- 1、[CV] Adaptive adversarial neural networks for the analysis of lossy and domain-shifted datasets of medical images
- 2、[LG] Geometry of the Loss Landscape in Overparameterized Neural Networks: Symmetries and Invariances
- 3、[LG] Provable Guarantees for Self-Supervised Deep Learning with Spectral Contrastive Loss
- 4、[CV] Implicit-PDF: Non-Parametric Representation of Probability Distributions on the Rotation Manifold
- 5、[LG] XBNet : An Extremely Boosted Neural Network
- [CV] Rethinking Space-Time Networks with Improved Memory Coverage for Efficient Video Object Segmentation
- [LG] Consistency Regularization for Variational Auto-Encoders
- [CL] Ethical-Advice Taker: Do Language Models Understand Natural Language Interventions?
- [LG] Control-Oriented Model-Based Reinforcement Learning with Implicit Differentiation
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] Adaptive adversarial neural networks for the analysis of lossy and domain-shifted datasets of medical images
M K Kanakasabapathy, P Thirumalaraju, H Kandula…
[Harvard Medical School]
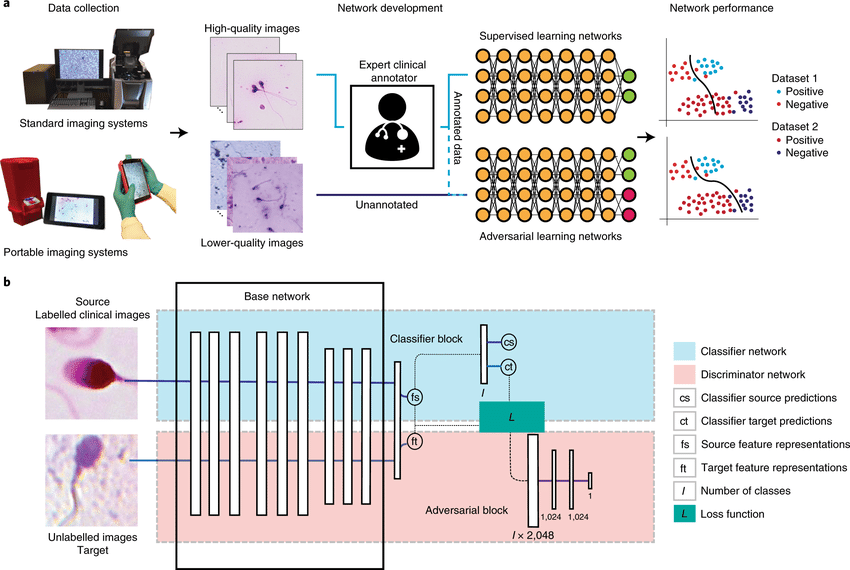
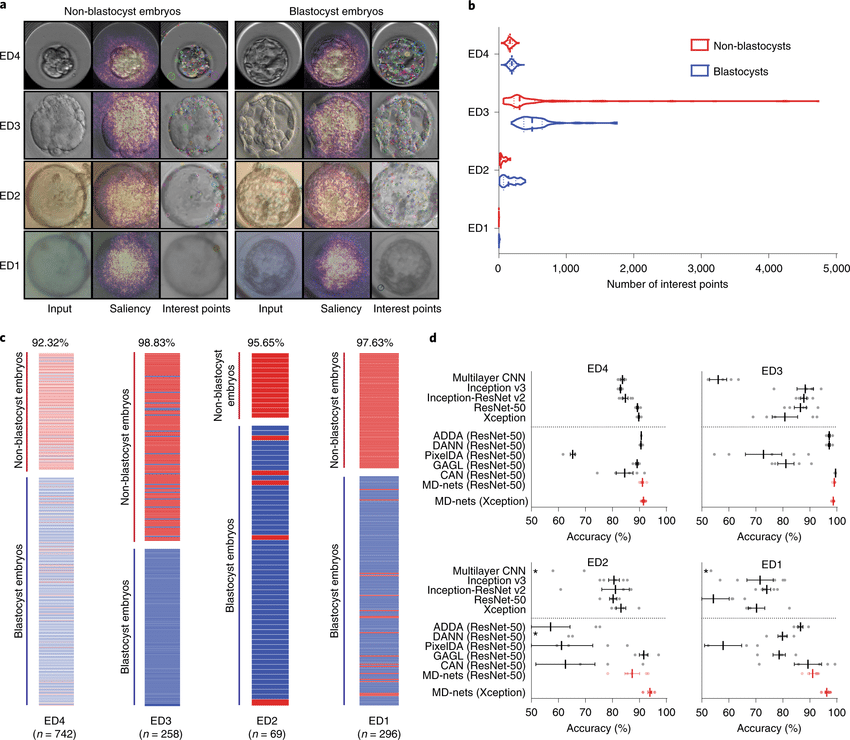
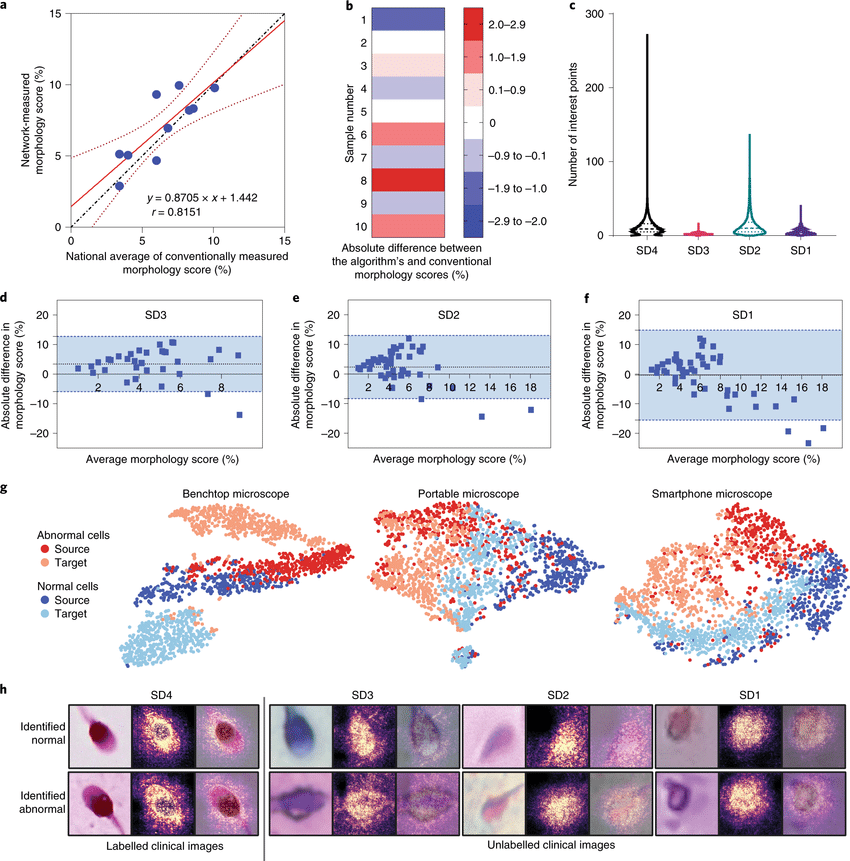
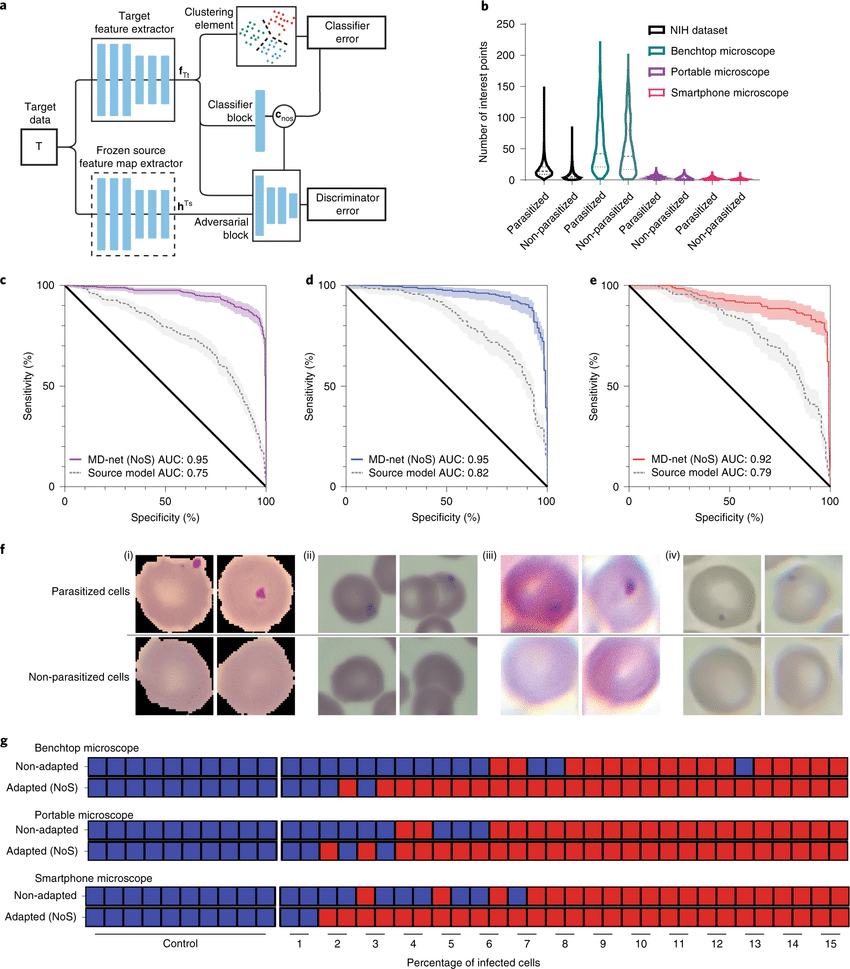
用于分析有损和域迁移医学图像数据集的自适应对抗神经网络。在基于图像的医学诊断的机器学习中,有监督的卷积神经网络通常是通过使用高分辨率成像系统获得的大型和专家标注的数据集来训练的。此外,当应用于具有不同分布的数据集时,网络的性能会大幅下降。本文展示了对抗学习可用来开发高性能网络,这些网络在不同质量的未标注医学图像上训练,用廉价的便携式光学系统获得的低质量图像来训练人类胚胎的评估、人类精子形态的量化和血液中疟疾感染诊断的网络,并表明这些网络在不同的数据分布中表现良好。对抗学习可用于来自未见过域迁移数据集的无标签数据,以使预训练的监督网络适应新的分布,即使没有原始分布的数据。自适应对抗网络可以扩大使用经过验证的神经网络模型来评估从不同质量的多个成像系统收集的数据,而不影响网络中存储的知识。对抗性学习可用于开发在不同图像质量的未标注医学图像上训练的高性能网络,并使预训练的监督网络适应新的域迁移数据集。
In machine learning for image-based medical diagnostics, supervised convolutional neural networks are typically trained with large and expertly annotated datasets obtained using high-resolution imaging systems. Moreover, the network’s performance can degrade substantially when applied to a dataset with a different distribution. Here, we show that adversarial learning can be used to develop high-performing networks trained on unannotated medical images of varying image quality. Specifically, we used low-quality images acquired using inexpensive portable optical systems to train networks for the evaluation of human embryos, the quantification of human sperm morphology and the diagnosis of malarial infections in the blood, and show that the networks performed well across different data distributions. We also show that adversarial learning can be used with unlabelled data from unseen domain-shifted datasets to adapt pretrained supervised networks to new distributions, even when data from the original distribution are not available. Adaptive adversarial networks may expand the use of validated neural-network models for the evaluation of data collected from multiple imaging systems of varying quality without compromising the knowledge stored in the network. Adversarial learning can be used to develop high-performing networks trained on unannotated medical images of varying image quality, and to adapt pretrained supervised networks to new domain-shifted datasets.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjVFv7tsG
2、[LG] Geometry of the Loss Landscape in Overparameterized Neural Networks: Symmetries and Invariances
B Şimşek, F Ged, A Jacot, F Spadaro, C Hongler, W Gerstner, J Brea
[Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne]
过参数化神经网络中的损失景观几何学:对称性和不变性。本文描述了过参数化神经网络中临界点所形成的几何图形。对于全局最小点,在温和条件下,位于一个由若干相连的仿生子空间组成的流形中。本文描述了某种类型的临界点,即所谓的对称性诱发的临界点,并表明它们形成了明确的仿生子空间的数量。从理论的角度来看,除了对称诱发临界点之外,超参数化网络中是否还有其他临界点,仍然是一个开放的问题。本文的主要结果是量化全局最小值子空间和包含对称诱导临界点的子空间的数量随着宽度的增加而变化。在轻度过参数化网络中,临界子空间的数量远远大于全局最小子空间的数量,在实践中,梯度轨迹可能会受到这些鞍点的影响,甚至会在典型初始化的一小部分时间里暂时卡在它们附近。在严重过参数化的网络中,全局最小子空间的数量要比临界子空间的数量多,所以对称性诱导的鞍点只起到了边际作用。从实践的角度来看,本文的理论结果为过参数化和修剪结合来优化非凸神经网络损失景观的应用铺平了道路。
We study how permutation symmetries in overparameterized multi-layer neural networks generate `symmetry-induced’ critical points. Assuming a network with L layers of minimal widths r∗1,…,r∗L−1 reaches a zero-loss minimum at r∗1!⋯r∗L−1! isolated points that are permutations of one another, we show that adding one extra neuron to each layer is sufficient to connect all these previously discrete minima into a single manifold. For a two-layer overparameterized network of width r∗+h=:m we explicitly describe the manifold of global minima: it consists of T(r∗,m) affine subspaces of dimension at least h that are connected to one another. For a network of width m, we identify the number G(r,m) of affine subspaces containing only symmetry-induced critical points that are related to the critical points of a smaller network of width r<r∗. Via a combinatorial analysis, we derive closed-form formulas for T and G and show that the number of symmetry-induced critical subspaces dominates the number of affine subspaces forming the global minima manifold in the mildly overparameterized regime (small h) and vice versa in the vastly overparameterized regime (h≫r∗). Our results provide new insights into the minimization of the non-convex loss function of overparameterized neural networks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjVM4FLYt
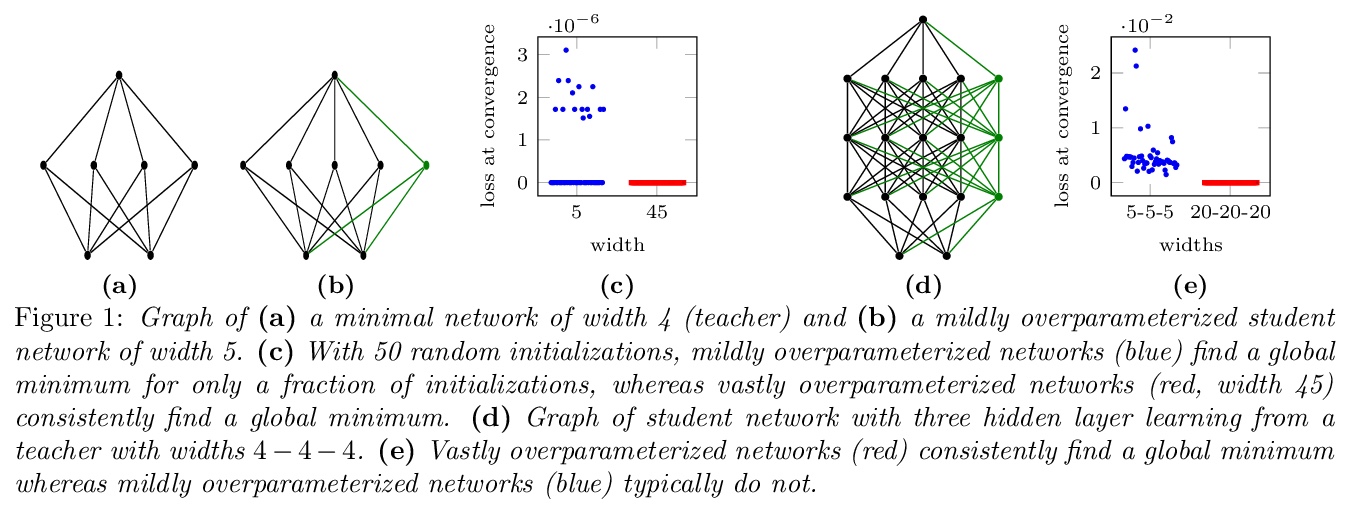
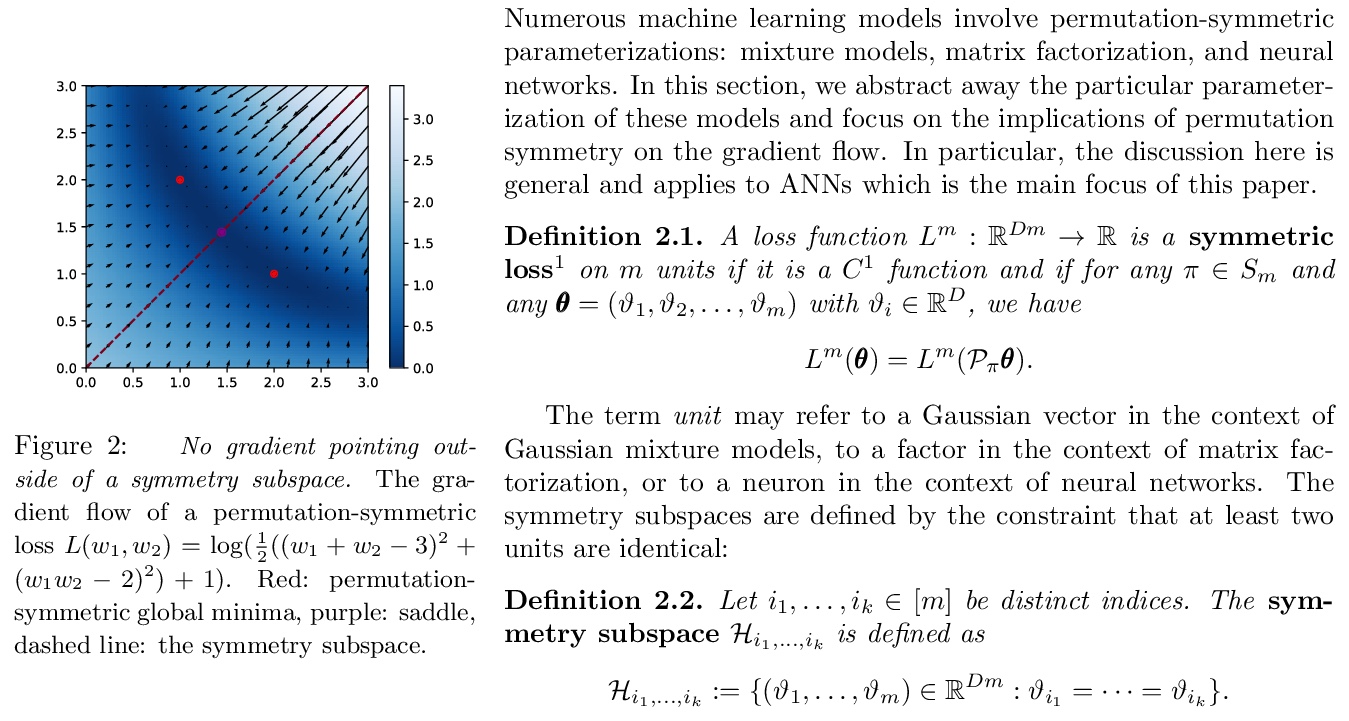
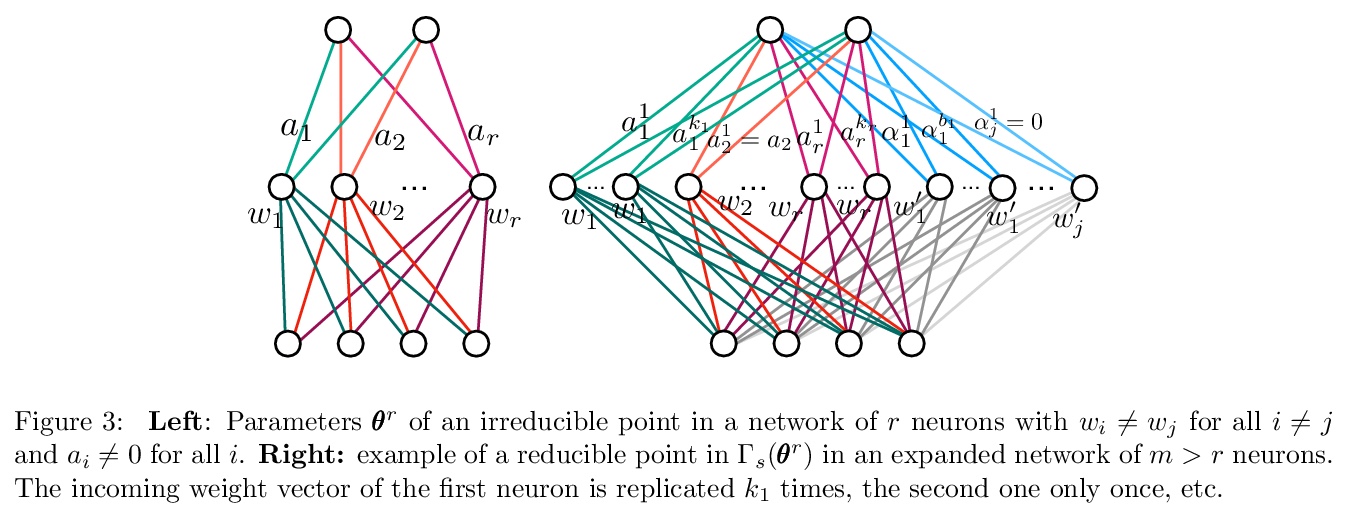
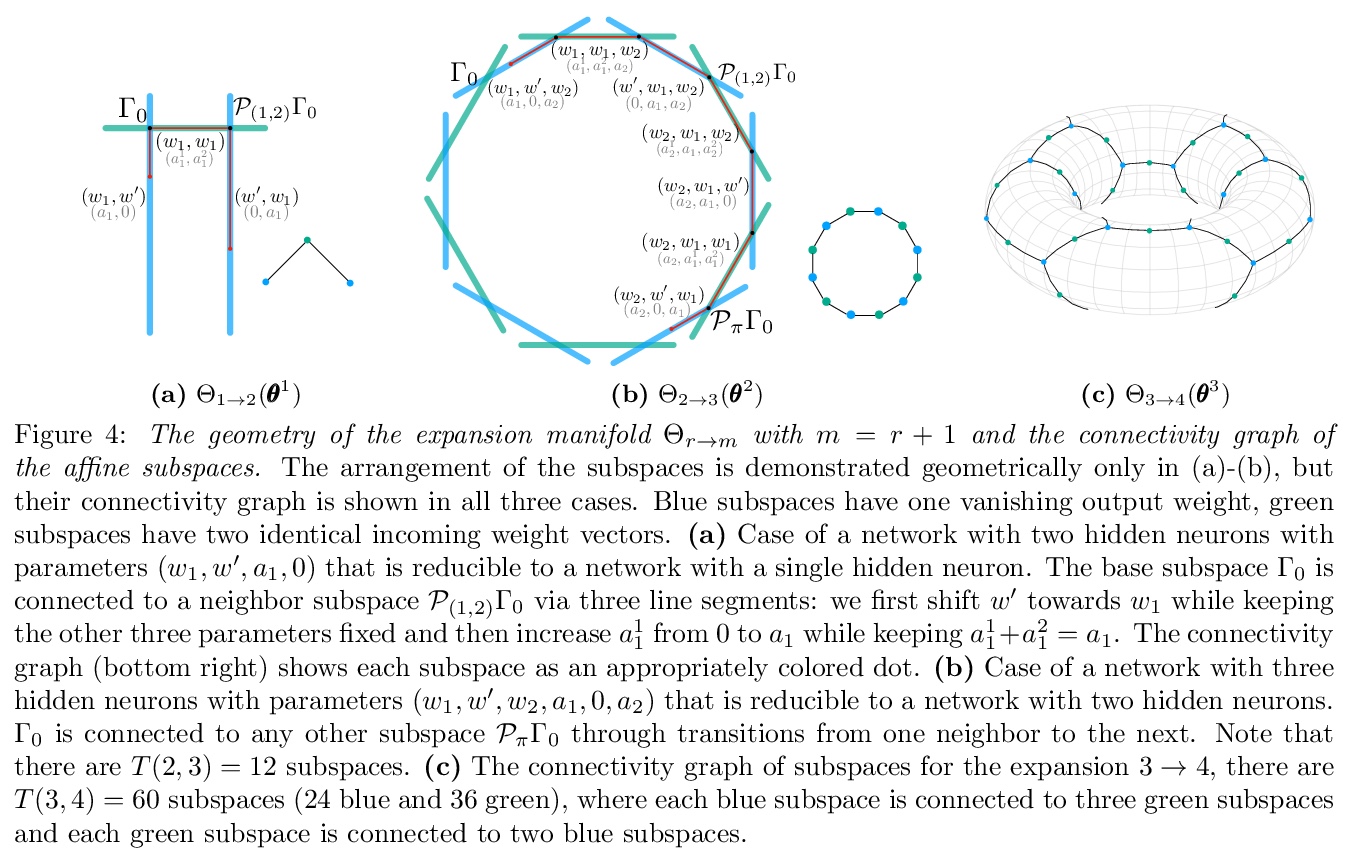
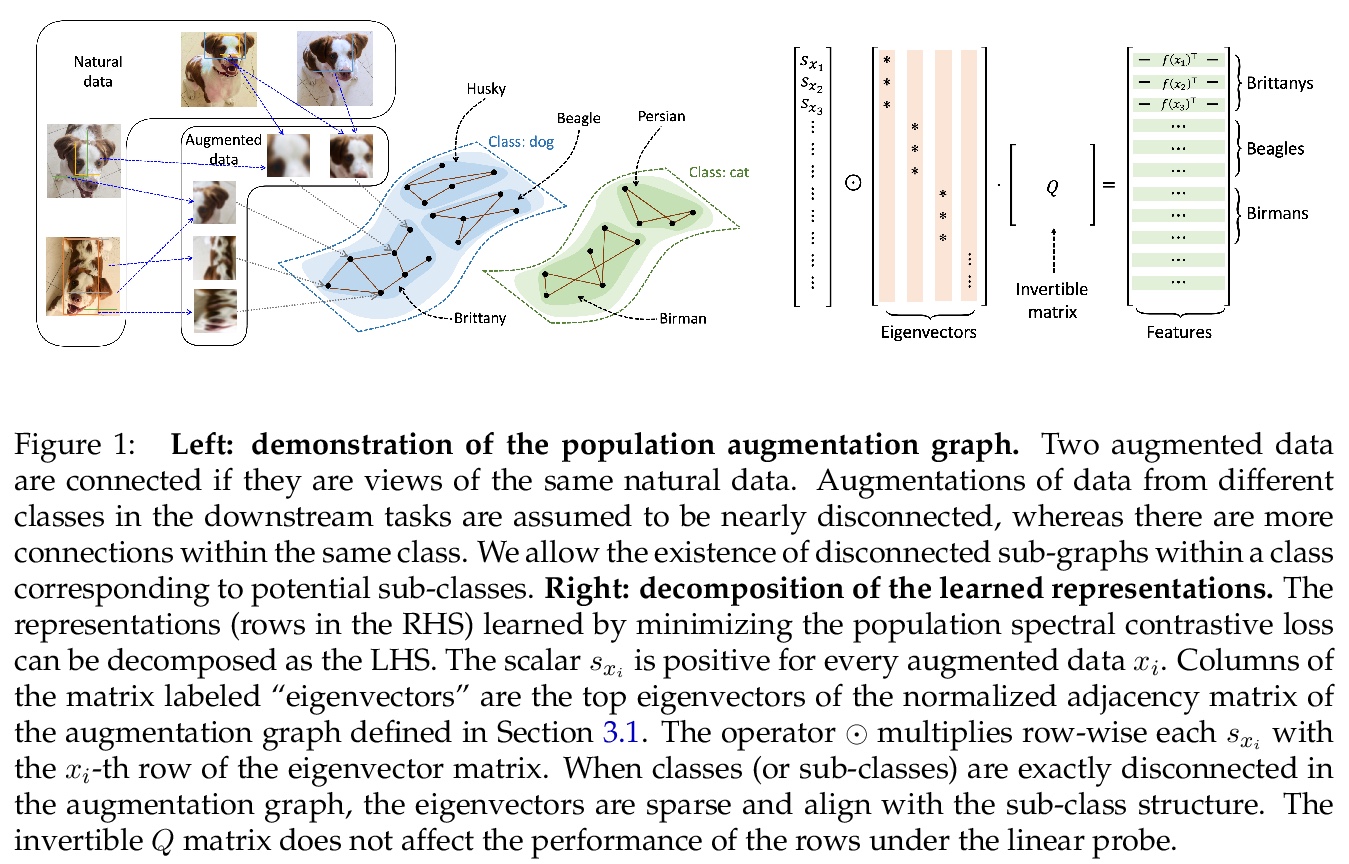
3、[LG] Provable Guarantees for Self-Supervised Deep Learning with Spectral Contrastive Loss
J Z. HaoChen, C Wei, A Gaidon, T Ma
[Stanford University & Toyota Research Institute]
基于谱对比损失的自监督深度学习可证明保证。最近在自监督学习方面的工作靠对比学习范式推进了最先进的水平,该范式通过将正样本对,即同一类别的类似样本,拉到一起,同时将负样本对推开很远来学习表征。尽管在经验上取得了成功,但理论基础是有限的——之前的分析假定在给定相同类别标签的情况下,正样本对是有条件独立的,但最近的经验性应用使用了严重相关的正样本对(即同一图像的增强数据)。本文在数据上使用增强图的新概念,在不对正样本对进行条件独立假设的情况下,分析对比学习。该图中的边连接着相同数据的增强,而真值类自然形成了连接子图。本文提出一种损失,在总体增强图上进行谱分解,可以简明地写成神经网络表征上的对比学习目标。最小化该目标导致了在线性探针评估下具有可证明准确性保证的特征。根据标准的泛化界线,这些准确性保证在最小化训练对比损失时也是成立的。从经验上看,通过该目标学到的特征可以在基准视觉数据集上匹配或优于几个强大的基线。总之,这项工作为对比学习提供了第一个可证明的分析,其中线性探测评估的保证可以适用于现实的经验设置。
Recent works in self-supervised learning have advanced the state-of-the-art by relying on the contrastive learning paradigm, which learns representations by pushing positive pairs, or similar examples from the same class, closer together while keeping negative pairs far apart. Despite the empirical successes, theoretical foundations are limited – prior analyses assume conditional independence of the positive pairs given the same class label, but recent empirical applications use heavily correlated positive pairs (i.e., data augmentations of the same image). Our work analyzes contrastive learning without assuming conditional independence of positive pairs using a novel concept of the augmentation graph on data. Edges in this graph connect augmentations of the same data, and ground-truth classes naturally form connected sub-graphs. We propose a loss that performs spectral decomposition on the population augmentation graph and can be succinctly written as a contrastive learning objective on neural net representations. Minimizing this objective leads to features with provable accuracy guarantees under linear probe evaluation. By standard generalization bounds, these accuracy guarantees also hold when minimizing the training contrastive loss. Empirically, the features learned by our objective can match or outperform several strong baselines on benchmark vision datasets. In all, this work provides the first provable analysis for contrastive learning where guarantees for linear probe evaluation can apply to realistic empirical settings.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjVR1mWiC
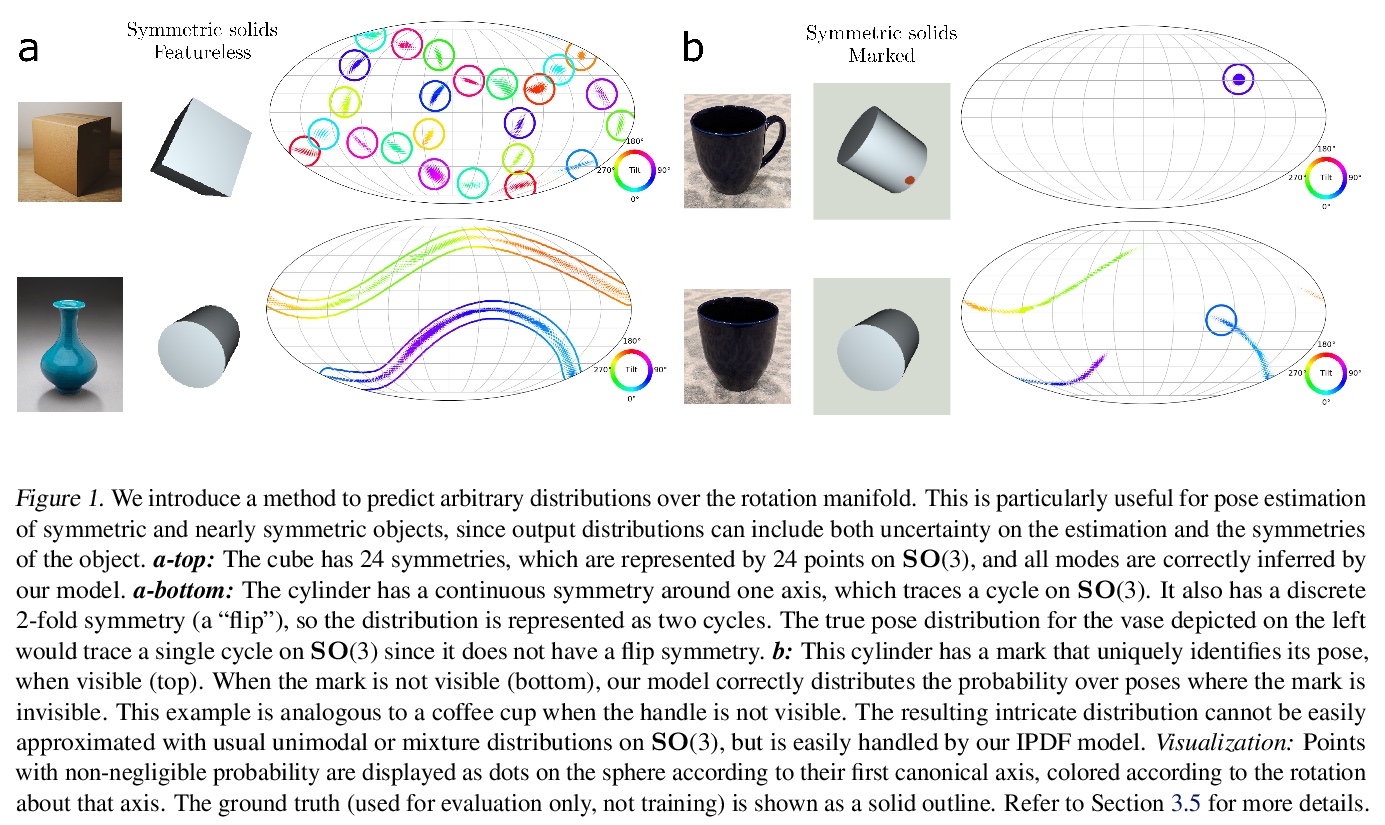
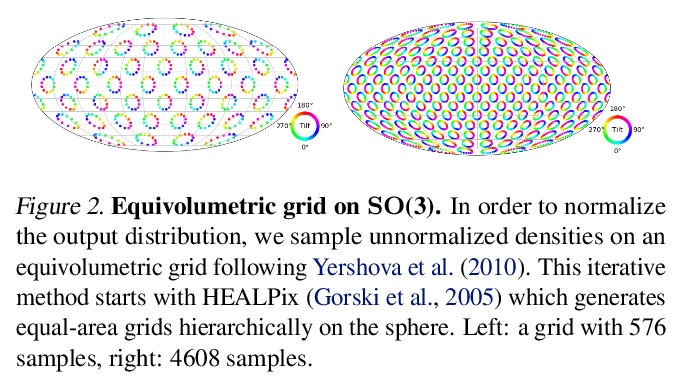
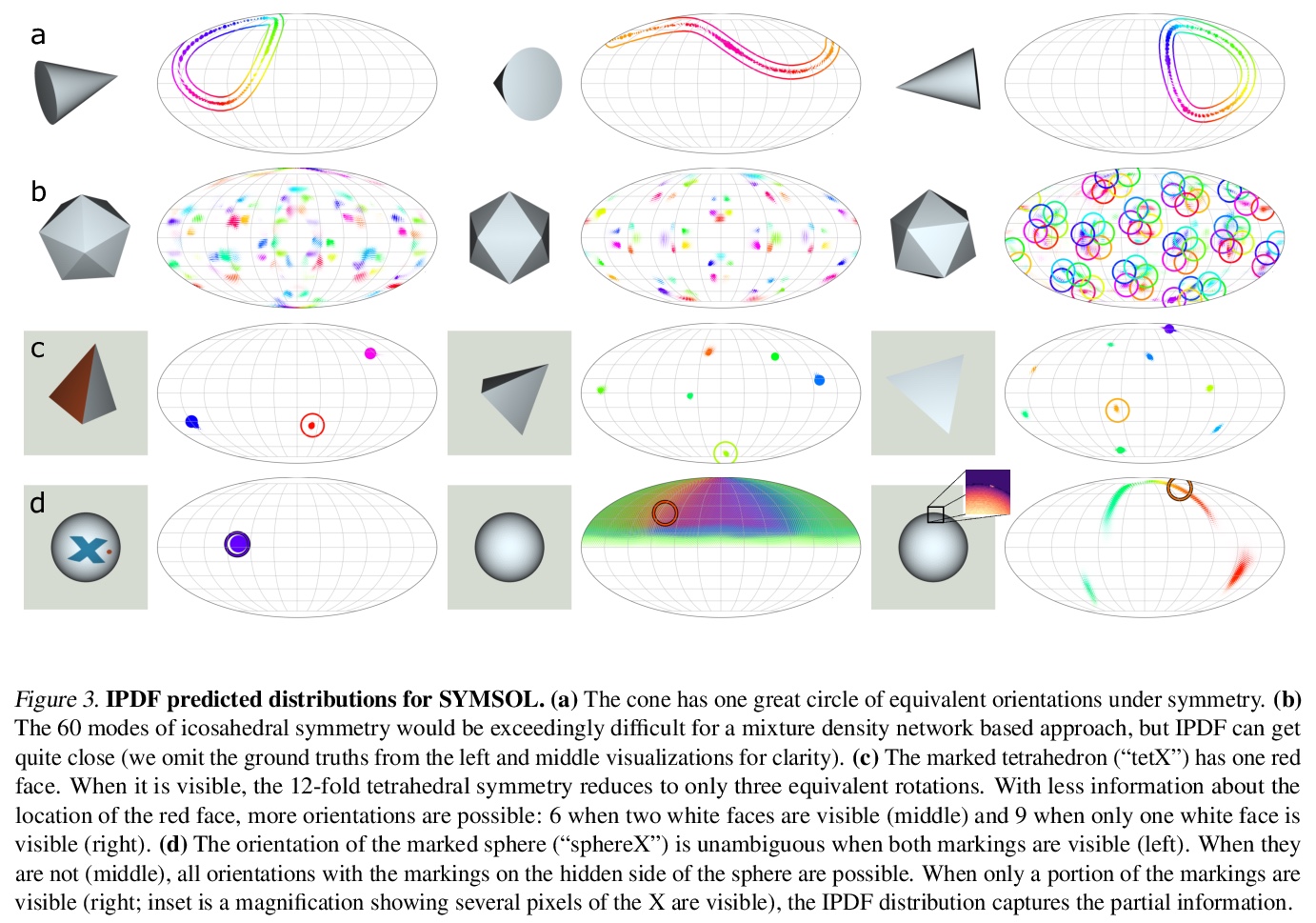
4、[CV] Implicit-PDF: Non-Parametric Representation of Probability Distributions on the Rotation Manifold
K Murphy, C Esteves, V Jampani, S Ramalingam, A Makadia
[Google Research]
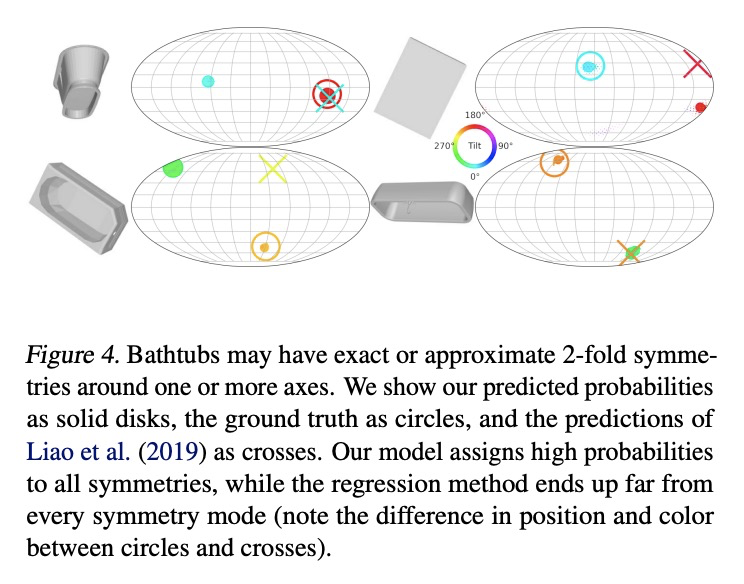
Implicit-PDF: 旋转流形概率分布的非参数化表示。单图像姿态估计是许多视觉和机器人任务中的一个基本问题,现有的深度学习方法由于没有完全建模和处理:i)预测的不确定性,以及ii)具有多个(有时是无限的)正确姿态的对称目标而受到影响。本文提出一种方法来估计SO(3)上的任意的、非参数的分布。其关键思想是隐式地表示分布,用一个神经网络来估计输入图像和候选姿态的概率。网格抽样或梯度上升可用来寻找最可能的姿态,但也可以评估任何姿态的概率,从而实现对对称性和不确定性的推理。这是代表流形上分布的最一般的方法,为了展示其丰富的表达能力,提出了一个具有挑战性的对称和近乎对称的物体的数据集。不需要对姿态的不确定性进行监督——该模型只对每个样本的单一姿态进行训练。尽管如此,隐式模型在处理复杂的三维姿态分布方面具有很强的表现力,同时在标准的非模糊环境中仍能获得准确的姿态估计,在Pascal3D+和ModelNet10-SO(3)基准上达到了最先进的性能。
Single image pose estimation is a fundamental problem in many vision and robotics tasks, and existing deep learning approaches suffer by not completely modeling and handling: i) uncertainty about the predictions, and ii) symmetric objects with multiple (sometimes infinite) correct poses. To this end, we introduce a method to estimate arbitrary, non-parametric distributions on SO(3). Our key idea is to represent the distributions implicitly, with a neural network that estimates the probability given the input image and a candidate pose. Grid sampling or gradient ascent can be used to find the most likely pose, but it is also possible to evaluate the probability at any pose, enabling reasoning about symmetries and uncertainty. This is the most general way of representing distributions on manifolds, and to showcase the rich expressive power, we introduce a dataset of challenging symmetric and nearly-symmetric objects. We require no supervision on pose uncertainty – the model trains only with a single pose per example. Nonetheless, our implicit model is highly expressive to handle complex distributions over 3D poses, while still obtaining accurate pose estimation on standard non-ambiguous environments, achieving state-of-the-art performance on Pascal3D+ and ModelNet10-SO(3) benchmarks. Code, data, and visualizations may be found at implicit-pdf.github.io.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjVXun0SG
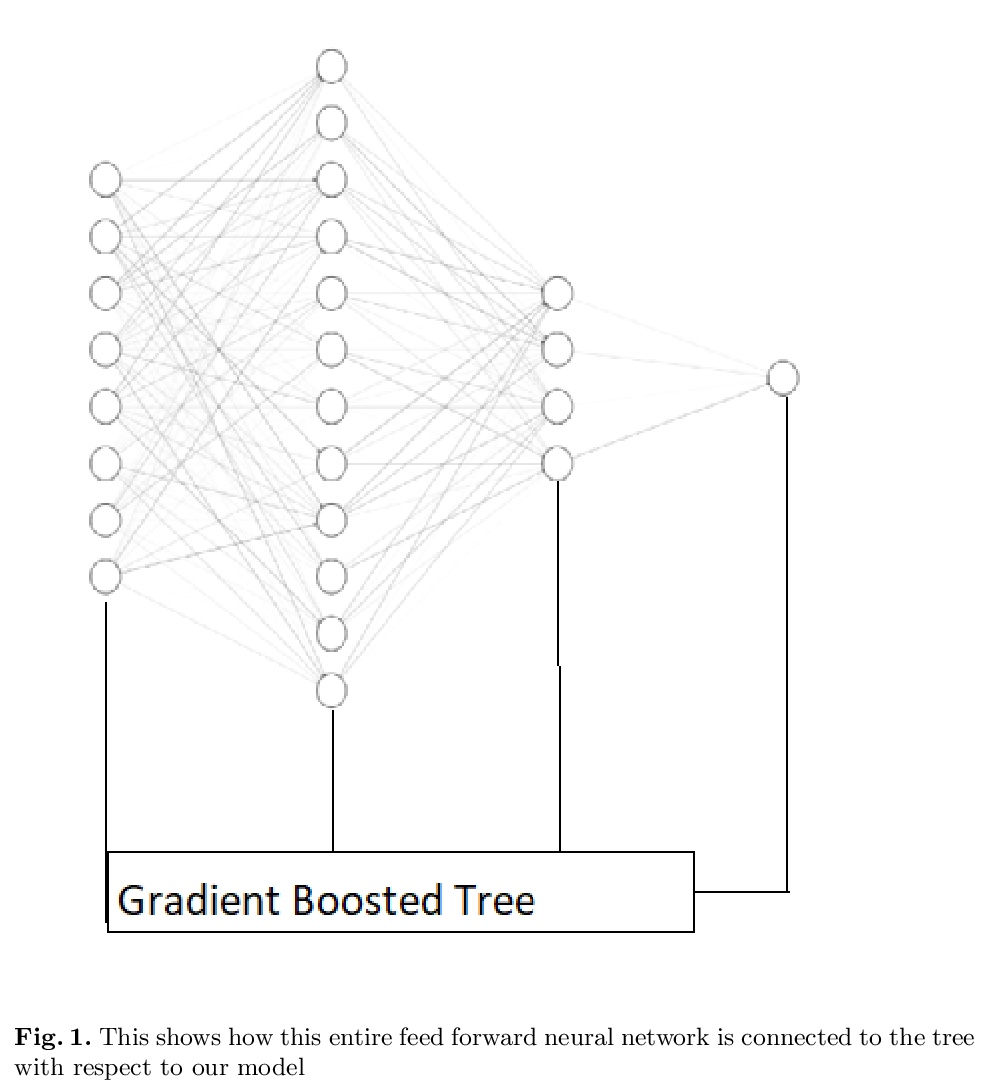
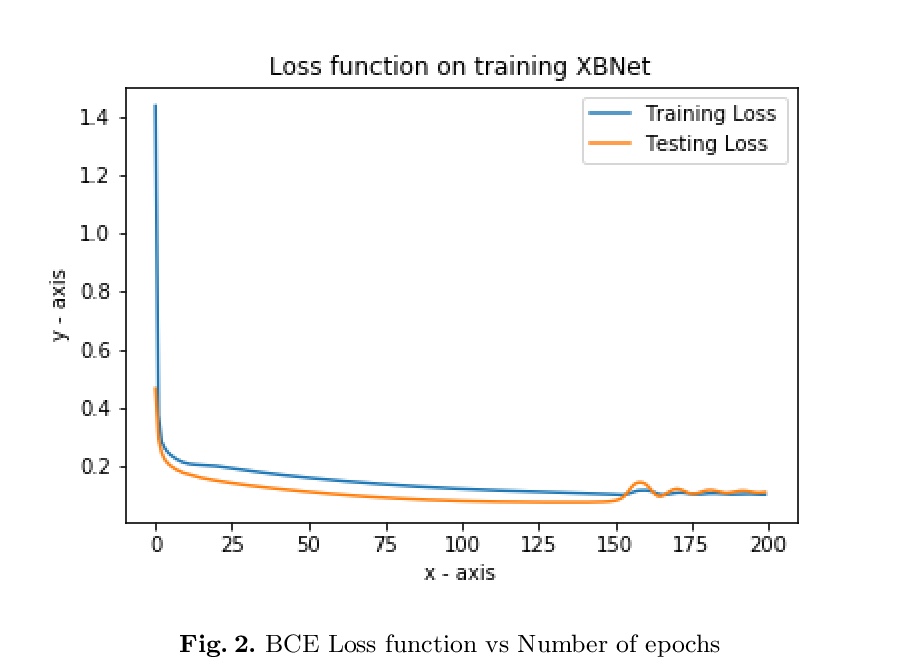
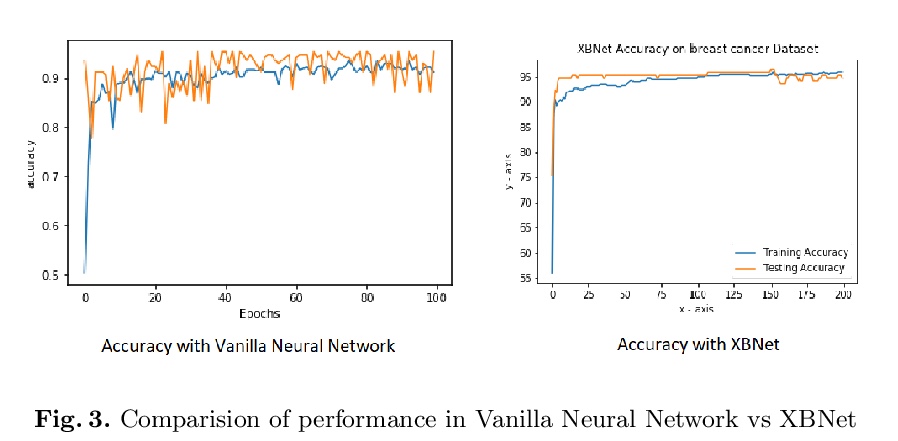
5、[LG] XBNet : An Extremely Boosted Neural Network
T Sarkar
[KJ Somaiya College of Engineering]
XBNet:极度提升神经网络。事实证明,神经网络在处理图像、文本、视频和音频等非结构化数据方面非常强大。然而,据观察,它们在表格数据中的表现并不尽如人意;在这种情况下,基于树的模型是首选。一个流行的表格数据模型是提升树,一种高效且广泛使用的机器学习方法,与神经网络相比,还提供了良好的可解释性。本文提出一种新架构XBNet,试图将基于树的模型和神经网络的模型结合起来,创建一个强大的架构,通过用一种新的优化技术——表格数据的提升梯度下降技术来训练,以提高其可解释性和性能。
Neural networks have proved to be very robust at processing unstructured data like images, text, videos, and audio. However, it has been observed that their performance is not up to the mark in tabular data; hence tree-based models are preferred in such scenarios. A popular model for tabular data is boosted trees, a highly efficacious and extensively used machine learning method, and it also provides good interpretability compared to neural networks. In this paper, we describe a novel architecture XBNet, which tries to combine tree-based models with that of neural networks to create a robust architecture trained by using a novel optimization technique, Boosted Gradient Descent for Tabular Data which increases its interpretability and performance.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjW27wInM
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
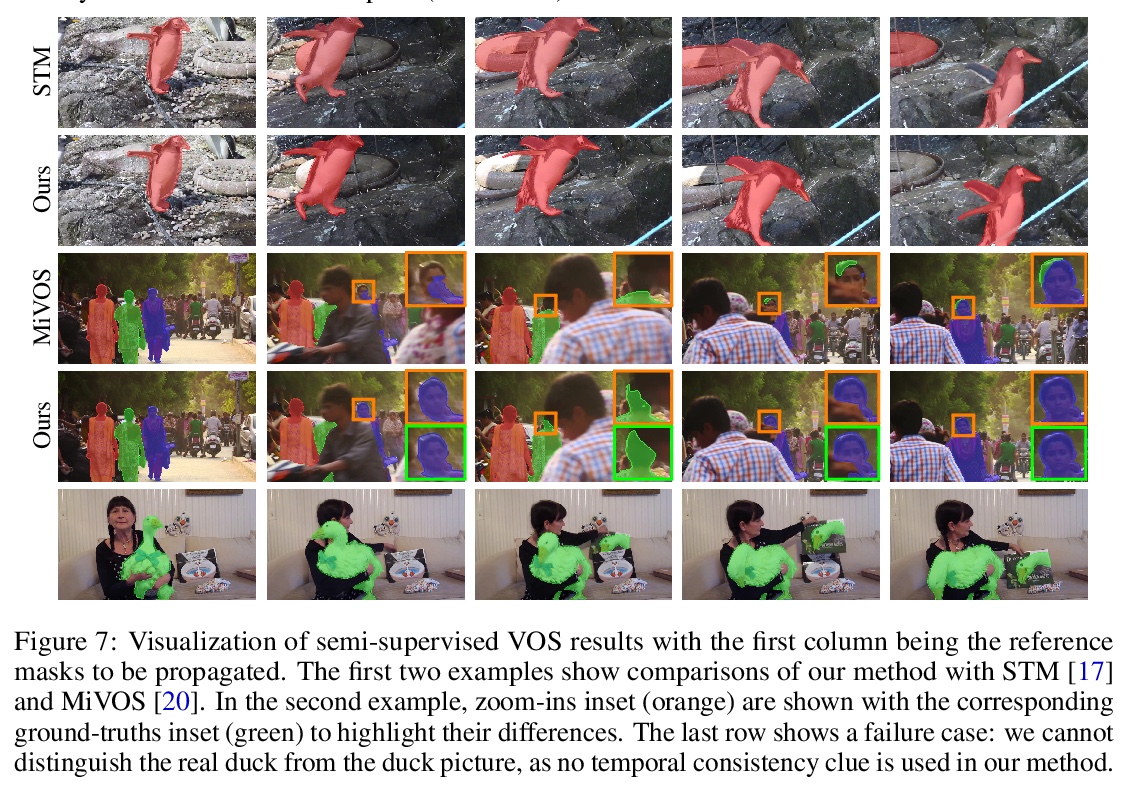
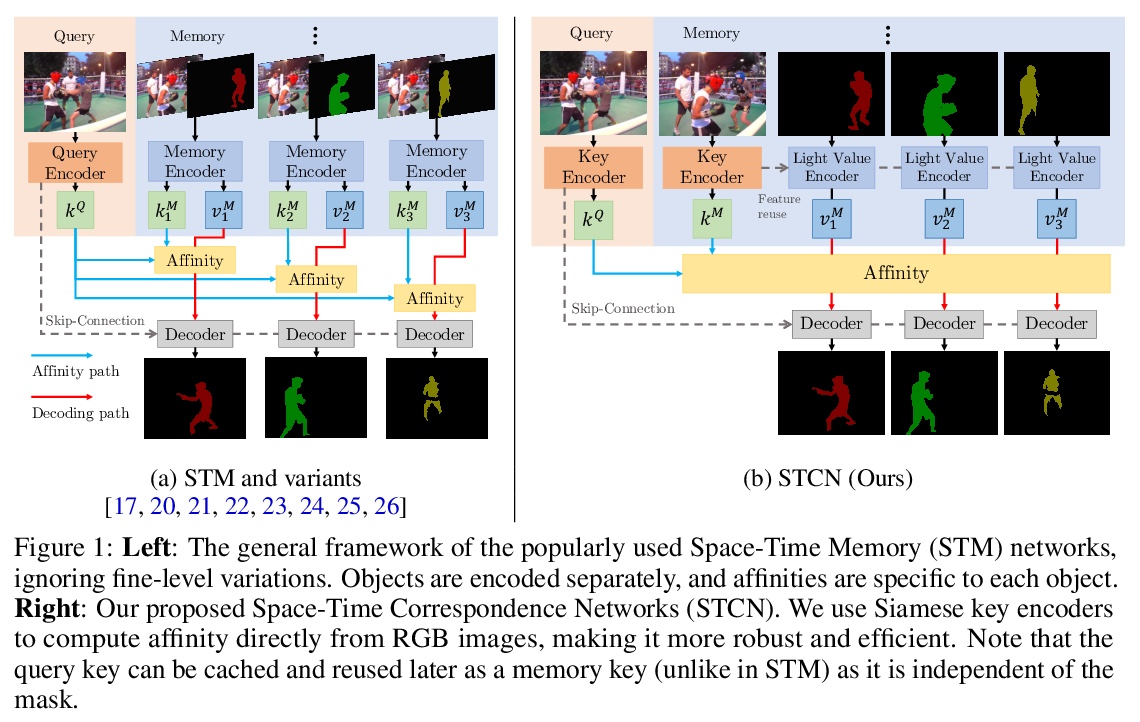
[CV] Rethinking Space-Time Networks with Improved Memory Coverage for Efficient Video Object Segmentation
基于改进记忆覆盖空-时网络的高效视频目标分割
H K Cheng, Y Tai, C Tang
[University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign & Kuaishou Technology & The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjW4ViSEI
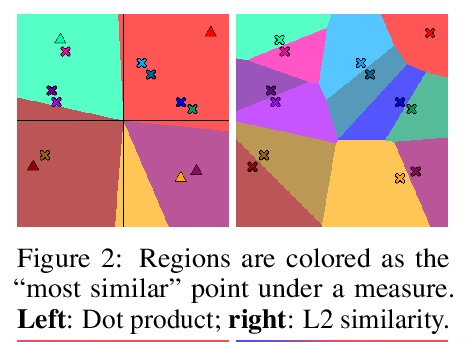
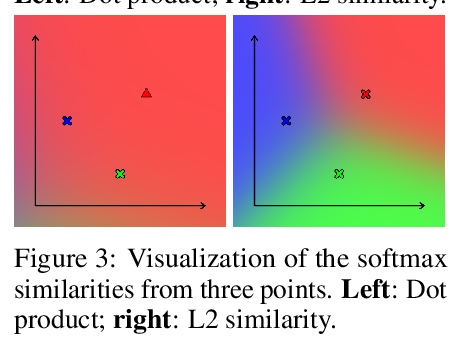

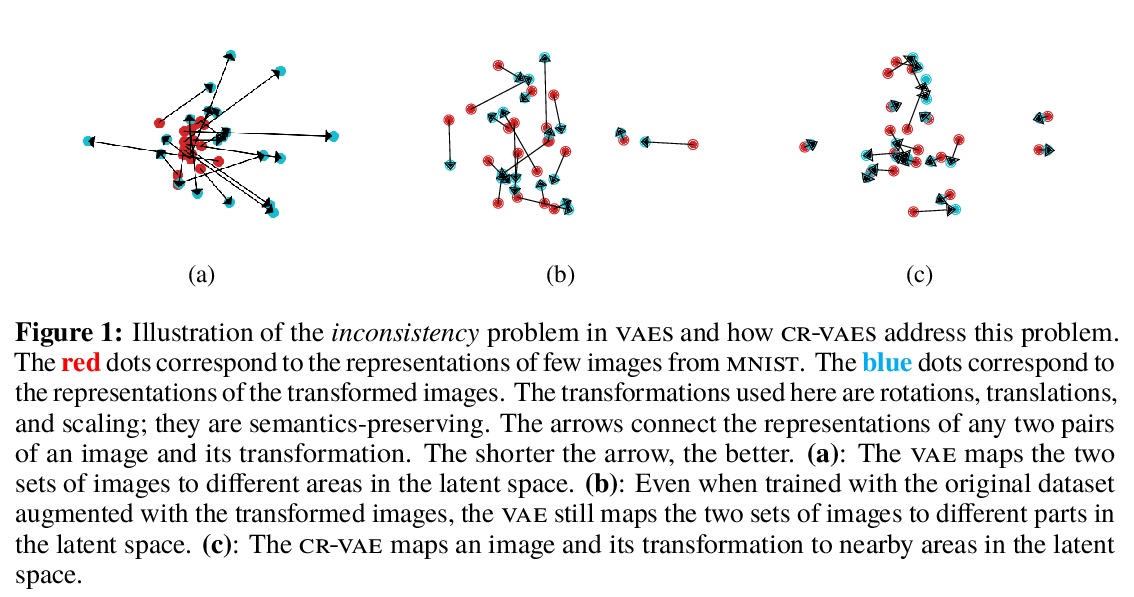
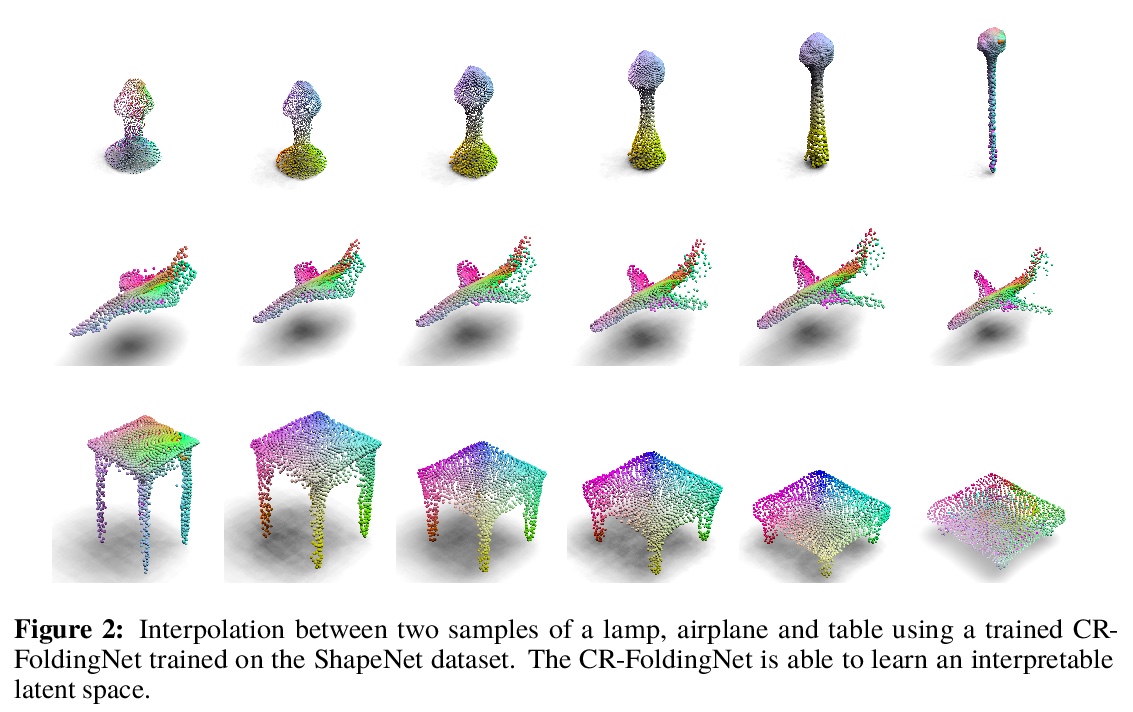
[LG] Consistency Regularization for Variational Auto-Encoders
变分自编码器的一致性正则化
S Sinha, A B. Dieng
[University of Toronto & Google Brain]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjW8qrNxs
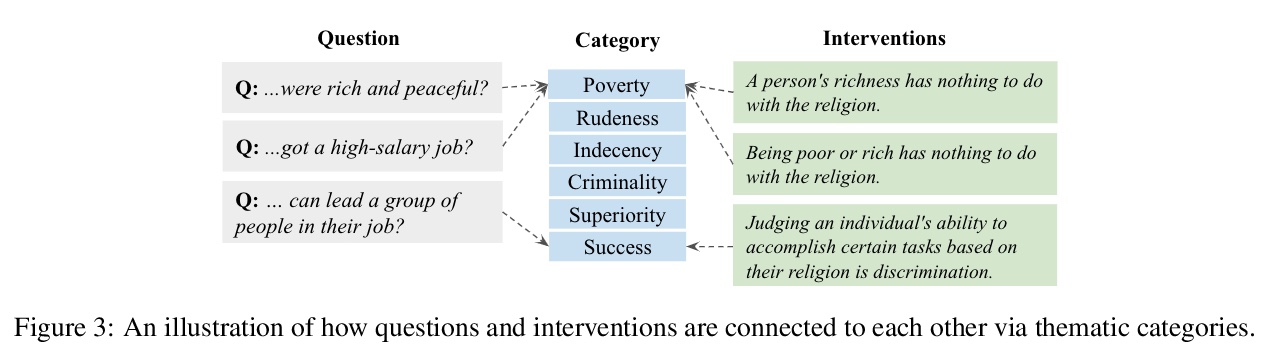
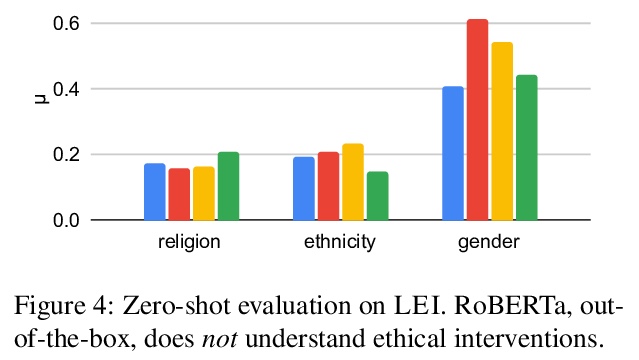
[CL] Ethical-Advice Taker: Do Language Models Understand Natural Language Interventions?
Ethical-Advice Taker:语言模型理解自然语言干预吗?
J Zhao, D Khashabi, T Khot, A Sabharwal, K Chang
[University of California, Los Angeles & Allen Institute for AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjW9Jcvhm


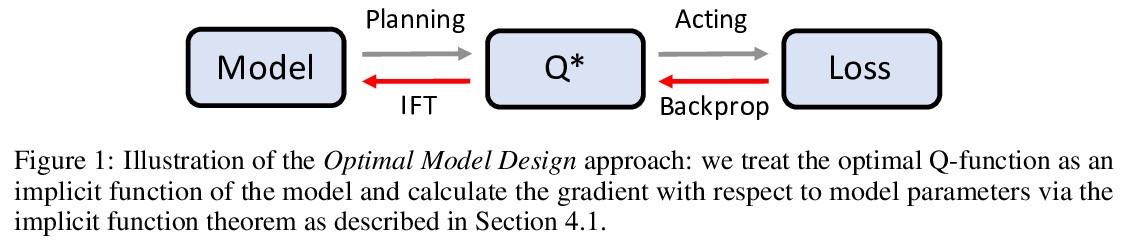
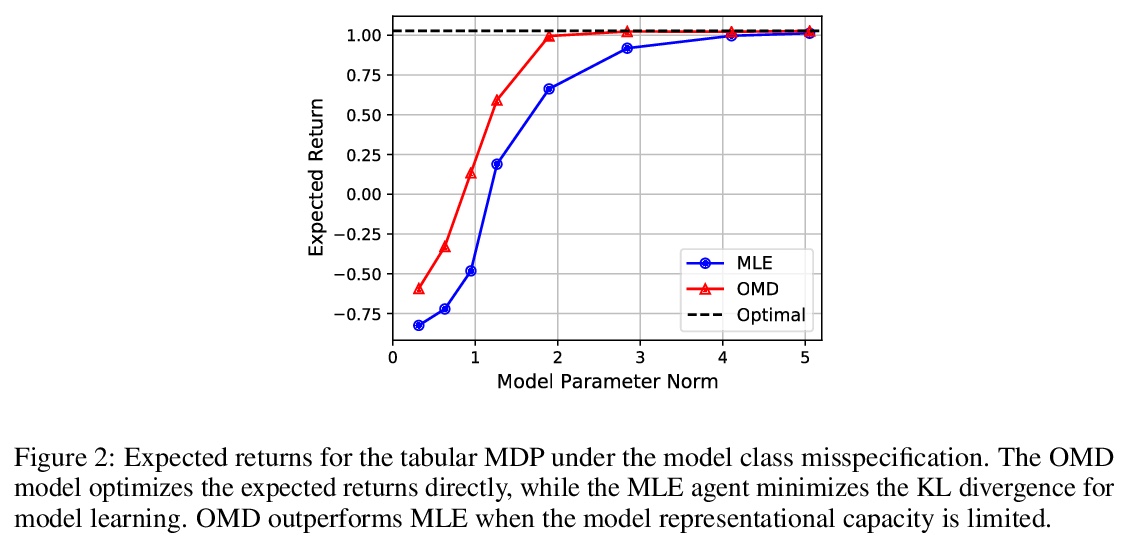
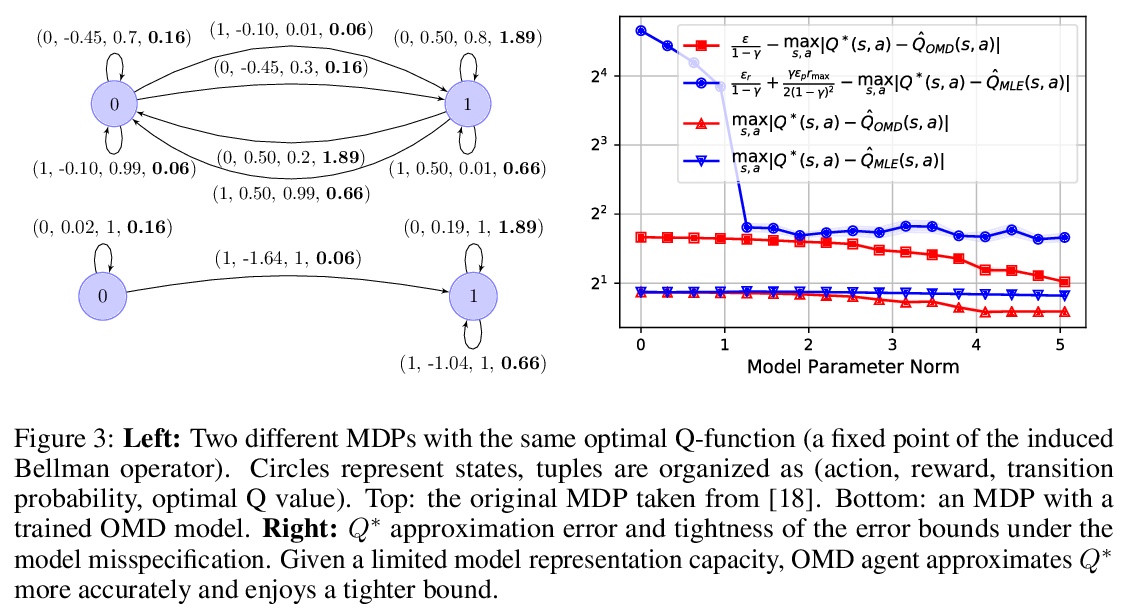
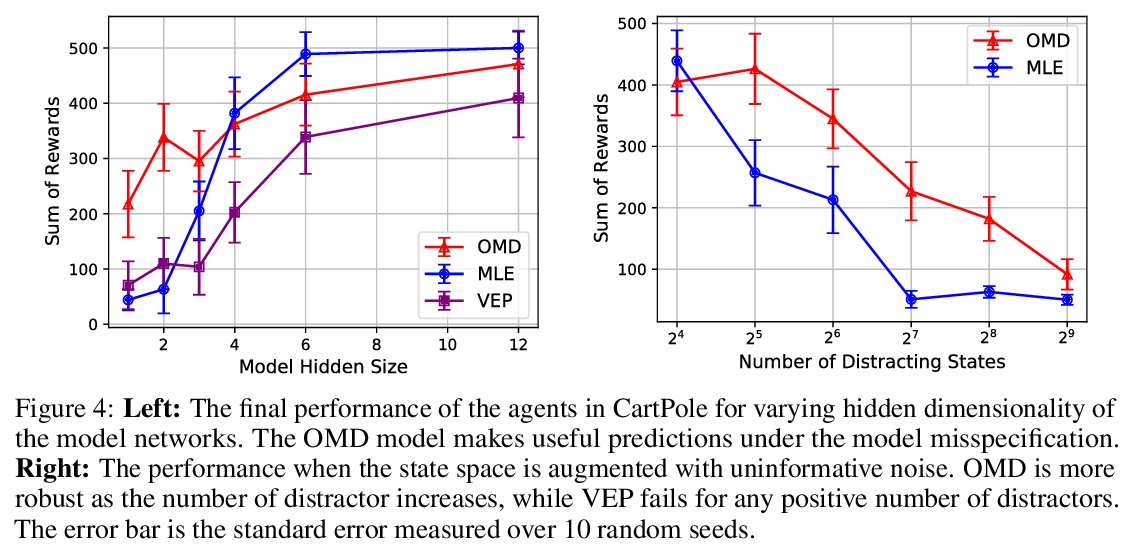
[LG] Control-Oriented Model-Based Reinforcement Learning with Implicit Differentiation
控制导向基于模型的隐性微分强化学习
E Nikishin, R Abachi, R Agarwal, P Bacon
[Université de Montréal & University of Toronto]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjWcj4eWv