- 1、[LG] RATT: Leveraging Unlabeled Data to Guarantee Generalization
- 2、[CL] MetaXL: Meta Representation Transformation for Low-resource Cross-lingual Learning
- 3、[CV] Cuboids Revisited: Learning Robust 3D Shape Fitting to Single RGB Images
- 4、[CV] Interactive Monte Carlo Denoising using Affinity of Neural Features
- 5、[CV] Animatable Neural Radiance Fields for Human Body Modeling
- [CL] TABBIE: Pretrained Representations of Tabular Data
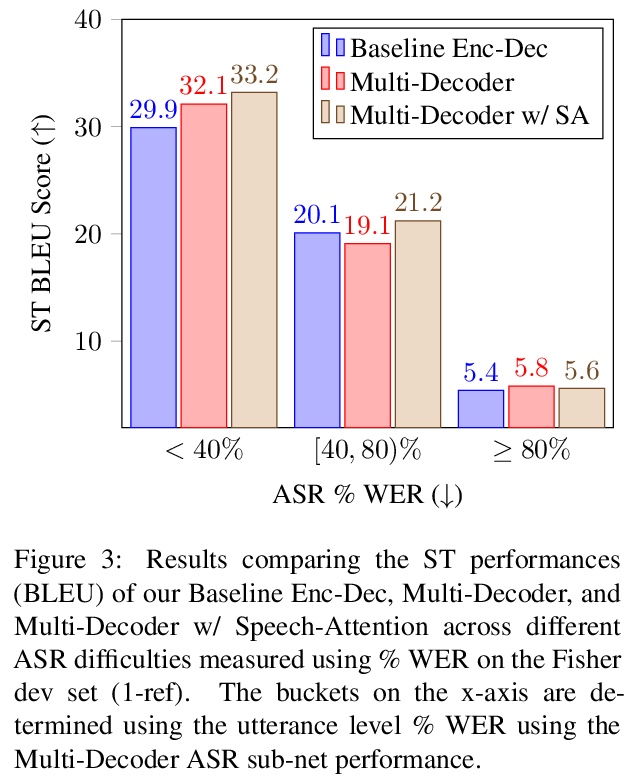
- [CL] Searchable Hidden Intermediates for End-to-End Models of Decomposable Sequence Tasks
- [CV] Unsupervised Layered Image Decomposition into Object Prototypes
- [CV] See through Gradients: Image Batch Recovery via GradInversion
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] RATT: Leveraging Unlabeled Data to Guarantee Generalization
S Garg, S Balakrishnan, J. Z Kolter, Z C. Lipton
[CMU]
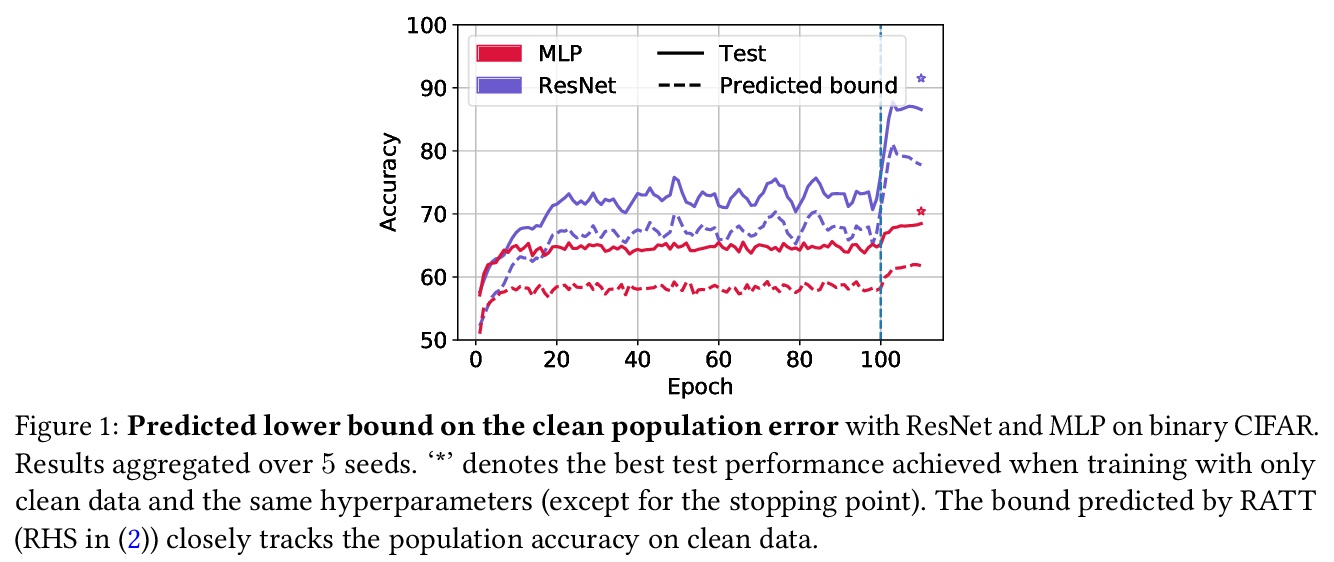
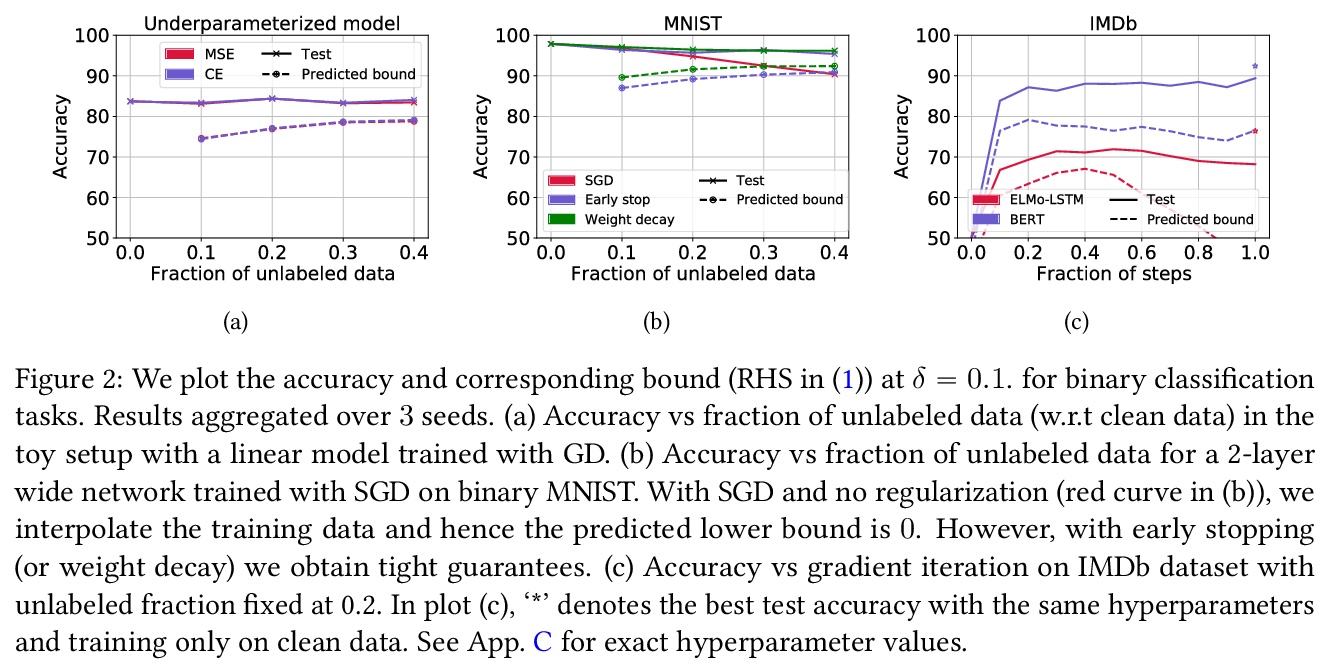
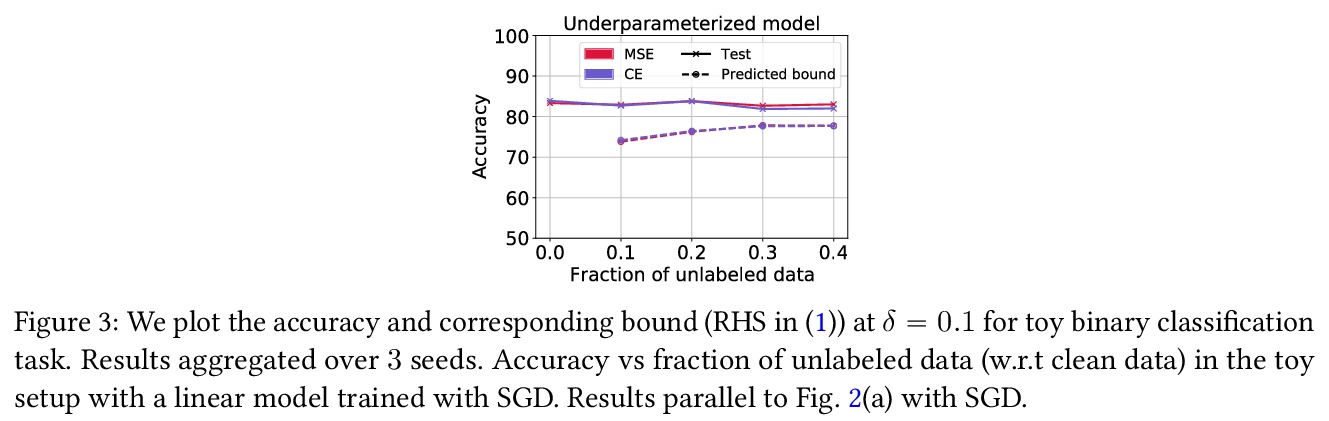
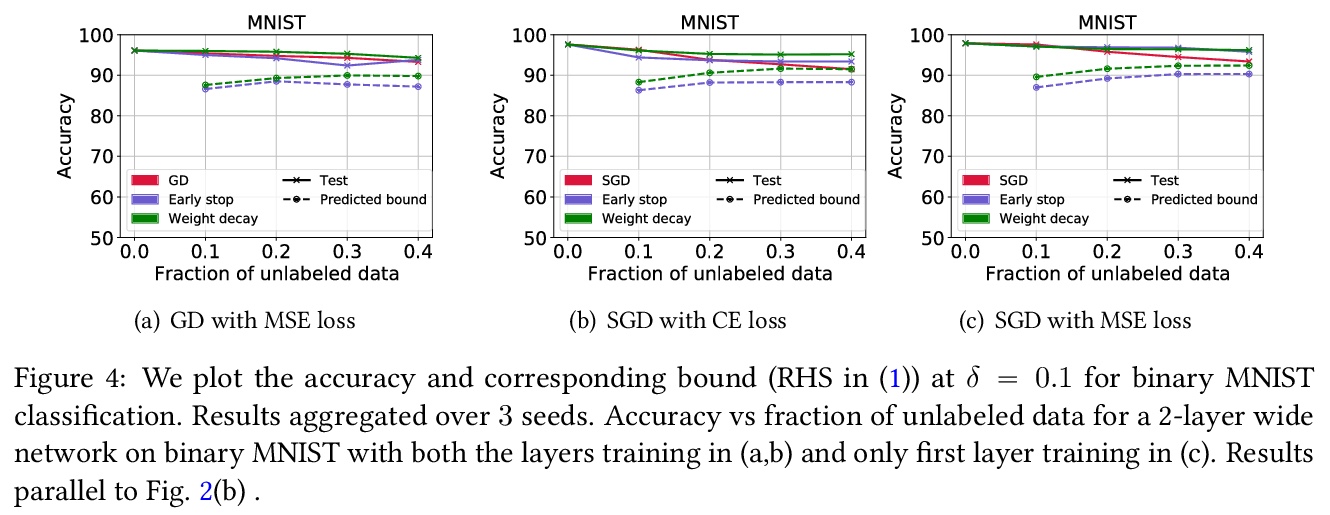
RATT:用无标记数据保证泛化性。为了评估泛化,机器学习科学家们通常要么(i)约束泛化差距,然后(在训练后)插入经验风险以获得真实风险约束;要么(ii)在保留数据上进行经验验证。然而,(i)通常对超参数化模型产生空洞的保证。(ii)缩减了训练集,其保证随着每次重复使用保留集而减弱。本文提出一种利用无标记数据来产生泛化界的方法,以获得不直接依赖于模型类基本复杂性的泛化界。在用随机标记的新样本增强(有标记)训练集后,以标准方式进行训练。当分类器在干净数据上实现低误差,而在含噪数据上实现高误差时,就为真实风险提供了一个严格的上界。证明了该约束对于0-1经验风险最小化和通过梯度下降训练的线性分类器是有效的。该方法在与深度学习结合时特别有用,因为早期学习现象使网络在含噪标记之前拟合真实标记,但需要一个直观的假设。根据经验,在典型的计算机视觉和NLP任务上,该约束提供了非空洞的泛化保证,密切跟踪实际表现。
To assess generalization, machine learning scientists typically either (i) bound the generalization gap and then (after training) plug in the empirical risk to obtain a bound on the true risk; or (ii) validate empirically on holdout data. However, (i) typically yields vacuous guarantees for overparameterized models. Furthermore, (ii) shrinks the training set and its guarantee erodes with each re-use of the holdout set. In this paper, we introduce a method that leverages unlabeled data to produce generalization bounds. After augmenting our (labeled) training set with randomly labeled fresh examples, we train in the standard fashion. Whenever classifiers achieve low error on clean data and high error on noisy data, our bound provides a tight upper bound on the true risk. We prove that our bound is valid for 0-1 empirical risk minimization and with linear classi ers trained by gradient descent. Our approach is especially useful in conjunction with deep learning due to the early learning phenomenon whereby networks fit true labels before noisy labels but requires one intuitive assumption. Empirically, on canonical computer vision and NLP tasks, our bound provides non-vacuous generalization guarantees that track actual performance closely. This work provides practitioners with an option for certifying the generalization of deep nets even when unseen labeled data is unavailable and provides theoretical insights into the relationship between random label noise and generalization.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeL0Utxb8
2、[CL] MetaXL: Meta Representation Transformation for Low-resource Cross-lingual Learning
M Xia, G Zheng, S Mukherjee, M Shokouhi, G Neubig, A H Awadallah
[Princenton University & CMU & Microsoft Research]
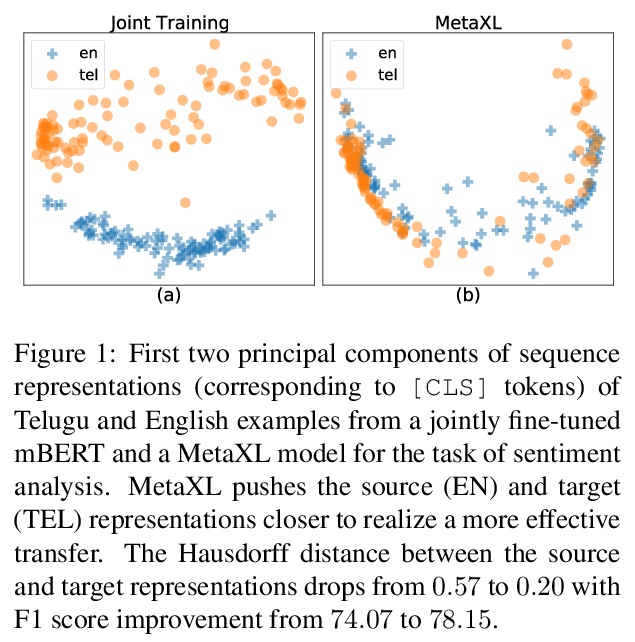
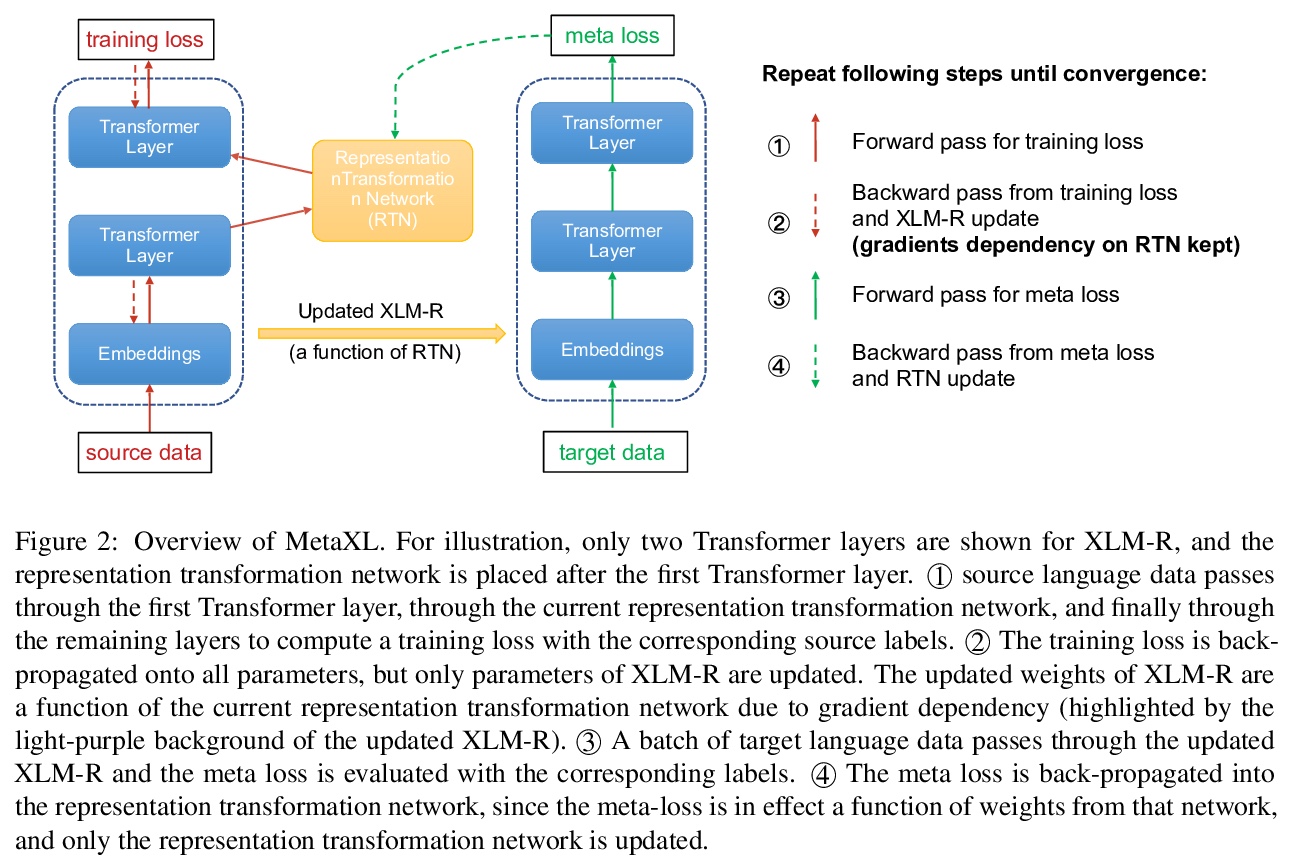
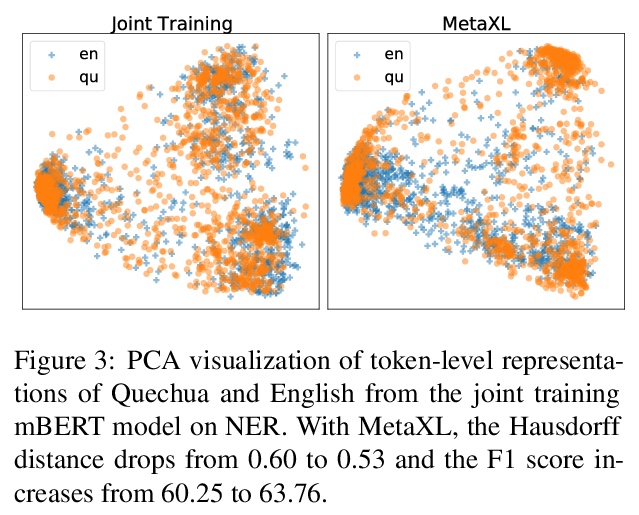
MetaXL: 面向低资源跨语言学习的元表示变换。多语言预训练表示和跨语言迁移学习的结合,是为低资源语言建立功能NLP系统的最有效方法之一。然而,对于那些没有大规模单语语料进行预训练,或没有足够的标注数据进行微调的极低资源语言,迁移学习仍然是一项研究不足且具有挑战性的任务。此外,最近工作表明,多语言表示在不同语言之间是非常不相干的,为迁移到极低资源语言带来了额外的挑战。本文提出基于元学习的框架MetaXL,学习将表示从辅助语言明智地转换到目标语言,并使它们的表示空间更接近,以实现有效的迁移。在现实世界中的低资源语言上进行了广泛的实验——无法获得大规模单语语料库或大量标记数据——用于跨语言情感分析和命名实体识别等任务,该方法的有效性。
The combination of multilingual pre-trained representations and cross-lingual transfer learning is one of the most effective methods for building functional NLP systems for lowresource languages. However, for extremely low-resource languages without large-scale monolingual corpora for pre-training or sufficient annotated data for fine-tuning, transfer learning remains an under-studied and challenging task. Moreover, recent work shows that multilingual representations are surprisingly disjoint across languages (Singh et al., 2019), bringing additional challenges for transfer onto extremely low-resource languages. In this paper, we propose MetaXL, a meta-learning based framework that learns to transform representations judiciously from auxiliary languages to a target one and brings their representation spaces closer for effective transfer. Extensive experiments on real-world low-resource languages – without access to large-scale monolingual corpora or large amounts of labeled data – for tasks like crosslingual sentiment analysis and named entity recognition show the effectiveness of our approach. Code for MetaXL is publicly available at github.com/microsoft/MetaXL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeL6AsIZ9
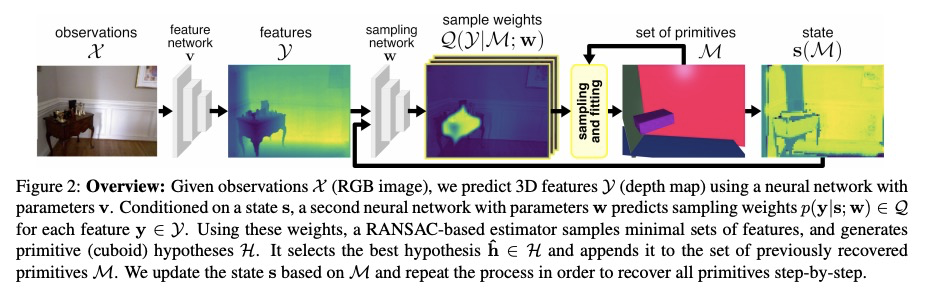
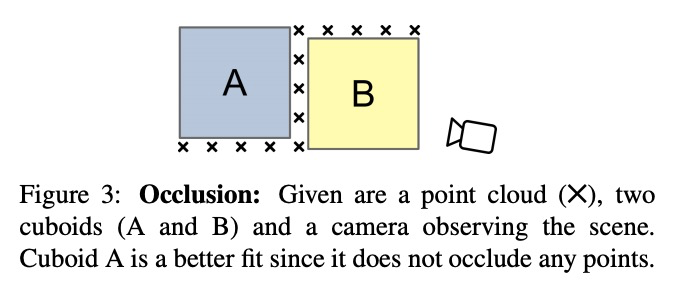
3、[CV] Cuboids Revisited: Learning Robust 3D Shape Fitting to Single RGB Images
F Kluger, H Ackermann, E Brachmann, M Y Yang, B Rosenhahn
[Leibniz University Hannover & Niantic & University of Twente]
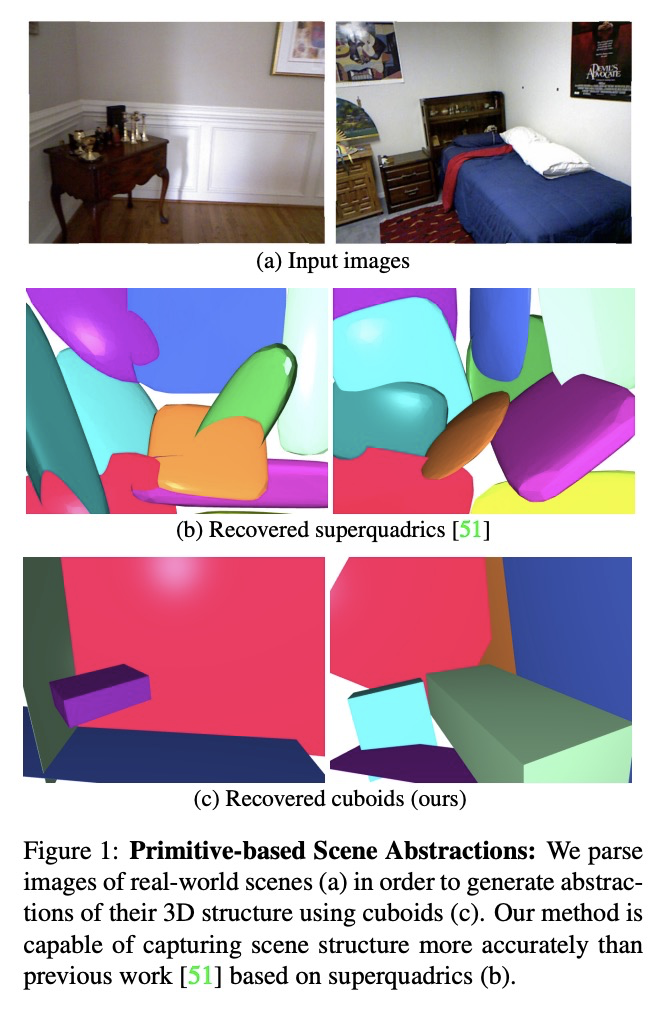
学习用鲁棒3D形状拟合单幅RGB图像。人们将周围世界看作是简单参数化模型的排列,人工环境通常由立方体或圆柱体这样的体基元组成。推断这些基元是实现高层次、抽象场景描述的一个重要步骤。之前的方法直接从二维或三维输入中估计形状参数,只能再现简单物体,无法准确解析更复杂的三维场景。相比之下,本文提出一种鲁棒的基元拟合估计器,用于解析三维场景,可使用立方体有意义地抽象出真实世界的环境。一个由神经网络指导的RANSAC估计器,将这些基元与三维特征(如深度图)相匹配。将之先前检测到的场景部分作为网络的条件,逐一进行解析。为了从单一的RGB图像中获得3D特征,以端到端方式优化了一个特征提取CNN。然而,简单地最小化点到原始距离会导致大的或虚假的立方体遮挡住后面的场景部分,提出一种闭塞感知的距离度量,可以正确处理不透明场景。所提出的算法不需要劳动密集型标记,如立方体标记,用于训练。在具有挑战性的NYU Depth v2数据集上的结果表明,所提出的算法成功地抽象出杂乱的现实世界的三维场景布局。
Humans perceive and construct the surrounding world as an arrangement of simple parametric models. In particular, man-made environments commonly consist of volumetric primitives such as cuboids or cylinders. Inferring these primitives is an important step to attain high-level, abstract scene descriptions. Previous approaches directly estimate shape parameters from a 2D or 3D input, and are only able to reproduce simple objects, yet unable to accurately parse more complex 3D scenes. In contrast, we propose a robust estimator for primitive fitting, which can meaningfully abstract real-world environments using cuboids. A RANSAC estimator guided by a neural network fits these primitives to 3D features, such as a depth map. We condition the network on previously detected parts of the scene, thus parsing it one-by-one. To obtain 3D features from a single RGB image, we additionally optimise a feature extraction CNN in an end-to-end manner. However, naively minimising pointto-primitive distances leads to large or spurious cuboids occluding parts of the scene behind. We thus propose an occlusion-aware distance metric correctly handling opaque scenes. The proposed algorithm does not require labourintensive labels, such as cuboid annotations, for training. Results on the challenging NYU Depth v2 dataset demonstrate that the proposed algorithm successfully abstracts cluttered real-world 3D scene layouts.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeLaTxXrO

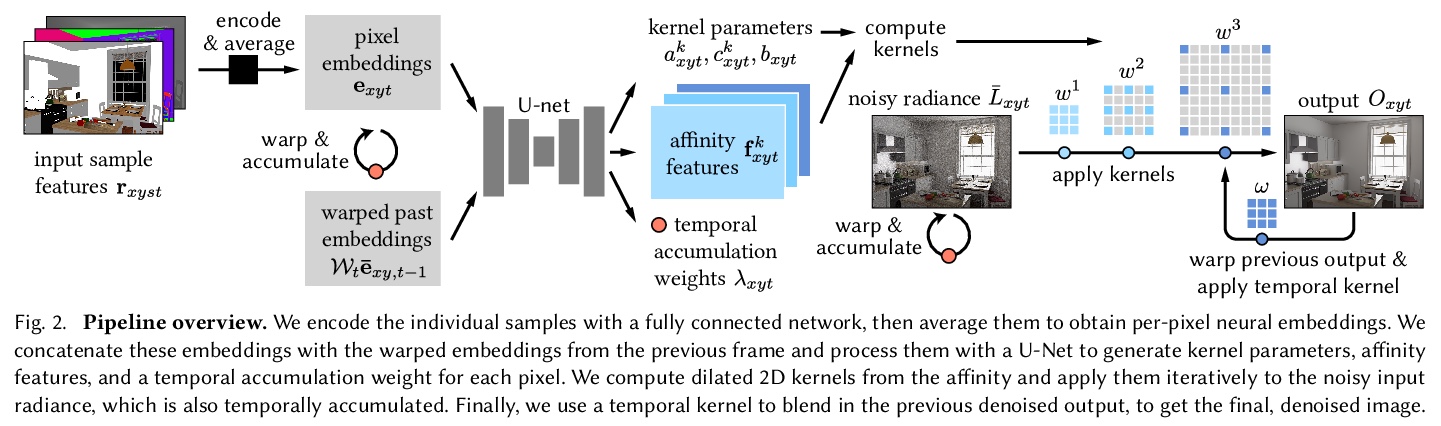
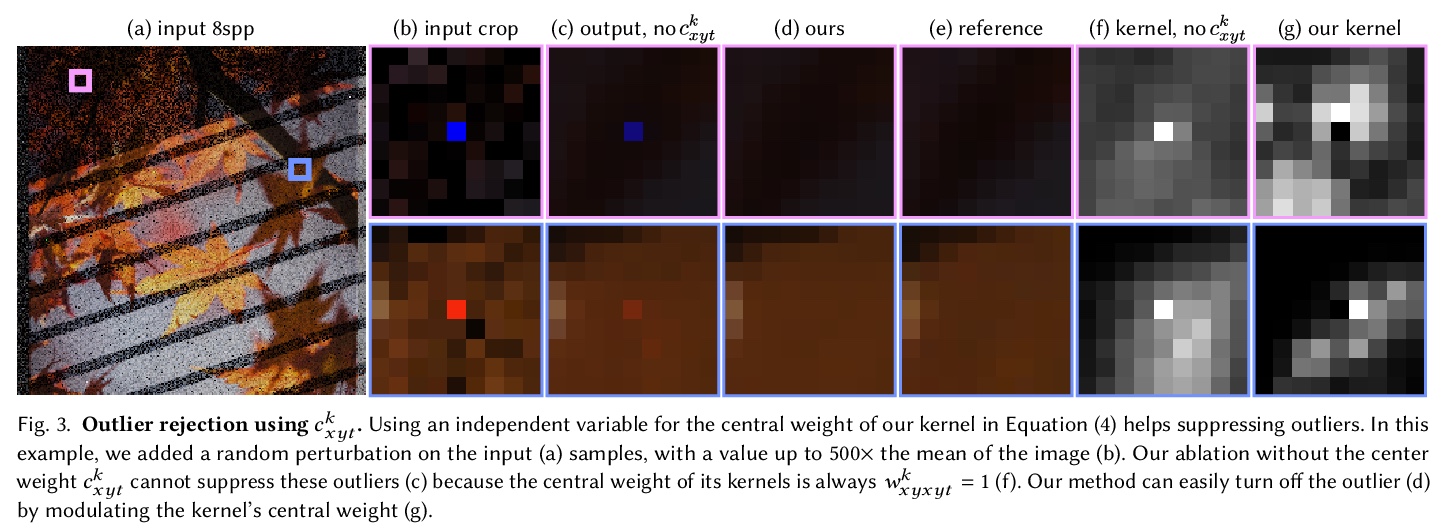
4、[CV] Interactive Monte Carlo Denoising using Affinity of Neural Features
M işik, K Mullia, M Fisher, J Eisenmann, M Gharbi
[Technical University of Munich & Adobe]
基于神经特征亲和力的交互式蒙特卡洛去噪。蒙特卡洛低采样渲染的高质量去噪仍然是实际交互式光线追踪的一个关键挑战。本文提出一种新的基于学习的去噪器,能达到最先进的质量,并能以交互式速率运行。模型用一个轻量的神经网络来处理各路径追踪的采样,以提取每像素的特征向量,管线的其余部分在像素空间运行。在像素邻域的特征上定义了一个新的成对亲和力,从该亲和力中组合出扩张空间核来过滤噪声辐射。该去噪器在时间上是稳定的,这归功于两个机制:首先,用具有学习权重的每像素递归滤波器,保持噪声辐射度和中间特征的运行平均值。其次,用一个基于连续帧特征间成对亲和力的小型时间核。实验表明,与计算成本相当的技术相比,新亲和力导致了更高的输出质量,并且比核预测方法有更好的高频细节。该模型在低采样数系统中与最先进的离线去噪器相匹配或优于后者,在1080p分辨率下以交互式帧速率运行。
High-quality denoising of Monte Carlo low-sample renderings remains a critical challenge for practical interactive ray tracing. We present a new learning-based denoiser that achieves state-of-the-art quality and runs at interactive rates. Our model processes individual path-traced samples with a lightweight neural network to extract per-pixel feature vectors. The rest of our pipeline operates in pixel space. We define a novel pairwise affinity over the features in a pixel neighborhood, from which we assemble dilated spatial kernels to filter the noisy radiance. Our denoiser is temporally stable thanks to two mechanisms. First, we keep a running average of the noisy radiance and intermediate features, using a per-pixel recursive filter with learned weights. Second, we use a small temporal kernel based on the pairwise affinity between features of consecutive frames. Our experiments show our new affinities lead to higher quality outputs than techniques with comparable computational costs, and better high-frequency details than kernel-predicting approaches. Our model matches or outperfoms state-ofthe-art offline denoisers in the low-sample count regime (2–8 samples per pixel), and runs at interactive frame rates at 1080p resolution.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeLg6wlj0


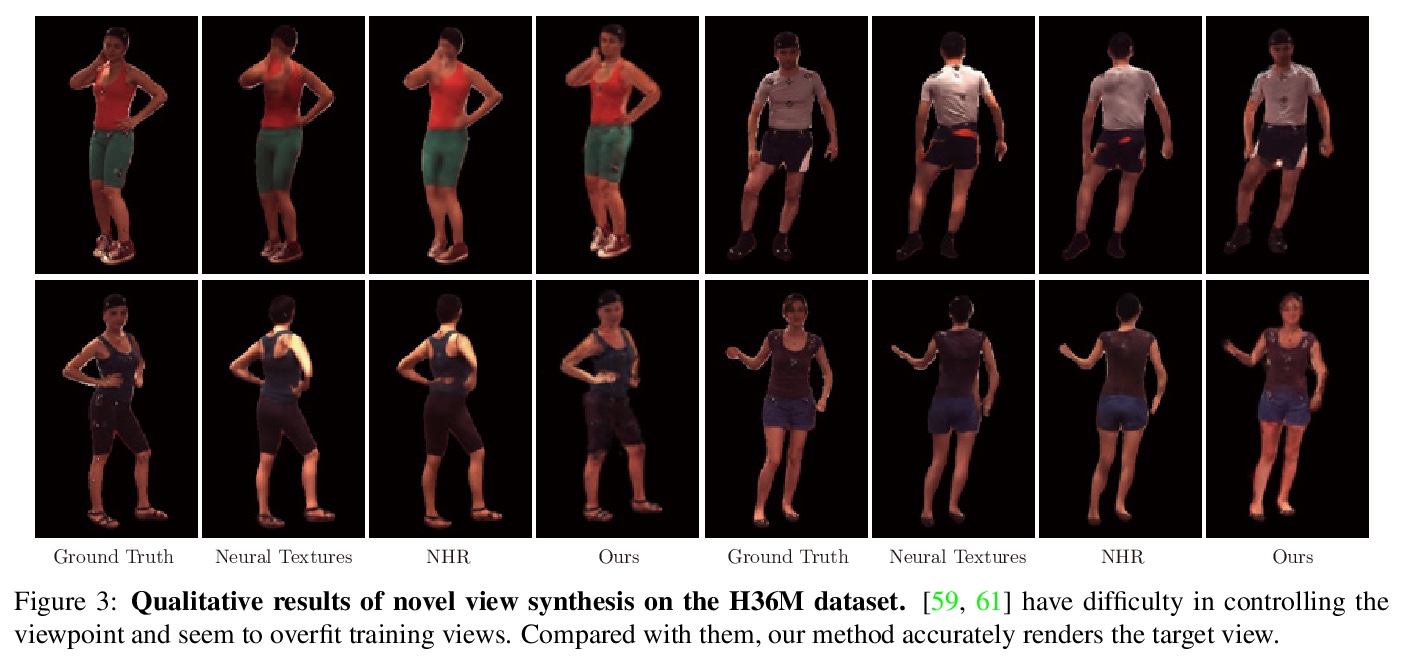
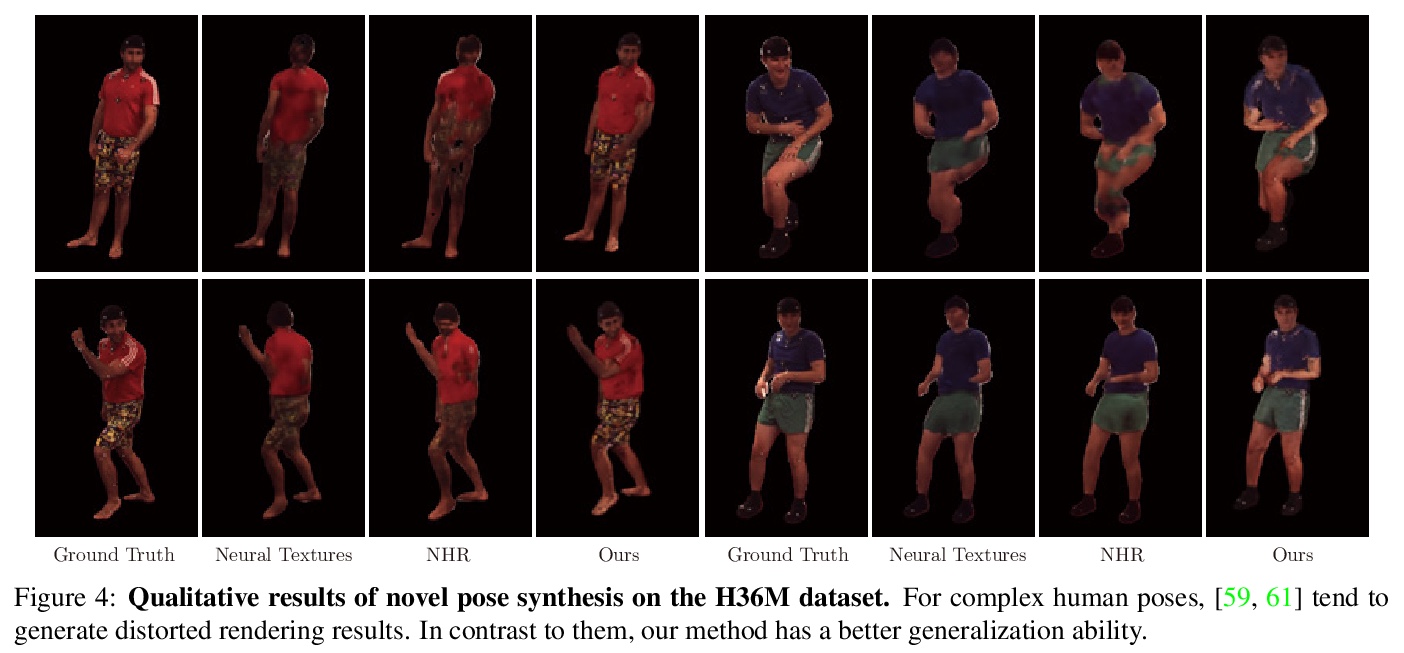
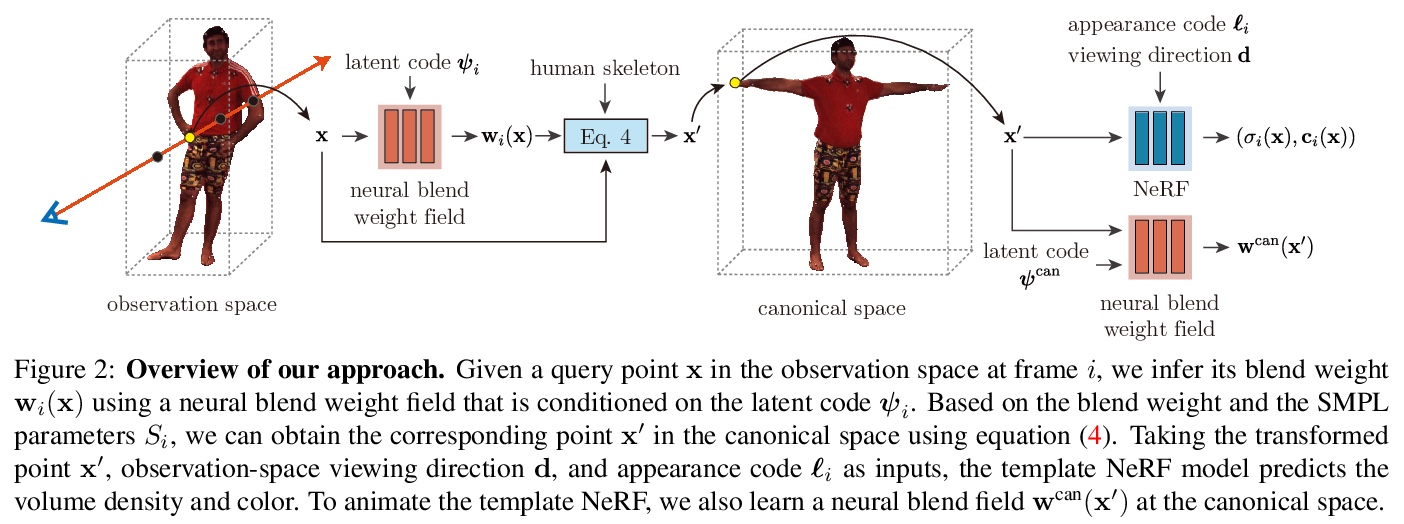
5、[CV] Animatable Neural Radiance Fields for Human Body Modeling
S Peng, J Dong, Q Wang, S Zhang, Q Shuai, H Bao, X Zhou
[Zhejiang University & Cornell University]
可动画化神经辐射场人体建模。讨论了从多视角视频重建可动画人体模型的挑战。最近一些工作建议将动态场景分解为一个规范化神经辐射场和一组变形场,将观察空间的点映射到规范化空间,使其能从图像中学习动态场景。然而,将变形场表示为平移矢量场,会使得优化严重受限,这些表示不能由输入运动明确控制。本文提出神经混合权重场来产生变形场。基于骨架驱动的变形,混合权重场与三维人体骨架一起使用,以产生观察-规范化和规范化-观察的对应关系。由于三维人体骨架更易观察,可以使变形场的学习规范化。此外,学到的混合权重场可以与输入的骨架运动结合起来,生成新的变形场,为人体模型制作动画。实验表明,该方法明显优于最近的人体合成方法。
This paper addresses the challenge of reconstructing an animatable human model from a multi-view video. Some recent works have proposed to decompose a dynamic scene into a canonical neural radiance field and a set of deformation fields that map observation-space points to the canonical space, thereby enabling them to learn the dynamic scene from images. However, they represent the deformation field as translational vector field or SE(3) field, which makes the optimization highly under-constrained. Moreover, these representations cannot be explicitly controlled by input motions. Instead, we introduce neural blend weight fields to produce the deformation fields. Based on the skeletondriven deformation, blend weight fields are used with 3D human skeletons to generate observation-to-canonical and canonical-to-observation correspondences. Since 3D human skeletons are more observable, they can regularize the learning of deformation fields. Moreover, the learned blend weight fields can be combined with input skeletal motions to generate new deformation fields to animate the human model. Experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms recent human synthesis methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeLlnozHC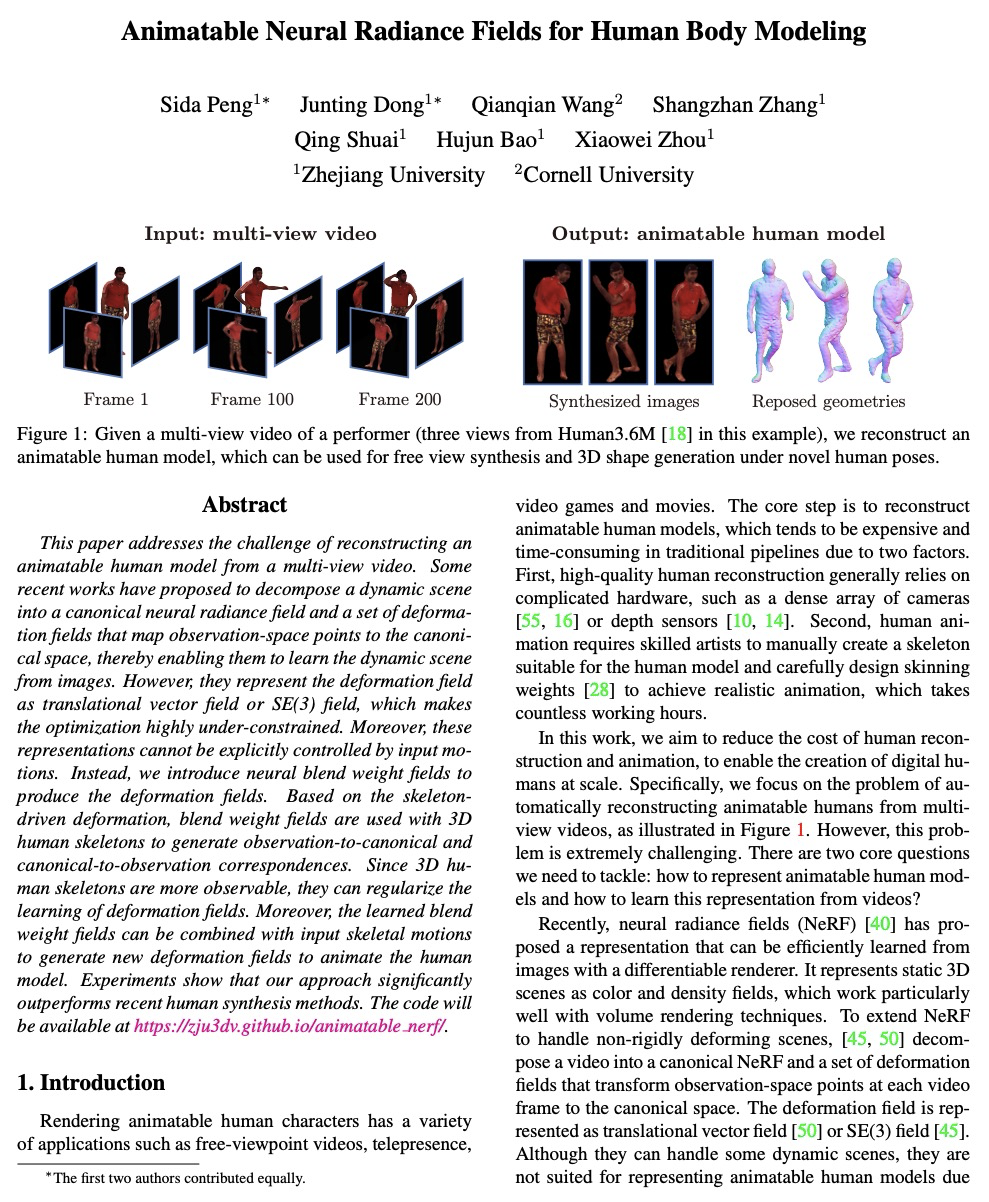


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
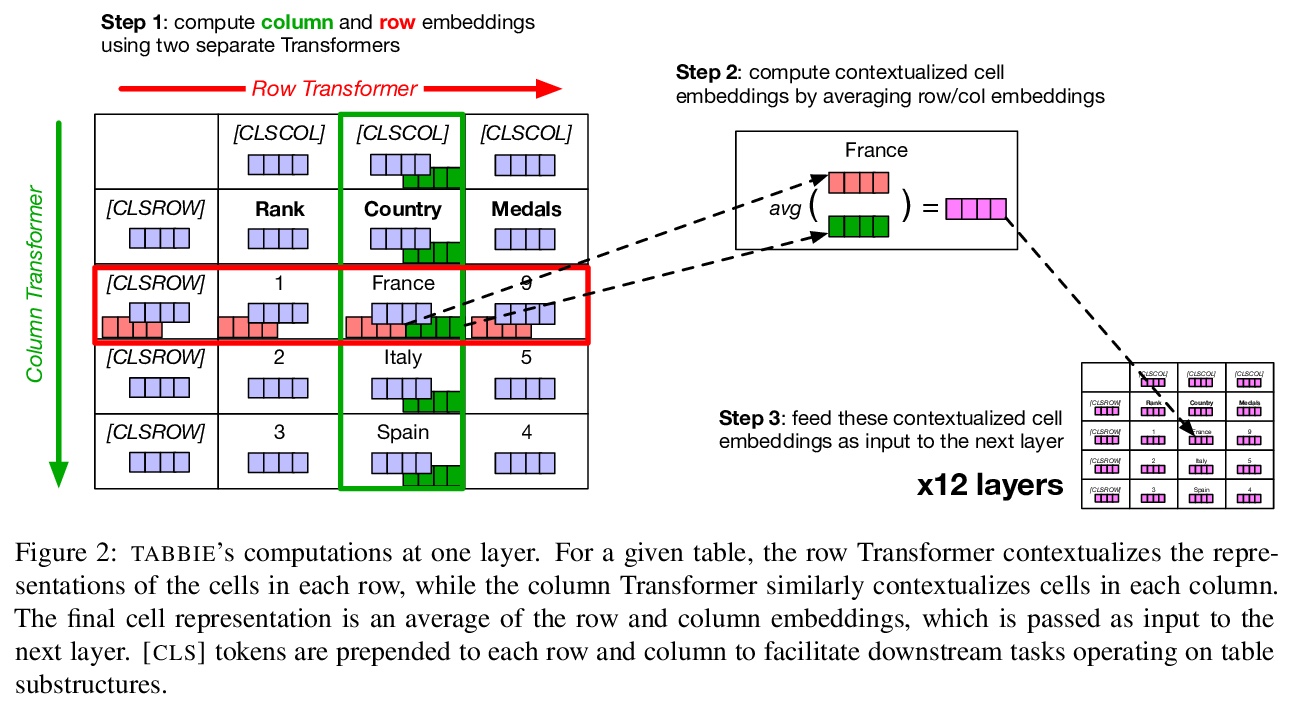
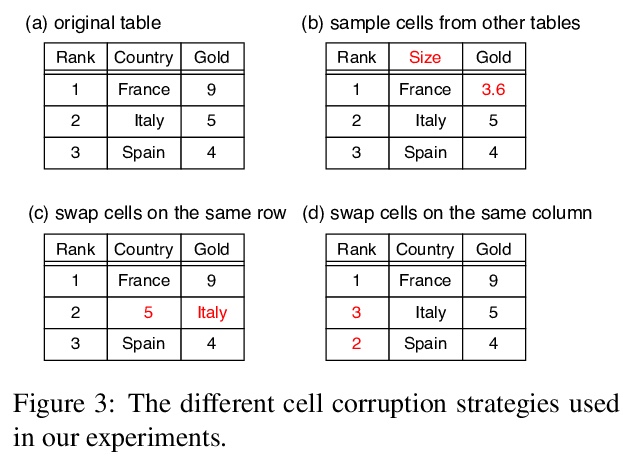
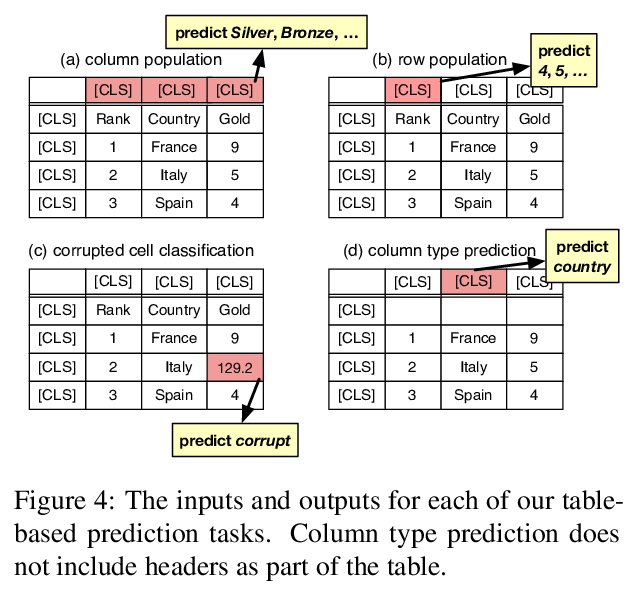
[CL] TABBIE: Pretrained Representations of Tabular Data
TABBIE:表格数据的预训练表示
H Iida, D Thai, V Manjunatha, M Iyyer
[Sony Corporation & UMass Amherst & Adobe Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeLp5eTrR
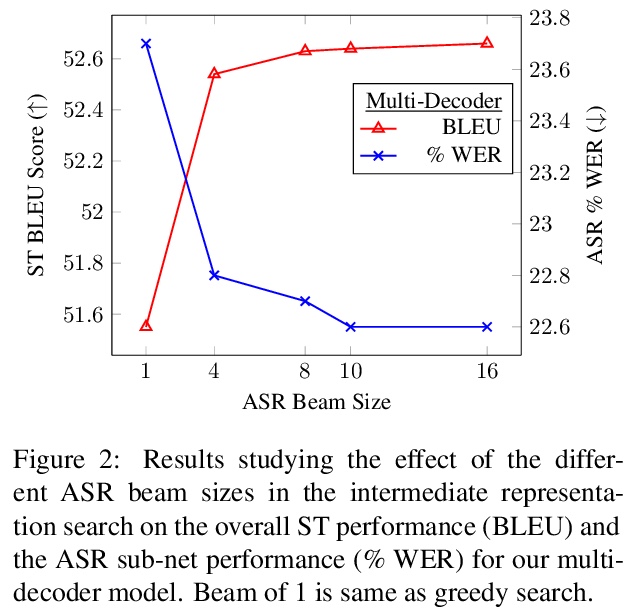
[CL] Searchable Hidden Intermediates for End-to-End Models of Decomposable Sequence Tasks
基于可搜索隐藏中间体的可分解序列任务端到端模型
S Dalmia, B Yan, V Raunak, F Metze, S Watanabe
[CMU]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeLqBvAUe

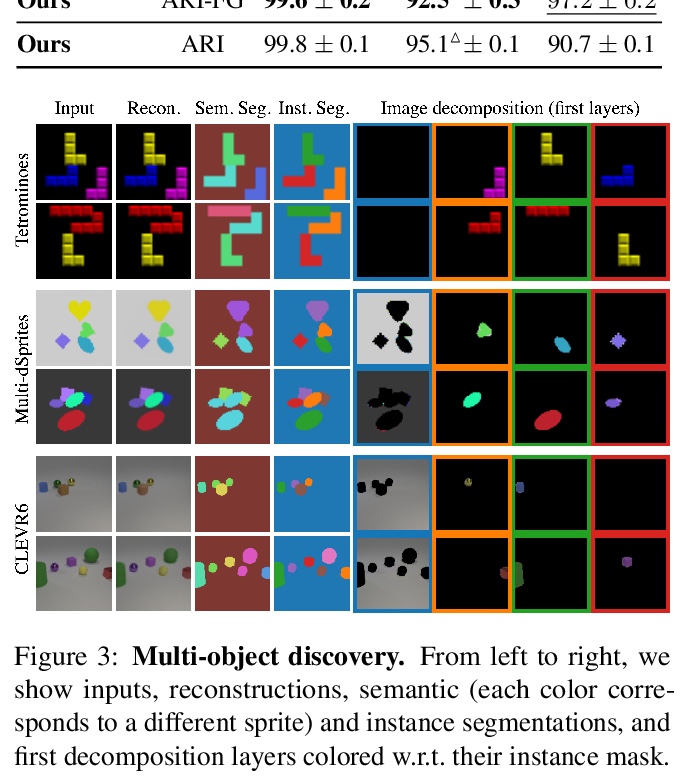
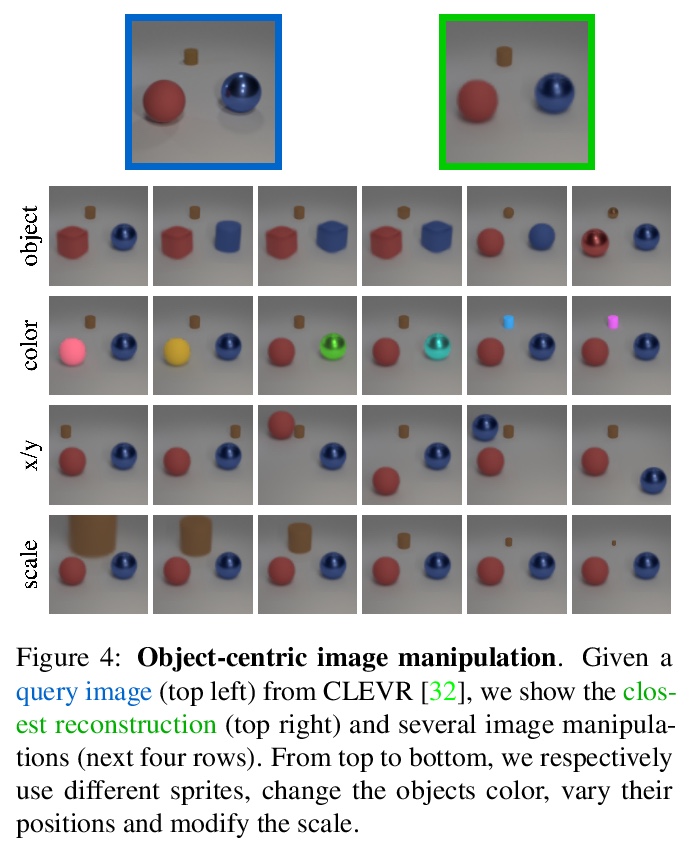
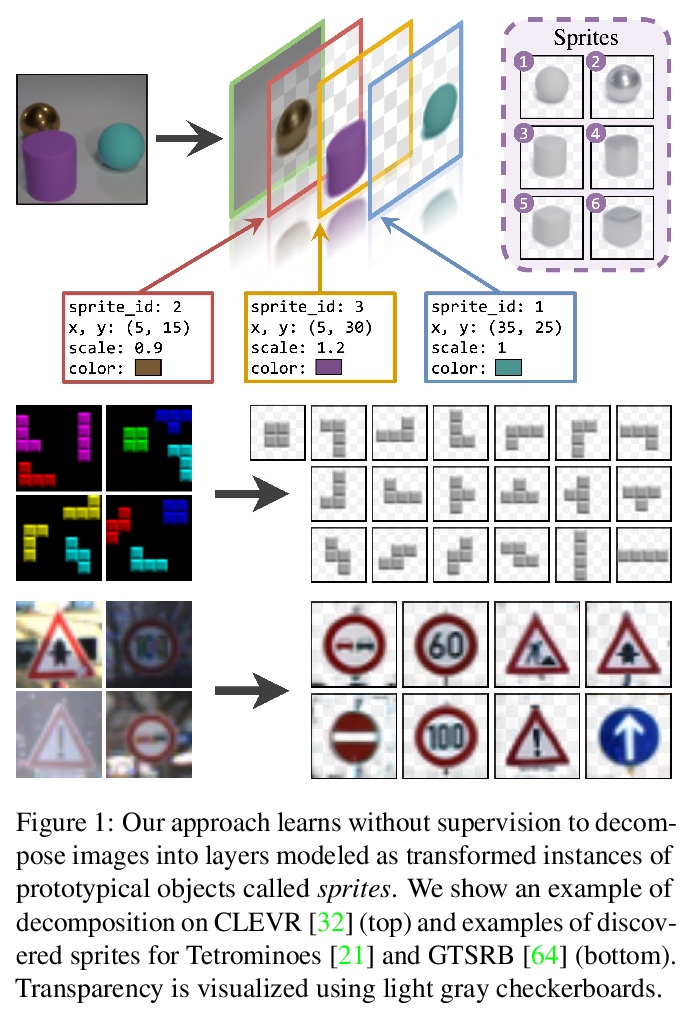
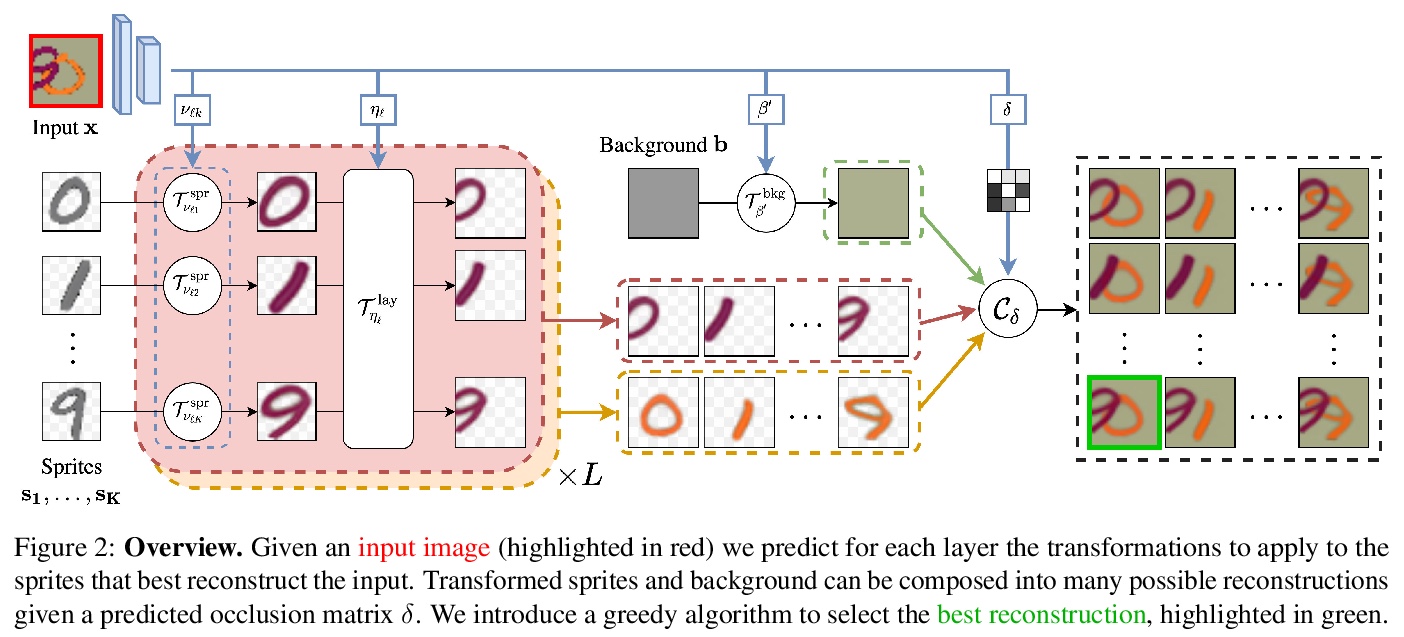
[CV] Unsupervised Layered Image Decomposition into Object Prototypes
无监督分层图像分解到对象原型
T Monnier, E Vincent, J Ponce, M Aubry
[Univ Gustave Eiffel & PSL Research University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeLsBAQsQ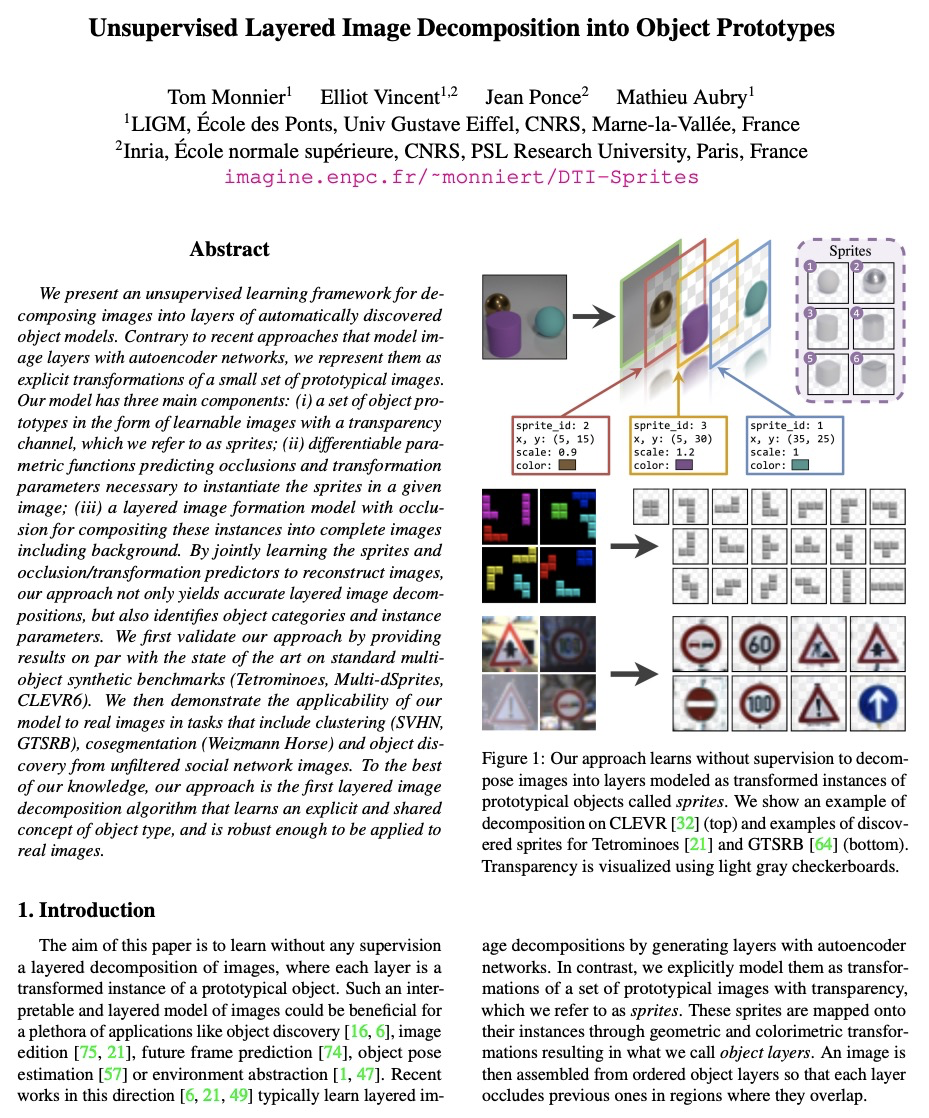


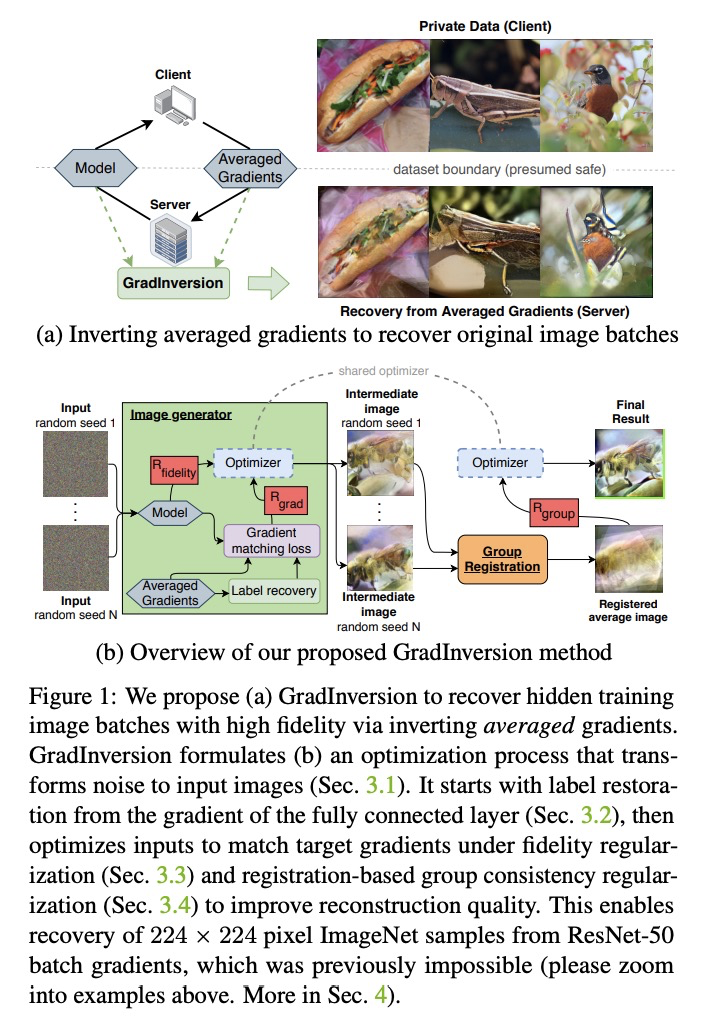
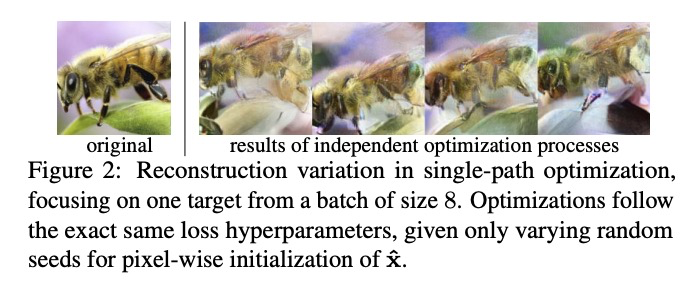
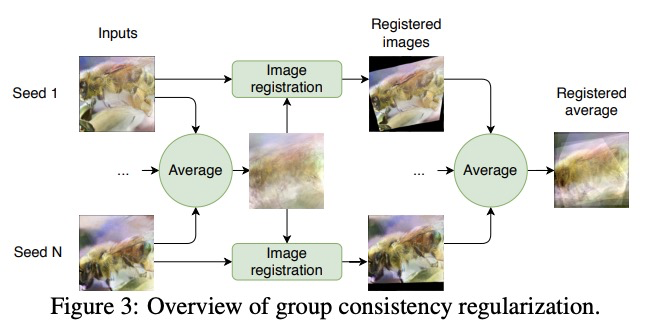
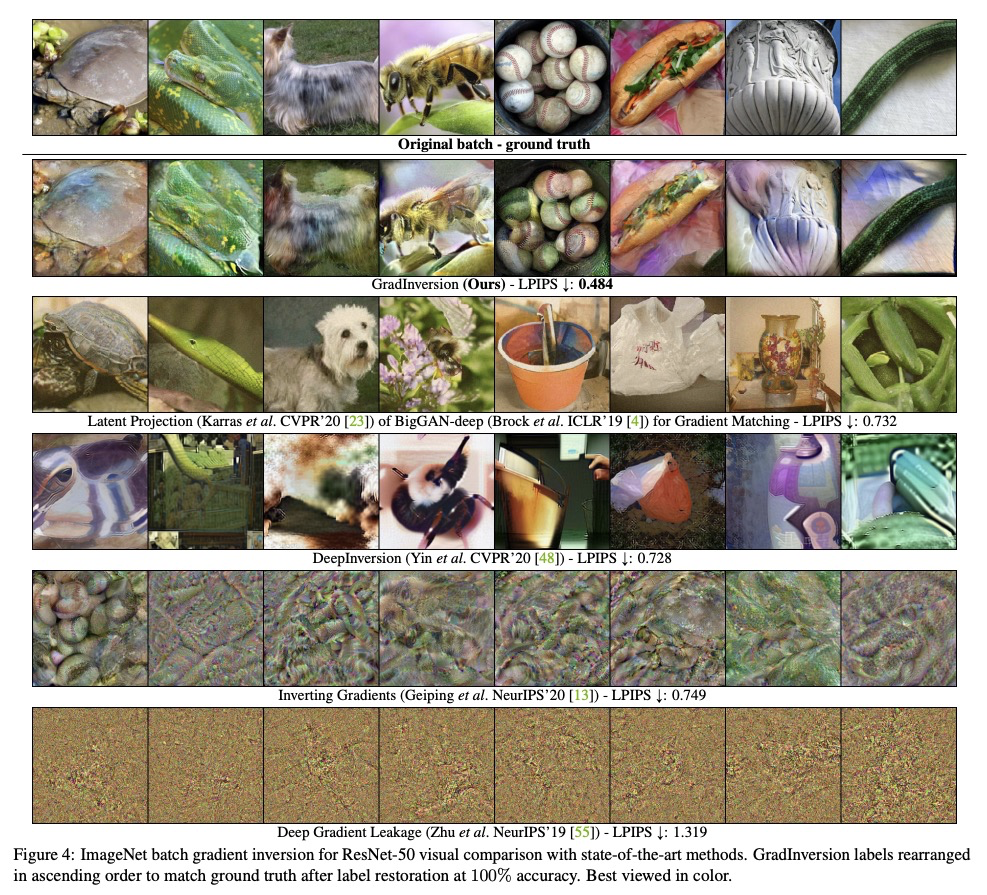
[CV] See through Gradients: Image Batch Recovery via GradInversion
基于GradInversion的图像批恢复
H Yin, A Mallya, A Vahdat, J M. Alvarez, J Kautz, P Molchanov
[NVIDIA]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeLuZ6k58