- 1、[LG] Optimal Rates for Averaged Stochastic Gradient Descent under Neural Tangent Kernel Regime
- 2、[LG] Rethinking Architecture Selection in Differentiable NAS
- 3、[CL] Share or Not? Learning to Schedule Language-Specific Capacity for Multilingual Translation
- 4、[LG] Learning with Feature-Dependent Label Noise: A Progressive Approach
- 5、[LG] Metadata Normalization
- [RO] OmniHang: Learning to Hang Arbitrary Objects using Contact Point Correspondences and Neural Collision Estimation
- [CV] High-fidelity Face Tracking for AR/VR via Deep Lighting Adaptation
- [LG] Muesli: Combining Improvements in Policy Optimization
- [LG] Differentiable Model Compression via Pseudo Quantization Noise
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
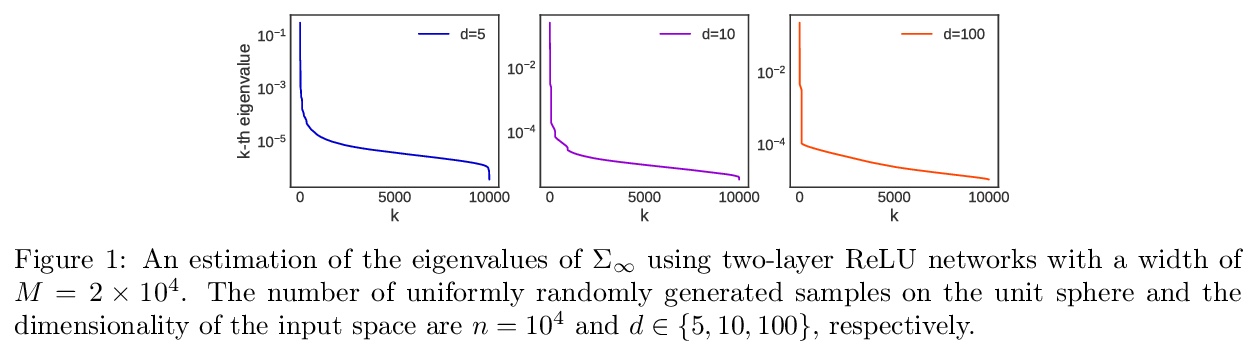
1、[LG] Optimal Rates for Averaged Stochastic Gradient Descent under Neural Tangent Kernel Regime
A Nitanda, T Suzuki
[The University of Tokyo]
神经切线核平均随机梯度下降最佳速率。分析了用于回归问题的超参数化两层神经网络的平均随机梯度下降的收敛性。最近发现,在神经切核(NTK)体制下,超参数化神经网络的学习动态大多可以由相关的再现核Hilbert空间(RKHS)来描述,NTK在揭示基于梯度的方法的全局收敛方面起着重要作用。然而,在NTK体制下,仍然存在着收敛率分析的空间。本文展示了平均随机梯度下降法的全局收敛性,利用目标函数和与NTK相关的RKHS的复杂性,推导出最佳收敛率。在一定条件下,通过对ReLU网络的平滑逼近,ReLU网络的NTK所指定的目标函数可以以最佳收敛率进行学习。
We analyze the convergence of the averaged stochastic gradient descent for over-parameterized two-layer neural networks for regression problems. It was recently found that, under the neural tangent kernel (NTK) regime, where the learning dynamics for overparameterized neural networks can be mostly characterized by that for the associated reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS), an NTK plays an important role in revealing the global convergence of gradient-based methods. However, there is still room for a convergence rate analysis in the NTK regime. In this study, we show the global convergence of the averaged stochastic gradient descent and derive the optimal convergence rate by exploiting the complexities of the target function and the RKHS associated with the NTK. Moreover, we show that the target function specified by the NTK of a ReLU network can be learned at the optimal convergence rate through a smooth approximation of ReLU networks under certain conditions.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcD6E1N9m
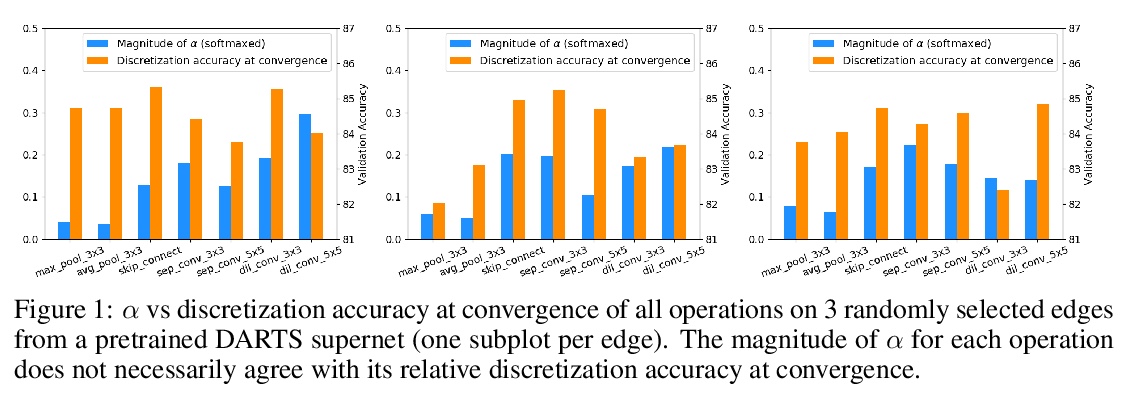
2、[LG] Rethinking Architecture Selection in Differentiable NAS
R Wang, M Cheng, X Chen, X Tang, C Hsieh
[UCLA & DiDi AI Labs]
可微神经网络架构搜索(NAS)架构选择的反思。可微神经架构搜索是最受欢迎的神经架构搜索(NAS)方法之一,因为其搜索效率和简单性,通过基于梯度的算法在权重分享超网中共同优化模型权重和结构参数来完成。在搜索阶段结束时,具有最大架构参数的操作将被选中,形成最终的架构,隐含的假设是架构参数的值反映了操作的强度。虽然关于超网的优化已经讨论了很多,但架构选择过程却很少得到关注。经验和理论分析表明,架构参数的大小并不一定表明该操作对超网的性能有多大贡献。本文试图从架构选择的角度来理解可微NAS方法,提出另一种基于扰动的架构选择方法,通过其对超网性能的贡献直接测量操作强度。用提议的架构选择重新评估了几个可微的NAS方法,发现其能从底层超网中持续提取明显改进的架构。DARTS的几种失败模式可以通过所提出的选择方法得到极大缓解,表明在DARTS中观察到的大部分不良泛化现象可以归因于基于量级的架构选择的失败,而不完全是其超网的优化。
Differentiable Neural Architecture Search is one of the most popular Neural Architecture Search (NAS) methods for its search efficiency and simplicity, accomplished by jointly optimizing the model weight and architecture parameters in a weight-sharing supernet via gradient-based algorithms. At the end of the search phase, the operations with the largest architecture parameters will be selected to form the final architecture, with the implicit assumption that the values of architecture parameters reflect the operation strength. While much has been discussed about the supernet’s optimization, the architecture selection process has received little attention. We provide empirical and theoretical analysis to show that the magnitude of architecture parameters does not necessarily indicate how much the operation contributes to the supernet’s performance. We propose an alternative perturbation-based architecture selection that directly measures each operation’s influence on the supernet. We re-evaluate several differentiable NAS methods with the proposed architecture selection and find that it is able to extract significantly improved architectures from the underlying supernets consistently. Furthermore, we find that several failure modes of DARTS can be greatly alleviated with the proposed selection method, indicating that much of the poor generalization observed in DARTS can be attributed to the failure of magnitude-based architecture selection rather than entirely the optimization of its supernet.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcDatyYvo
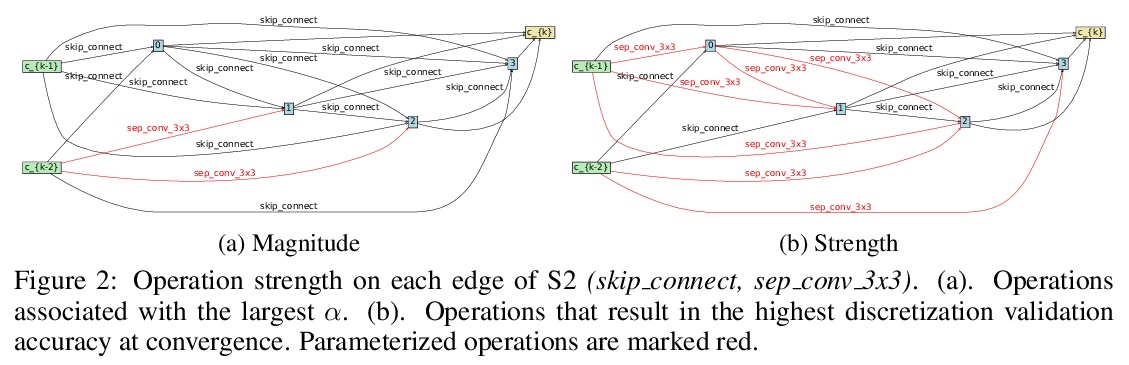

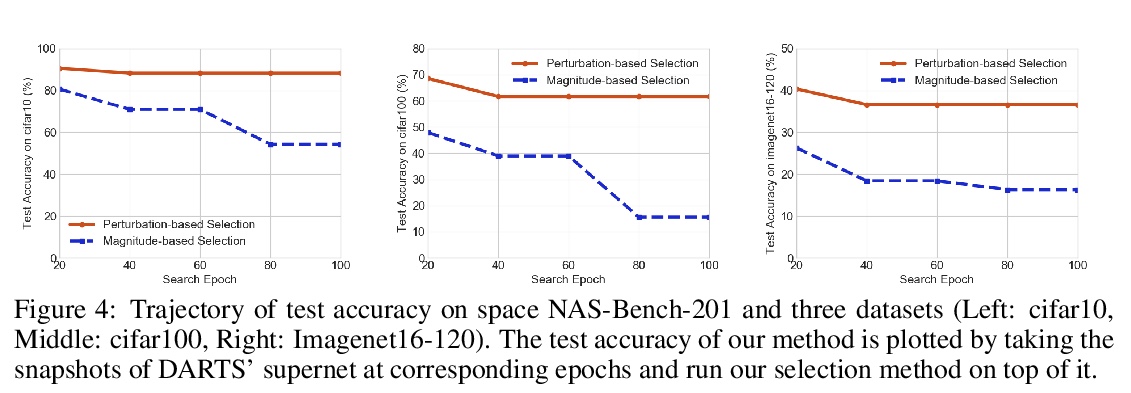
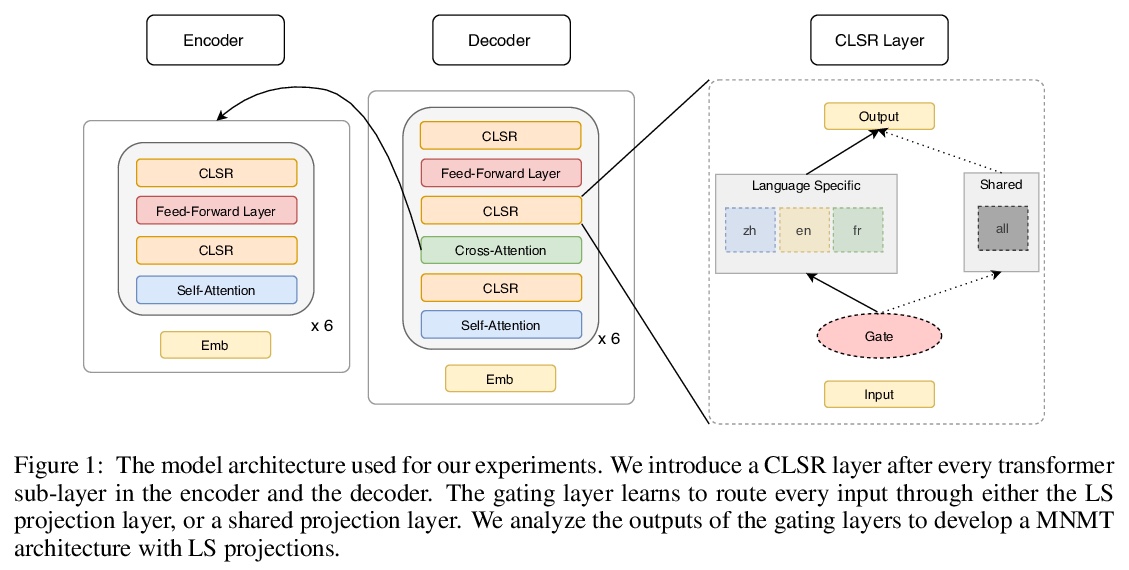
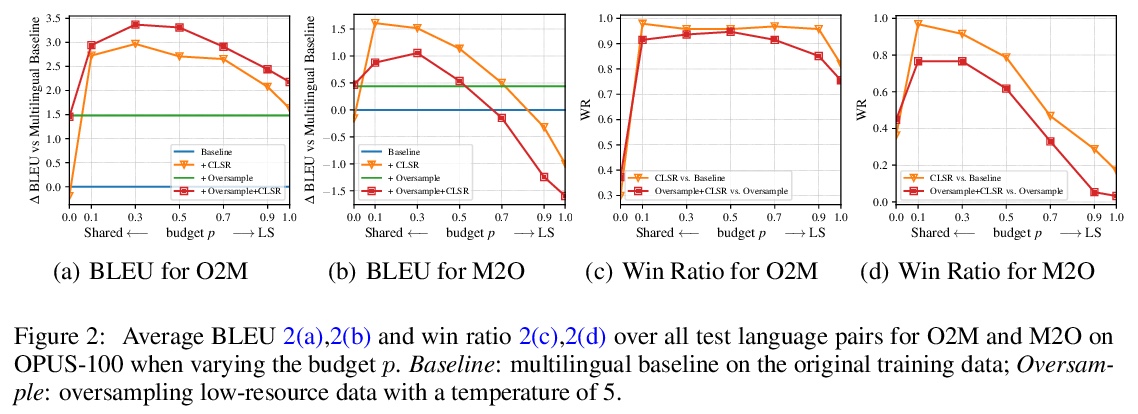
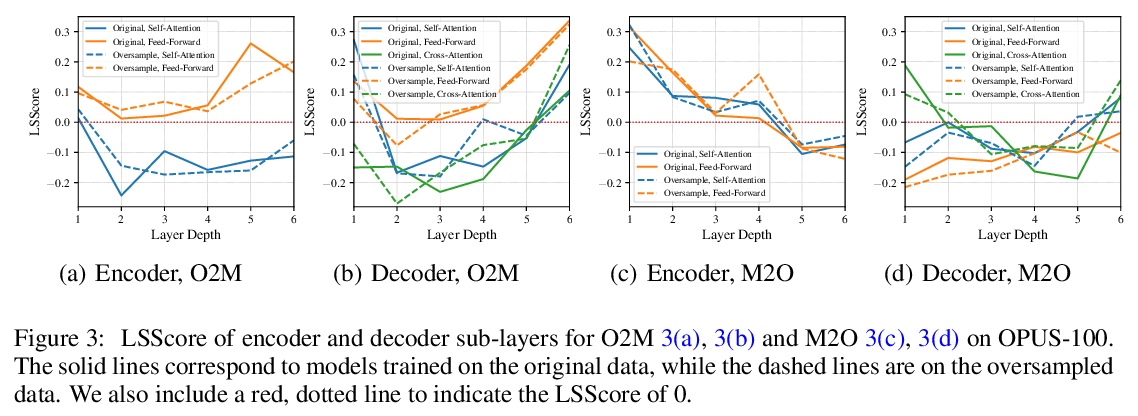
3、[CL] Share or Not? Learning to Schedule Language-Specific Capacity for Multilingual Translation
B Zhang, A Bapna, R Sennrich, O Firat
[University of Edinburgh & Google Research & University of Zurich]
多语言翻译共享参数和特定语言参数的权衡。在多语言神经机器翻译(MNMT)中,混合使用共享和特定语言(LS)参数已显示出良好的前景,但对特定语言能力何时何地最重要的问题仍未进行研究。本文通过提出条件特定语言路由(CLSR)来进行研究。CLSR采用硬二元门,以token表示为条件,动态选择特定语言或共享路径。通过操纵这些门,可根据翻译信号的指导和预算约束,在MNMT的各子层中安排LS的容量,很容易扩展到大规模多语言环境。在OPUS-100和WMT数据集上用Transformer进行的实验表明。1)MNMT对LS建模的数量和位置都很敏感:将10%-30%的LS计算分配到顶部和/或底部的编码器/解码器层可以提供最好的性能;2)与多对一翻译相比,一对多翻译从CLSR中获益更多,特别是在不平衡的训练数据下。该研究进一步验证了多语言翻译的共享能力和LS能力之间的权衡。
Using a mix of shared and language-specific (LS) parameters has shown promise in multilingual neural machine translation (MNMT), but the question of when and where LS capacity matters most is still under-studied. We offer such a study by proposing conditional language-specific routing (CLSR). CLSR employs hard binary gates conditioned on token representations to dynamically select LS or shared paths. By manipulating these gates, it can schedule LS capacity across sub-layers in MNMT subject to the guidance of translation signals and budget constraints. Moreover, CLSR can easily scale up to massively multilingual settings. Experiments with Transformer on OPUS-100 and WMT datasets show that: 1) MNMT is sensitive to both the amount and the position of LS modeling: distributing 10%-30% LS computation to the top and/or bottom encoder/decoder layers delivers the best performance; and 2) one-to-many translation benefits more from CLSR compared to many-to-one translation, particularly with unbalanced training data. Our study further verifies the trade-off between the shared capacity and LS capacity for multilingual translation. We corroborate our analysis by confirming the soundness of our findings as foundation of our improved multilingual Transformers. Source code and models are available at https://github.com/googleinterns/cct-m4.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcDfTwlXV
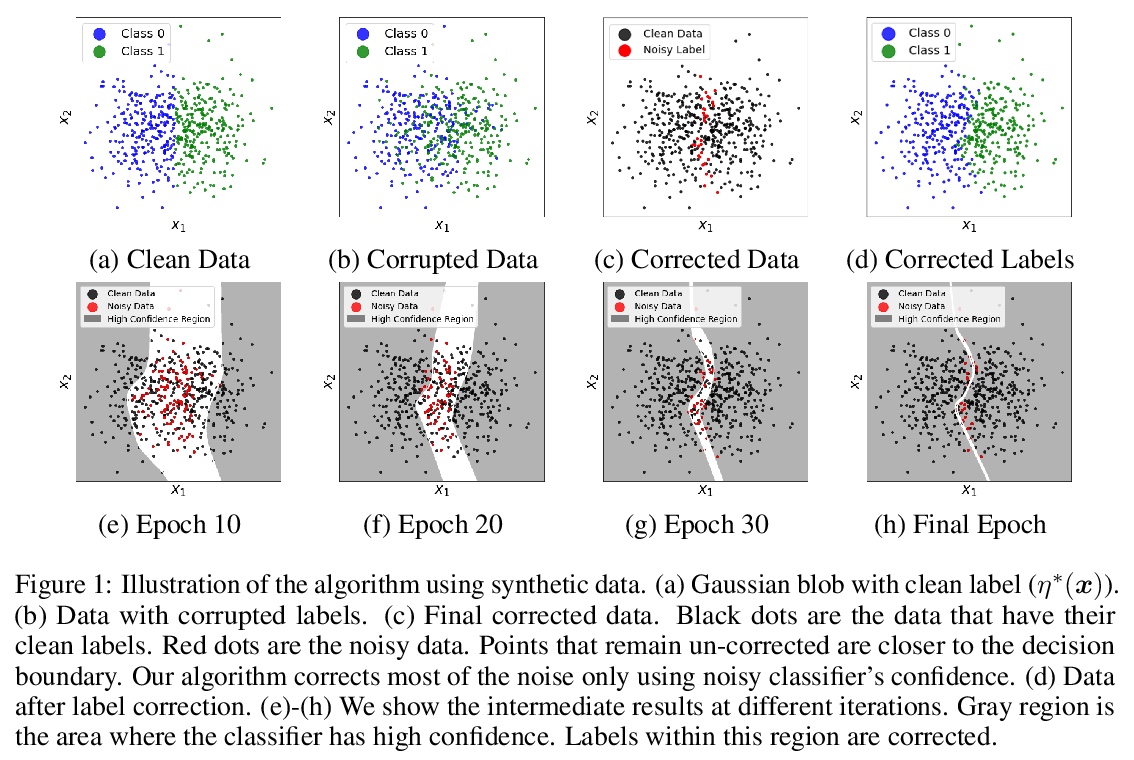
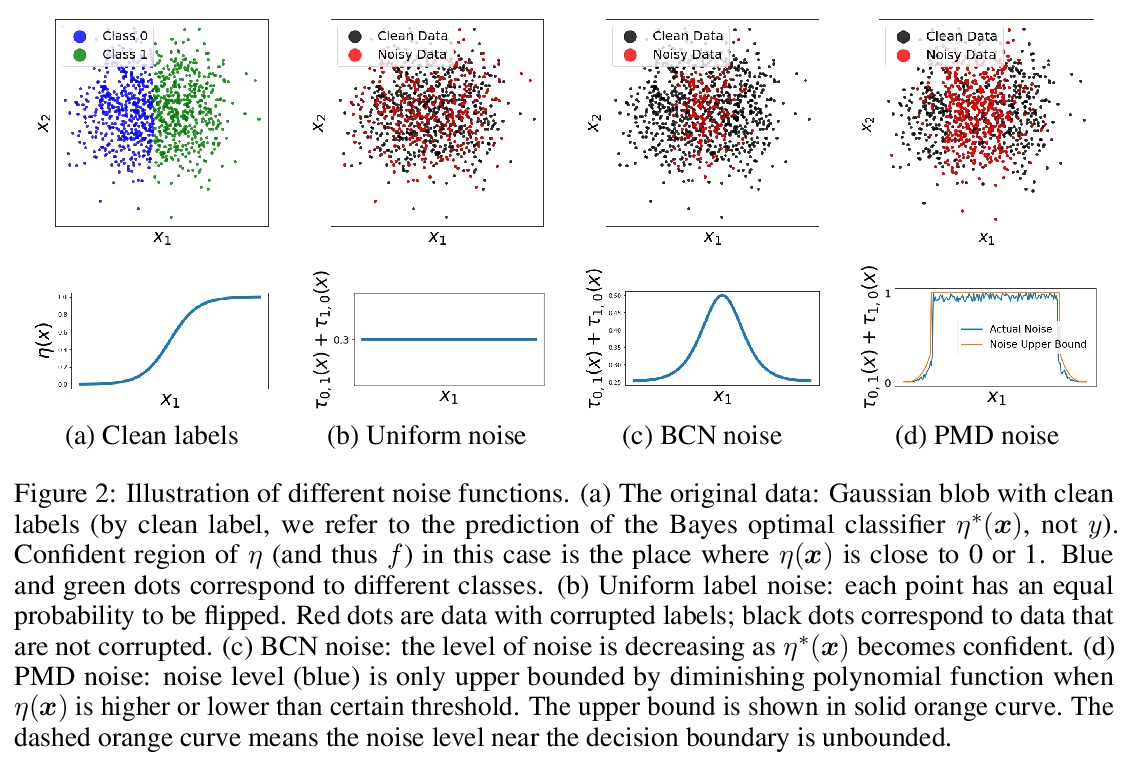
4、[LG] Learning with Feature-Dependent Label Noise: A Progressive Approach
Y Zhang, S Zheng, P Wu, M Goswami, C Chen
[Stony Brook University & Stony Brook University]
特征依赖标签噪声学习的渐进方法。现实世界的大规模数据集经常观察到标签噪声。噪声是由多种原因引入的,是异质的和特征依赖的。大多数现有处理噪声标签的方法分为两类:要么假定有一个理想的与特征无关的噪声,要么仍然是没有理论保证的启发式方法。本文提出一种新的特征依赖的标签噪声族,比常用的即得式标签噪声更普遍,且包含了广泛的噪声模式。针对这个一般的噪声族,提出了一种渐进式的标签校正算法,可迭代校正标签并完善模型。本文提供了理论上的保证,表明对于各种(未知)噪声模式,用这种策略训练的分类器会收敛到与Bayes分类器一致。在实验中,该方法优于SOTA基线,并对各种噪声类型和水平具有鲁棒性。
Label noise is frequently observed in real-world large-scale datasets. The noise is introduced due to a variety of reasons; it is heterogeneous and feature-dependent. Most existing approaches to handling noisy labels fall into two categories: they either assume an ideal feature-independent noise, or remain heuristic without theoretical guarantees. In this paper, we propose to target a new family of feature-dependent label noise, which is much more general than commonly used i.i.d. label noise and encompasses a broad spectrum of noise patterns. Focusing on this general noise family, we propose a progressive label correction algorithm that iteratively corrects labels and refines the model. We provide theoretical guarantees showing that for a wide variety of (unknown) noise patterns, a classifier trained with this strategy converges to be consistent with the Bayes classifier. In experiments, our method outperforms SOTA baselines and is robust to various noise types and levels.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcDkBufEO
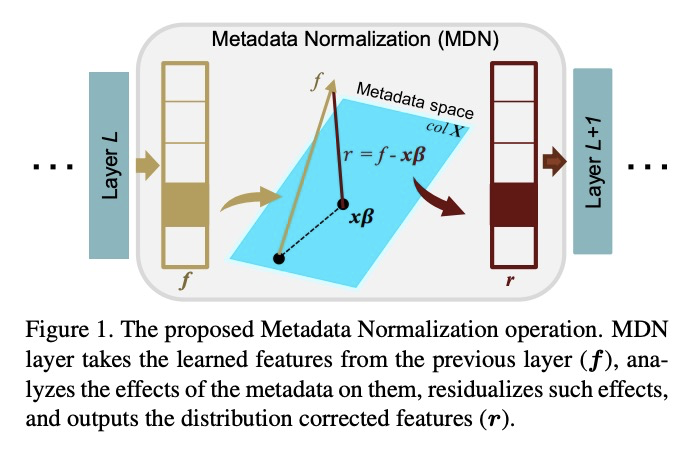
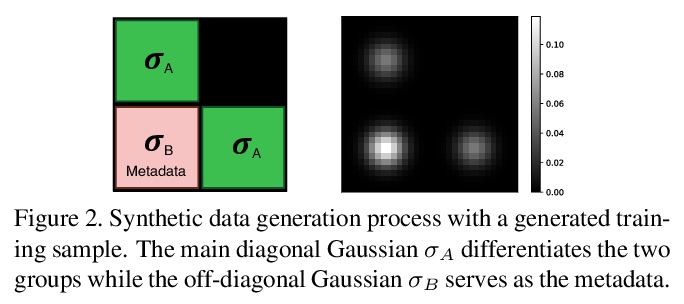
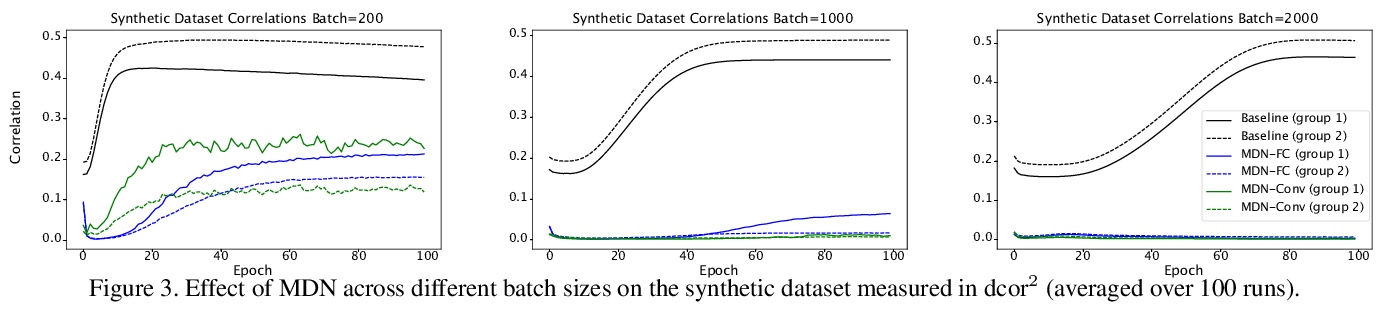
5、[LG] Metadata Normalization
M Lu, Q Zhao, J Zhang, K M. Pohl, L Fei-Fei, J C Niebles, E Adeli
[Stanford University]
元数据规范化。批量规范化(BN)及其变种在对抗深度学习方法训练步骤所引起的协变漂移方面取得了巨大成功。虽然这些技术通过批量统计的标准化来规范特征分布,但并没有纠正不相干的变量或多个分布对特征的影响。这种额外的变量,即元数据,可能会产生偏差或混杂效应。本文提出元数据规范化,以纠正数据在额外的元数据信息方面的分布。提出基于GLM的去除无关变量影响的理论基础,介绍了在(小)批量级设置中实现这一操作的新策略。对于输出预测变量与元数据有内在关联的情况,概述了MDN的简单扩展,以确保只去除元数据的无关影响,而不是那些与实际输出变量有关的影响。
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcDnauWlo

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
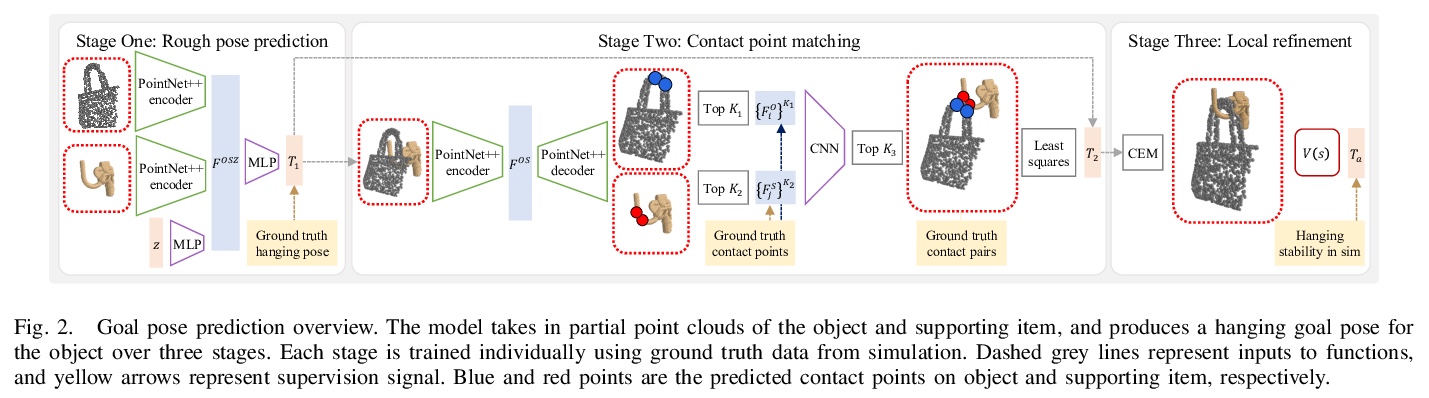
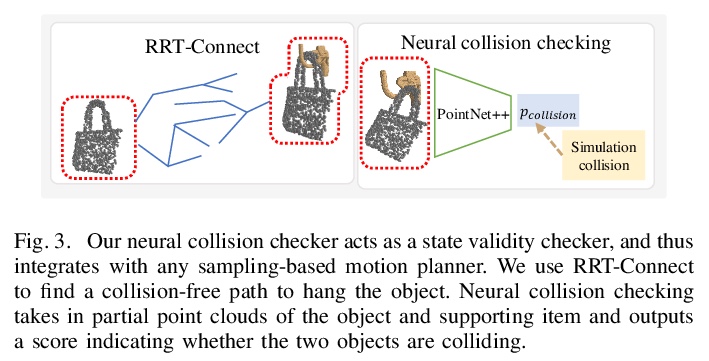
[RO] OmniHang: Learning to Hang Arbitrary Objects using Contact Point Correspondences and Neural Collision Estimation
OmniHang:用触点对应和神经碰撞估计学习悬挂物体
Y You, L Shao, T Migimatsu, J Bohg
[University of California, Los Angeles & Stanford University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcDqlzoer

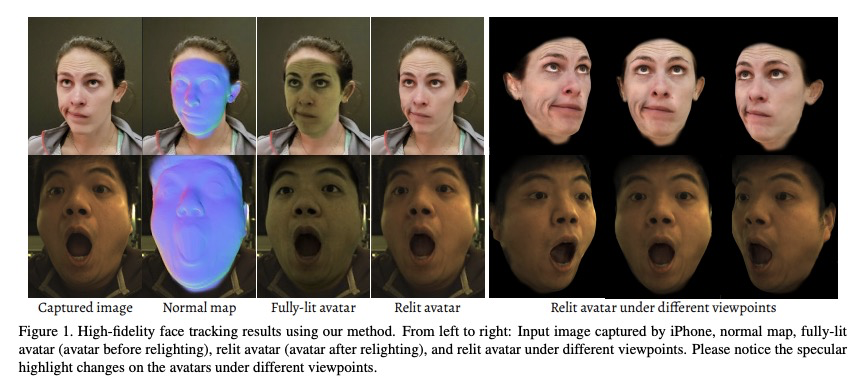
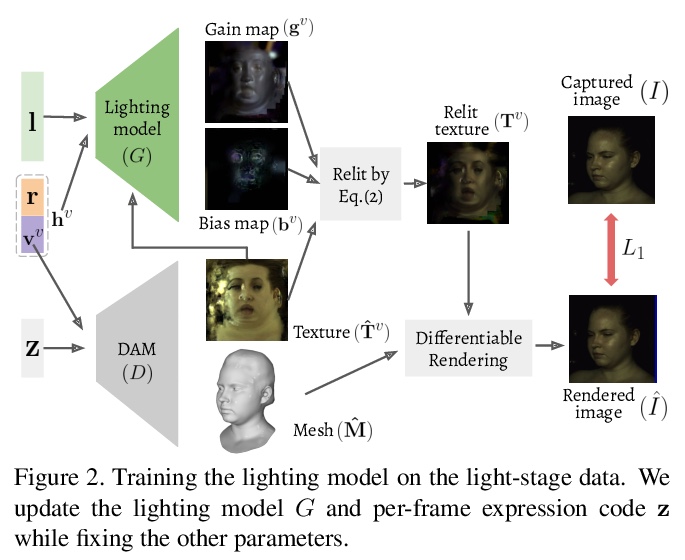
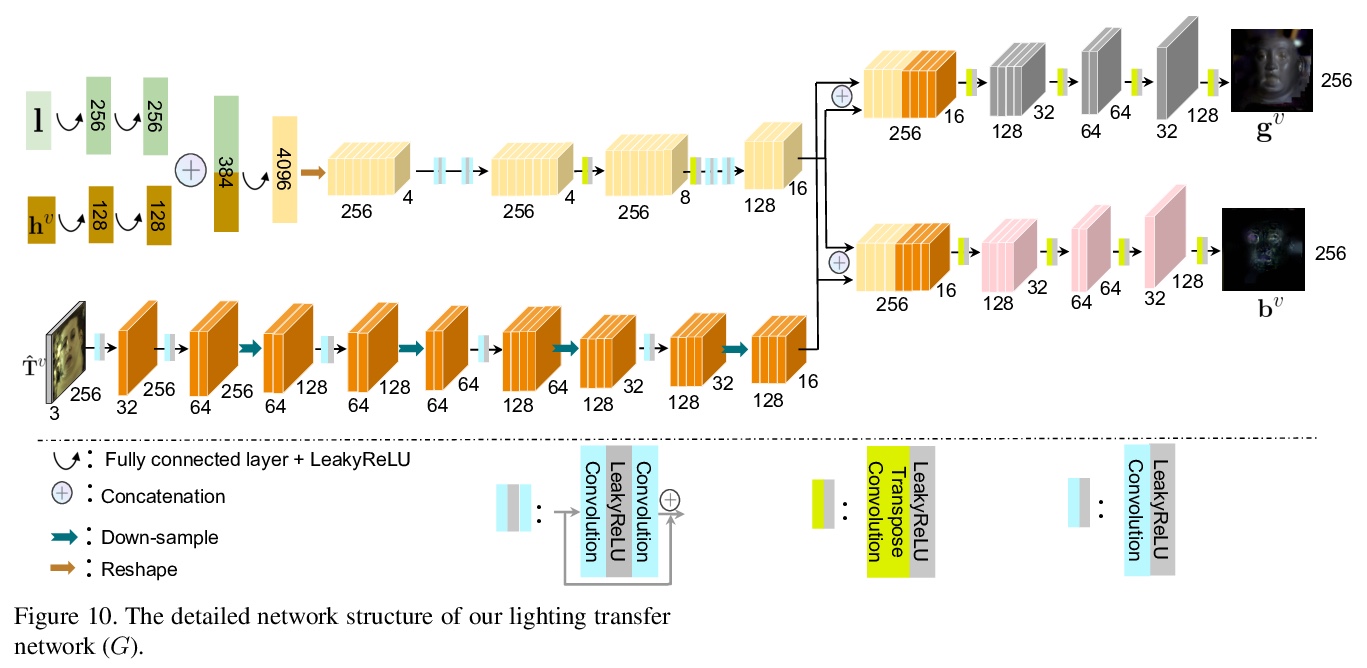
[CV] High-fidelity Face Tracking for AR/VR via Deep Lighting Adaptation
基于深度光照自适应的AR/VR高保真人脸跟踪
L Chen, C Cao, F D l Torre, J Saragih, C Xu, Y Sheikh
[Facebook Reality Labs & Univeristy of Rochester]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcDsfbUW5
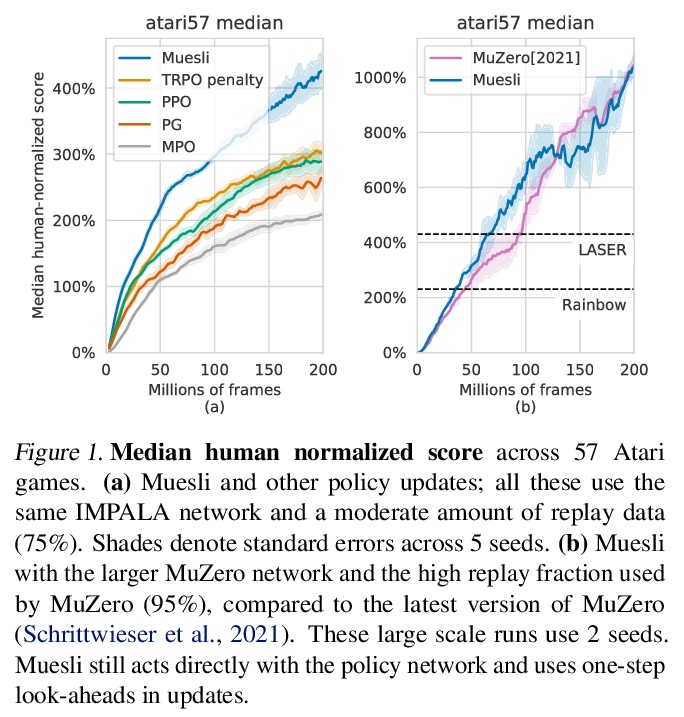
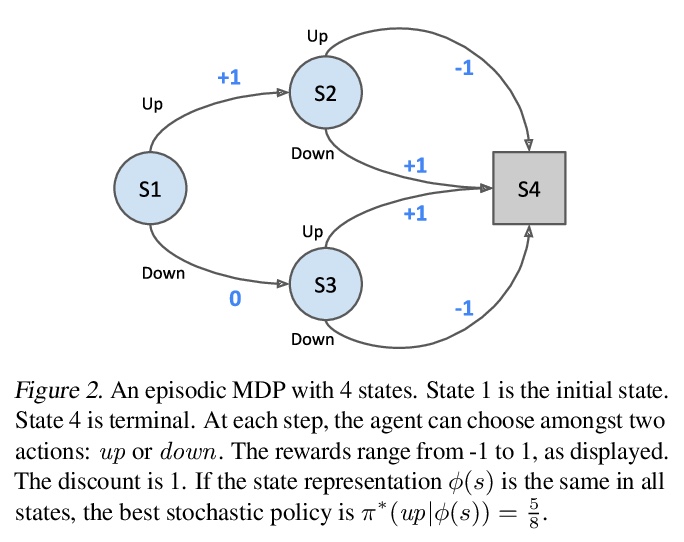
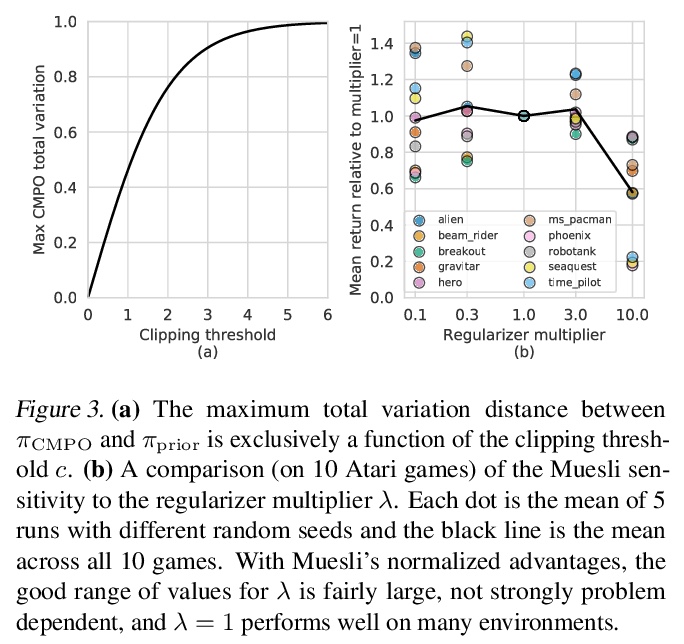
[LG] Muesli: Combining Improvements in Policy Optimization
Muesli:策略优化的组合改进
M Hessel, I Danihelka, F Viola, A Guez, S Schmitt, L Sifre, T Weber, D Silver, H v Hasselt
[DeepMind]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcDupzlPf
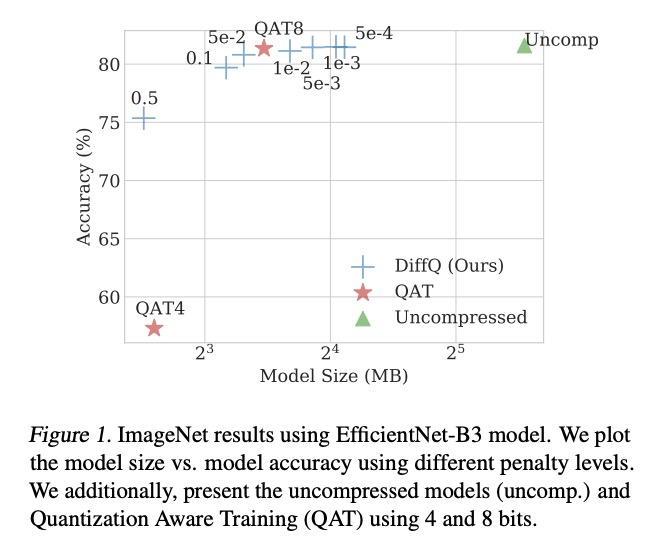
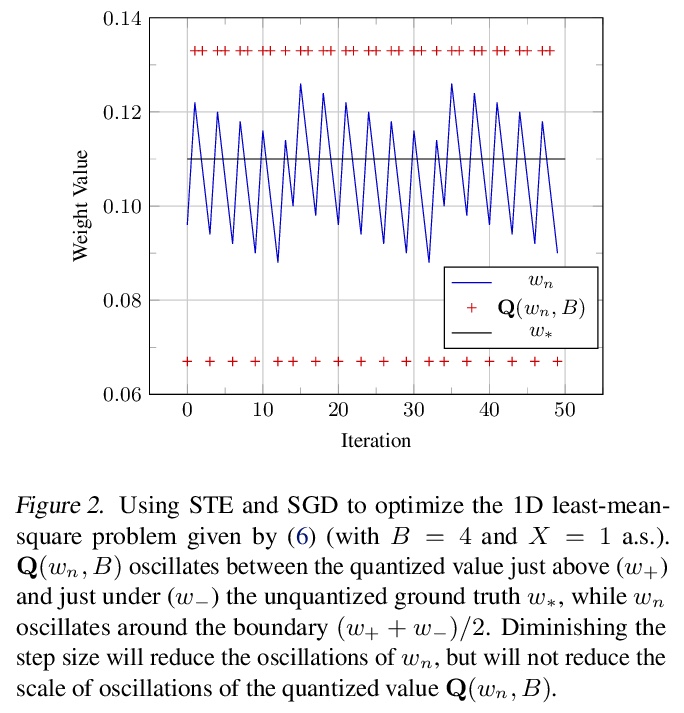
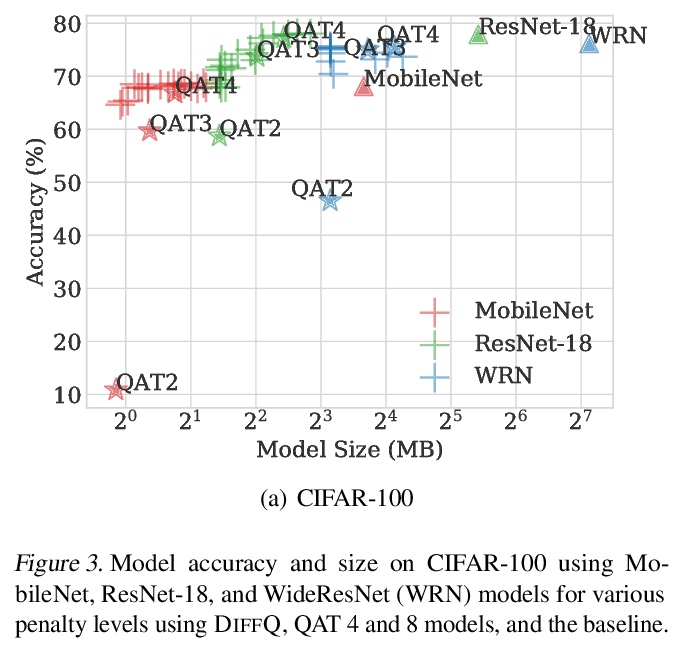
[LG] Differentiable Model Compression via Pseudo Quantization Noise
伪量化噪声可微模型压缩
A Défossez, Y Adi, G Synnaeve
[Facebook AI Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcDwthXCn