- 1、[LG] WILDS: A Benchmark of in-the-Wild Distribution Shifts
- 2、[LG] Accelerating Quadratic Optimization with Reinforcement Learning
- 3、[CV] High carbon stock mapping at large scale with optical satellite imagery and spaceborne LIDAR
- 4、[CV] QVHighlights: Detecting Moments and Highlights in Videos via Natural Language Queries
- 5、[LG] Scalable Evaluation of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Melting Pot
- [LG] Universal Approximation for Log-concave Distributions using Well-conditioned Normalizing Flows
- [LG] Tensor networks for unsupervised machine learning
- [CV] Explicit Clothing Modeling for an Animatable Full-Body Avatar
- [CV] Robust Pose Transfer with Dynamic Details using Neural Video Rendering
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] WILDS: A Benchmark of in-the-Wild Distribution Shifts
P W Koh, S Sagawa, H Marklund, S M Xie, M Zhang, A Balsubramani, W Hu, M Yasunaga, R L Phillips, I Gao, T Lee, E David, I Stavness, W Guo, B A. Earnshaw, I S. Haque, S Beery, J Leskovec, A Kundaje, E Pierson, S Levine, C Finn, P Liang
[Stanford University]
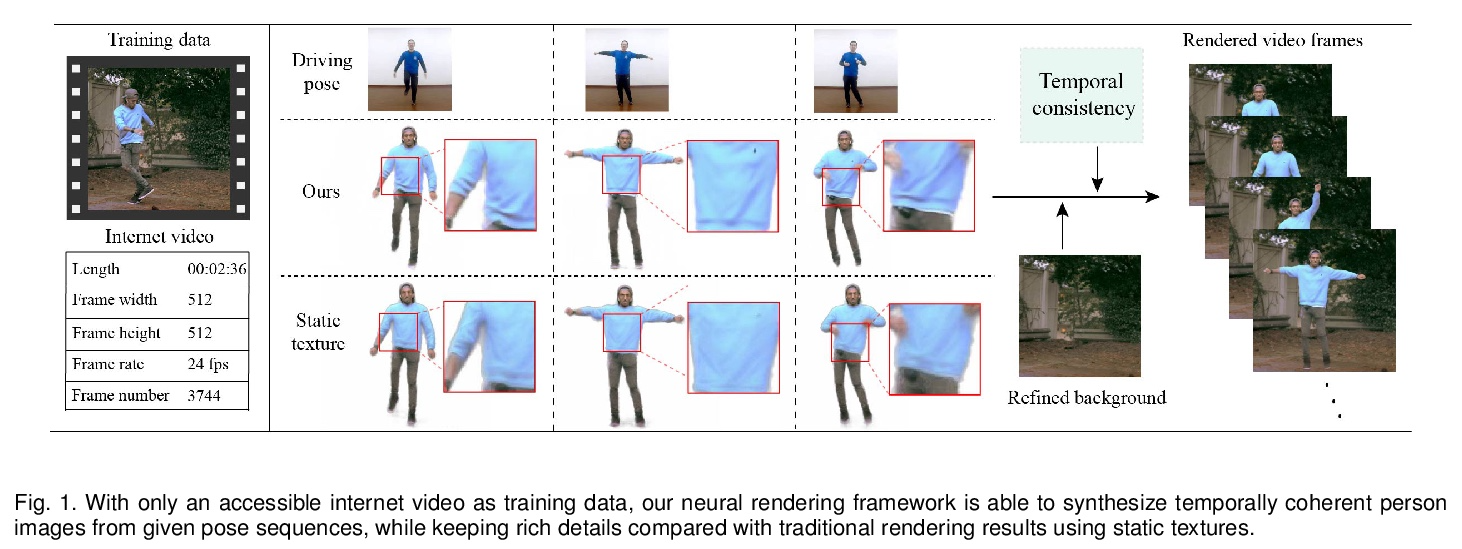
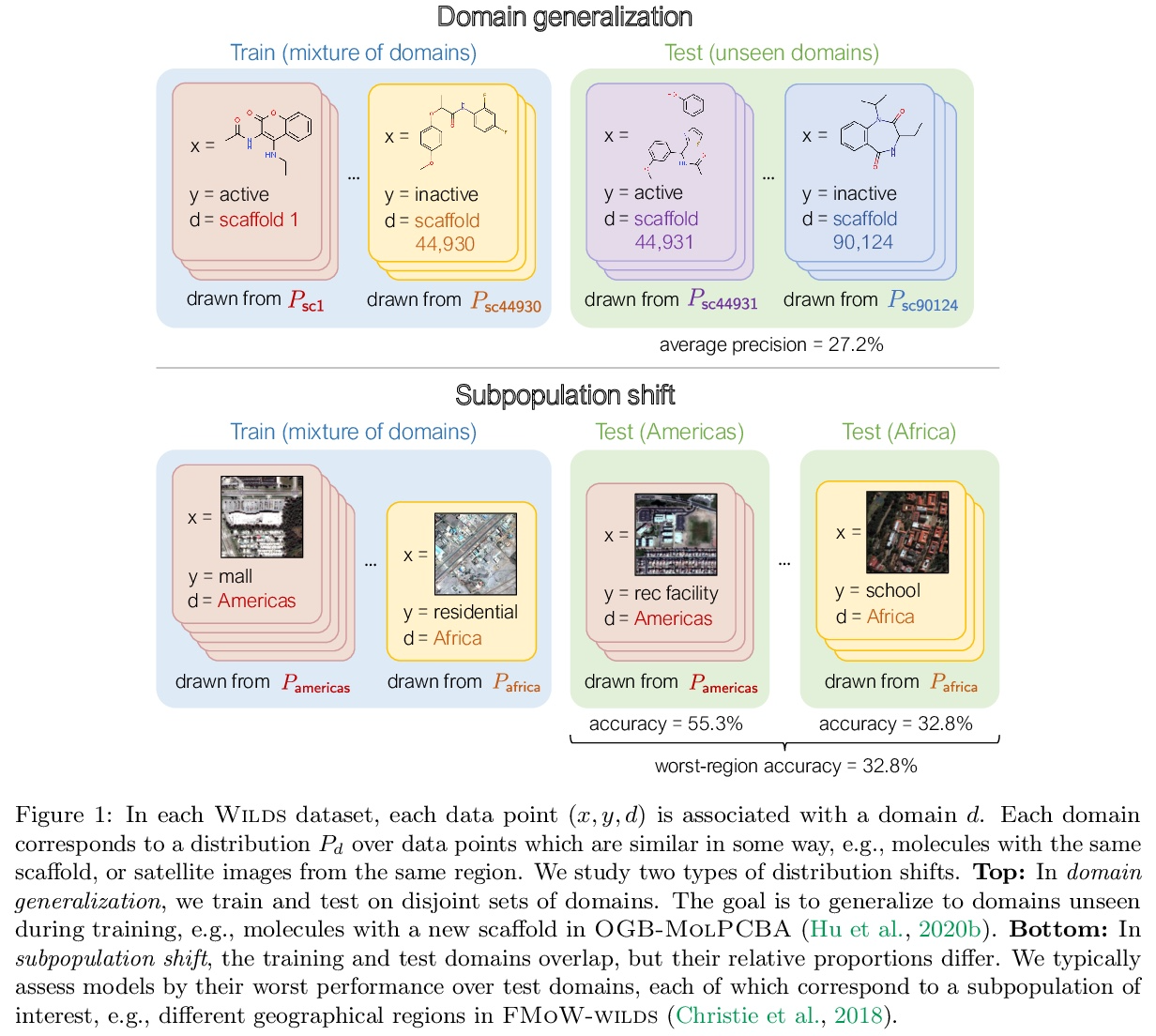
WILDS:真实场景分布漂移基准。分布漂移——训练分布与测试分布不同——会大大降低在真实环境中部署机器学习系统的精度。尽管在现实世界的部署中无处不在,但这些分布漂移在当今ML社区广泛使用的数据集中却没有得到充分的体现。为解决该问题,本文提出了WILDS,一个由10个数据集组成的基准,反映了现实世界应用中自然产生的各种分布变化,如医院间的肿瘤识别变化;野生动物监测中的相机陷阱变化;以及卫星成像和贫困制图中的时间和地点变化。在每个数据集上,标准训练产生的分布外性能大大低于分布内性能。这种差距甚至在用现有方法训练的模型中仍然存在,这突出表明需要有新的方法来训练模型,使其对实践中出现的分布变化类型更加强大。为了促进方法的发展,提供了一个开源包,可自动加载数据集,包含默认的模型架构和超参数,并对评估进行标准化。
Distribution shifts—where the training distribution differs from the test distribution—can substantially degrade the accuracy of machine learning (ML) systems deployed in the wild. Despite their ubiquity in the real-world deployments, these distribution shifts are under-represented in the datasets widely used in the ML community today. To address this gap, we present Wilds, a curated benchmark of 10 datasets reflecting a diverse range of distribution shifts that naturally arise in real-world applications, such as shifts across hospitals for tumor identification; across camera traps for wildlife monitoring; and across time and location in satellite imaging and poverty mapping. On each dataset, we show that standard training yields substantially lower out-of-distribution than in-distribution performance. This gap remains even with models trained by existing methods for tackling distribution shifts, underscoring the need for new methods for training models that are more robust to the types of distribution shifts that arise in practice. To facilitate method development, we provide an open-source package that automates dataset loading, contains default model architectures and hyperparameters, and standardizes evaluations.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqtaztqCJ 
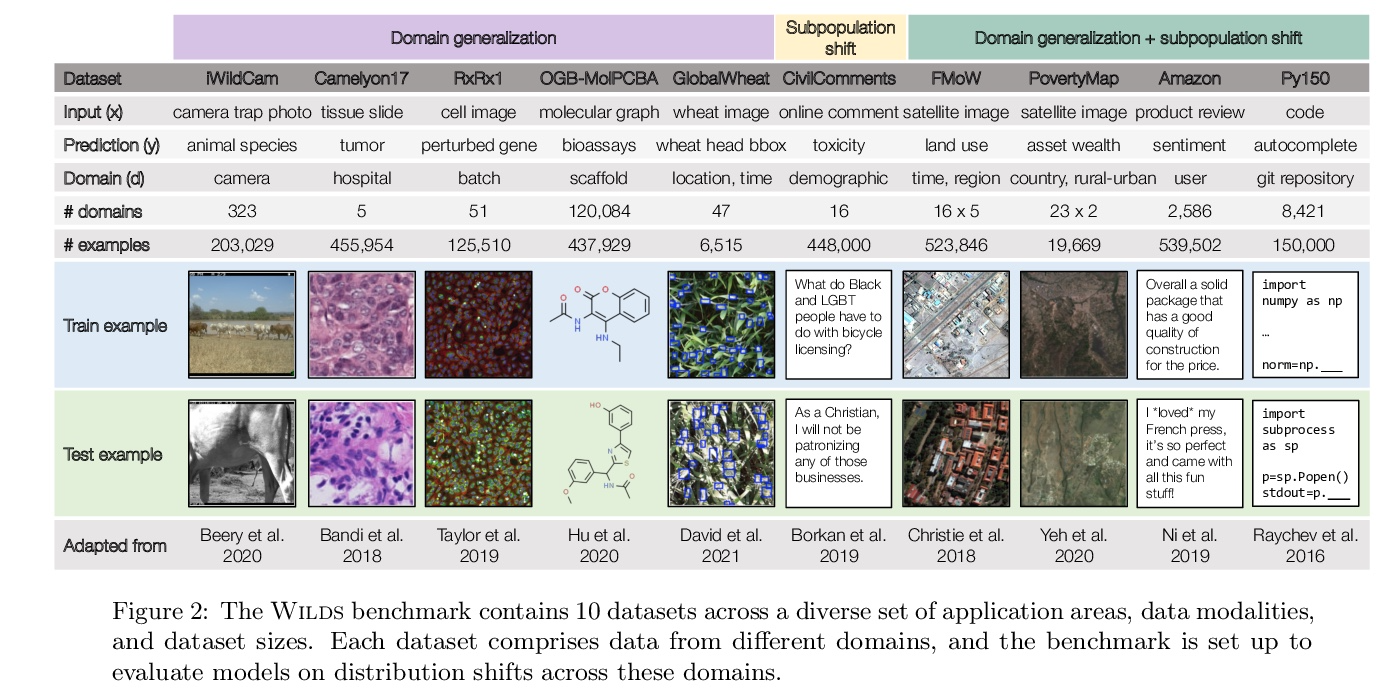
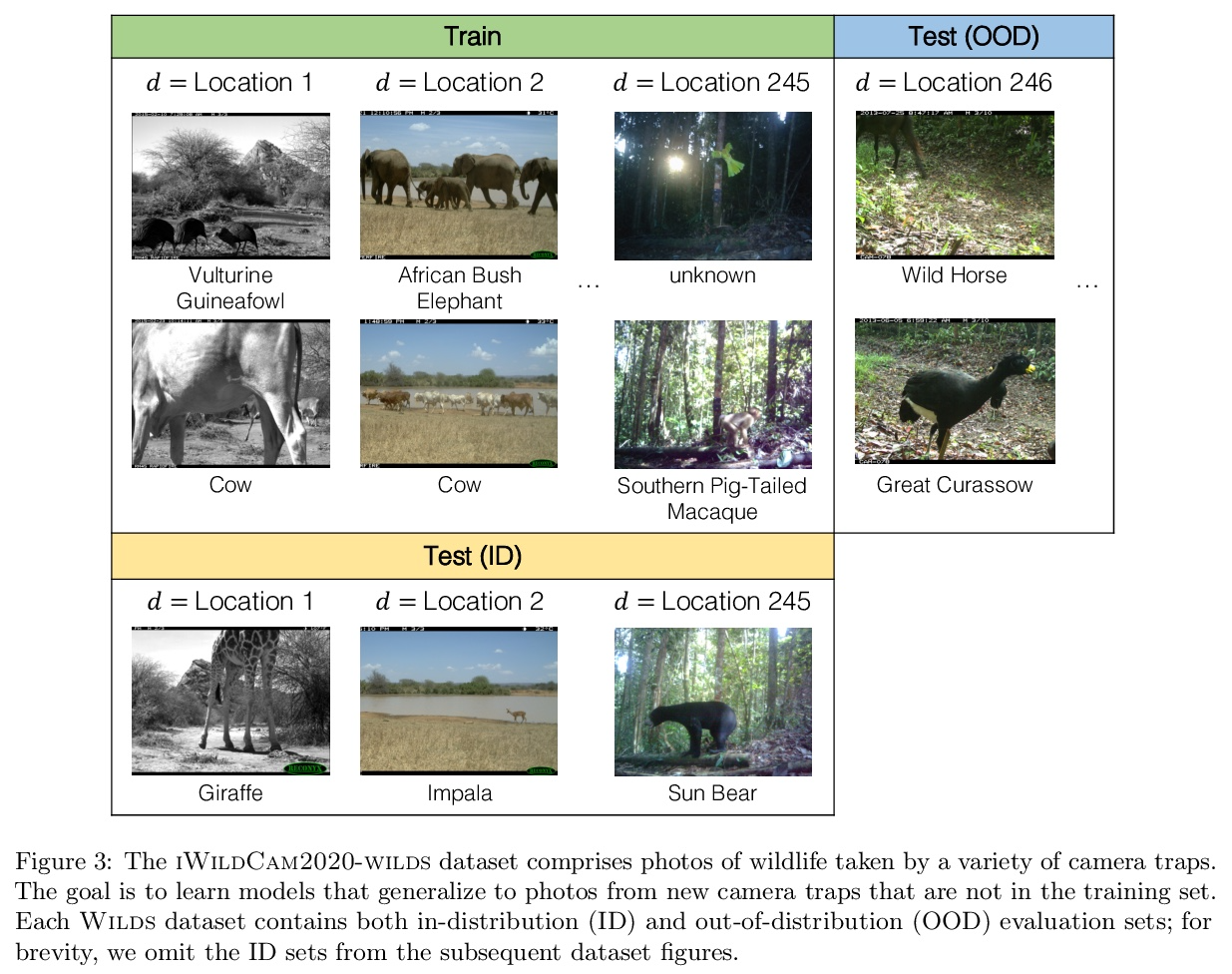
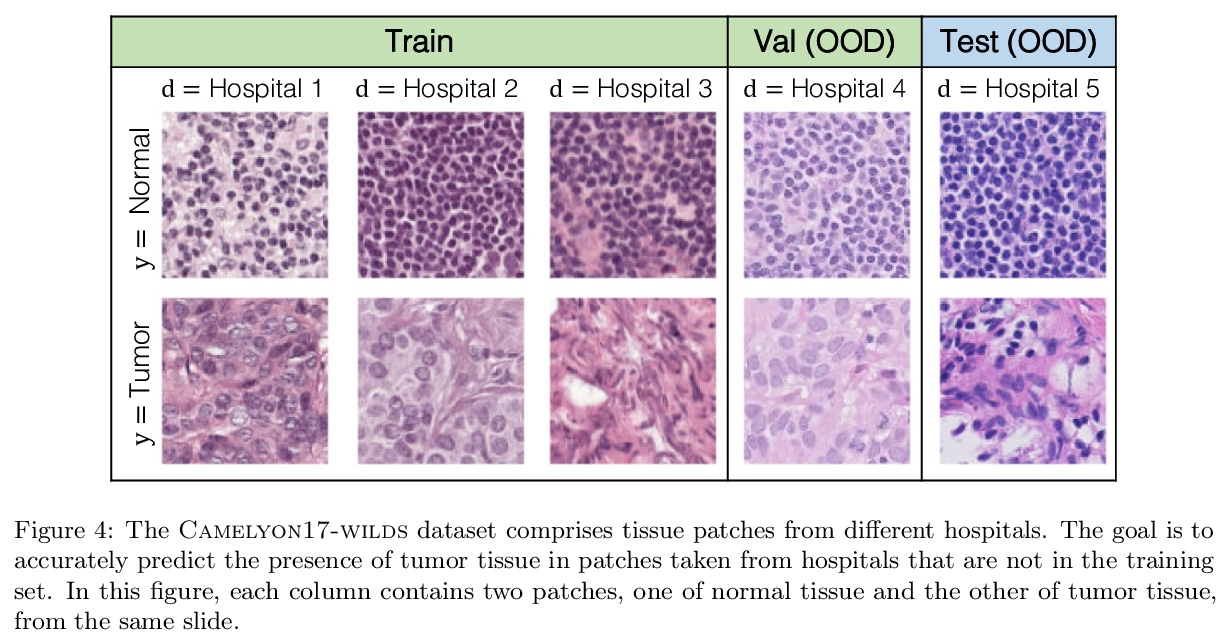
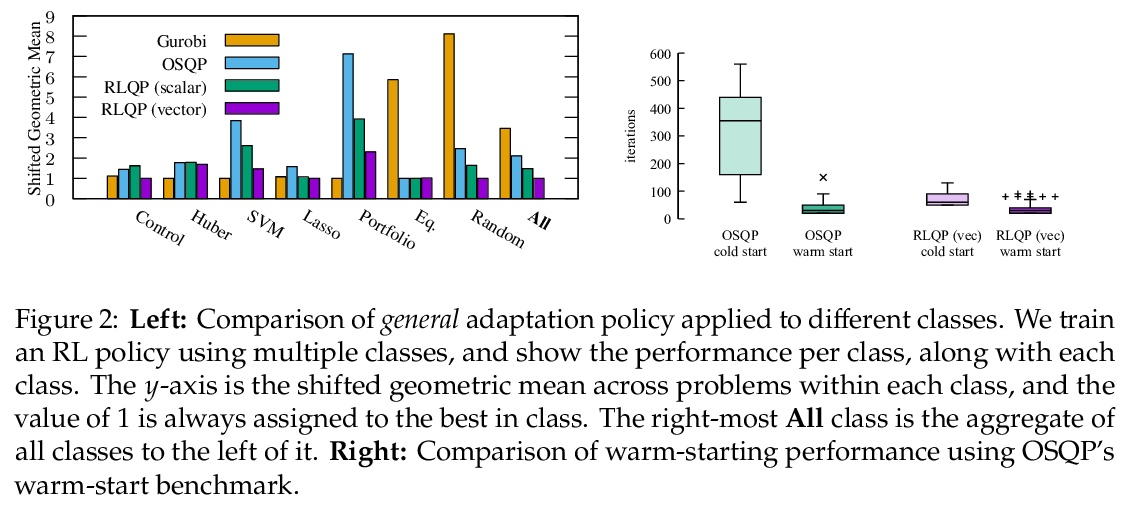
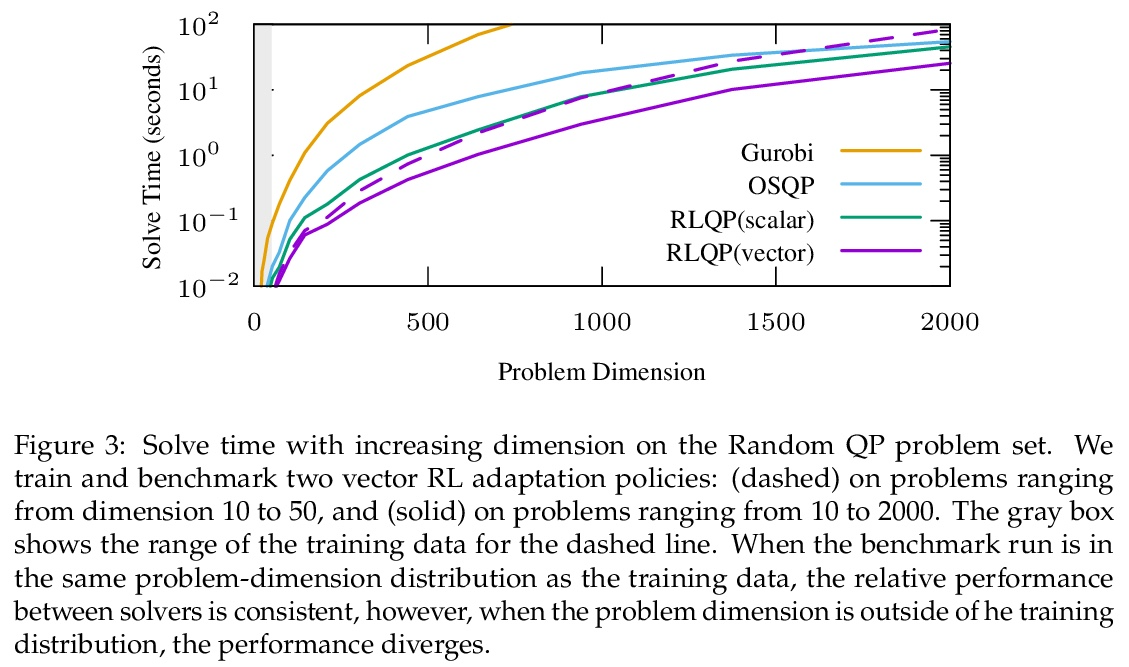
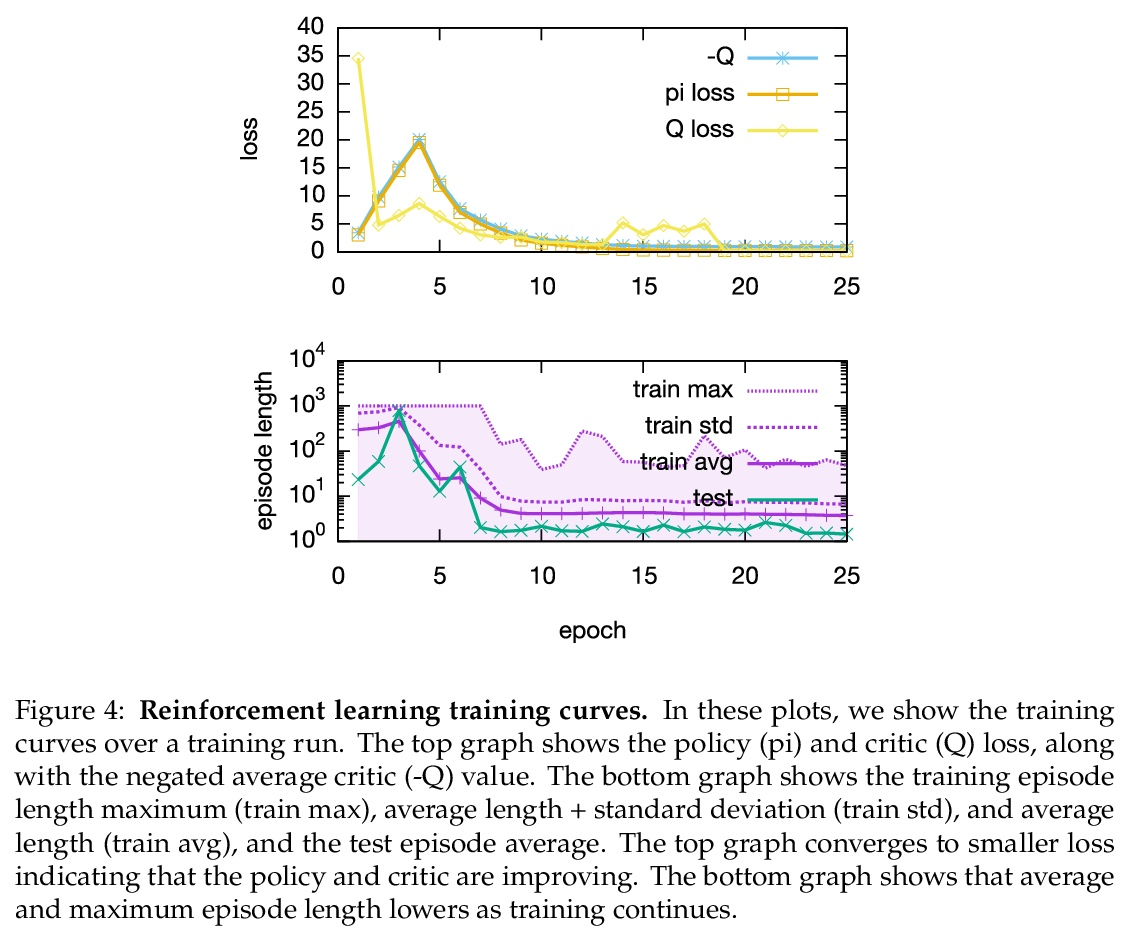
2、[LG] Accelerating Quadratic Optimization with Reinforcement Learning
J Ichnowski, P Jain, B Stellato, G Banjac, M Luo, F Borrelli, J E. Gonzalez, I Stoica, K Goldberg
[UC Berkeley & Princeton University & ETH Zurich]
基于强化学习的二次优化加速。二次优化的一阶方法,如OSQP,被广泛用于大型机器学习和嵌入优化控制,其中许多相关问题必须快速解决。这些方法面临着两个持续挑战:手动调整超参数和收敛时间,以获得高精度的解决方案。为了解决这些问题,本文探讨了强化学习(RL)如何学习策略来调整参数以加速收敛。在著名的QP基准实验中,所提出的的强化学习策略,RLQP,明显优于最先进的QP求解器,最高可达3倍。RLQP对以前未见过的具有不同维度和结构的不同应用的问题,包括QPLIB、Netlib LP和Maros-Mészáros问题,具有惊人的泛化性。
First-order methods for quadratic optimization such as OSQP arewidely used for largescalemachine learning and embedded optimal control, wheremany related problemsmust be rapidly solved. These methods face two persistent challenges: manual hyperparameter tuning and convergence time to high-accuracy solutions. To address these, we explore how Reinforcement Learning (RL) can learn a policy to tune parameters to accelerate convergence. In experiments with well-known QP benchmarks we find that our RL policy, RLQP, significantly outperforms state-of-the-art QP solvers by up to 3x. RLQP generalizes surprisingly well to previously unseen problems with varying dimension and structure fromdifferent applications, including theQPLIB,Netlib LP andMaros-Mészáros problems.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqteBb0MI 
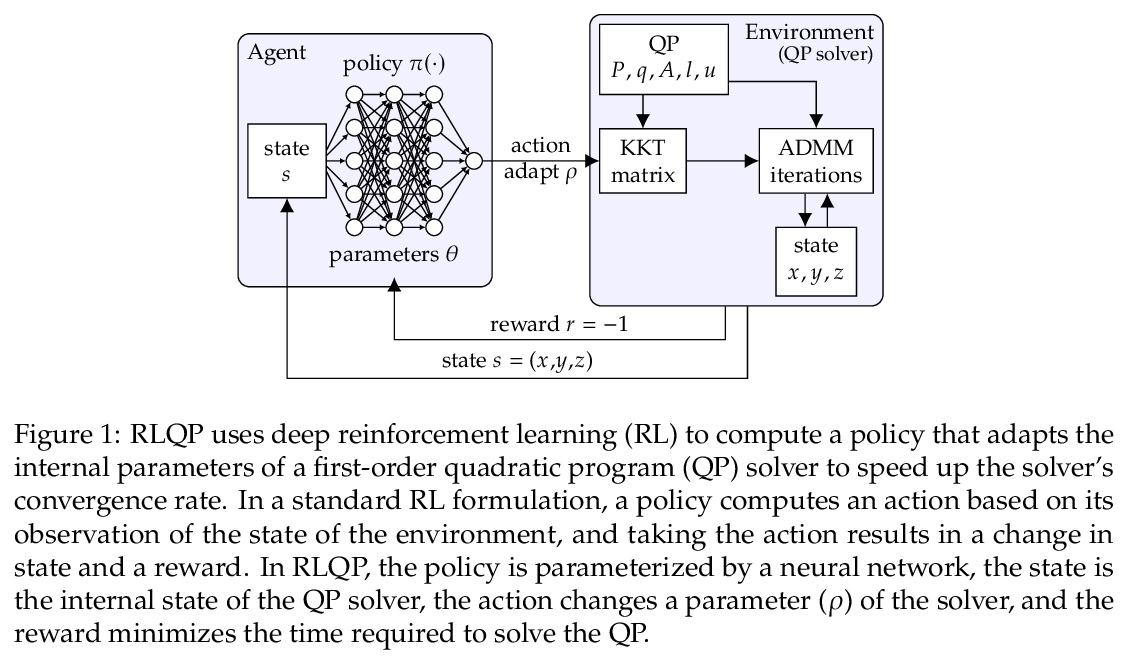
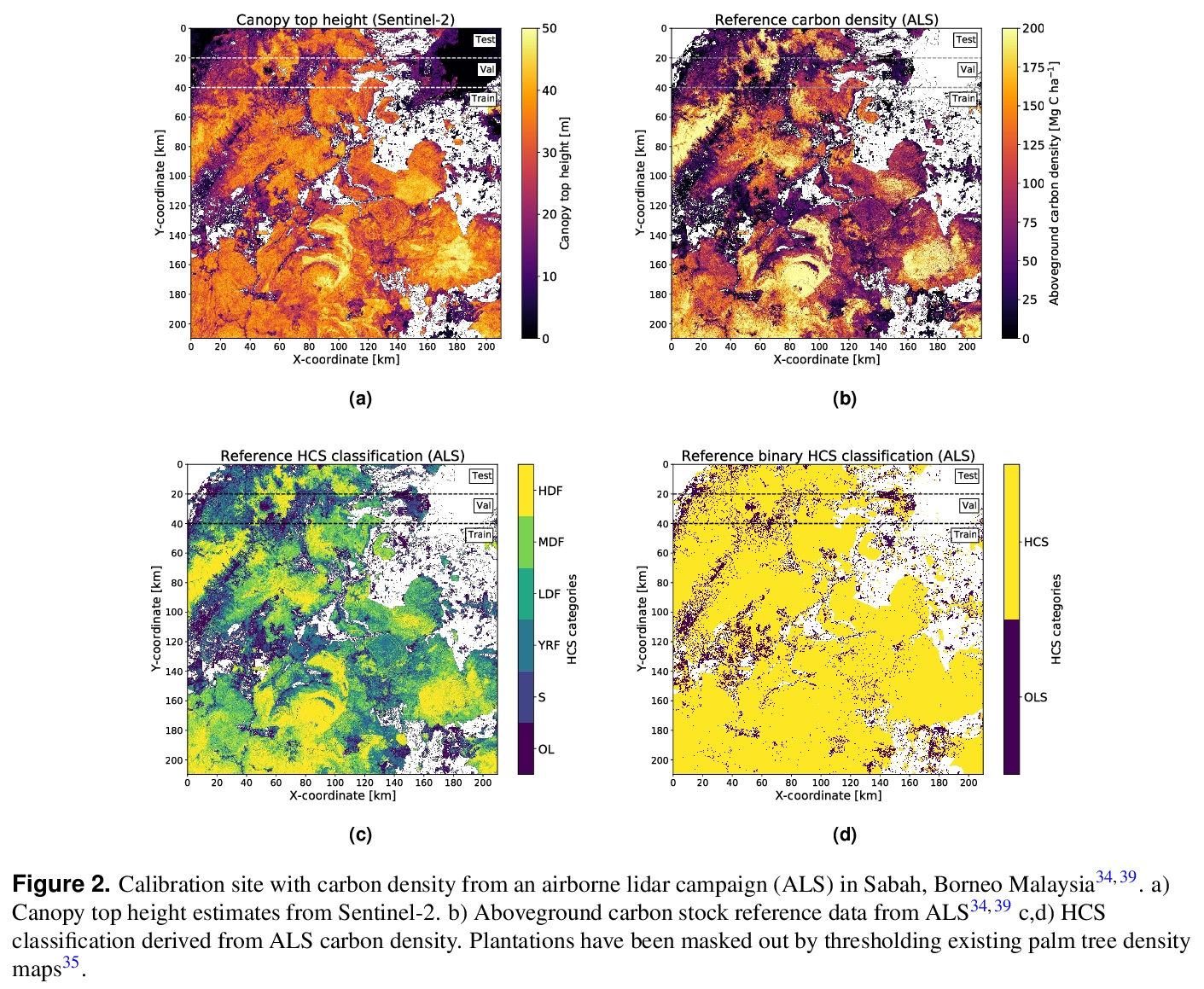
3、[CV] High carbon stock mapping at large scale with optical satellite imagery and spaceborne LIDAR
N Lang, K Schindler, J D Wegner
[ETH Zurich]
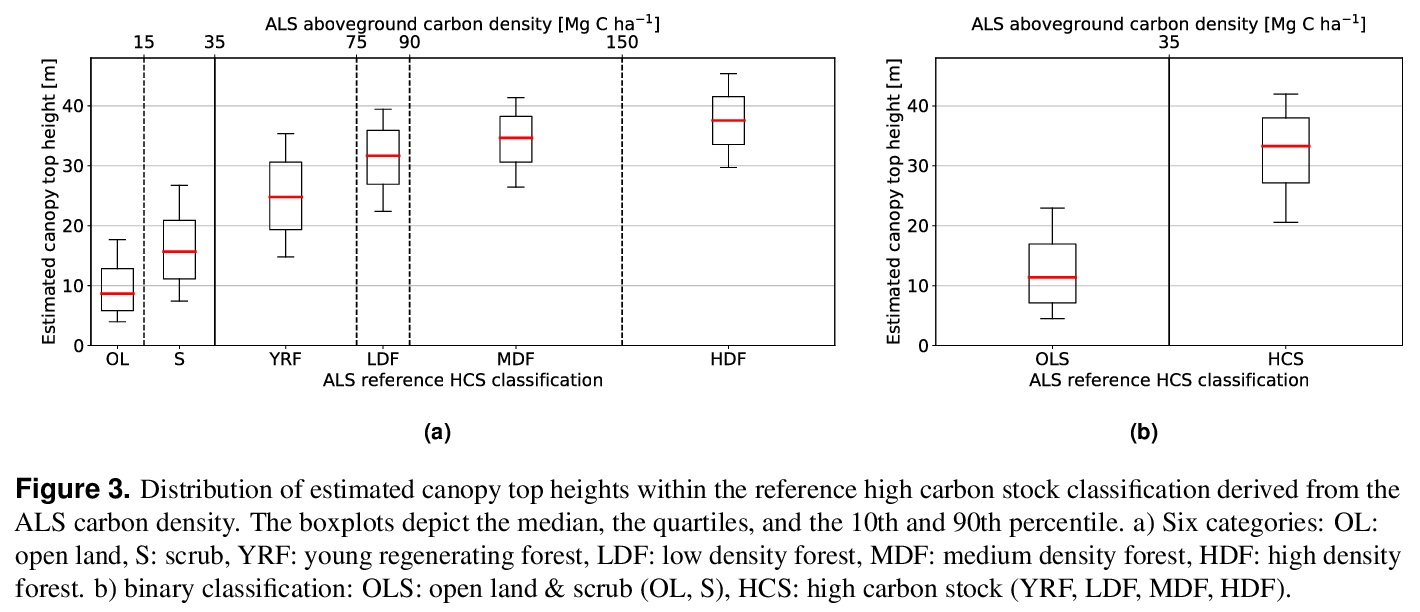
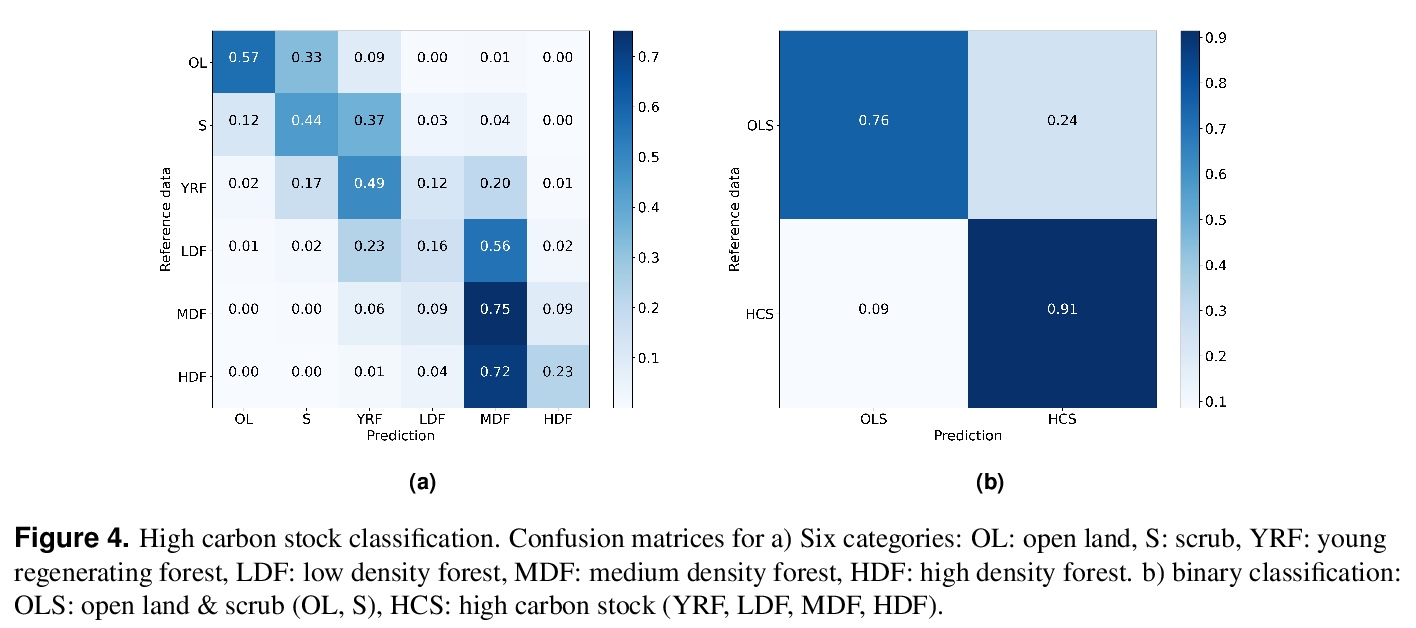
利用光学卫星图像和空间激光雷达的大规模高碳存量测绘。对商品需求的增加导致了全世界土地利用的变化。在热带地区,导致高碳排放和威胁生物多样性的森林砍伐往往与农业扩张有关。虽然对无毁林的全球供应链的需求被广泛认可,但在实践中取得进展仍然是一个挑战。本文提出了一种自动化方法,旨在通过按照高碳存量(HCS)的方法,在大尺度和高空间分辨率上绘制热带景观,支持保护和可持续的土地使用规划决策。开发了一种深度学习方法,通过从稀疏的GEDI激光雷达参考数据中学习来估计每个10米Sentinel-2像素的冠层高度,实现了6.3米的总体RMSE。这些覆盖全部地面的冠层高度地图对于HCS森林和退化地区的分类具有预测作用,总体准确率为86%,并为印度尼西亚、马来西亚和菲律宾绘制了第一张高碳存量地图。
The increasing demand for commodities is leading to changes in land use worldwide. In the tropics, deforestation, which causes high carbon emissions and threatens biodiversity, is often linked to agricultural expansion. While the need for deforestation-free global supply chains is widely recognized, making progress in practice remains a challenge. Here, we propose an automated approach that aims to support conservation and sustainable land use planning decisions by mapping tropical landscapes at large scale and high spatial resolution following the High Carbon Stock (HCS) approach. A deep learning approach is developed that estimates canopy height for each 10 m Sentinel-2 pixel by learning from sparse GEDI LIDAR reference data, achieving an overall RMSE of 6.3 m. We show that these wall-to-wall maps of canopy top height are predictive for classifying HCS forests and degraded areas with an overall accuracy of 86 % and produce a first high carbon stock map for Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kqtjcfxm5 

4、[CV] QVHighlights: Detecting Moments and Highlights in Videos via Natural Language Queries
J Lei, T L. Berg, M Bansal
[University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill]
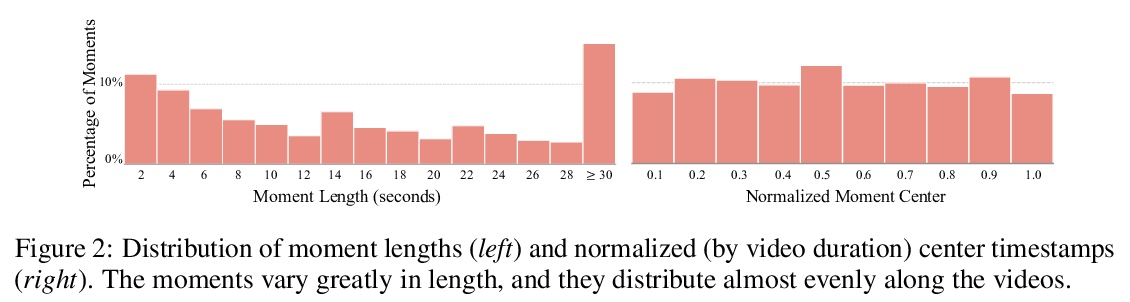
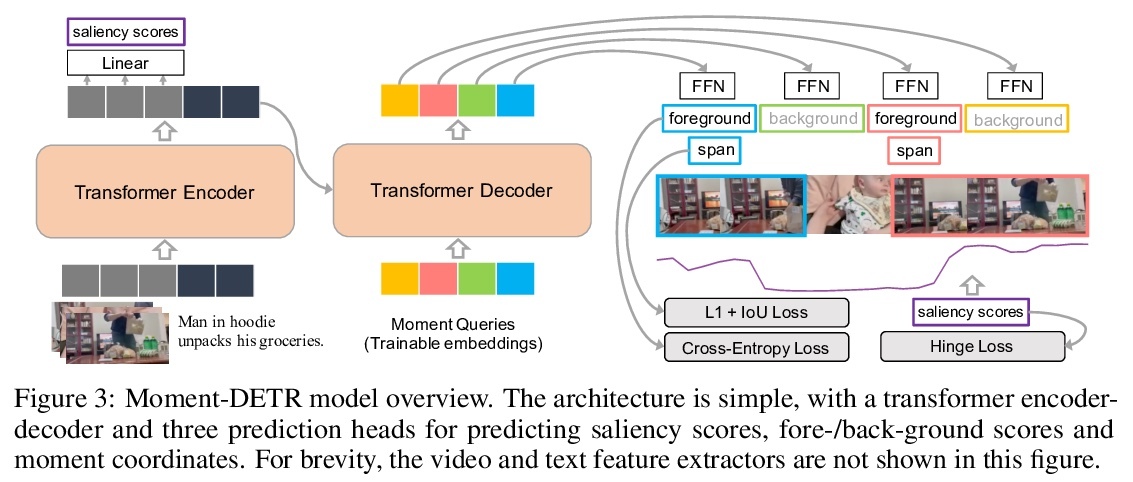
QVHIGHLIGHTS: 通过自然语言查询检测视频中的瞬间和亮点。通过自然语言(NL)用户查询,检测视频中的自定义瞬间和亮点是一个重要但研究不足的课题。追求这一方向的挑战之一是缺乏标注数据。为解决该问题,本文提出基于查询的视频亮点(QVHIGHLIGHTS)数据集,由超过10,000个YouTube视频组成,涵盖了广泛的主题,从生活方式视频中的日常活动和旅行到新闻视频中的社会和政治活动。数据集中每个视频都有标注。(1)人工写的自由形式的自然语言查询,(2)视频中与查询相关的时刻,以及(3)所有与查询相关的片段的五分制显著性得分。这种全面的标注使得为不同的、灵活的用户查询检测相关的时刻和显著亮点开发和评估系统成为可能。本文为这项任务提出了一个强大的基线,即Moment-DETR,一个transformer编码器-解码器模型,将时刻检索视为一个直接的集合预测问题,将提取的视频和查询表示作为输入,并对时刻坐标和显著性分数进行端到端预测。虽然模型没有利用任何人工先验,但与精心设计的架构相比,其表现具有竞争力。通过使用ASR字幕的弱监督预训练,MomentDETR的表现大大超过了以前的方法。
Detecting customized moments and highlights from videos given natural language (NL) user queries is an important but under-studied topic. One of the challenges in pursuing this direction is the lack of annotated data. To address this issue, we present the Query-based Video Highlights (QVHIGHLIGHTS) dataset. It consists of over 10,000 YouTube videos, covering a wide range of topics, from everyday activities and travel in lifestyle vlog videos to social and political activities in news videos. Each video in the dataset is annotated with: (1) a human-written free-form NL query, (2) relevant moments in the video w.r.t. the query, and (3) five-point scale saliency scores for all query-relevant clips. This comprehensive annotation enables us to develop and evaluate systems that detect relevant moments as well as salient highlights for diverse, flexible user queries. We also present a strong baseline for this task, Moment-DETR, a transformer encoder-decoder model that views moment retrieval as a direct set prediction problem, taking extracted video and query representations as inputs and predicting moment coordinates and saliency scores end-to-end. While our model does not utilize any human prior, we show that it performs competitively when compared to well-engineered architectures. With weakly supervised pretraining using ASR captions, MomentDETR substantially outperforms previous methods. Lastly, we present several ablations and visualizations of Moment-DETR.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqtmvBoxK 


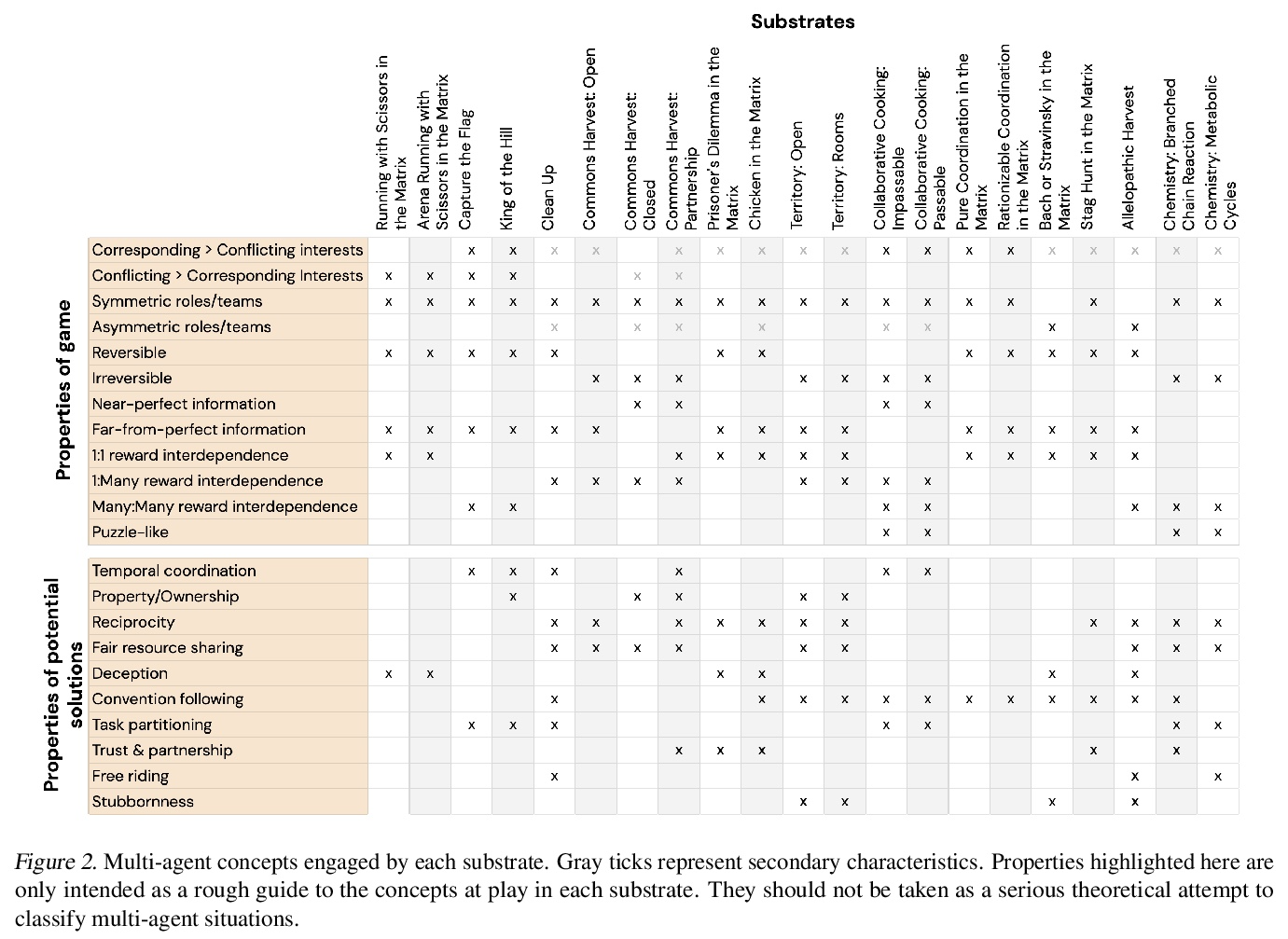
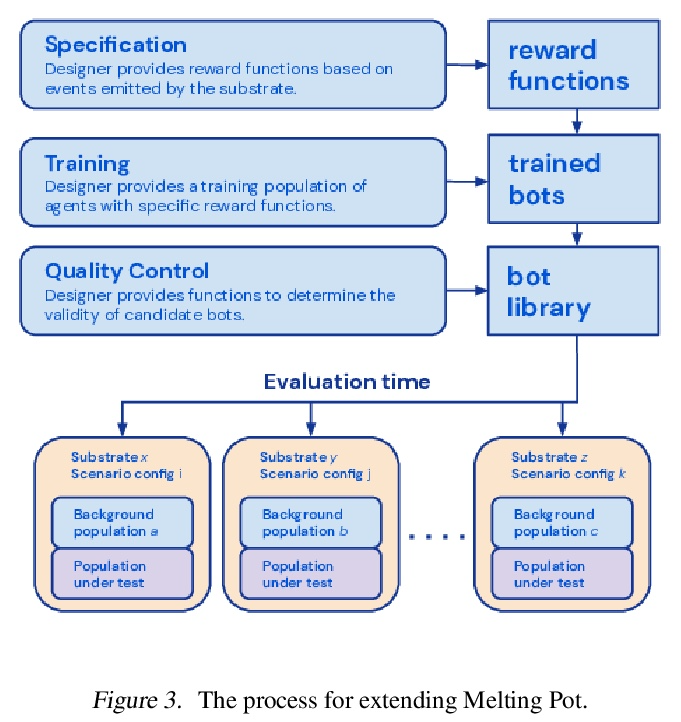
5、[LG] Scalable Evaluation of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Melting Pot
J Z. Leibo, E Duéñez-Guzmán, A S Vezhnevets, J P. Agapiou, P Sunehag, R Koster, J Matyas, C Beattie, I Mordatch, T Graepel
[DeepMind & Google Brain]
基于Melting Pot对多智能体强化学习进行可扩展评估。现有的多智能体强化学习(MARL)评估组件并没有把对新情况的泛化性作为其主要目标(与监督学习基准不同)。本文提出Melting Pot,一个MARL评估组件,填补了这一空白,使用强化学习来减少创建新的测试场景所需的人力劳动。一个智能体的行为构成了另一个智能体的环境(的一部分)。为证明可扩展性,创建了80多个独特的测试场景,涵盖了广泛的研究主题,如社会困境、互惠、资源共享和任务划分。将这些测试场景应用于标准的MARL训练算法,并展示了Melting Pot是如何揭示出仅从训练性能上看不出的弱点的。
Existing evaluation suites for multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) do not assess generalization to novel situations as their primary objective (unlike supervised-learning benchmarks). Our contribution, Melting Pot, is a MARL evaluation suite that fills this gap, and uses reinforcement learning to reduce the human labor required to create novel test scenarios. This works because one agent’s behavior constitutes (part of) another agent’s environment. To demonstrate scalability, we have created over 80 unique test scenarios covering a broad range of research topics such as social dilemmas, reciprocity, resource sharing, and task partitioning. We apply these test scenarios to standard MARL training algorithms, and demonstrate how Melting Pot reveals weaknesses not apparent from training performance alone.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kqtqw9eMp 


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[LG] Universal Approximation for Log-concave Distributions using Well-conditioned Normalizing Flows
基于良好条件化归一化流的对数凹分布通用近似
H Lee, C Pabbaraju, A Sevekari, A Risteski
[Duke University & CMU]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kqtt9jbJ1 
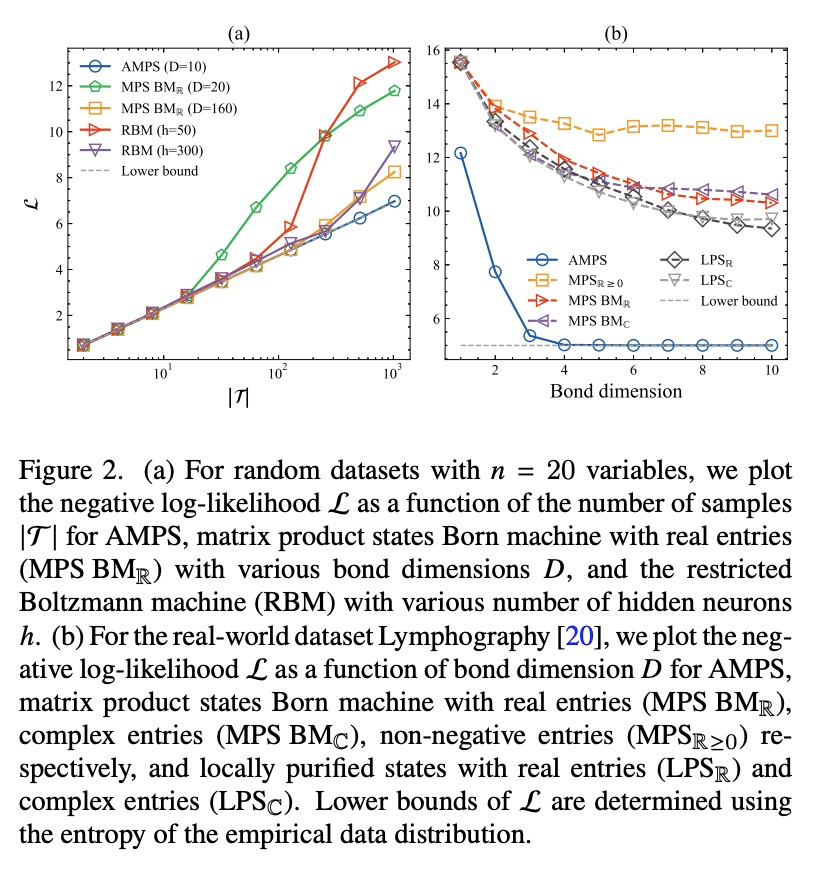
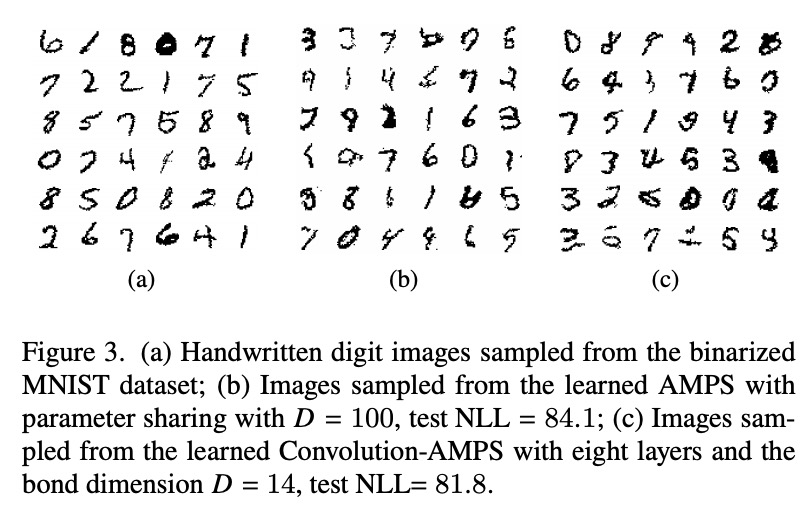
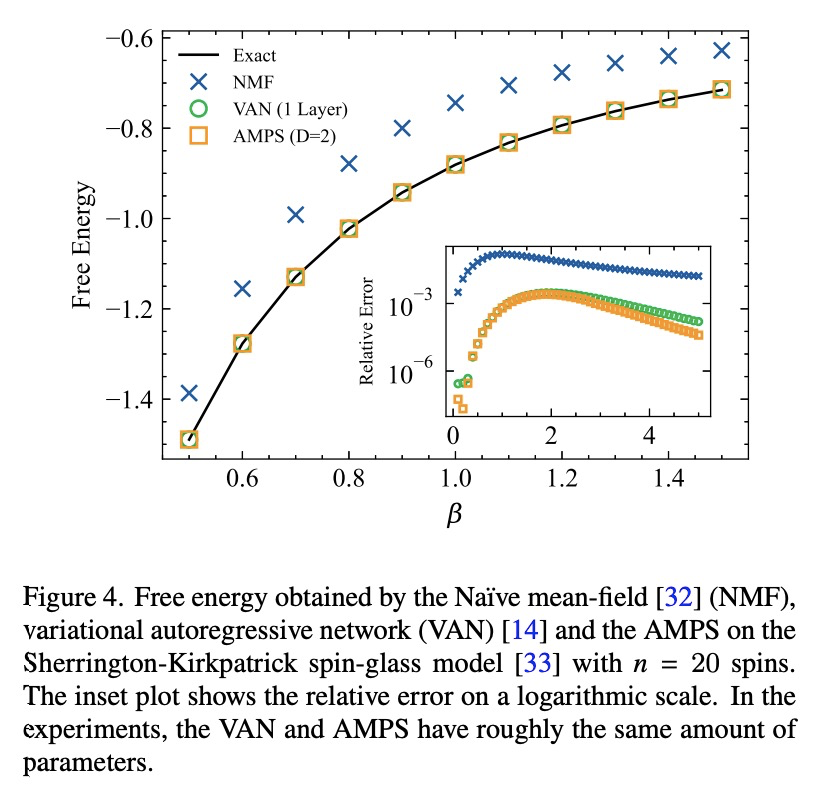
[LG] Tensor networks for unsupervised machine learning
面向无监督机器学习的张量网络
J Liu, S Li, J Zhang, P Zhang
[Beijing Normal University & Chinese Academy of Sciences]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqtvNeFEW 
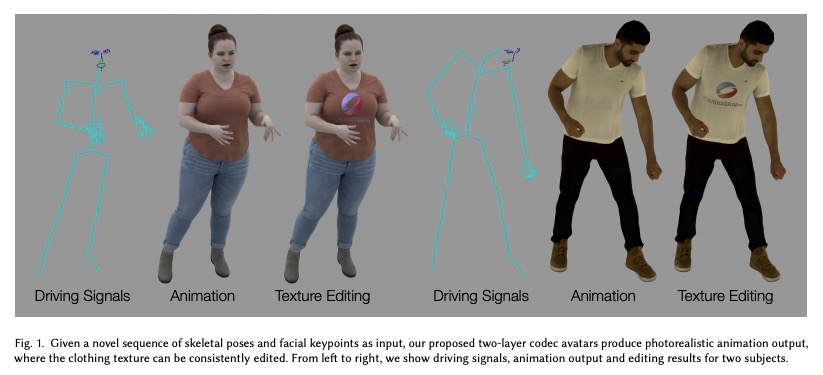
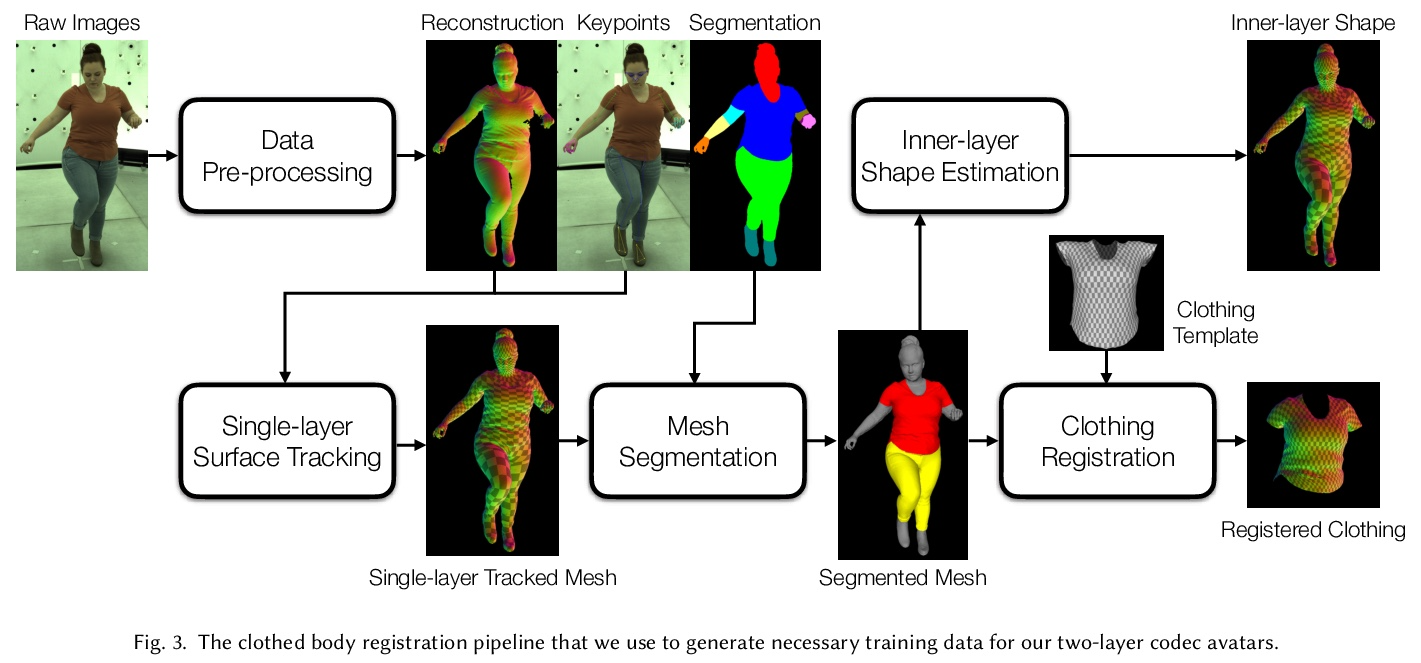
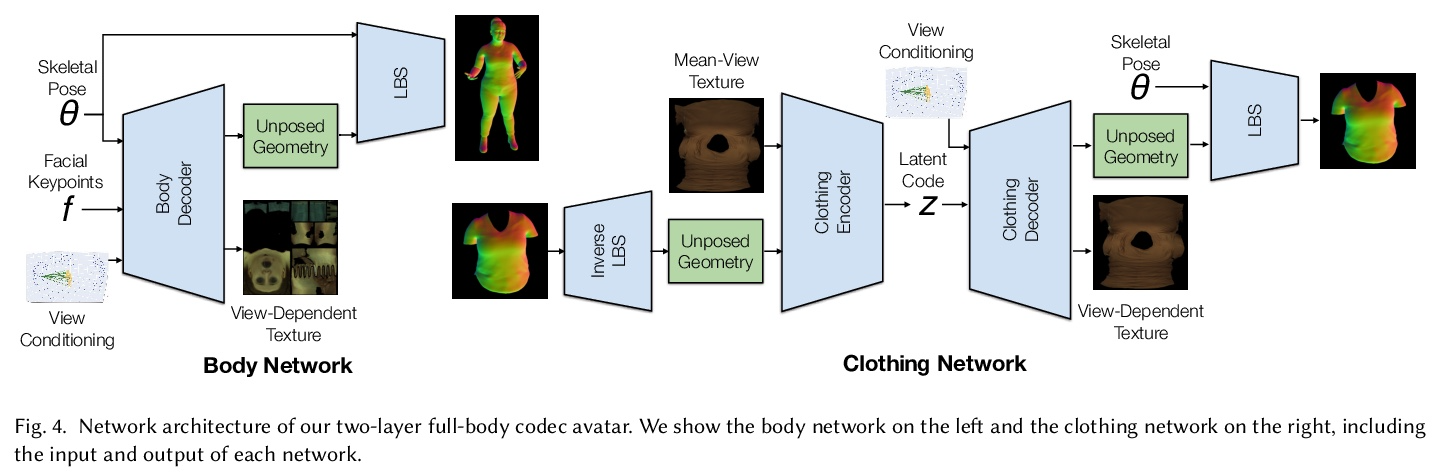
[CV] Explicit Clothing Modeling for an Animatable Full-Body Avatar
可动画化全身化身的显式服装建模
D Xiang, F A Prada, T Bagautdinov, W Xu, Y Dong, H Wen, J Hodgins, C Wu
[CMU & Facebook Reality Labs Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kqty9wS4H 
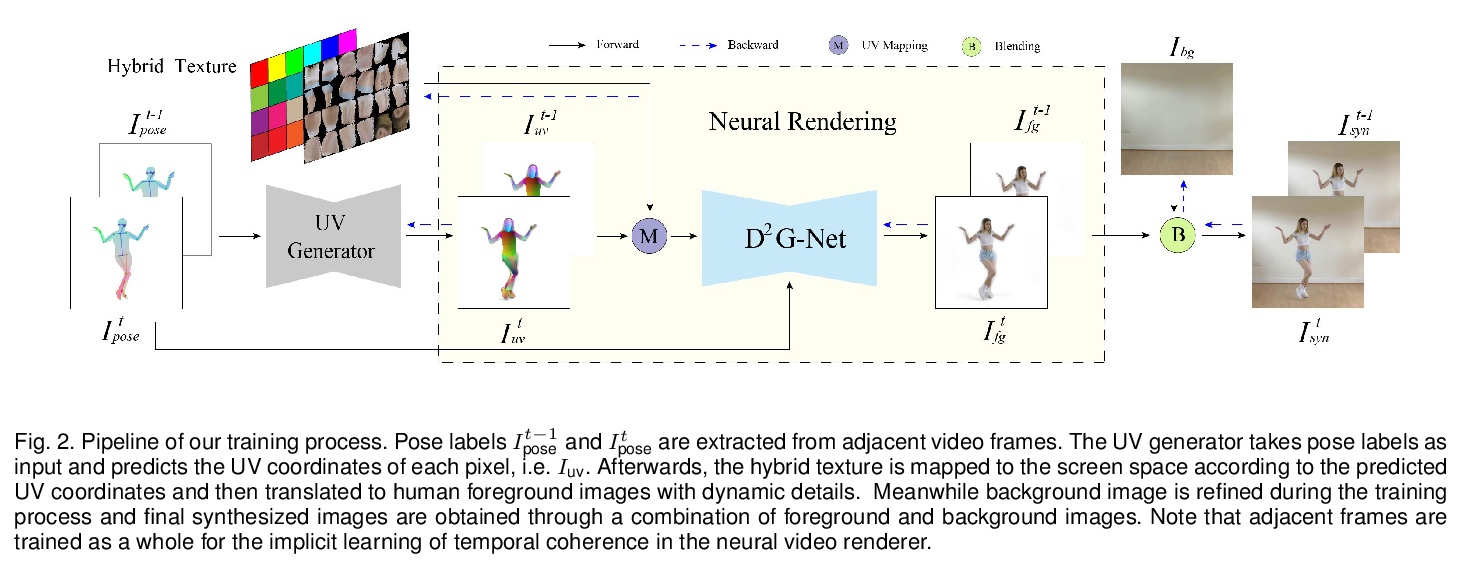
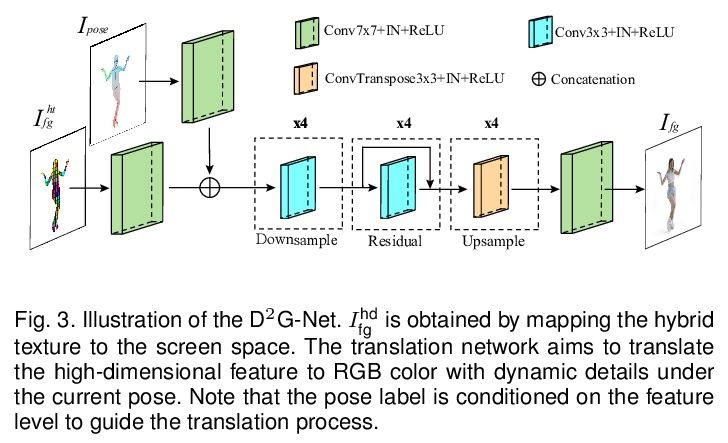
[CV] Robust Pose Transfer with Dynamic Details using Neural Video Rendering
基于神经视频渲染的动态细节鲁棒姿态迁移
Y Sun, H Huang, X Wang, Y Lai, W Liu, L Gao
[Chinese Academy of Sciences & Tencent AI Lab & Cardiff University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqtAtFun9