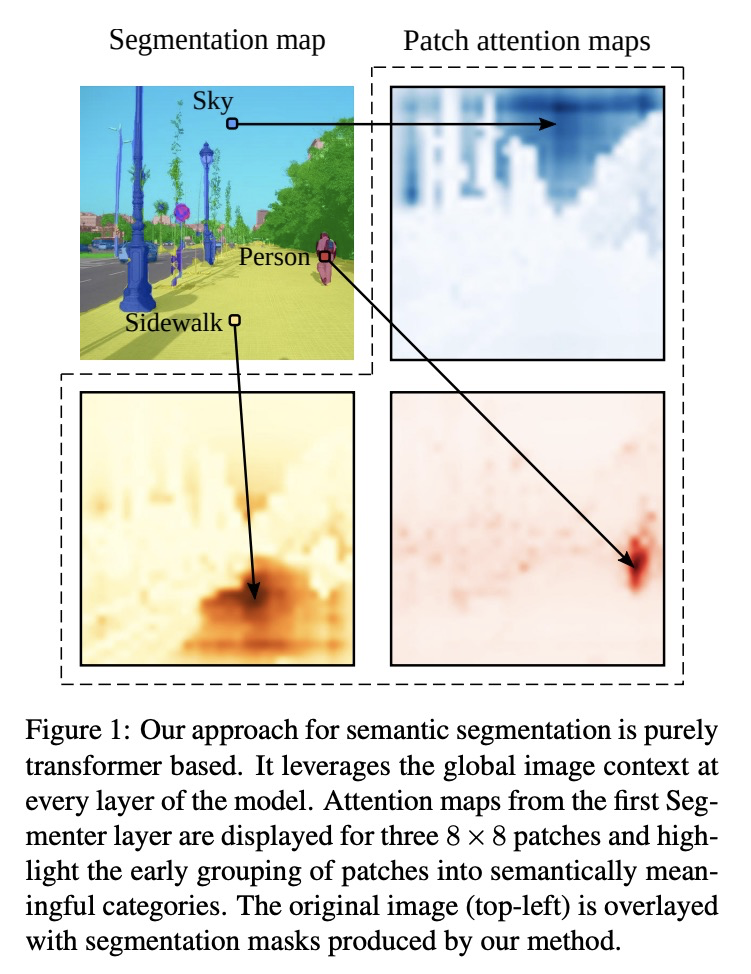
- 1、[CV] Segmenter: Transformer for Semantic Segmentation
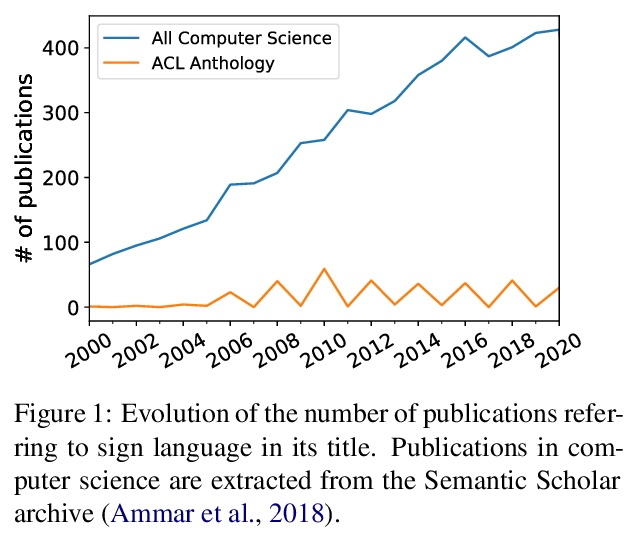
- 2、[CL] Including Signed Languages in Natural Language Processing
- 3、[CV] When Does Contrastive Visual Representation Learning Work?
- 4、[LG] How could Neural Networks understand Programs?
- 5、[CV] TextOCR: Towards large-scale end-to-end reasoning for arbitrary-shaped scene text
- [CV] Collaborative Regression of Expressive Bodies using Moderation
- [CV] Operation-wise Attention Network for Tampering Localization Fusion
- [CV] PoseContrast: Class-Agnostic Object Viewpoint Estimation in the Wild with Pose-Aware Contrastive Learning
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] Segmenter: Transformer for Semantic Segmentation
R Strudel, R Garcia, I Laptev, C Schmid
[Inria]
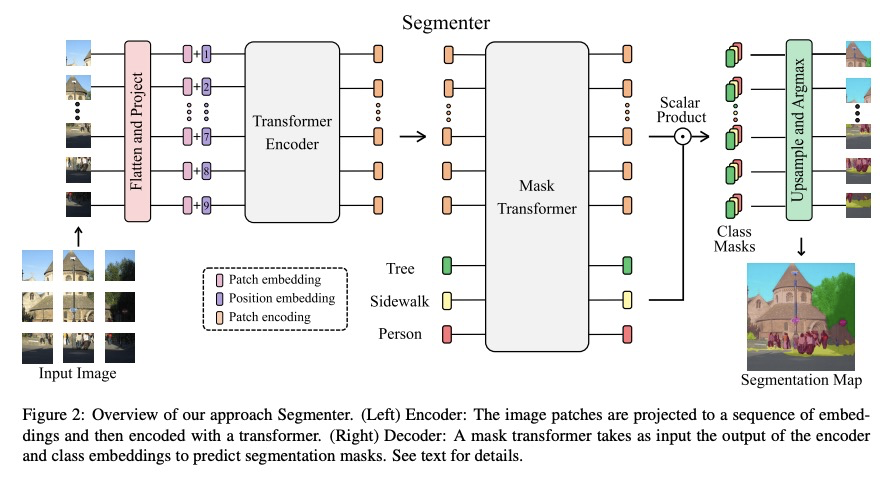
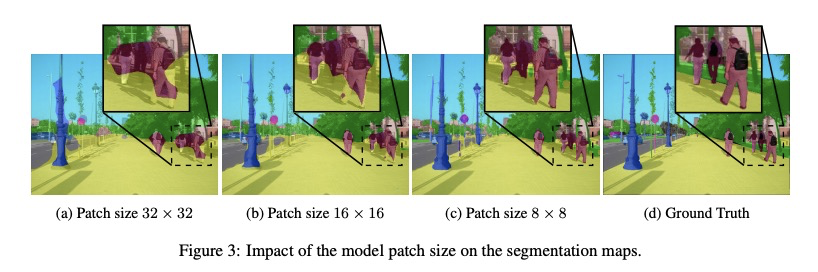
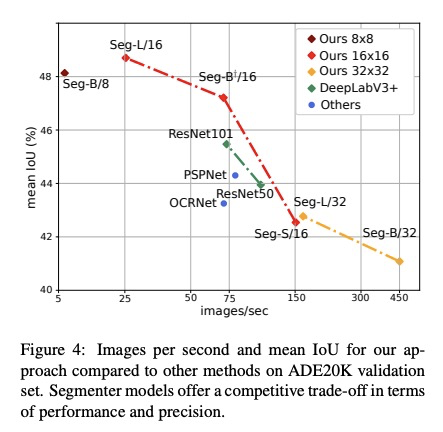
Segmenter: 面向语义分割的Transformer。图像分割在单图块层面往往是模糊的,需要背景信息来达成标记共识。本文提出一种用于语义分割的Transformer模型Segmenter。与基于卷积的方法相比,该方法可在第一层和整个网络中对全局背景进行建模。将最近的Vision Transformer(ViT)扩展到语义分割上,依靠与图块相对应的输出嵌入,通过逐点线性解码器或掩码Transformer解码器,从这些嵌入中获得类标记。利用为图像分类预训练的模型,在中等规模的数据集上对其进行微调,以用于语义分割。线性解码器已可获得很好的结果,通过生成类掩码的掩码Transformer可进一步提高性能。消融研究显示了不同参数的影响,特别是大模型和小图块尺寸的性能更好。分割器在语义分割方面取得了很好的成绩,在具有挑战性的ADE20K数据集上的表现优于目前的技术水平,在Pascal Context和Cityscapes上的表现也不差。
Image segmentation is often ambiguous at the level of individual image patches and requires contextual information to reach label consensus. In this paper we introduce Segmenter, a transformer model for semantic segmentation. In contrast to convolution-based methods, our approach allows to model global context already at the first layer and throughout the network. We build on the recent Vision Transformer (ViT) and extend it to semantic segmentation. To do so, we rely on the output embeddings corresponding to image patches and obtain class labels from these embeddings with a point-wise linear decoder or a mask transformer decoder. We leverage models pre-trained for image classification and show that we can fine-tune them on moderate sized datasets available for semantic segmentation. The linear decoder allows to obtain excellent results already, but the performance can be further improved by a mask transformer generating class masks. We conduct an extensive ablation study to show the impact of the different parameters, in particular the performance is better for large models and small patch sizes. Segmenter attains excellent results for semantic segmentation. It outperforms the state of the art on the challenging ADE20K dataset and performs on-par on Pascal Context and Cityscapes.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfmHZbITS

2、[CL] Including Signed Languages in Natural Language Processing
K Yin, A Moryossef, J Hochgesang, Y Goldberg, M Alikhani
[CMU & Bar-Ilan University & University of Pittsburgh]
将手语纳入自然语言处理中。由于手语表现出自然语言的所有基本语言特性,本文认为自然语言处理的工具和理论对手语建模至关重要。但现有的手语处理(SLP)研究很少尝试探索和利用手语的语言组织。本意见书呼吁NLP界将手语作为一个具有高度社会影响和科学影响的研究领域。讨论了在建模过程中需要考虑的手语的语言学特性,回顾了目前SLP模型的局限性,确定了将NLP扩展到手语的开放挑战,并敦促(1)采用有效的标记化方法;(2)开发有语言学依据的模型;(3)收集真实世界的手语数据;(4)将本地手语社区作为研究方向的一个积极和主导的声音。
Signed languages are the primary means of communication for many deaf and hard of hearing individuals. Since signed languages exhibit all the fundamental linguistic properties of natural language, we believe that tools and theories of Natural Language Processing (NLP) are crucial towards its modeling. However, existing research in Sign Language Processing (SLP) seldom attempt to explore and leverage the linguistic organization of signed languages. This position paper calls on the NLP community to include signed languages as a research area with high social and scientific impact. We first discuss the linguistic properties of signed languages to consider during their modeling. Then, we review the limitations of current SLP models and identify the open challenges to extend NLP to signed languages. Finally, we urge (1) the adoption of an efficient tokenization method; (2) the development of linguistically-informed models; (3) the collection of real-world signed language data; (4) the inclusion of local signed language communities as an active and leading voice in the direction of research.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfmMBhbx9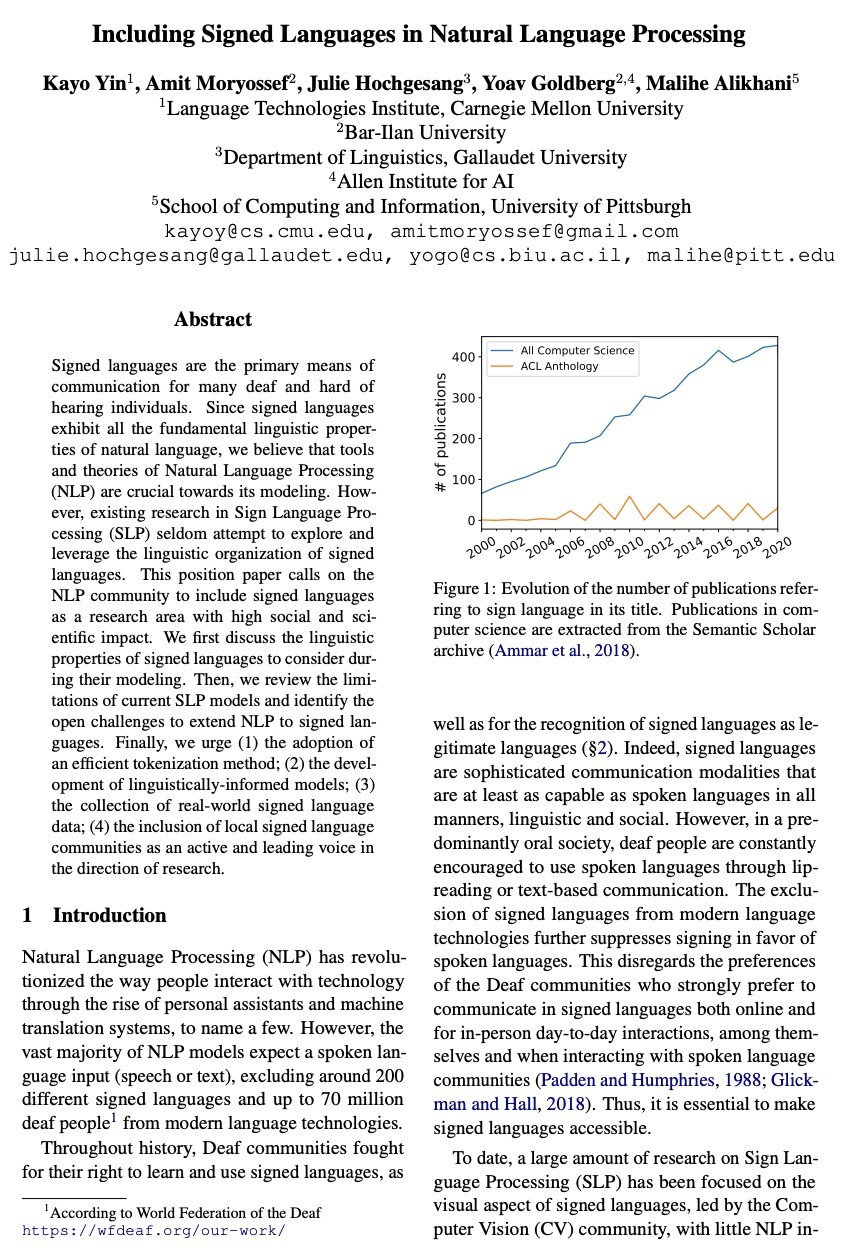
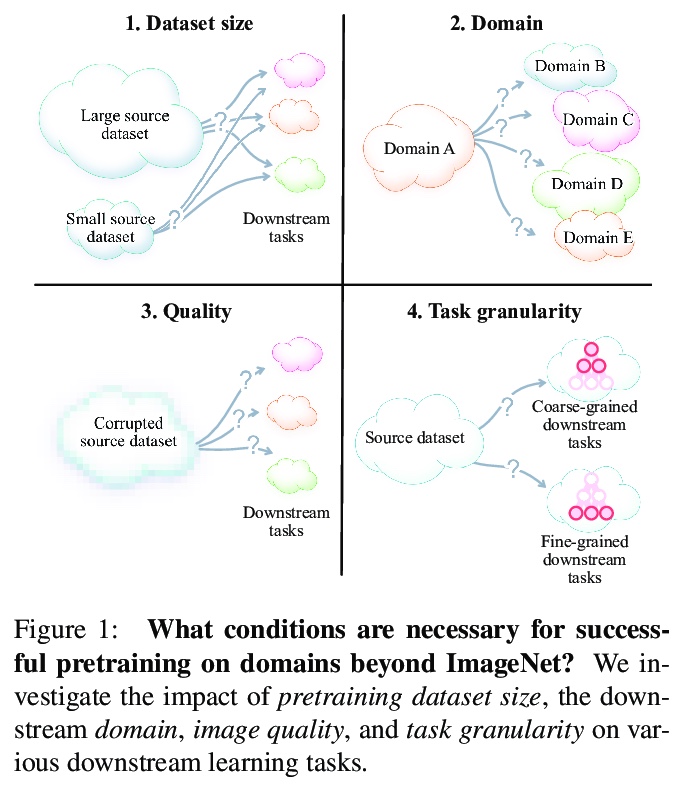
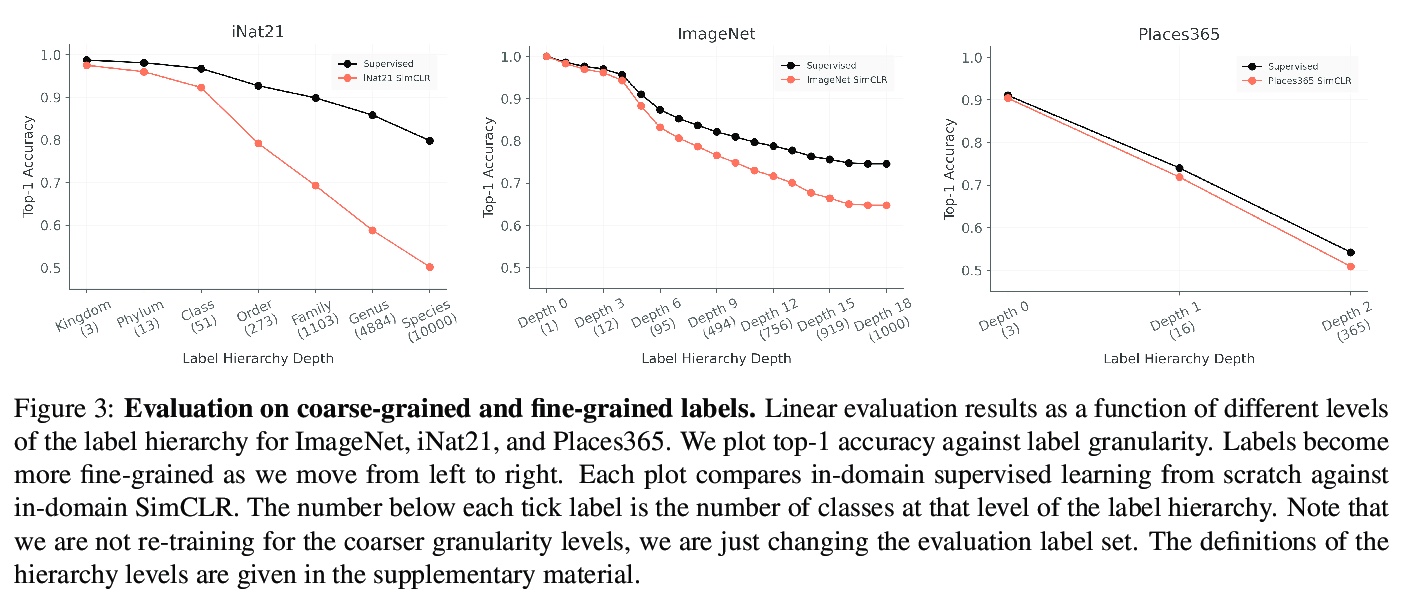
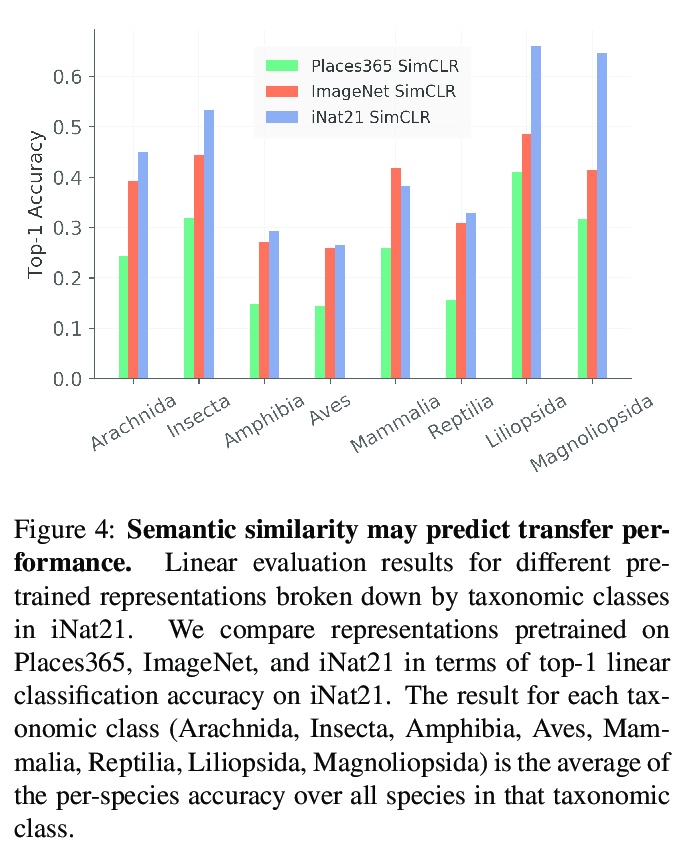
3、[CV] When Does Contrastive Visual Representation Learning Work?
E Cole, X Yang, K Wilber, O M Aodha, S Belongie
[Caltech & Google & University of Edinburgh]
对比视觉表示学习什么情况下有用?最近的自监督表示学习技术,很大程度上缩小了ImageNet分类中监督和无监督学习之间的差距。虽然现在对ImageNet的预训练的具体细节已经有了比较好的了解,但该领域仍然缺乏广泛接受的最佳实践,无法在其他数据集上复制这一成功。作为这个方向的第一步,本文在四个不同的大规模数据集上研究了对比自监督学习。通过对数据量、数据域、数据质量和任务颗粒度的观察,对成功的自监督学习的必要条件有了新的认识。主要发现包括:(i)超过50万张图像的额外预训练数据的好处不大,(ii)增加另一个领域的预训练图像不会导致泛化更好的的表示,(iii)损坏的预训练图像对监督和自监督预训练有不同的影响,以及(iv)在细粒度的视觉分类任务上,对比学习远远落后于监督学习。
Recent self-supervised representation learning techniques have largely closed the gap between supervised and unsupervised learning on ImageNet classification. While the particulars of pretraining on ImageNet are now relatively well understood, the field still lacks widely accepted best practices for replicating this success on other datasets. As a first step in this direction, we study contrastive selfsupervised learning on four diverse large-scale datasets. By looking through the lenses of data quantity, data domain, data quality, and task granularity, we provide new insights into the necessary conditions for successful selfsupervised learning. Our key findings include observations such as: (i) the benefit of additional pretraining data beyond 500k images is modest, (ii) adding pretraining images from another domain does not lead to more general representations, (iii) corrupted pretraining images have a disparate impact on supervised and self-supervised pretraining, and (iv) contrastive learning lags far behind supervised learning on fine-grained visual classification tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfmPrCejF
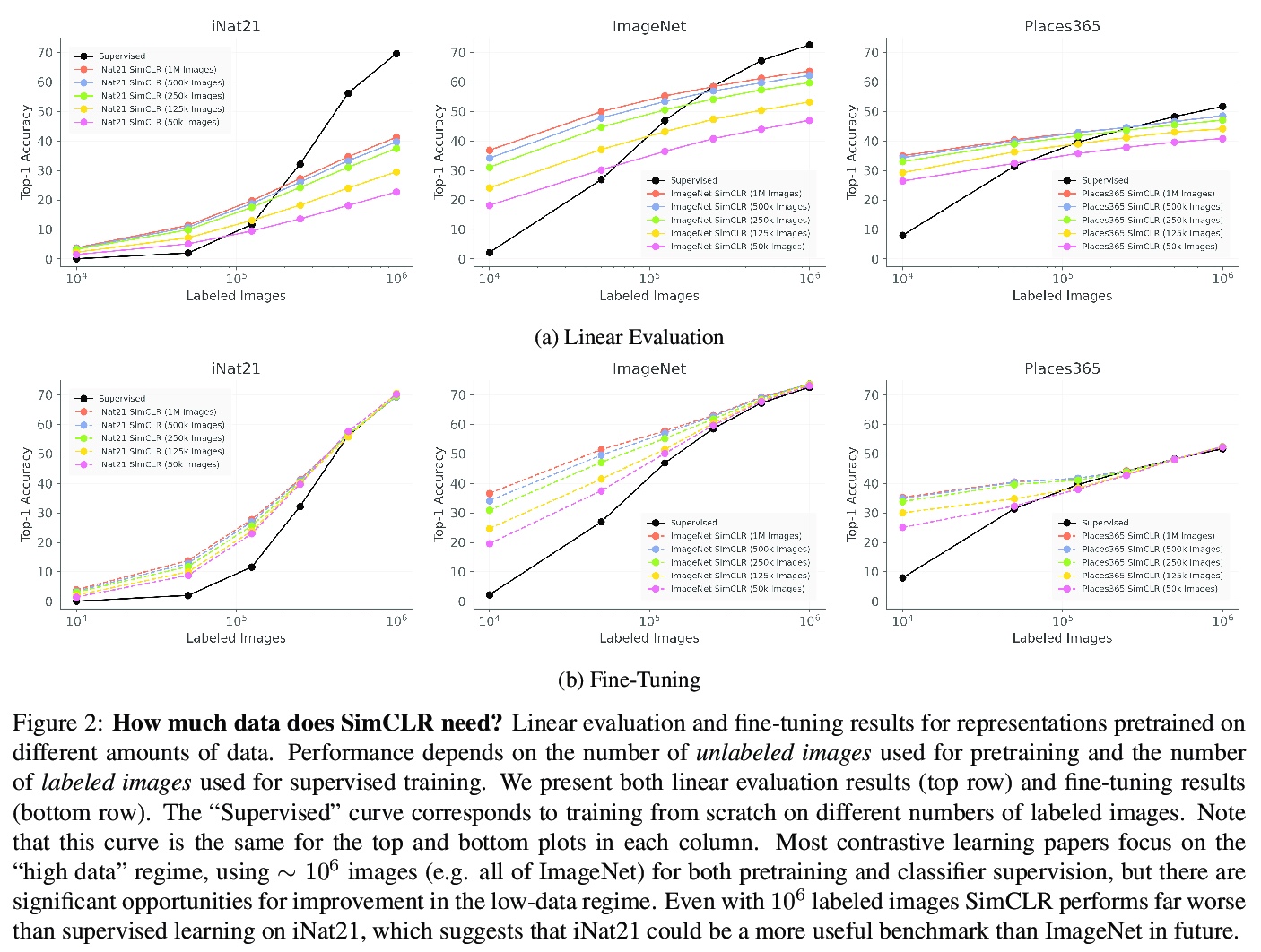
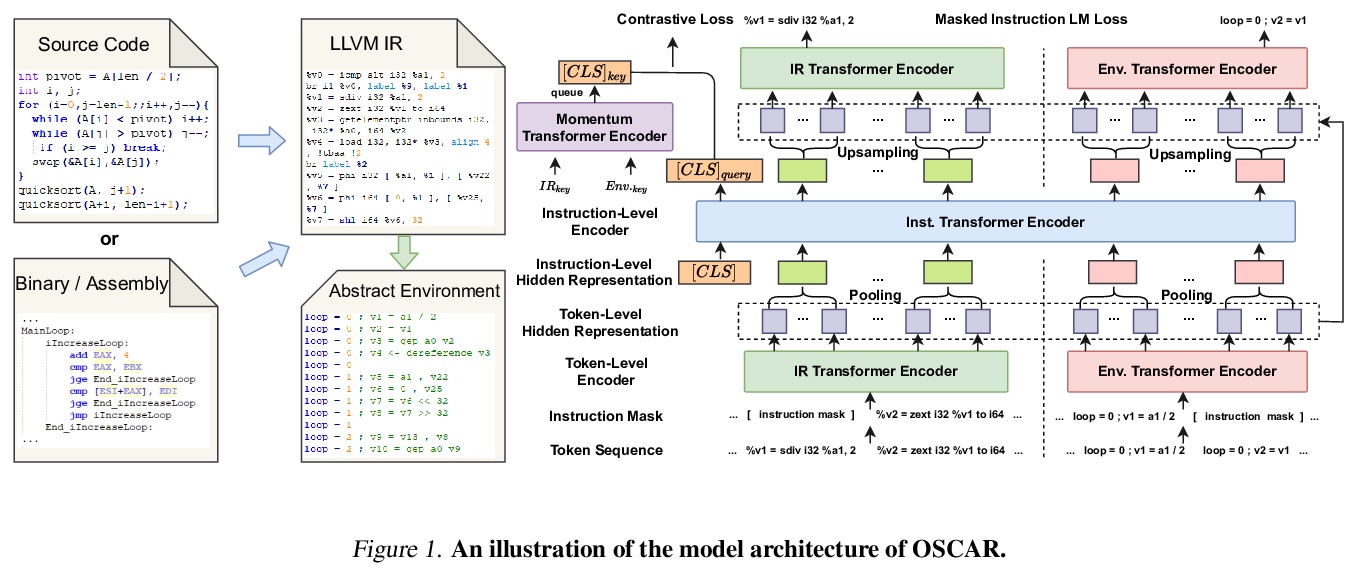
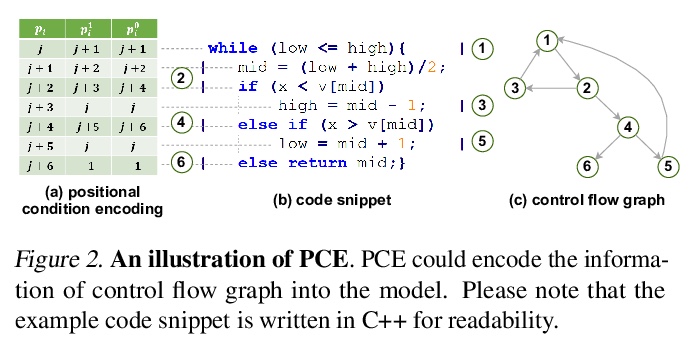
4、[LG] How could Neural Networks understand Programs?
D Peng, S Zheng, Y Li, G Ke, D He, T Liu
[University of Science and Technology of China & Microsoft Research Asia]
神经网络如何能理解代码?程序的语义理解是编程语言处理(PLP)的一个基本问题。最近的工作在NLP的预训练技术基础上学习代码的表示,在该方向上推动了前沿的发展。然而,编程语言和自然语言的语义有本质区别,忽略了这些,很难建立模型来更好地理解程序,要么直接将现成的NLP预训练技术应用于源码,要么通过启发式的方法向模型添加特征。事实上,程序的语义可以由编程语言理论中的形式语义来严格定义。例如,操作语义,将有效程序的意义,描述为通过基本操作更新环境(即内存地址-值函数),如内存I/O和条件分支。受此启发,本文提出一种新的程序语义学习范式,模型应从以下信息中学习:(1)与操作语义中的基本操作相一致的表示,以及(2)环境转换的信息,这是程序理解所不可缺少的。为了验证该建议,提出一种分层的基于Transformer的预训练模型OSCAR,以更好地促进程序的理解。OSCAR从中间表示法(IR)和源自静态分析的编码表示法中学习,这些表示法分别用于表示基本操作和近似环境转换。OSCAR在许多实际的软件工程任务上实证地显示了程序语义理解的显著能力。
Semantic understanding of programs is a fundamental problem for programming language processing (PLP). Recent works that learn representations of code based on pre-training techniques in NLP have pushed the frontiers in this direction. However, the semantics of PL and NL have essential differences. These being ignored, we believe it is difficult to build a model to better understand programs, by either directly applying off-the-shelf NLP pre-training techniques to the source code, or adding features to the model by the heuristic. In fact, the semantics of a program can be rigorously defined by formal semantics in PL theory. For example, the operational semantics, describes the meaning of a valid program as updating the environment (i.e., the memory address-value function) through fundamental operations, such as memory I/O and conditional branching. Inspired by this, we propose a novel program semantics learning paradigm, that the model should learn from information composed of (1) the representations which align well with the fundamental operations in operational semantics, and (2) the information of environment transition, which is indispensable for program understanding. To validate our proposal, we present a hierarchical Transformer-based pre-training model called OSCAR to better facilitate the understanding of programs. OSCAR learns from intermediate representation (IR) and an encoded representation derived from static analysis, which are used for representing the fundamental operations and approximating the environment transitions respectively. OSCAR empirically shows the outstanding capability of program semantics understanding on many practical software engineering tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfmRx1OKS
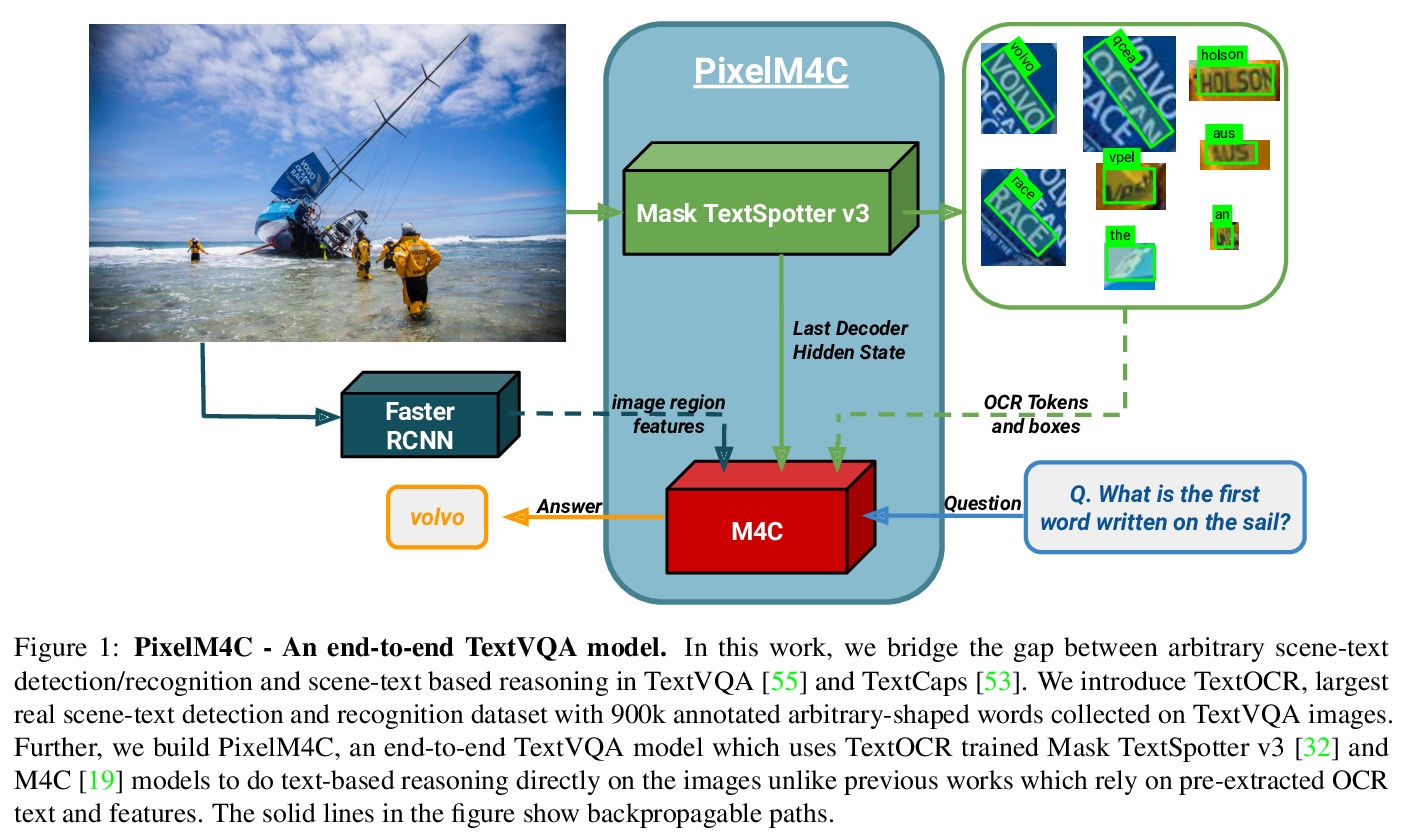
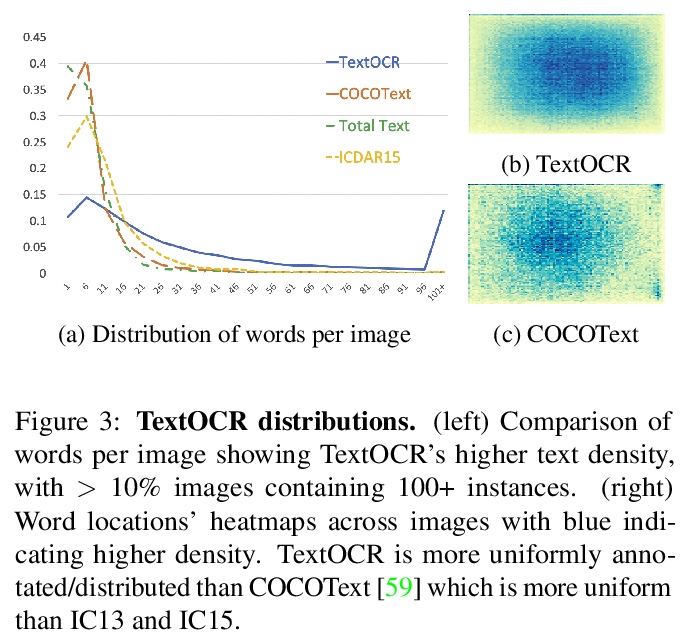
5、[CV] TextOCR: Towards large-scale end-to-end reasoning for arbitrary-shaped scene text
A Singh, G Pang, M Toh, J Huang, W Galuba, T Hassner
[Facebook AI Research]
TextOCR:面向任意形状场景文字的大规模端到端推理。TextVQA和TextCaps数据集所需的基于场景文字的推理的一个重要组成部分,涉及用光学字符识别(OCR)系统检测和识别图像中的文本。目前系统由于无法获得这些数据集的真实文本标注,以及缺乏真实图像上的场景文本检测和识别数据集而受到影响,这使得OCR领域的进展和基于场景文字推理的评估与OCR系统相分离。本文提出TextOCR,一种任意形状的场景文字检测和识别,在TextVQA数据集的真实图像上收集了90万个标注词。目前最先进的文本识别(OCR)模型在TextOCR上表现不佳,而在TextOCR上的训练也有助于在其他多个OCR数据集上实现最先进的性能。用经过TextOCR训练的OCR模型来创建PixelM4C模型,该模型能够以端到端的方式对图像进行基于场景的文本推理,从而重新审视若干设计选择,以便在TextVQA数据集上实现新的最先进的性能。
A crucial component for the scene text based reasoning required for TextVQA and TextCaps datasets involve detecting and recognizing text present in the images using an optical character recognition (OCR) system. The current systems are crippled by the unavailability of ground truth text annotations for these datasets as well as lack of scene text detection and recognition datasets on real images disallowing the progress in the field of OCR and evaluation of scene text based reasoning in isolation from OCR systems. In this work, we propose TextOCR, an arbitrary-shaped scene text detection and recognition with 900k annotated words collected on real images from TextVQA dataset. We show that current state-of-the-art text-recognition (OCR) models fail to perform well on TextOCR and that training on TextOCR helps achieve state-of-the-art performance on multiple other OCR datasets as well. We use a TextOCR trained OCR model to create PixelM4C model which can do scene text based reasoning on an image in an end-to-end fashion, allowing us to revisit several design choices to achieve new state-of-the-art performance on TextVQA dataset.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfmUw2I0d


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[IR] Fairness and Discrimination in Information Access Systems
信息访问系统中的公平性
M D. Ekstrand, A Das, R Burke, F Diaz
[Boise State University & University of Texas School of Information & University of Colorado & Mila]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfn1IuHqu
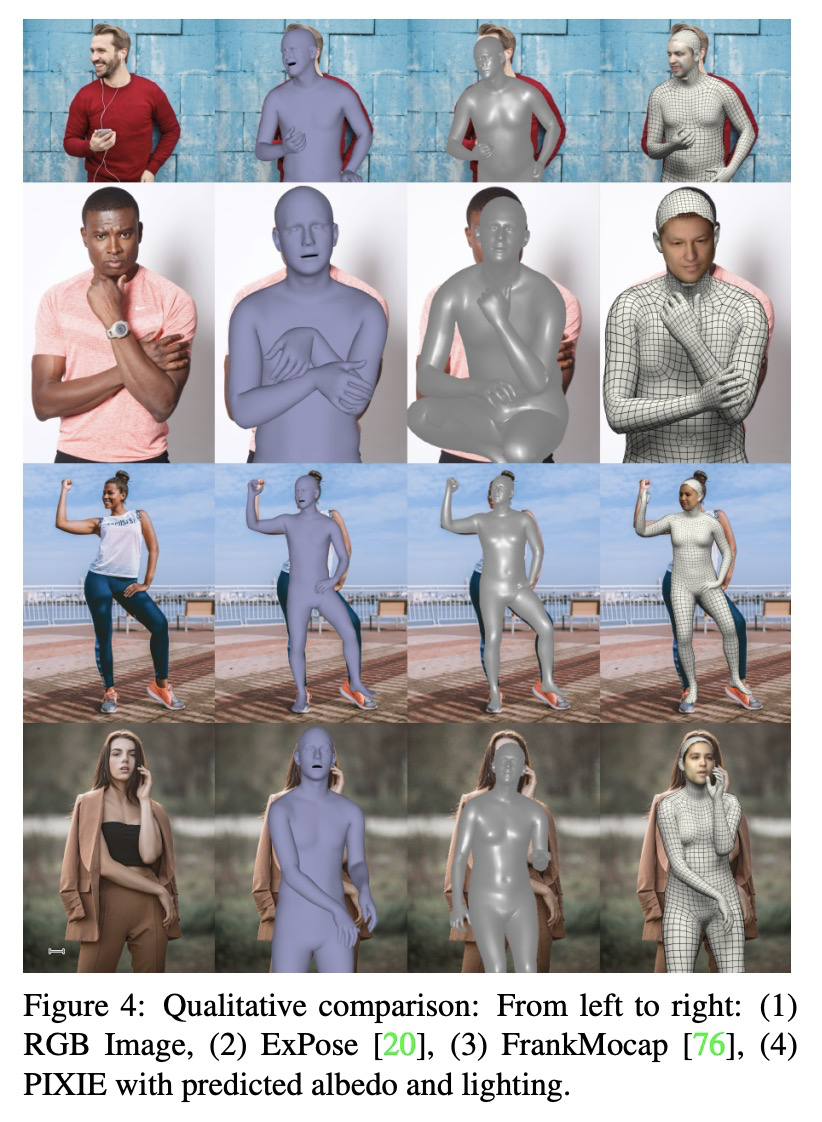
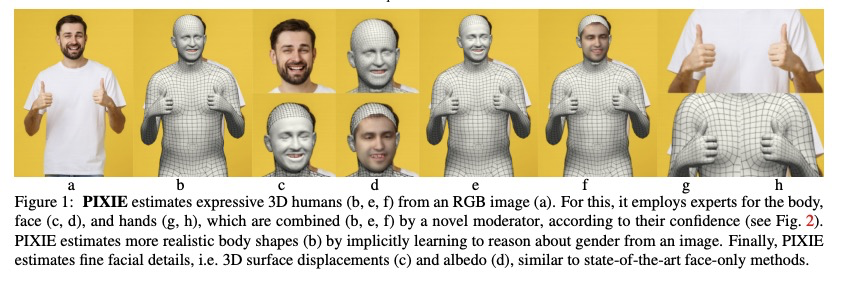
[CV] Collaborative Regression of Expressive Bodies using Moderation
从单张图片恢复具有详细脸部的可动画3D化身
Y Feng, V Choutas, T Bolkart, D Tzionas, M J. Black
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfn3WcNrY

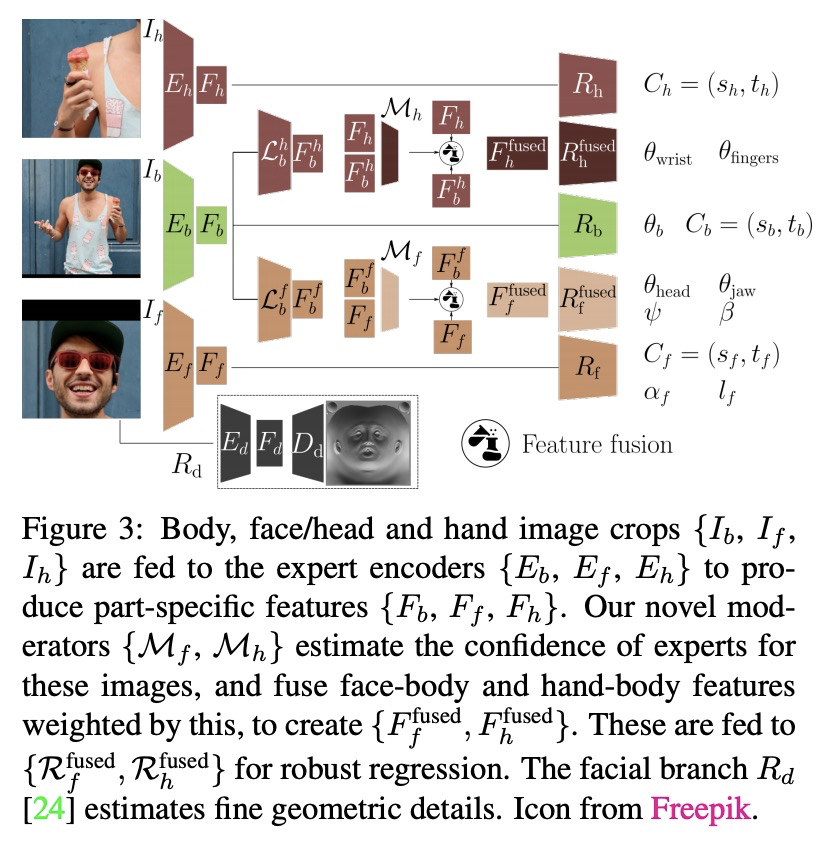

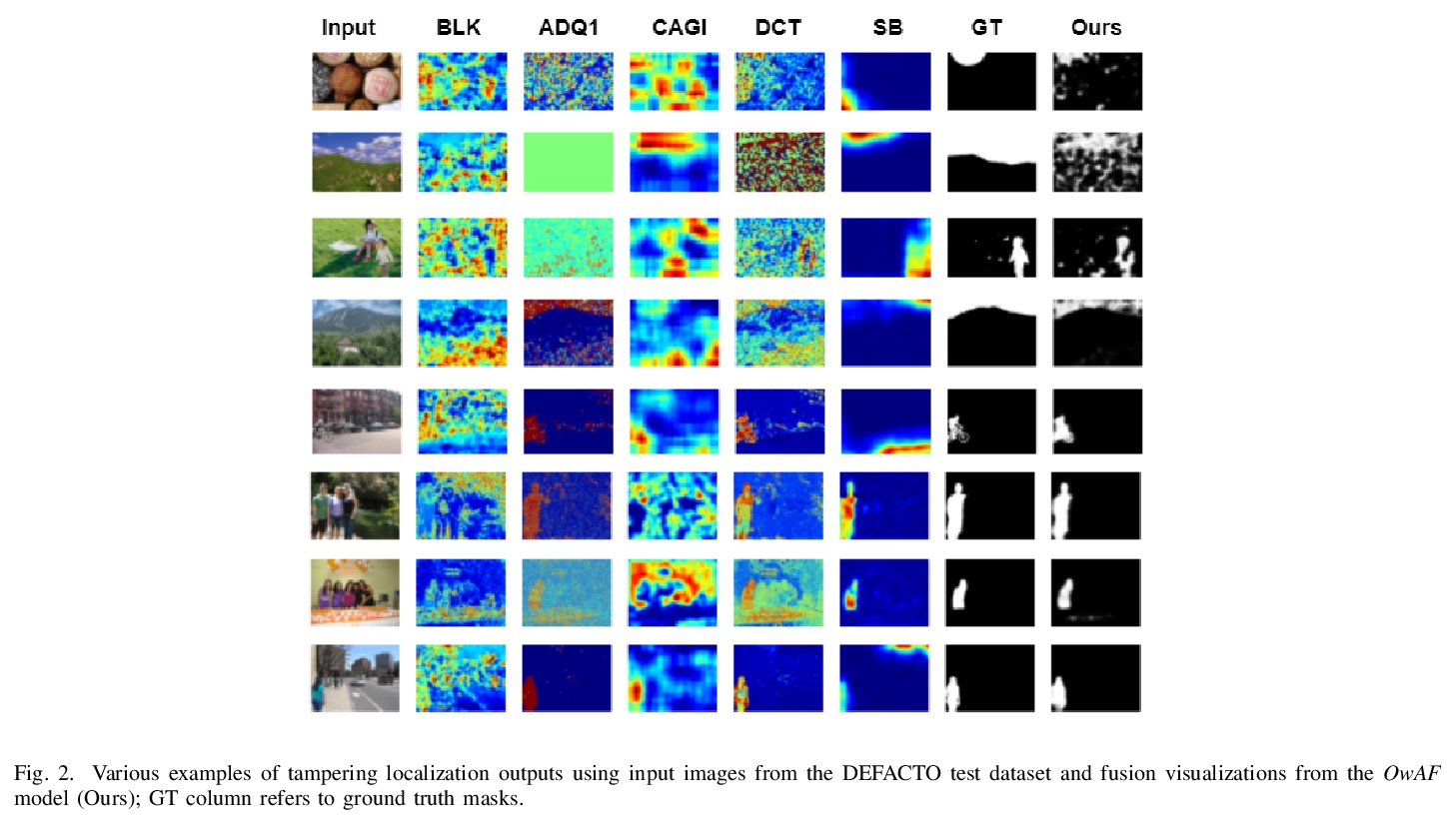
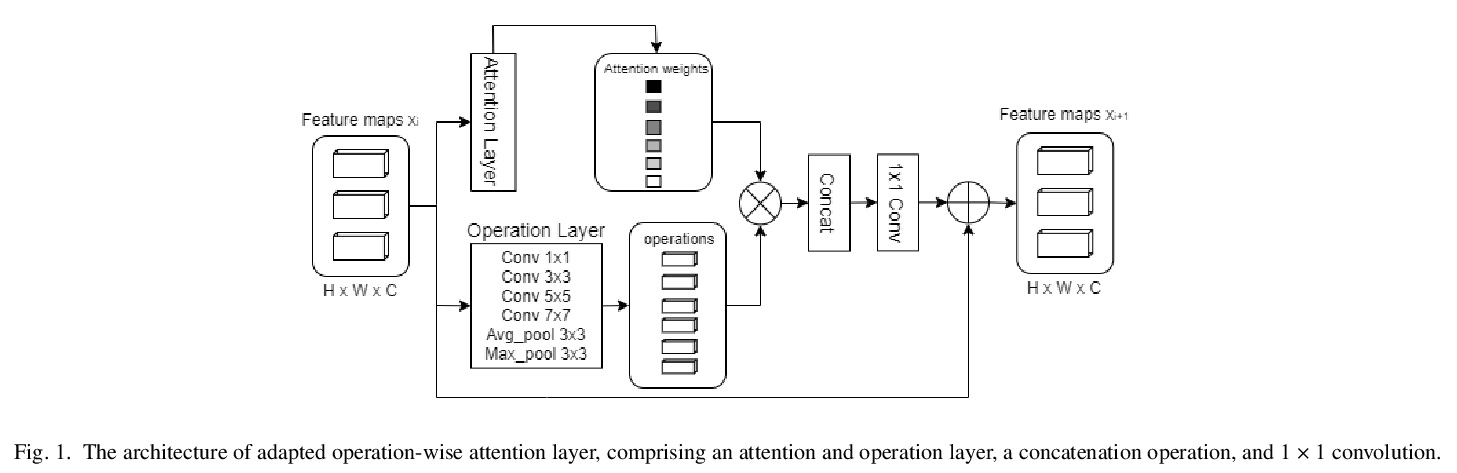
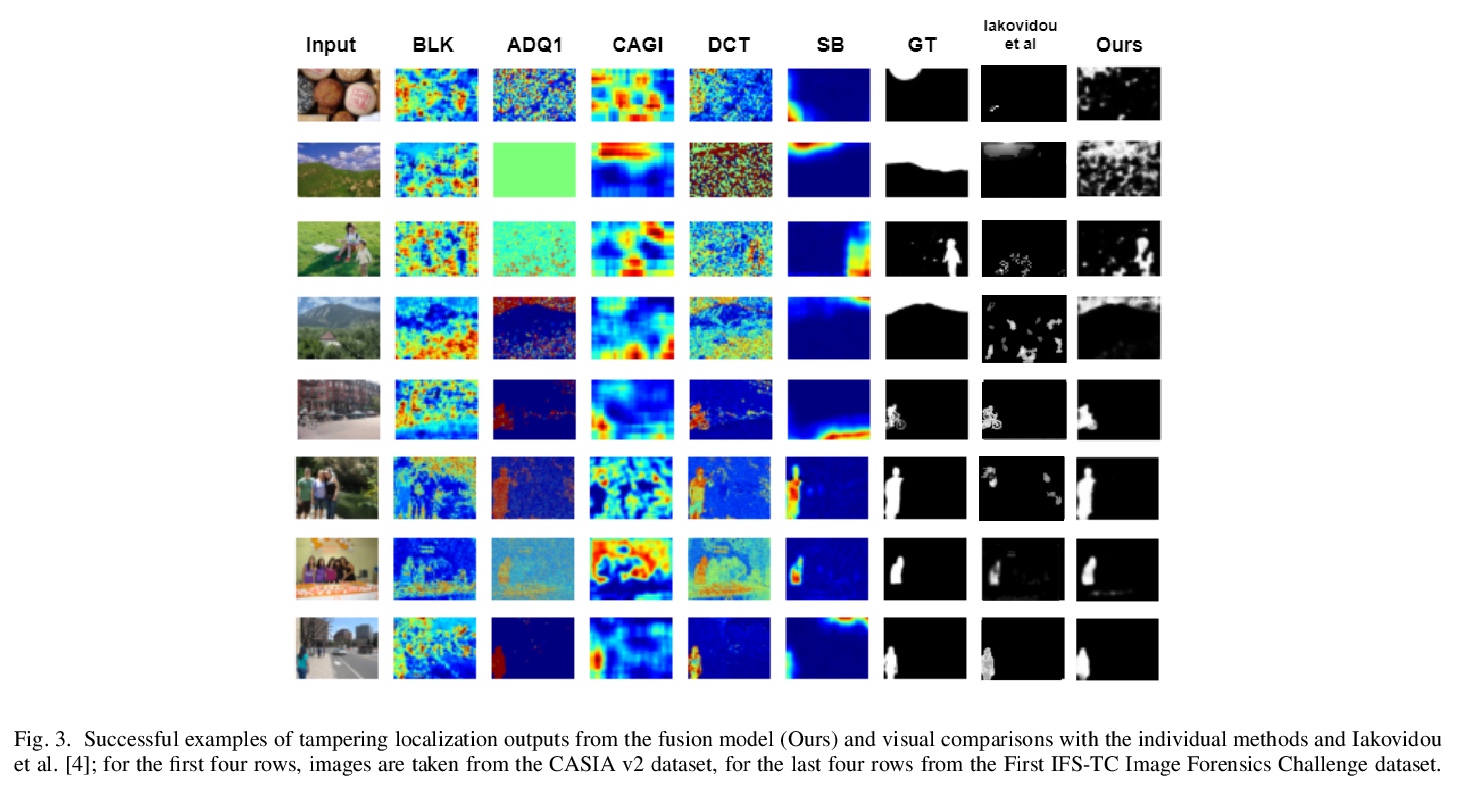
[CV] Operation-wise Attention Network for Tampering Localization Fusion
逐操作注意力网络篡改定位融合
P Charitidis, G Kordopatis-Zilos, S Papadopoulos, I Kompatsiaris
[ITI-CERTH]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfn6hj339

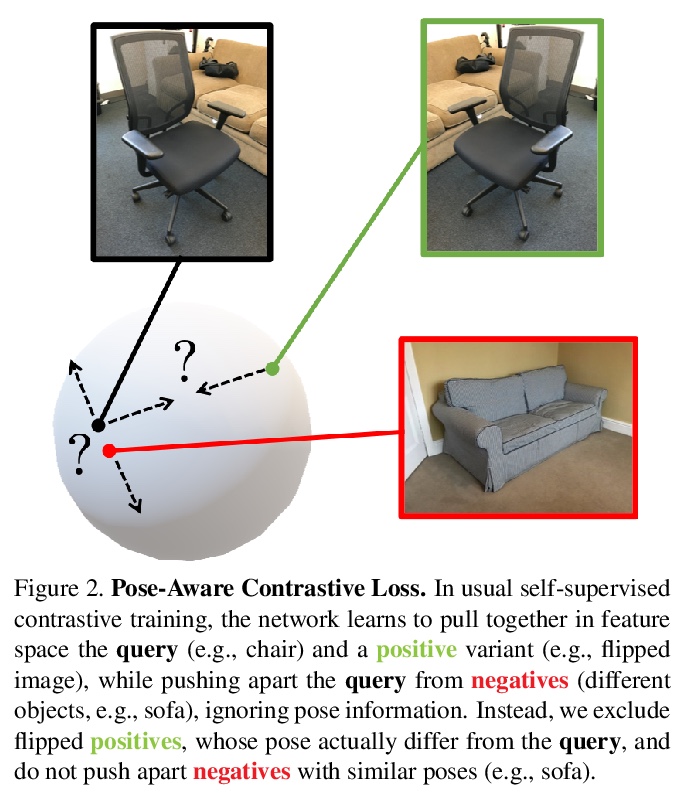
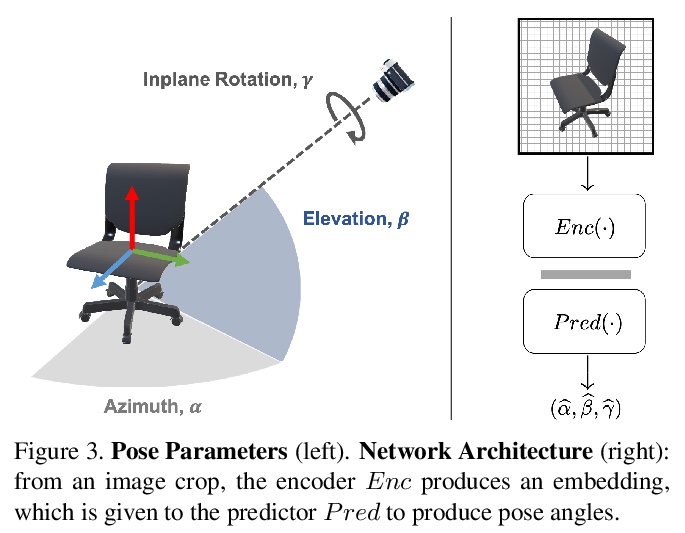
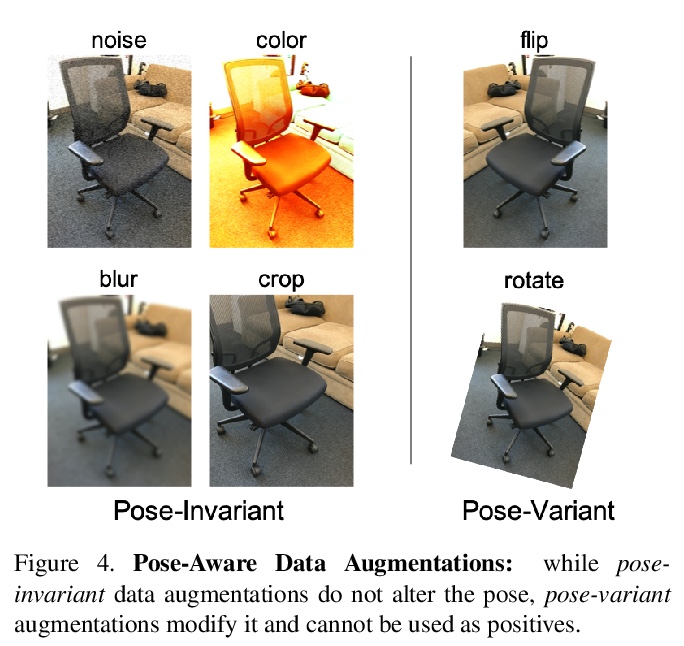
[CV] PoseContrast: Class-Agnostic Object Viewpoint Estimation in the Wild with Pose-Aware Contrastive Learning
PoseContrast:基于姿态感知对比学习的场景类别无关目标视点估计
Y Xiao, Y Du, R Marlet
[Univ Gustave Eiffel]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfn8soIRX