- 1、[LG] Revisiting the Calibration of Modern Neural Networks
- 2、[LG] Tree-Values: selective inference for regression trees
- 3、[LG] On Learnability via Gradient Method for Two-Layer ReLU Neural Networks in Teacher-Student Setting
- 4、[CL] Modeling Worlds in Text
- 5、[LG] Invariance Principle Meets Information Bottleneck for Out-of-Distribution Generalization
- [LG] A Neural Tangent Kernel Perspective of GANs
- [CV] SinIR: Efficient General Image Manipulation with Single Image Reconstruction
- [LG] Partial success in closing the gap between human and machine vision
- [LG] Training Graph Neural Networks with 1000 Layers
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Revisiting the Calibration of Modern Neural Networks
M Minderer, J Djolonga, R Romijnders, F Hubis, X Zhai, N Houlsby, D Tran, M Lucic
[Google Research]
重新审视现代神经网络校准问题。准确估计预测不确定性(模型校准)对于神经网络的安全应用至关重要。在现代神经网络中,有许多错误校准的例子,这表明一种趋势,即较新的、更精确的模型产生了较差的校准预测。本文用最先进的图像分类模型重新审视这个问题,系统地将模型的校准和准确性联系起来,发现最新的模型,特别是那些不使用卷积的模型,是最好的已校准模型。在之前的几代模型中观察到的趋势,如校准随分布变化或模型大小的衰减,在最新架构中并不明显。模型规模和预训练量并不能完全解释这些差异,架构是校准特性的一个主要决定因素。
Accurate estimation of predictive uncertainty (model calibration) is essential for the safe application of neural networks. Many instances of miscalibration in modern neural networks have been reported, suggesting a trend that newer, more accurate models produce poorly calibrated predictions. Here, we revisit this question for recent state-of-the-art image classification models. We systematically relate model calibration and accuracy, and find that the most recent models, notably those not using convolutions, are among the best calibrated. Trends observed in prior model generations, such as decay of calibration with distribution shift or model size, are less pronounced in recent architectures. We also show that model size and amount of pretraining do not fully explain these differences, suggesting that architecture is a major determinant of calibration properties.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl8UgDHLn




2、[LG] Tree-Values: selective inference for regression trees
A C. Neufeld, L L. Gao, D M. Witten
[University of Washington & University of Waterloo]
Tree-Values:回归树选择性推理。本文考虑对分类回归树(CART)算法的输出进行推理。不考虑树是由数据估计出来的事实的简单推理方法,将无法实现标准保证,如第一类错误率控制和标称覆盖。本文提出一种选择性推理框架,对拟合的CART树进行推理。该框架的基础,是该树根据数据进行估计的事实。提出了对一对终端节点之间的平均响应差异的测试,以控制选择性的第一类错误率,以及对单一终端节点内的平均响应的置信区间,以达到标称选择性覆盖。提供了计算必要条件集的高效算法,并将这些方法应用于模拟和涉及分量控制干预和卡路里摄入的数据集。
We consider conducting inference on the output of the Classification and Regression Tree (CART) [Breiman et al., 1984] algorithm. A naive approach to inference that does not account for the fact that the tree was estimated from the data will not achieve standard guarantees, such as Type 1 error rate control and nominal coverage. Thus, we propose a selective inference framework for conducting inference on a fitted CART tree. In a nutshell, we condition on the fact that the tree was estimated from the data. We propose a test for the difference in the mean response between a pair of terminal nodes that controls the selective Type 1 error rate, and a confidence interval for the mean response within a single terminal node that attains the nominal selective coverage. Efficient algorithms for computing the necessary conditioning sets are provided. We apply these methods in simulation and to a dataset involving the association between portion control interventions and caloric intake.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl908Fm9e




3、[LG] On Learnability via Gradient Method for Two-Layer ReLU Neural Networks in Teacher-Student Setting
S Akiyama, T Suzuki
[University of Tokyo]
师-生设置下双层ReLU神经网络梯度法可学习性。深度学习在许多应用中取得了很高的性能,但其训练动力学在理论上还没有得到充分的理解。本文探讨了在师-生回归模型中,训练双层ReLU神经网络的理论分析,其中学生网络通过其输出学习未知的教师网络。在特定的正则化和充分的超参数化下,学生网络可以通过梯度下降,以规范依赖步长高概率识别教师网络的参数,即使目标函数是高度非凸的。关键的理论工具是神经网络的度量表示,以及在度量空间上稀疏估计的双证论证的新应用。分析了度量空间中的全局最小值和全局收敛特性。
Deep learning empirically achieves high performance in many applications, but its training dynamics has not been fully understood theoretically. In this paper, we explore theoretical analysis on training two-layer ReLU neural networks in a teacher-student regression model, in which a student network learns an unknown teacher network through its outputs. We show that with a specific regularization and sufficient overparameterization, the student network can identify the parameters of the teacher network with high probability via gradient descent with a norm dependent stepsize even though the objective function is highly non-convex. The key theoretical tool is the measure representation of the neural networks and a novel application of a dual certificate argument for sparse estimation on a measure space. We analyze the global minima and global convergence property in the measure space.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl94n5rsq



4、[CL] Modeling Worlds in Text
P Ammanabrolu, M O. Riedl
[Georgia Institute of Technology]
文本的世界建模。本文提供了一个数据集,使学习型智能体能建立基于知识图谱的交互式叙事的世界模型。交互式叙事,或文本冒险游戏,是部分可观察环境,构架为长谜题或任务,其中智能体单纯通过文本自然语言感知世界并与之互动。每个单独的游戏通常包含数百个地点、人物和物体——每个都有自己独特的描述——这提供了一个机会,来研究给基于语言的智能体提供在这种世界中运作所需的结构化记忆的问题。数据集在丰富的自然语言观察中提供了24198个映射:(1)以地图形式反映世界状态的知识图谱;(2)保证会引起该特定世界状态变化的自然语言行为。训练数据是在多种类型的27个游戏中收集的,并在测试集中包含了另外9个游戏的7836个保留实例。除了对数据和相应的学习任务进行分析外,还提供了使用基于规则、问答和序列学习方法的基线模型。
We provide a dataset that enables the creation of learning agents that can build knowledge graph-based world models of interactive narratives.1 Interactive narratives—or text-adventure games—are partially observable environments structured as long puzzles or quests in which an agent perceives and interacts with the world purely through textual natural language. Each individual game typically contains hundreds of locations, characters, and objects—each with their own unique descriptions—providing an opportunity to study the problem of giving language-based agents the structured memory necessary to operate in such worlds. Our dataset provides 24198 mappings between rich natural language observations and: (1) knowledge graphs that reflect the world state in the form of a map; (2) natural language actions that are guaranteed to cause a change in that particular world state. The training data is collected across 27 games in multiple genres and contains a further 7836 heldout instances over 9 additional games in the test set. We further provide baseline models using rules-based, question-answering, and sequence learning approaches in addition to an analysis of the data and corresponding learning tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl987225R


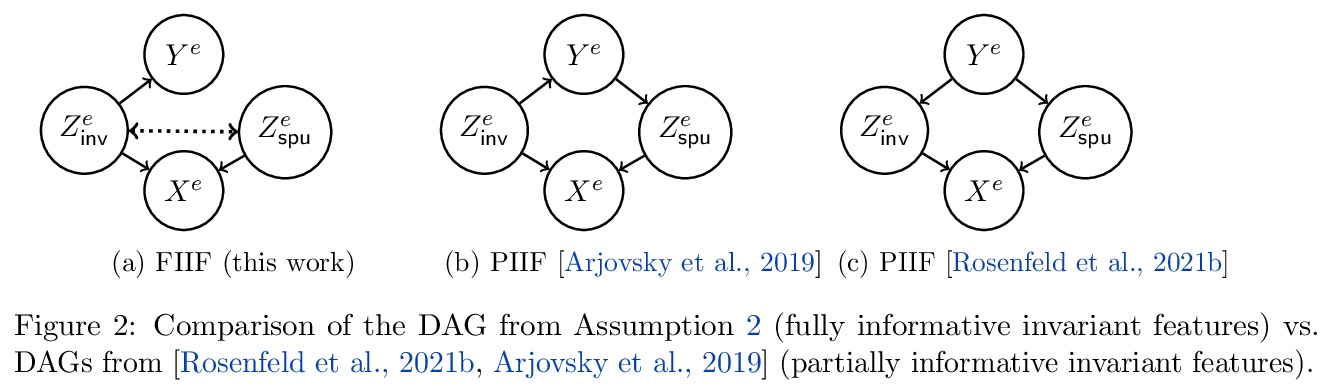
5、[LG] Invariance Principle Meets Information Bottleneck for Out-of-Distribution Generalization
K Ahuja, E Caballero, D Zhang, Y Bengio, I Mitliagkas, I Rish
[Mila]
面向分布外泛化的不变性原则与信息瓶颈。因果关系的不变性原则,是诸如不变性风险最小化(IRM)等著名方法的核心,这些方法试图解决分布外泛化(OOD)的失败。尽管理论很有前途,但基于不变性原则的方法在常见的分类任务中失败了,在这些任务中,不变性(因果性)特征捕获了关于标签的所有信息。这些失败是由于这些方法未能捕捉到不变性吗?还是不变性原则本身不足?为了回答这些问题,本文重新审视了线性回归任务中的基本假设,其中基于不变性的方法被证明可以泛化OOD。与线性回归任务相比,线性分类任务需要对分布偏移有更强的限制,否则不可能泛化OOD。即使对分布偏移有适当的限制,仅靠不变性原则是不够的。当不变性特征捕捉到关于标签的所有信息时,一种形式的信息瓶颈约束与不变性一起有助于解决关键的失败,而当它们没有捕捉到时,也能保留已有的成功。提出了一个包含这两个原则的方法,并在几个实验中证明了其有效性。
The invariance principle from causality is at the heart of notable approaches such as invariant risk minimization (IRM) that seek to address out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization failures. Despite the promising theory, invariance principle-based approaches fail in common classification tasks, where invariant (causal) features capture all the information about the label. Are these failures due to the methods failing to capture the invariance? Or is the invariance principle itself insufficient? To answer these questions, we revisit the fundamental assumptions in linear regression tasks, where invariance-based approaches were shown to provably generalize OOD. In contrast to the linear regression tasks, we show that for linear classification tasks we need much stronger restrictions on the distribution shifts, or otherwise OOD generalization is impossible. Furthermore, even with appropriate restrictions on distribution shifts in place, we show that the invariance principle alone is insufficient. We prove that a form of the information bottleneck constraint along with invariance helps address key failures when invariant features capture all the information about the label and also retains the existing success when they do not. We propose an approach that incorporates both of these principles and demonstrate its effectiveness in several experiments.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl9c5sgfj


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[LG] A Neural Tangent Kernel Perspective of GANs
神经切线核视角的GAN分析框架
J Franceschi, E d Bézenac, I Ayed, M Chen, S Lamprier, P Gallinari
[Sorbonne Université & Valeo.ai]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl9fI3ZeH




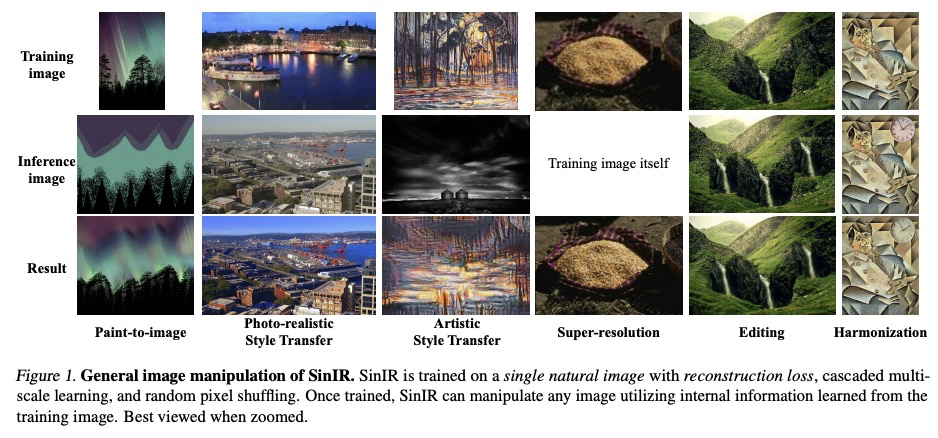
[CV] SinIR: Efficient General Image Manipulation with Single Image Reconstruction
SinIR:单幅图像重建高效通用图像处理
J Yoo, Q Chen
[Hong Kong University of Science and Technology]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl9hZjH1L



[LG] Partial success in closing the gap between human and machine vision
部分缩小人类视觉与机器视觉之间的差距
R Geirhos, K Narayanappa, B Mitzkus, T Thieringer, M Bethge, F A. Wichmann, W Brendel
[University of Tübingen]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl9mxbv0L




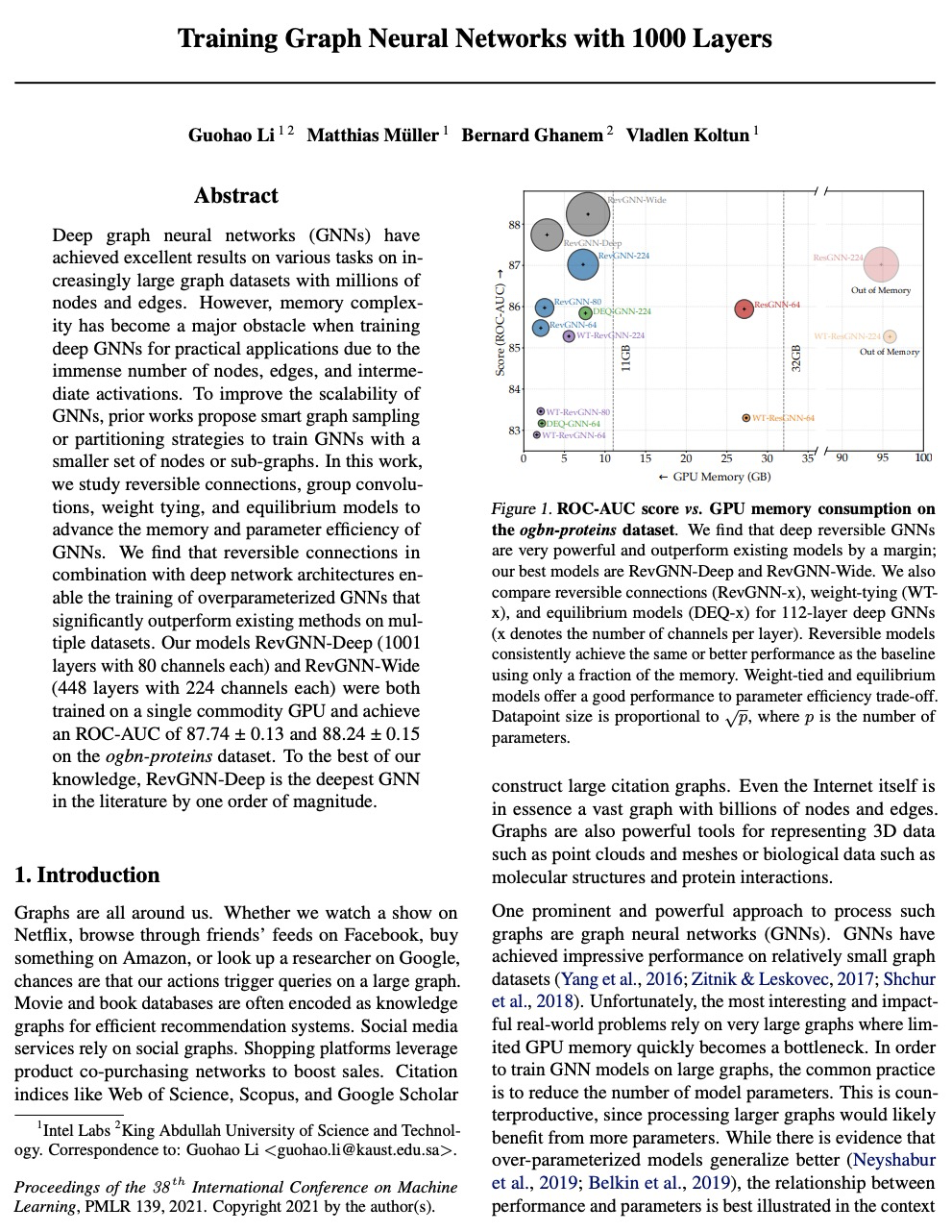
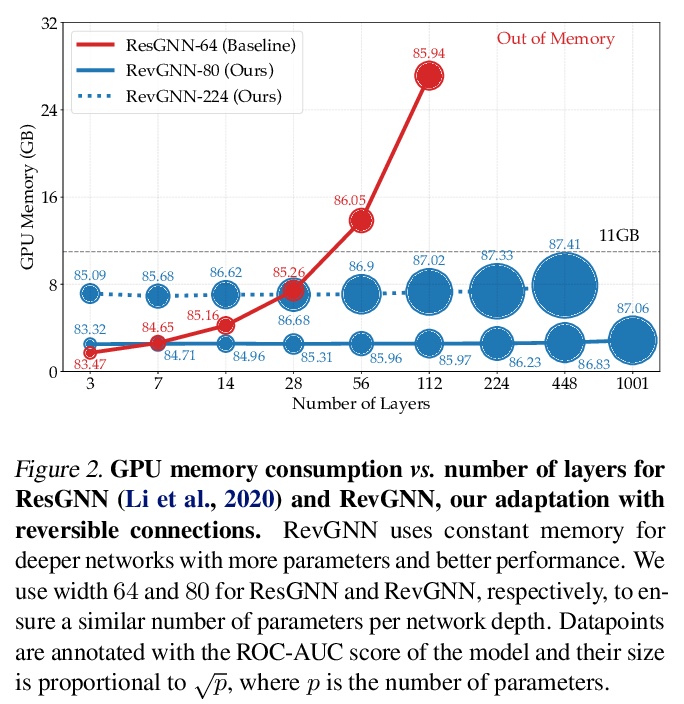
[LG] Training Graph Neural Networks with 1000 Layers
1000层图神经网络训练
G Li, M Müller, B Ghanem, V Koltun
[Intel Labs]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kl9oXllEr