaces spanned by these directions, (2) a method of projection onto subspaces that preserves information in these directions, and (3) an objective to optimize, namely the variance explained by projections. We generalize each of these concepts to the hyperbolic space and propose HOROPCA, a method for hyperbolic dimensionality reduction. By focusing on the core problem of extracting principal directions, HOROPCA theoretically better preserves information in the original data such as distances, compared to previous generalizations of PCA. Empirically, we validate that HOROPCA outperforms existing dimensionality reduction methods, significantly reducing error in distance preservation. As a data whitening method, it improves downstream classification by up to 3.9% compared to methods that don’t use whitening. Finally, we show that HOROPCA can be used to visualize hyperbolic data in two dimensions.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjtpCuh4u
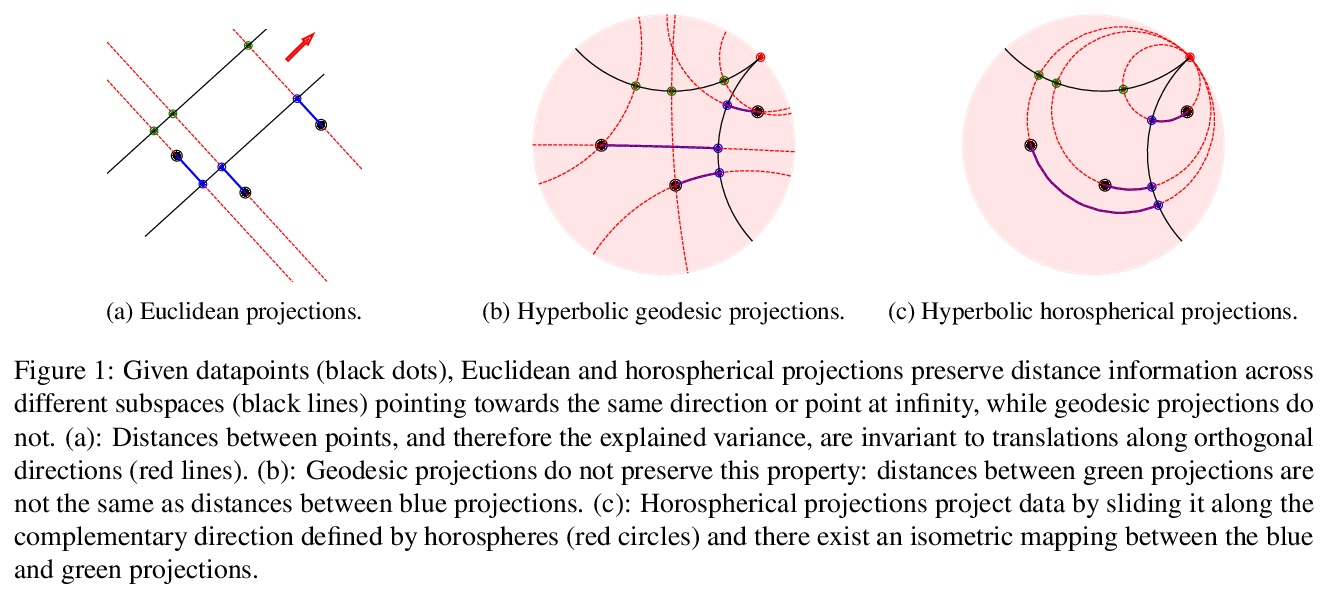
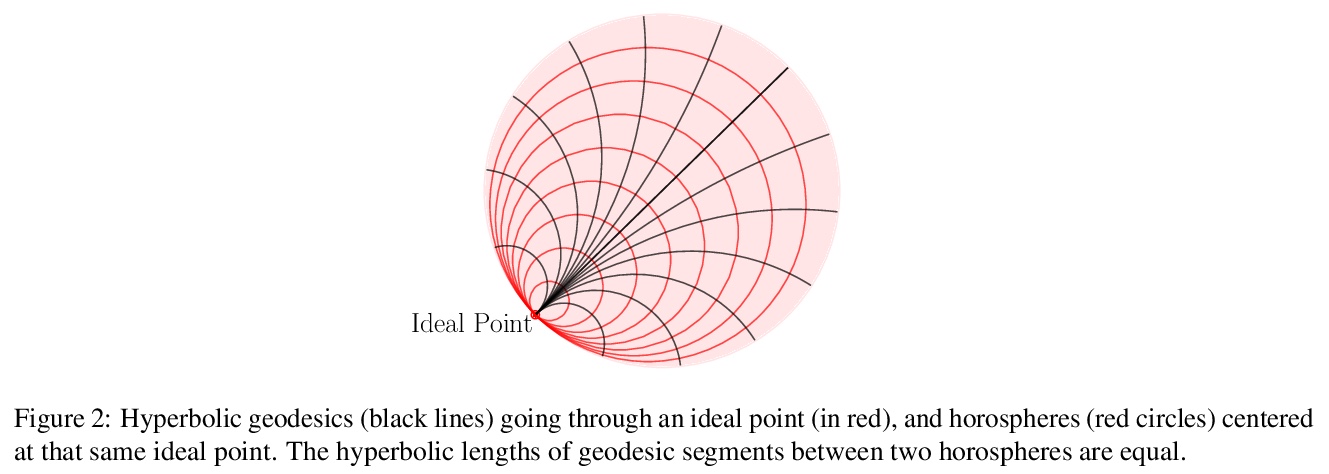
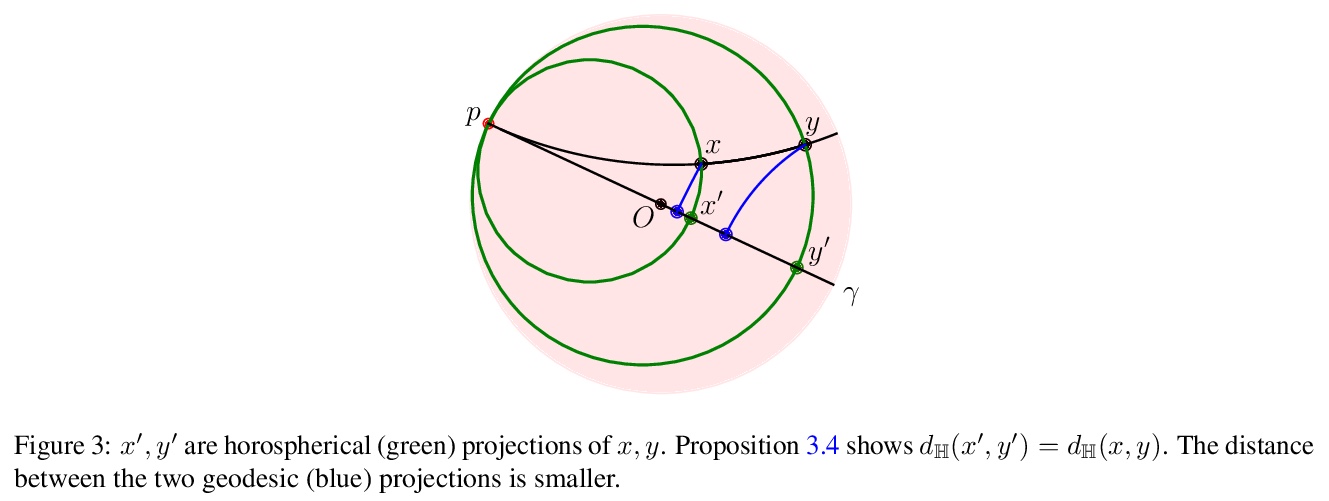
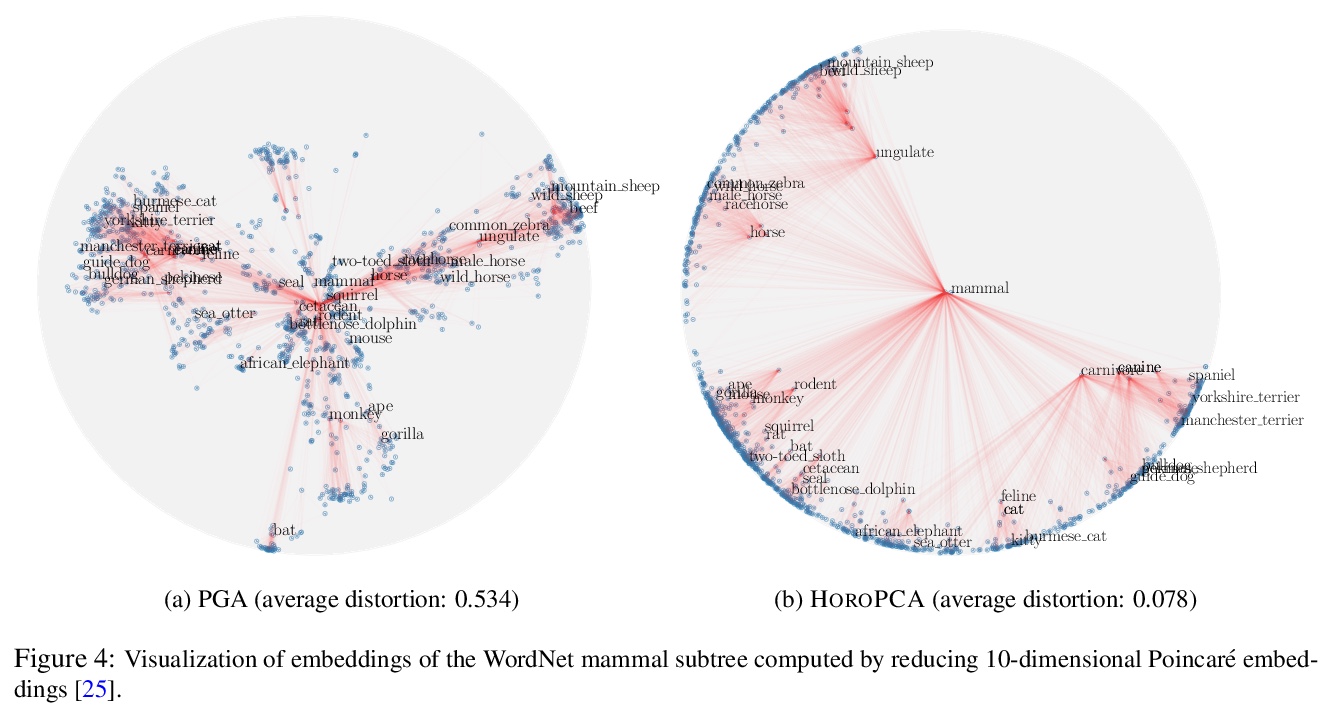
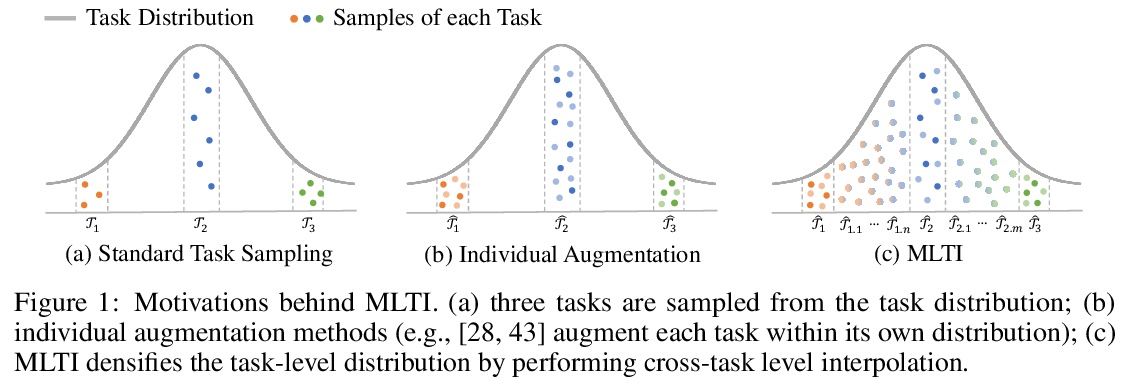
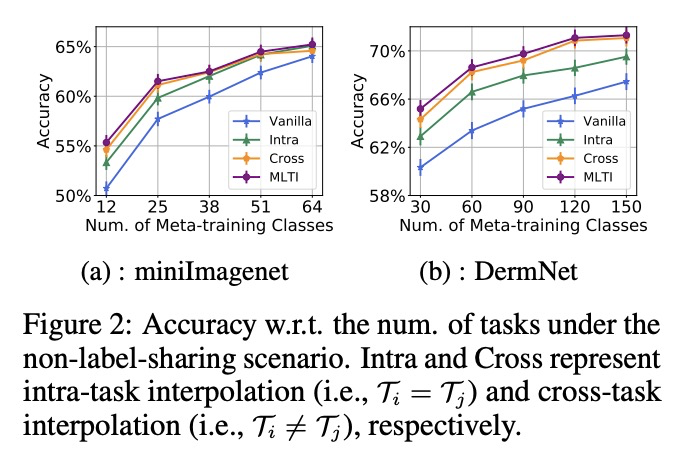
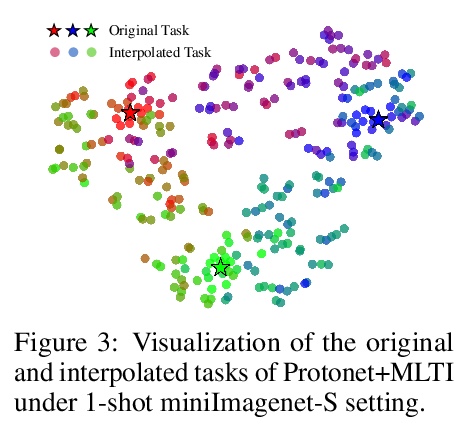
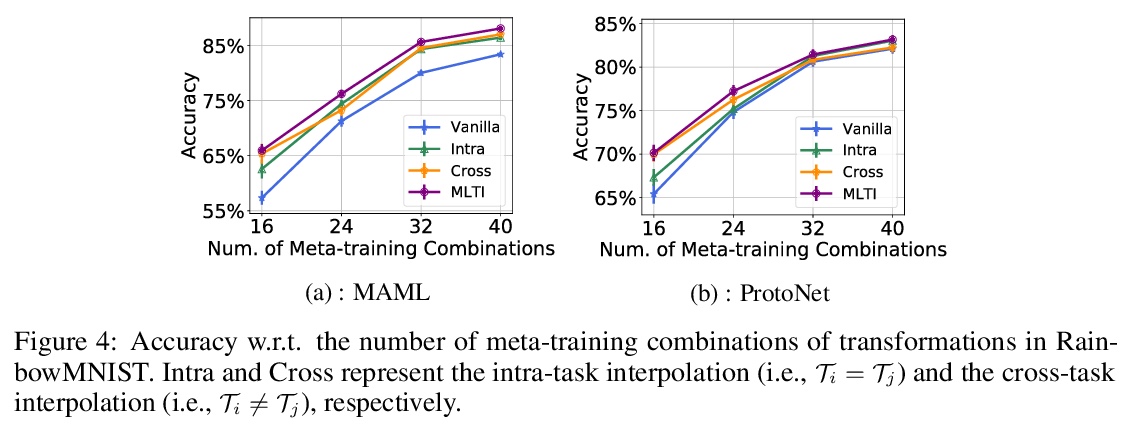
4、[LG] Meta-Learning with Fewer Tasks through Task Interpolation
H Yao, L Zhang, C Finn
[Stanford University & Rutgers University]
基于任务插值的更少量任务元学习。元学习使算法能通过迁移之前学到的知识,仅用几个标记的样本,就能快速学习一个新任务。然而,目前元学习算法的瓶颈,是需要大量的元训练任务,而这些任务在现实世界场景可能无法获得。为解决现有任务可能无法密集采样的问题,本文建议通过插值来增加任务集,即基于任务插值的元学习(MLTI),通过随机抽取一对任务,对相应的特征和标签进行插值,来有效地生成额外的任务。在基于梯度和基于度量的元学习设置下,理论分析表明MLTI对应于数据自适应的元正则化,并进一步提高泛化。对来自不同领域的8个数据集的实验中,包括图像识别、姿态预测、分子属性预测和医学图像分类,发现所提出的通用MLTI框架与代表性的元学习算法兼容,并总是优于其他先进的策略。
Meta-learning enables algorithms to quickly learn a newly encountered task with just a few labeled examples by transferring previously learned knowledge. However, the bottleneck of current meta-learning algorithms is the requirement of a large number of meta-training tasks, which may not be accessible in real-world scenarios. To address the challenge that available tasks may not densely sample the space of tasks, we propose to augment the task set through interpolation. By meta-learning with task interpolation (MLTI), our approach effectively generates additional tasks by randomly sampling a pair of tasks and interpolating the corresponding features and labels. Under both gradient-based and metric-based meta-learning settings, our theoretical analysis shows MLTI corresponds to a data-adaptive meta-regularization and further improves the generalization. Empirically, in our experiments on eight datasets from diverse domains including image recognition, pose prediction, molecule property prediction, and medical image classification, we find that the proposed general MLTI framework is compatible with representative meta-learning algorithms and consistently outperforms other state-of-the-art strategies.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjttCqtPV
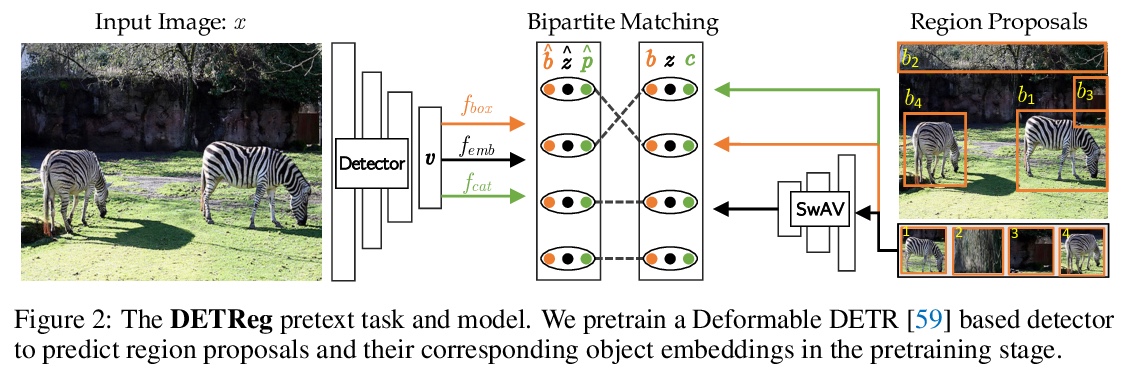
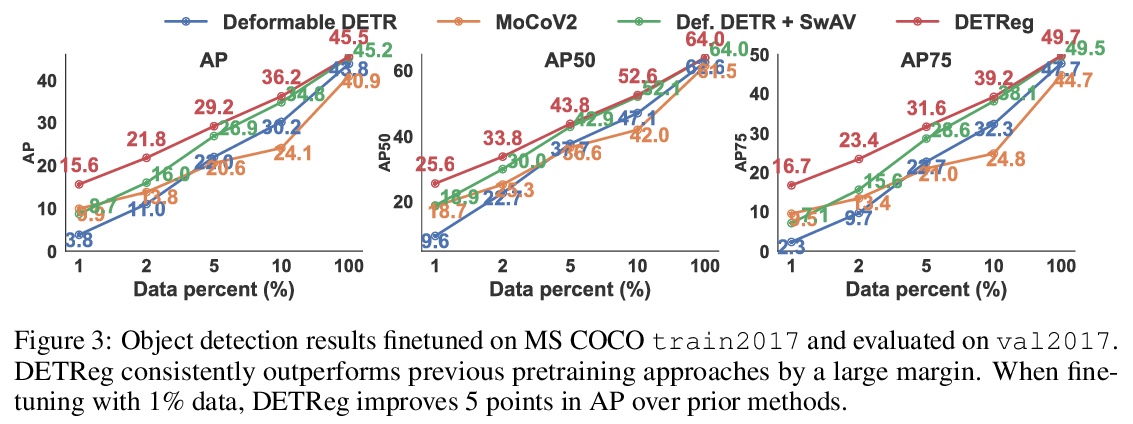
5、[CV] DETReg: Unsupervised Pretraining with Region Priors for Object Detection
A Bar, X Wang, V Kantorov, C J Reed, R Herzig, G Chechik, A Rohrbach, T Darrell, A Globerson
[Tel-Aviv University & Berkeley AI Research & NVIDIA]
DETReg:面向目标检测的区域先验无监督预训练。自监督预训练最近被证明有利于目标检测等计算机视觉任务。然而,之前的自监督方法,并未设计用来处理检测中的关键方面:目标定位。本文提出DETReg,一种无监督预训练方法,用区域先验Transformers进行目标检测。基于目标检测的两个任务:定位和分类,将两个互补信号结合起来进行自监督。对于目标定位信号,用来自现成的无监督候选区域提取方法——选择性搜索——的伪真值目标边界框,该方法不需要训练,可以高召回率和非常低的精度检测物体。分类信号来自目标嵌入损失,鼓励不变的目标表示,从中可推断出目标类别。展示了如何结合这两个信号,从大量未标记数据中训练可变形DETR检测架构。DETReg在标准基准(如MS COCO和PASCAL VOC)上的性能比竞争基线和之前的自监督方法要好。在MS COCO上只用1%、2%、5%和10%的标记数据进行训练时,DETReg在低数据设置下也优于之前的监督和无监督基线方法。
Self-supervised pretraining has recently proven beneficial for computer vision tasks, including object detection. However, previous self-supervised approaches are not designed to handle a key aspect of detection: localizing objects. Here, we present DETReg, an unsupervised pretraining approach for object DEtection with TRansformers using Region priors. Motivated by the two tasks underlying object detection: localization and categorization, we combine two complementary signals for self-supervision. For an object localization signal, we use pseudo ground truth object bounding boxes from an off-the-shelf unsupervised region proposal method, Selective Search, which does not require training and can detect objects at a high recall rate and very low precision. The categorization signal comes from an object embedding loss that encourages invariant object representations, from which the object category can be inferred. We show how to combine these two signals to train the Deformable DETR detection architecture from large amounts of unlabeled data. DETReg improves the performance over competitive baselines and previous self-supervised methods on standard benchmarks like MS COCO and PASCAL VOC. DETReg also outperforms previous supervised and unsupervised baseline approaches for a low-data regime when trained with only 1%, 2%, 5%, and 10% of the labeled data on MS COCO.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjtwFgPcl


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
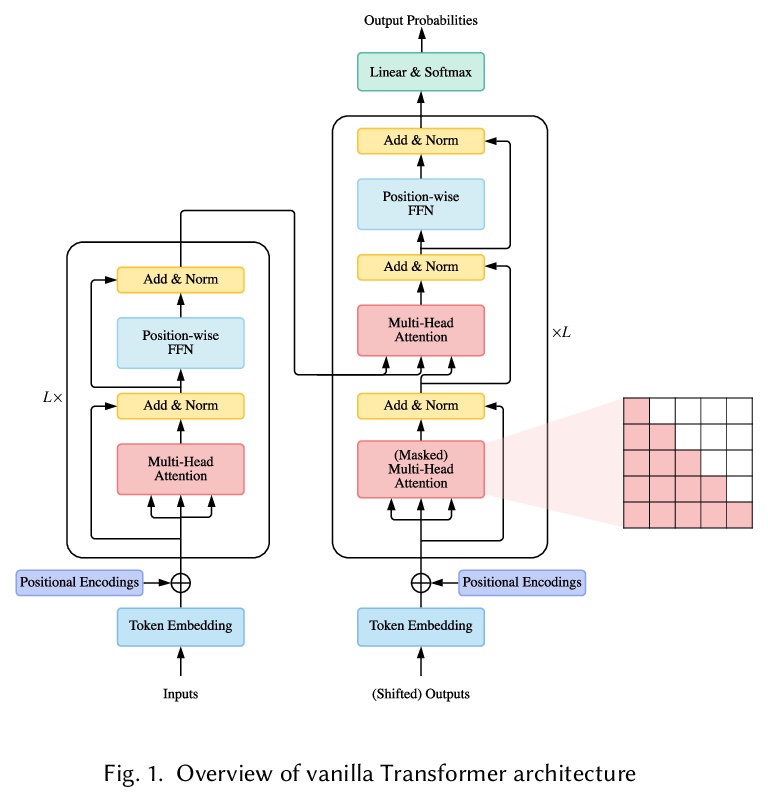
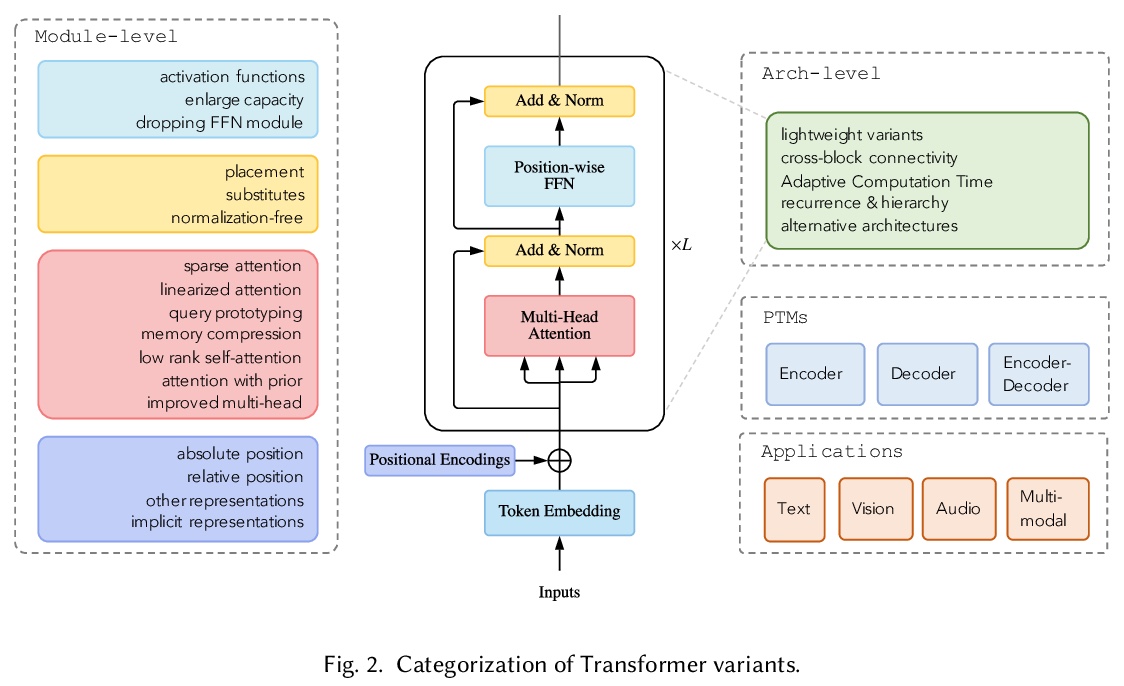
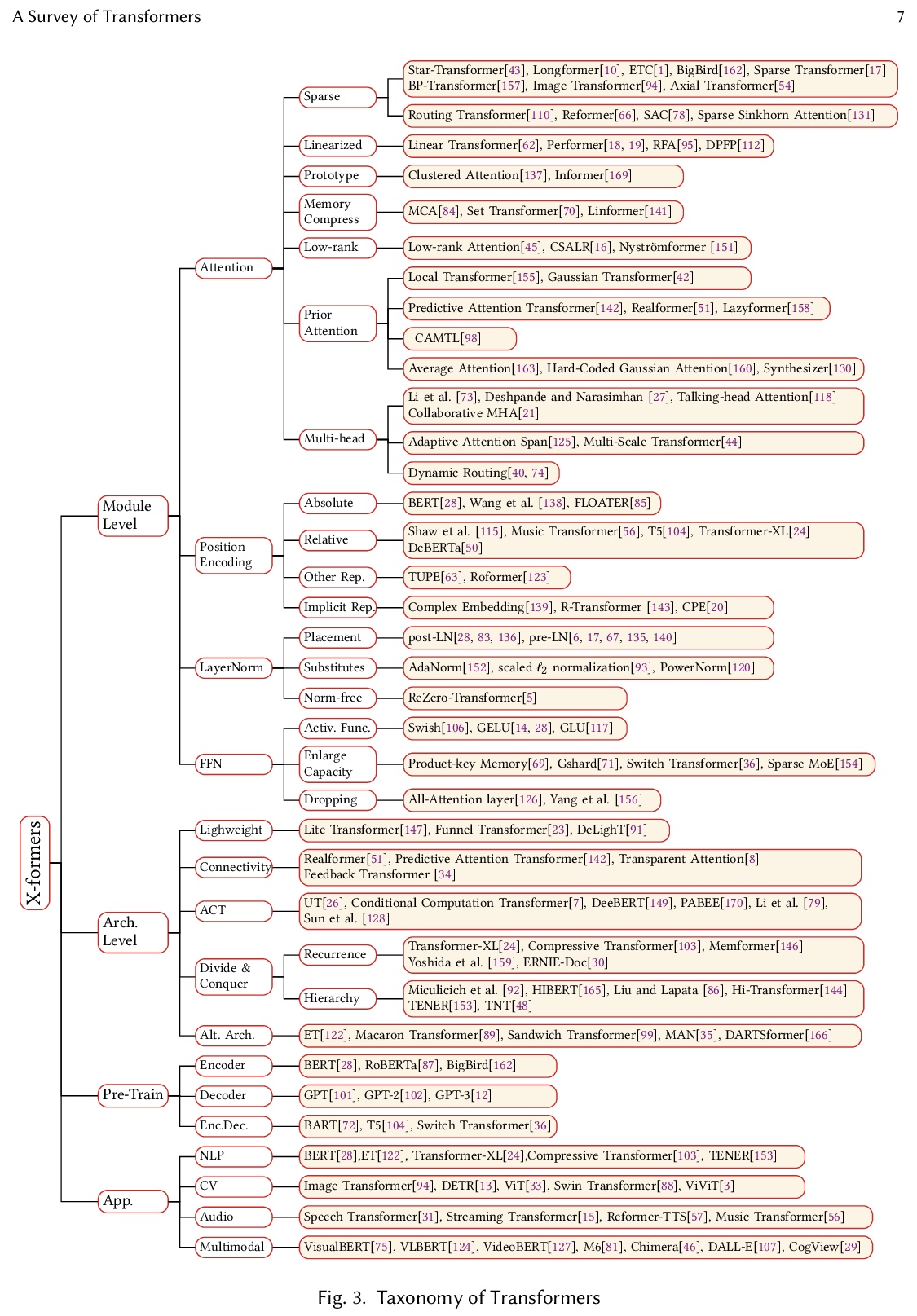
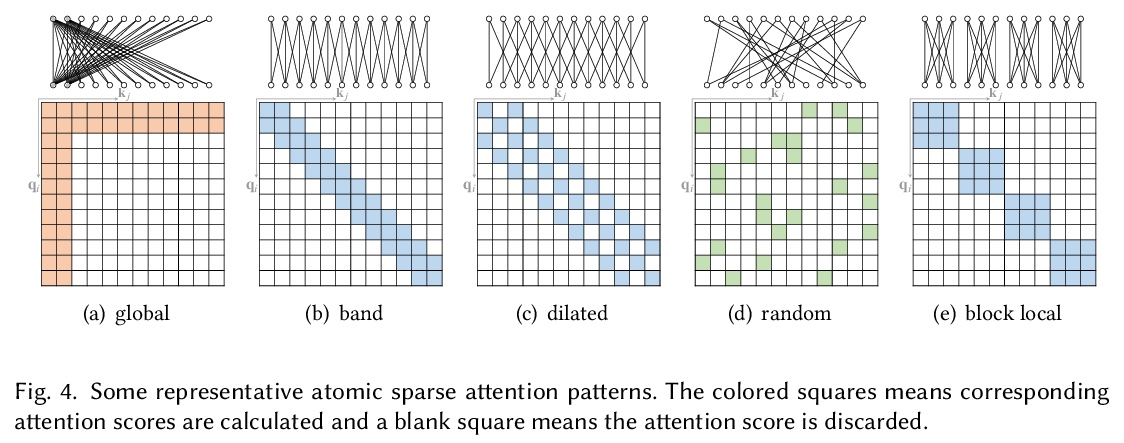
[LG] A Survey of Transformers
Transformer综述
T Lin, Y Wang, X Liu, X Qiu
[Fudan University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjtgUAaRN
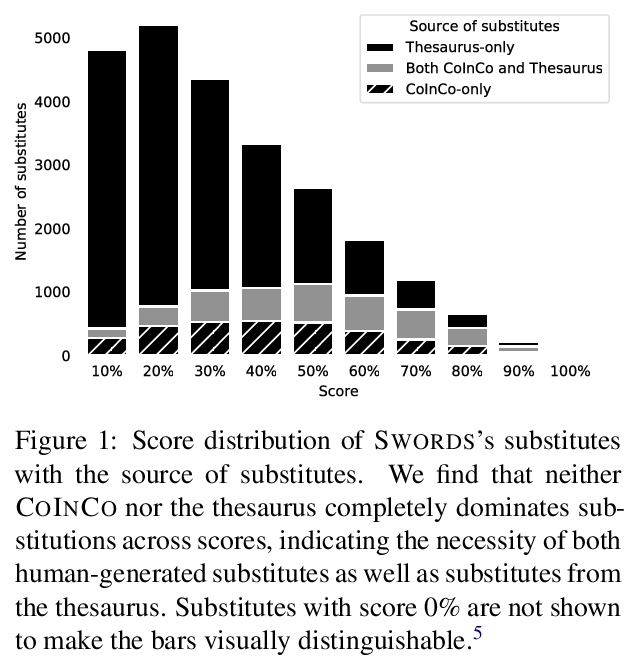
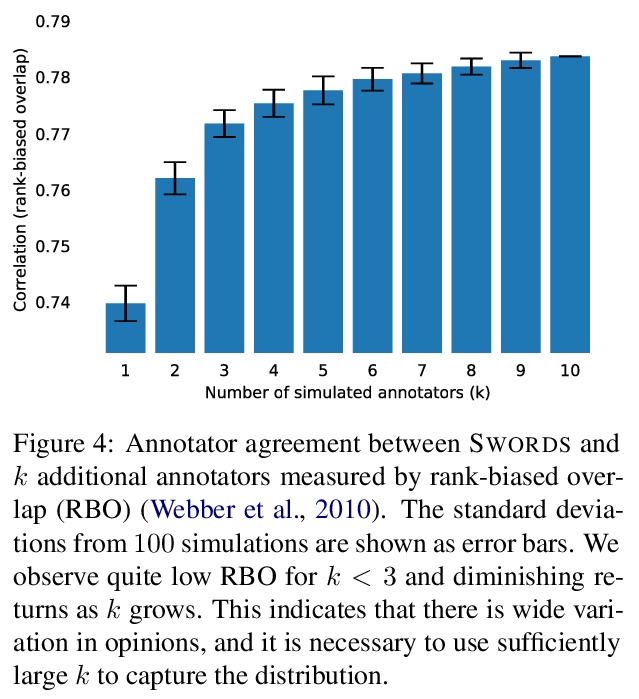
[CL] Swords: A Benchmark for Lexical Substitution with Improved Data Coverage and Quality
Swords:改进数据覆盖和质量的词汇替换基准
M Lee, C Donahue, A Iyabor, R Jia, P Liang
[Stanford University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjtACwdqD


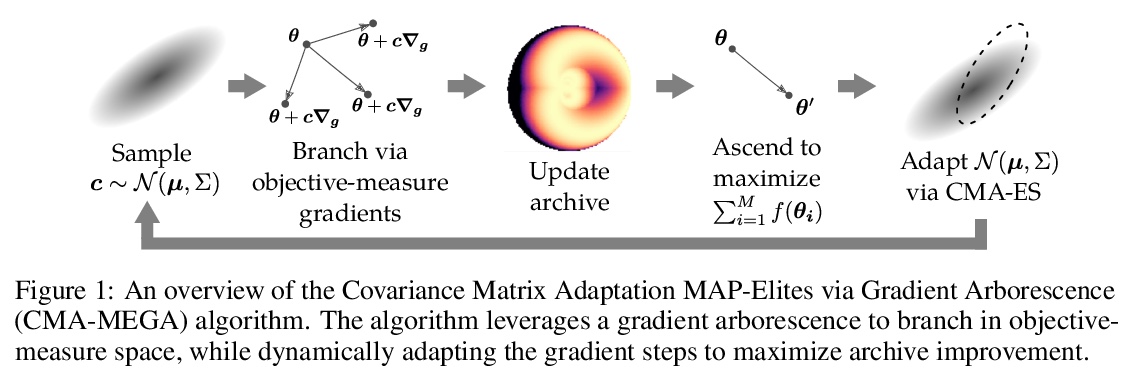
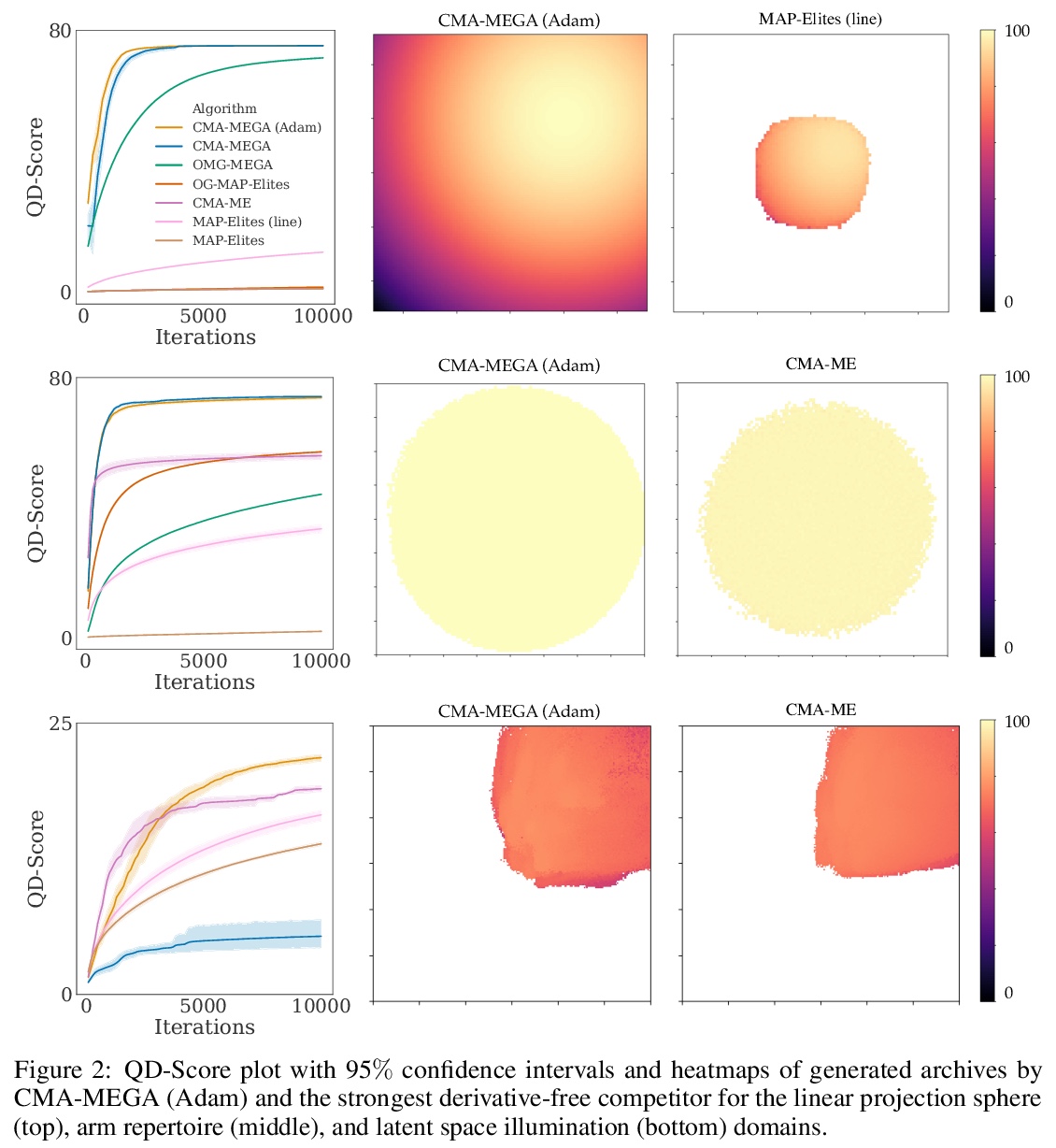
[AI] Differentiable Quality Diversity
可微质量歧异度
M C. Fontaine, S Nikolaidis
[University of Southern California]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjtDagzyq

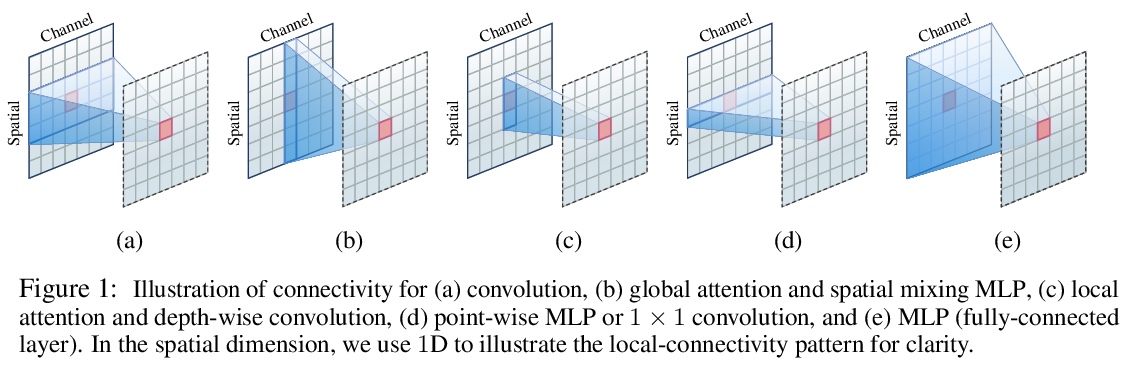
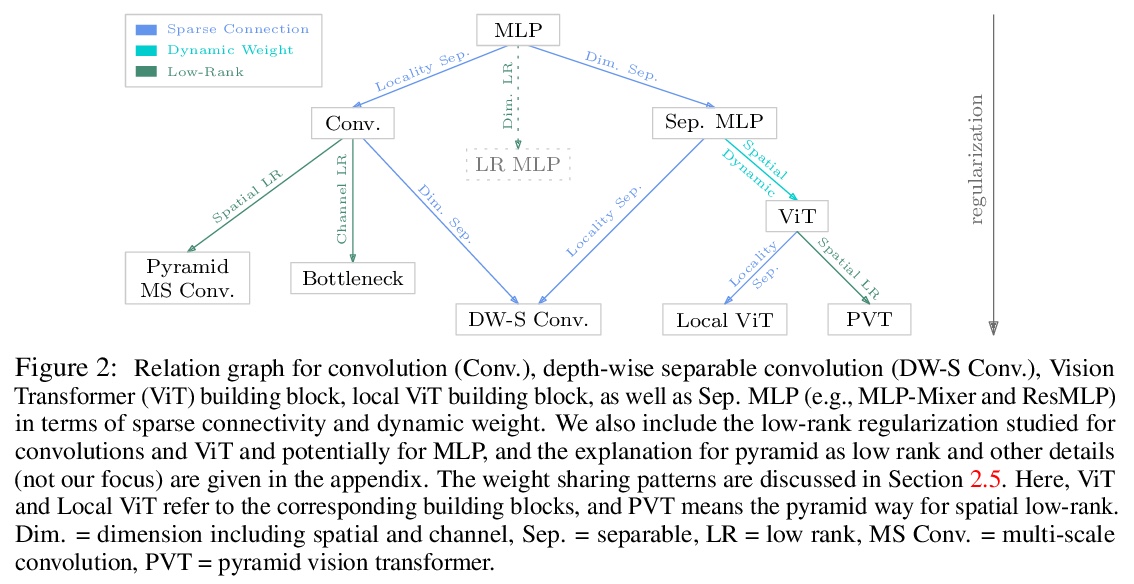
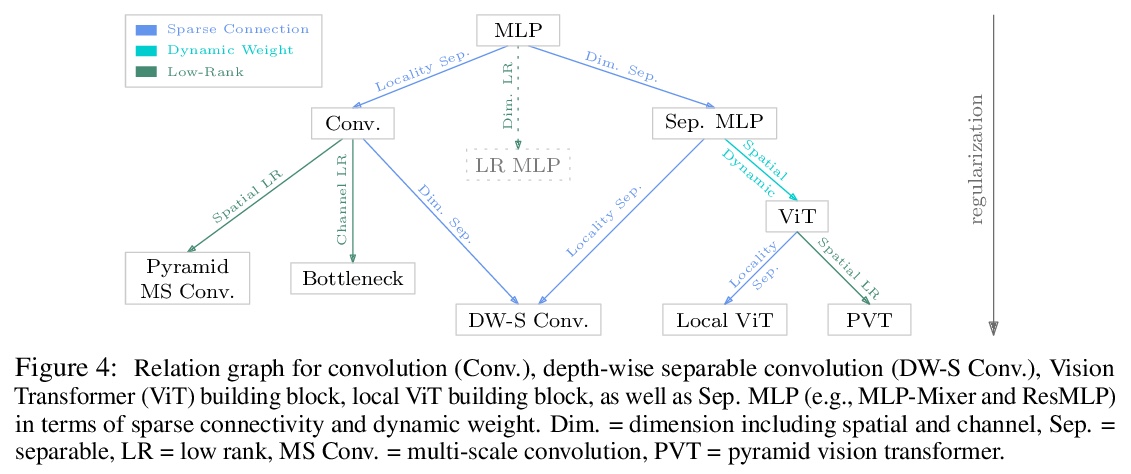
[CV] Demystifying Local Vision Transformer: Sparse Connectivity, Weight Sharing, and Dynamic Weight
局部视觉Transformer研究:稀疏连接、权重共享和动态权重
Q Han, Z Fan, Q Dai, L Sun, M Cheng, J Liu, J Wang
[Nankai University & Peking University & Microsoft Research Asia]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjtGcxtJf