- 1、[CL] Are Pre-trained Convolutions Better than Pre-trained Transformers?
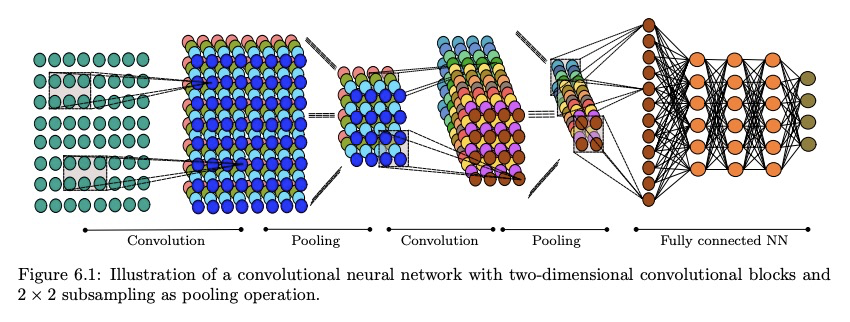
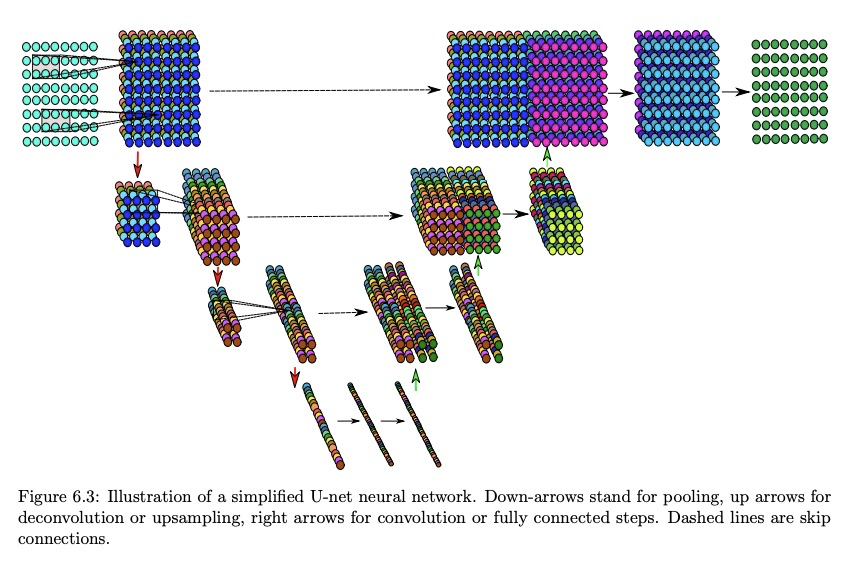
- 2、[LG] The Modern Mathematics of Deep Learning
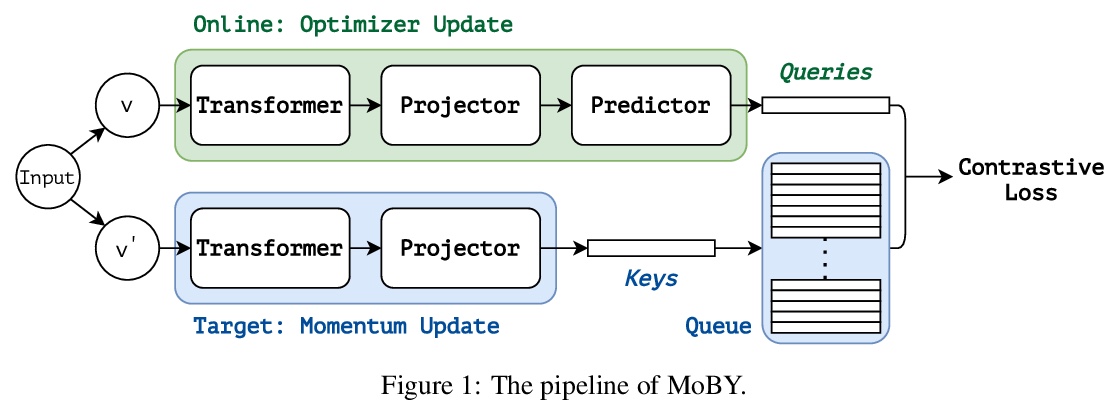
- 3、[CV] Self-Supervised Learning with Swin Transformers
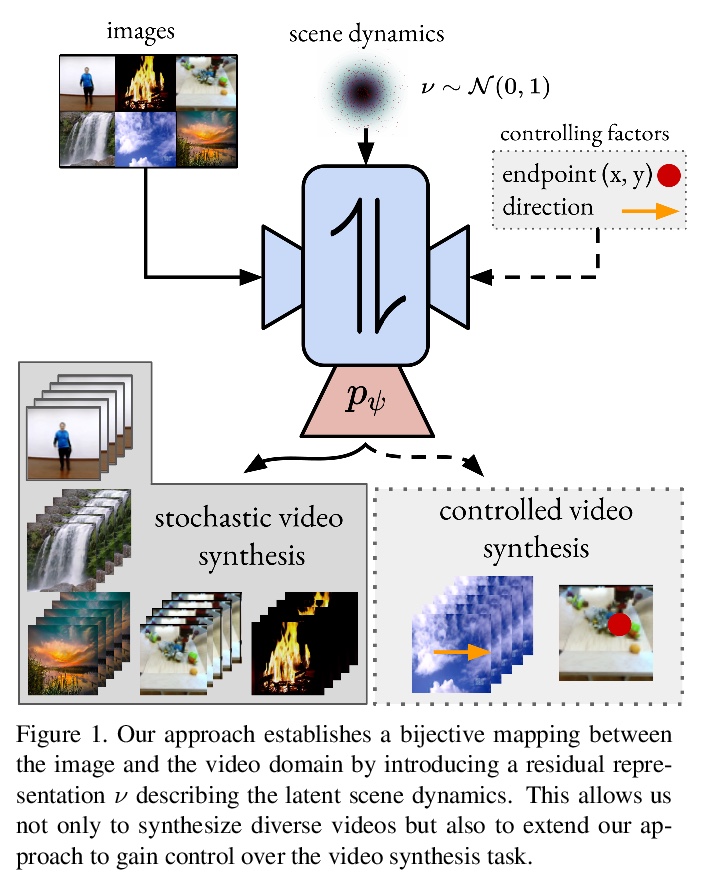
- 4、[CV] Stochastic Image-to-Video Synthesis using cINNs
- 5、[CL] ReadTwice: Reading Very Large Documents with Memories
- [CL] FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms
- [CL] Poolingformer: Long Document Modeling with Pooling Attention
- [LG] “Hey, that’s not an ODE”: Faster ODE Adjoints via Seminorms
- [LG] Continual Learning via Bit-Level Information Preserving
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CL] Are Pre-trained Convolutions Better than Pre-trained Transformers?
Y Tay, M Dehghani, J Gupta, D Bahri, V Aribandi, Z Qin, D Metzler
[Google Research]
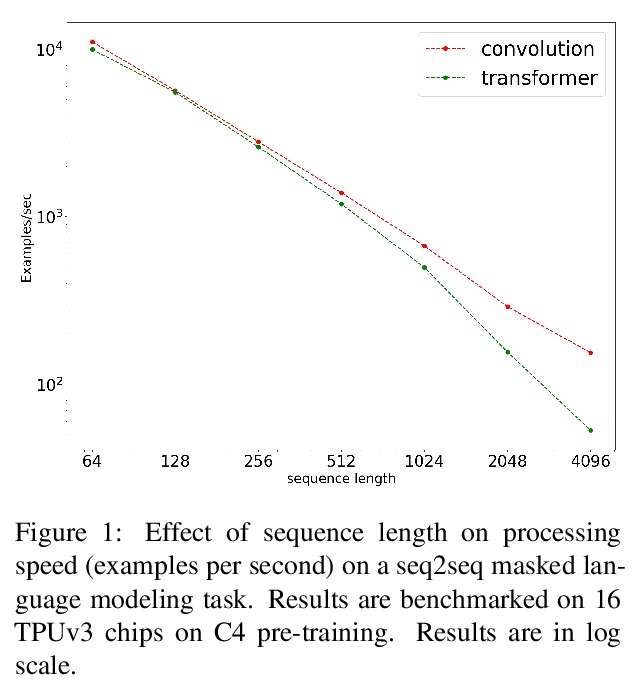
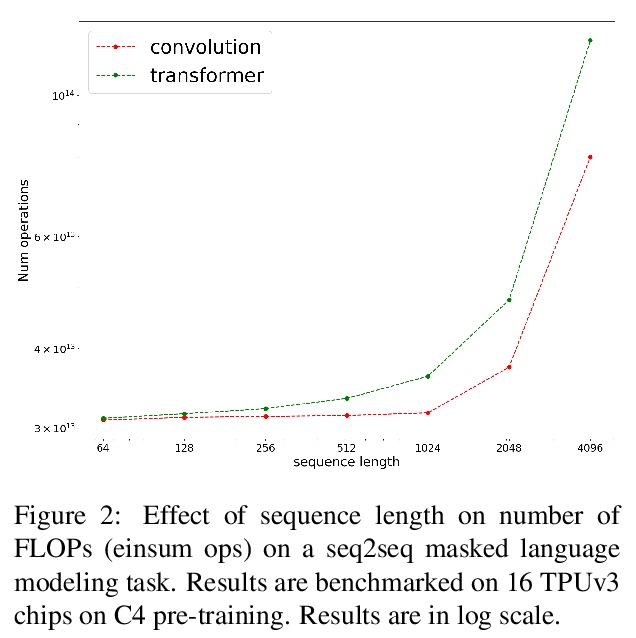
预训练的卷积会比预训练的Transformer表现更好吗?在预训练语言模型的时代,Transformer是模型架构事实上的选择。虽然最近的研究显示了全卷积CNN架构的前景,但还没有用预训练-微调范式进行过探索。在语言模型的背景下,卷积模型采用预训练对Transformer有竞争力吗?本文研究了这个问题,并提出了几个有趣的发现。在8个数据集/任务的大量实验中,发现基于CNN的预训练模型是有竞争力的,在某些情况下优于其Transformer对应模型,尽管有一些注意点。总的来说,本文概述的研究结果表明,将预训练和架构方面的进展混为一谈是错误的,这两类进展应该单独思考。
In the era of pre-trained language models, Transformers are the de facto choice of model architectures. While recent research has shown promise in entirely convolutional, or CNN, architectures, they have not been explored using the pre-train-fine-tune paradigm. In the context of language models, are convolutional models competitive to Transformers when pre-trained? This paper investigates this research question and presents several interesting findings. Across an extensive set of experiments on 8 datasets/tasks, we find that CNN-based pre-trained models are competitive and outperform their Transformer counterpart in certain scenarios, albeit with caveats. Overall, the findings outlined in this paper suggest that conflating pre-training and architectural advances is misguided and that both advances should be considered independently. We believe our research paves the way for a healthy amount of optimism in alternative architectures.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf3OzDAr8
2、[LG] The Modern Mathematics of Deep Learning
J Berner, P Grohs, G Kutyniok, P Petersen
[University of Vienna & University of Troms]
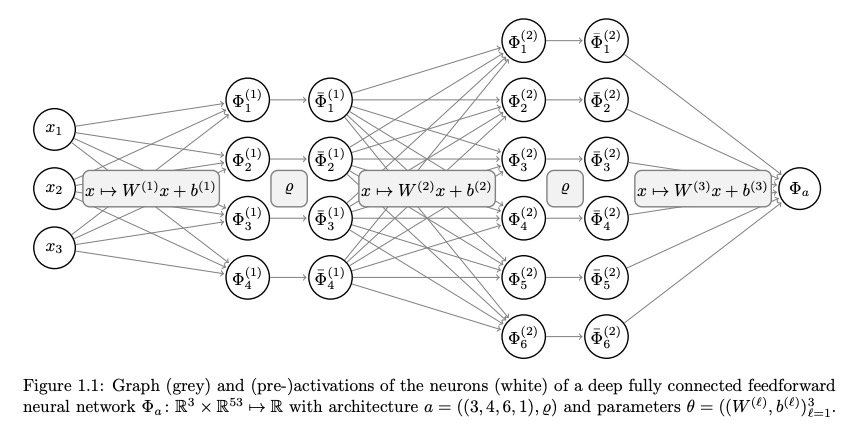
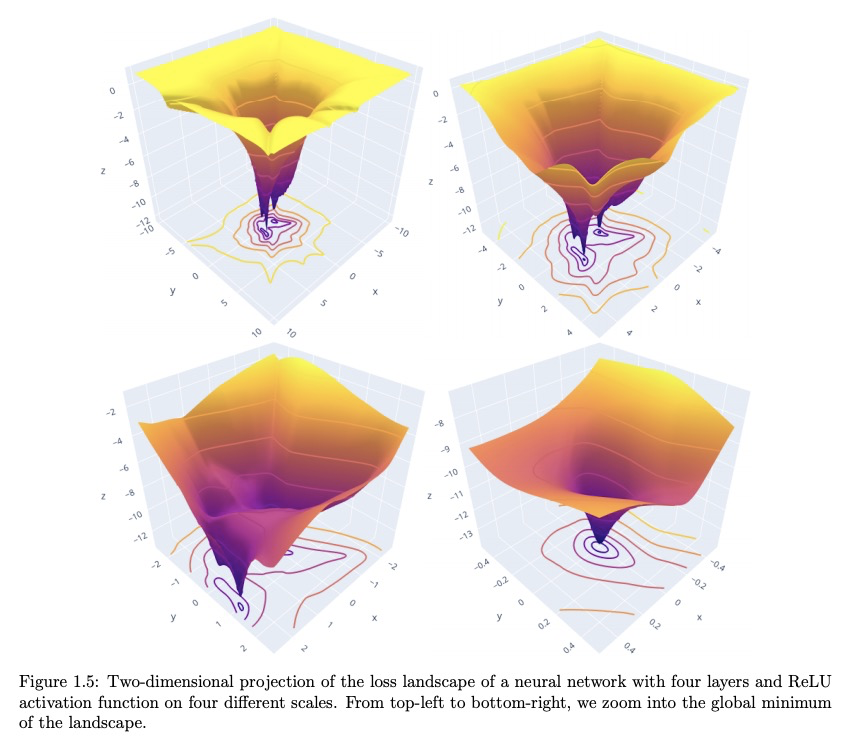
深度学习的现代数学。本文描述了深度学习数学分析这一新领域,该领域是围绕着一系列在学习理论经典框架内没有答案的研究问题而出现的,包括:超参数化神经网络杰出的泛化能力,深度架构中深度的作用,维度诅咒的失效,尽管问题非凸优化性能却很好,理解什么特征被学习,为什么深度架构在物理问题中表现特别好,以及架构的哪些细微方面以何种方式影响学习任务的行为。本文对产生这些问题的部分答案的现代方法进行了概述。
We describe the new field of mathematical analysis of deep learning. This field emerged around a list of research questions that were not answered within the classical framework of learning theory. These questions concern: the outstanding generalization power of overparametrized neural networks, the role of depth in deep architectures, the apparent absence of the curse of dimensionality, the surprisingly successful optimization performance despite the non-convexity of the problem, understanding what features are learned, why deep architectures perform exceptionally well in physical problems, and which fine aspects of an architecture affect the behavior of a learning task in which way. We present an overview of modern approaches that yield partial answers to these questions. For selected approaches, we describe the main ideas in more detail.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf3TzALGk
3、[CV] Self-Supervised Learning with Swin Transformers
Z Xie, Y Lin, Z Yao, Z Zhang, Q Dai, Y Cao, H Hu
[Xi’an Jiaotong University & Xi’an Jiaotong University & Microsoft Research Asia]
Swin Transformer自监督学习。我们正在见证计算机视觉中从CNN到Transformer的建模转变。本文提出一种名为MoBY的自监督学习方法,以视觉Transformer作为其骨干架构。该方法基本上是MoCo v2和BYOL的组合,经过调整,在ImageNet-1K线性评估中取得了合理的高精度:通过300轮训练,用DeiT-S和Swin-T分别达到72.8%和75.0%的最高精度。其性能略好于最近采用DeiT作为骨干的MoCo v3和DINO,但trick更少。通用的Swin Transformer主干能在下游任务(如目标检测和语义分割)上评估所学到的表征,而最近一些建立在ViT/DeiT上的方法由于ViT/DeiT无法用于这些密集的预测任务,因此只在ImageNet-1K上报告了线性评估结果。MoBY的表现与监督方法相当或略差,这表明用Transformer架构的自监督学习还有改进的空间。
We are witnessing a modeling shift from CNN to Transformers in computer vision. In this paper, we present a self-supervised learning approach called MoBY, with Vision Transformers as its backbone architecture. The approach is basically a combination of MoCo v2 and BYOL, tuned to achieve reasonably high accuracy on ImageNet-1K linear evaluation: 72.8% and 75.0% top-1 accuracy using DeiT-S and Swin-T, respectively, by 300-epoch training. The performance is slightly better than recent works of MoCo v3 and DINO which adopt DeiT as the backbone, but with much lighter tricks. More importantly, the general-purpose Swin Transformer backbone enables us to also evaluate the learnt representations on downstream tasks such as object detection and semantic segmentation, in contrast to a few recent approaches built on ViT/DeiT which only report linear evaluation results on ImageNet-1K due to ViT/DeiT not tamed for these dense prediction tasks. We hope our results can facilitate more comprehensive evaluation of self-supervised learning methods designed for Transformer architectures.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf3X83f3M
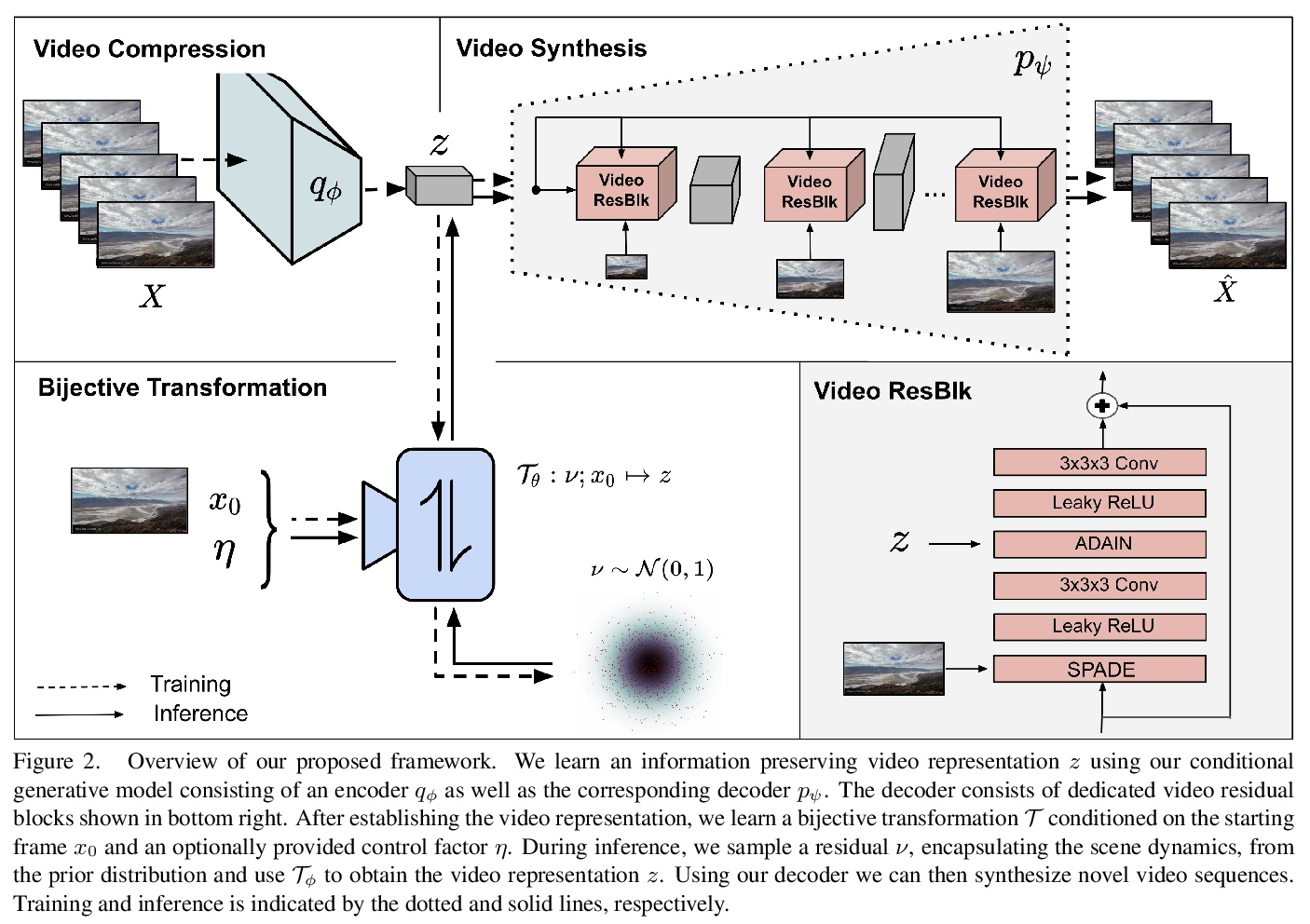
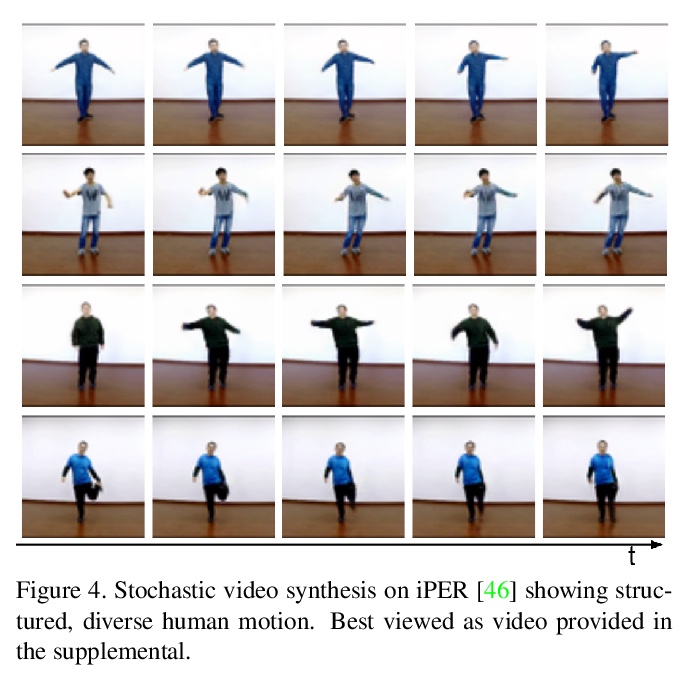
4、[CV] Stochastic Image-to-Video Synthesis using cINNs
M Dorkenwald, T Milbich, A Blattmann, R Rombach, K G. Derpanis, B Ommer
[Heidelberg University & Ryerson University]
基于cINNs的随机图像-视频合成。视频理解需要一个模型来学习静态场景内容及其动态之间的特征性相互作用。给定一个图像,模型必须能够预测所描绘场景的未来发展,反之,一个视频应该用它的静态图像内容和初始帧中不存在的所有其余特征来解释。这表明,在视频领域和静态内容以及残差信息之间存在着一种双项映射。与常见的随机图像-视频合成相比,这样的模型并不只是生成推进初始图片的任意视频。给定该图像,会在采样时提供了残差向量和具有随机结果的视频之间的一对一映射。该方法自然地使用条件可逆神经网络(cINN)来实现,该网络可通过独立建模静态和其他视频特征来解释视频,从而为可控视频合成奠定基础。在四个不同的视频数据集上的实验表明,该方法在合成结果的质量和多样性方面都很有效。
Video understanding calls for a model to learn the characteristic interplay between static scene content and its dynamics: Given an image, the model must be able to predict a future progression of the portrayed scene and, conversely, a video should be explained in terms of its static image content and all the remaining characteristics not present in the initial frame. This naturally suggests a bijective mapping between the video domain and the static content as well as residual information. In contrast to common stochastic image-to-video synthesis, such a model does not merely generate arbitrary videos progressing the initial image. Given this image, it rather provides a one-to-one mapping between the residual vectors and the video with stochastic outcomes when sampling. The approach is naturally implemented using a conditional invertible neural network (cINN) that can explain videos by independently modelling static and other video characteristics, thus laying the basis for controlled video synthesis. Experiments on four diverse video datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in terms of both the quality and diversity of the synthesized results. Our project page is available at https://bit.ly/3dg90fV .
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf41d1Wj2

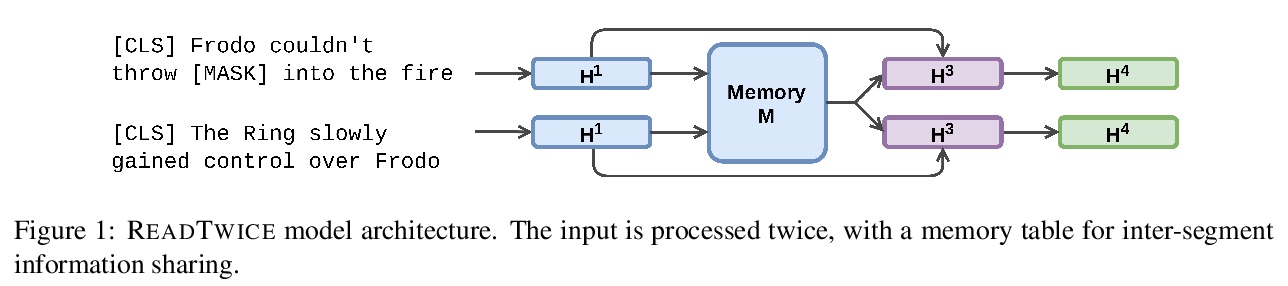
5、[CL] ReadTwice: Reading Very Large Documents with Memories
Y Zemlyanskiy, J Ainslie, M d Jong, P Pham, I Eckstein, F Sha
[University of Southern California & Google Research]
READTWICE: 用记忆阅读非常大的文档。知识密集型任务,如问题回答,往往需要从大型输入的不同部分吸收信息,如书籍或文章集。本文提出READTWICE,一种简单有效的技术,结合了之前方法的优点,用Transformer模拟长程依赖关系。其主要思想是分小段并行阅读文本,将每小段总结成一个记忆表,用于对文本的二次阅读。该方法在几个问题回答(QA)数据集上的表现优于同等规模的模型,并在具有挑战性的NarrativeQA任务(关于整本书的问题)上达到了新的技术水平。
Knowledge-intensive tasks such as question answering often require assimilating information from different sections of large inputs such as books or article collections. We propose READTWICE, a simple and effective technique that combines several strengths of prior approaches to model long-range dependencies with Transformers. The main idea is to read text in small segments, in parallel, summarizing each segment into a memory table to be used in a second read of the text. We show that the method outperforms models of comparable size on several question answering (QA) datasets and sets a new state of the art on the challenging NarrativeQA task, with questions about entire books.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf45M4AmW
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
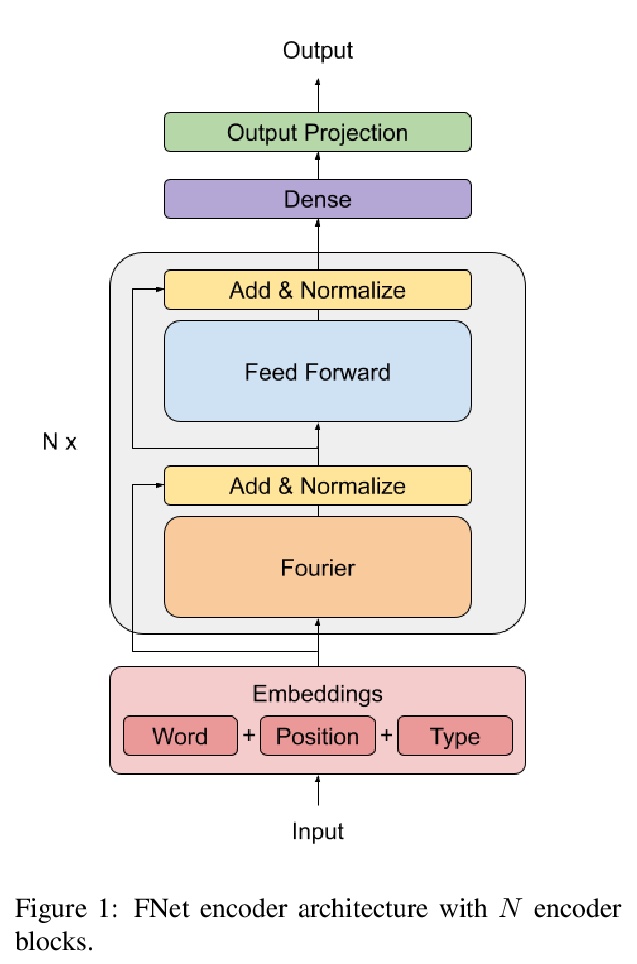
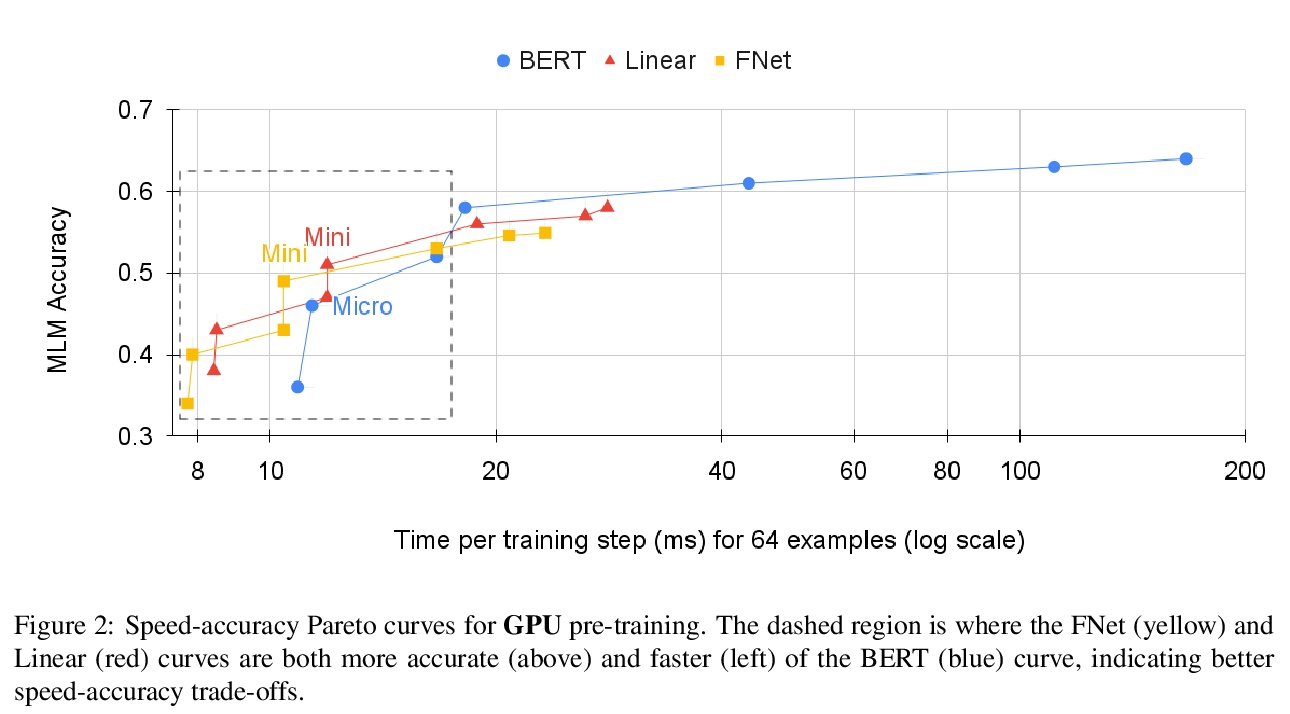
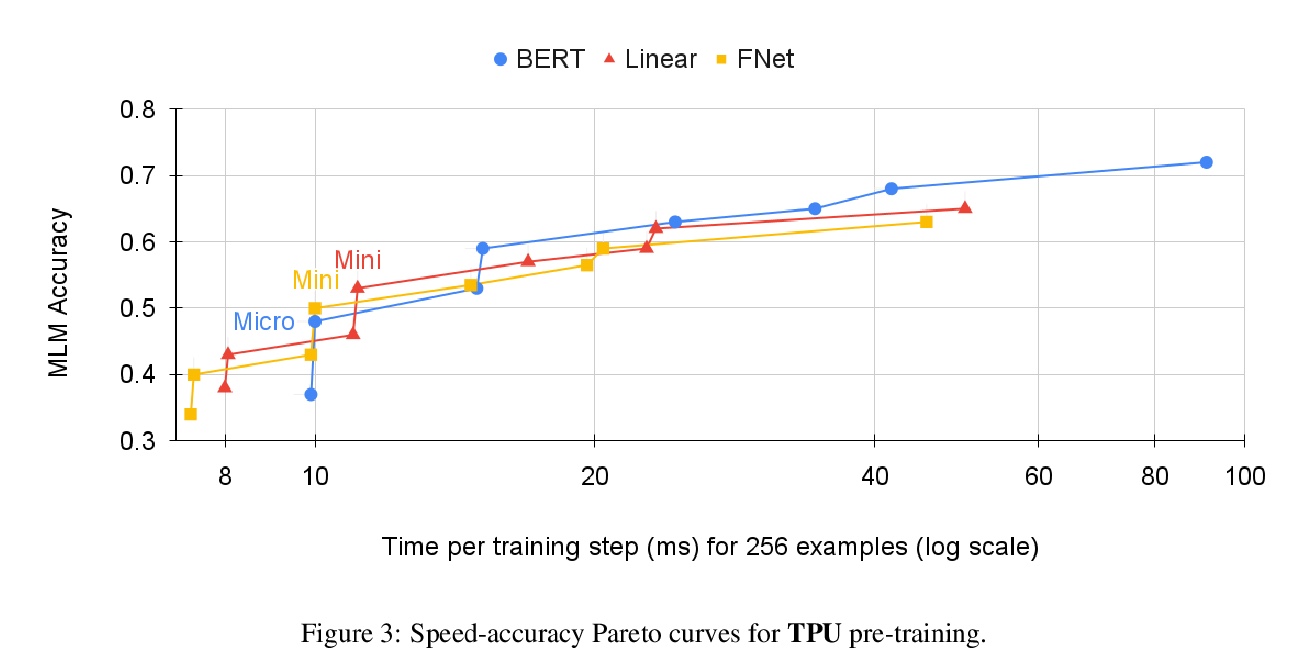
[CL] FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms
FNet:基于傅立叶变换的混合Tokens
J Lee-Thorp, J Ainslie, I Eckstein, S Ontanon
[Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf49m1HaC
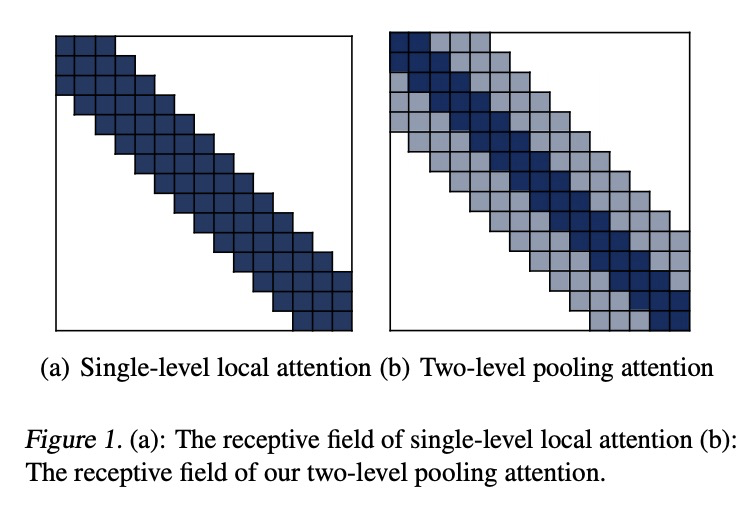
[CL] Poolingformer: Long Document Modeling with Pooling Attention
Poolingformer:池化注意力长文档建模
H Zhang, Y Gong, Y Shen, W Li, J Lv, N Duan, W Chen
[Sichuan University & Microsoft Research Asia & Microsoft Azure AI & University of Science and Technology of China]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf4b68qX0

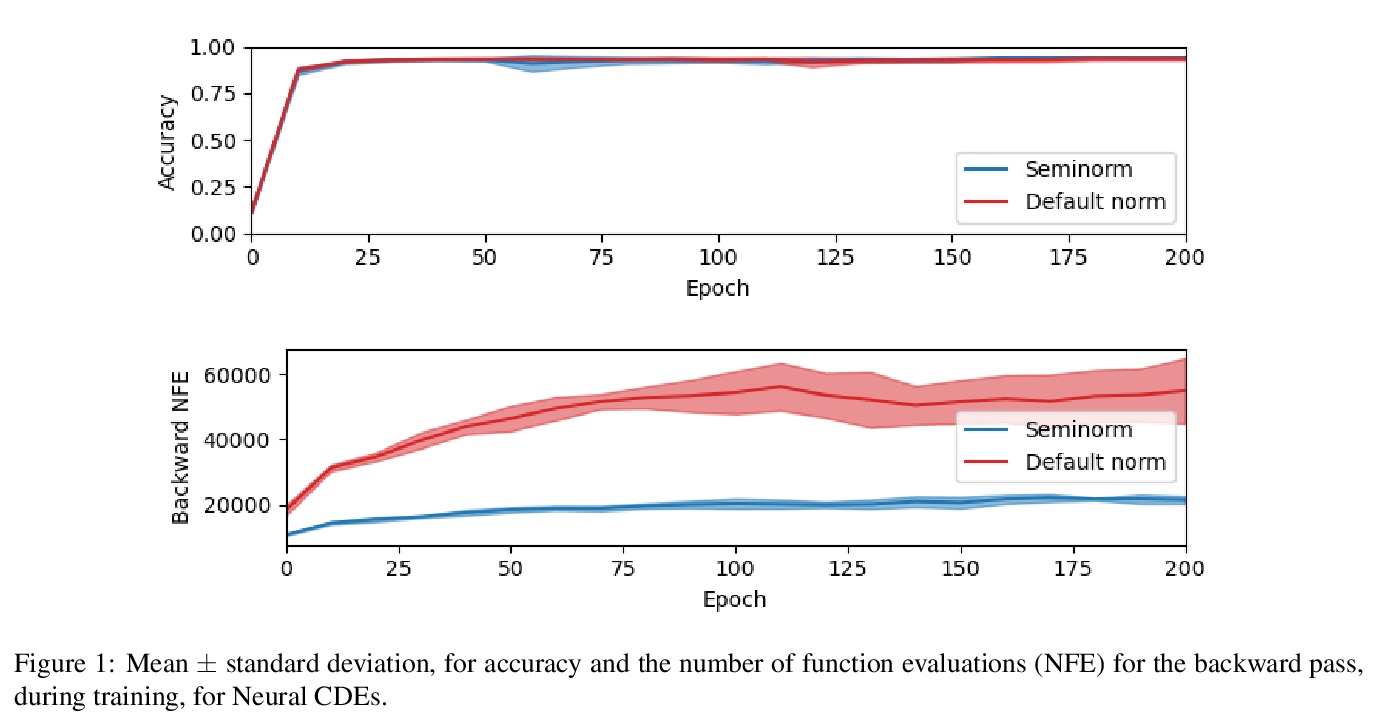
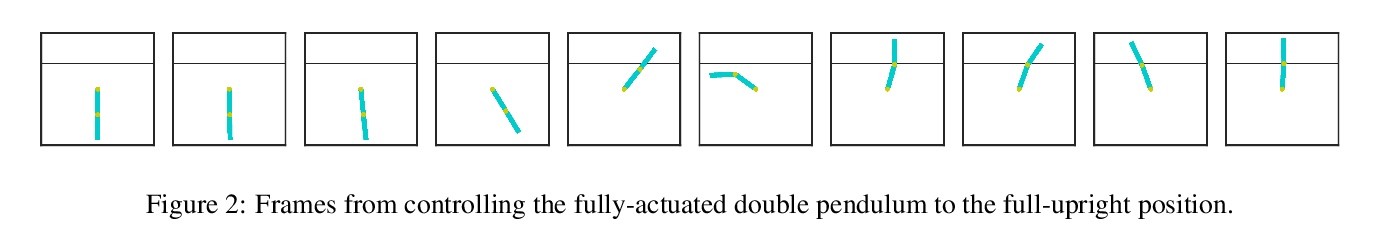
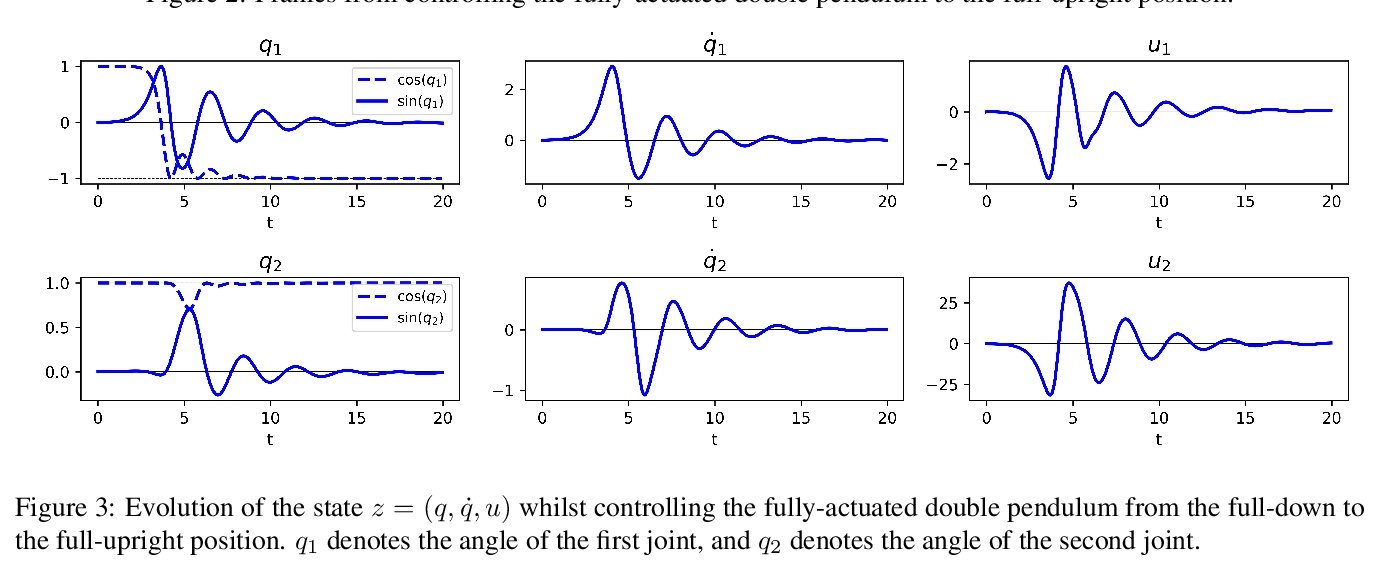
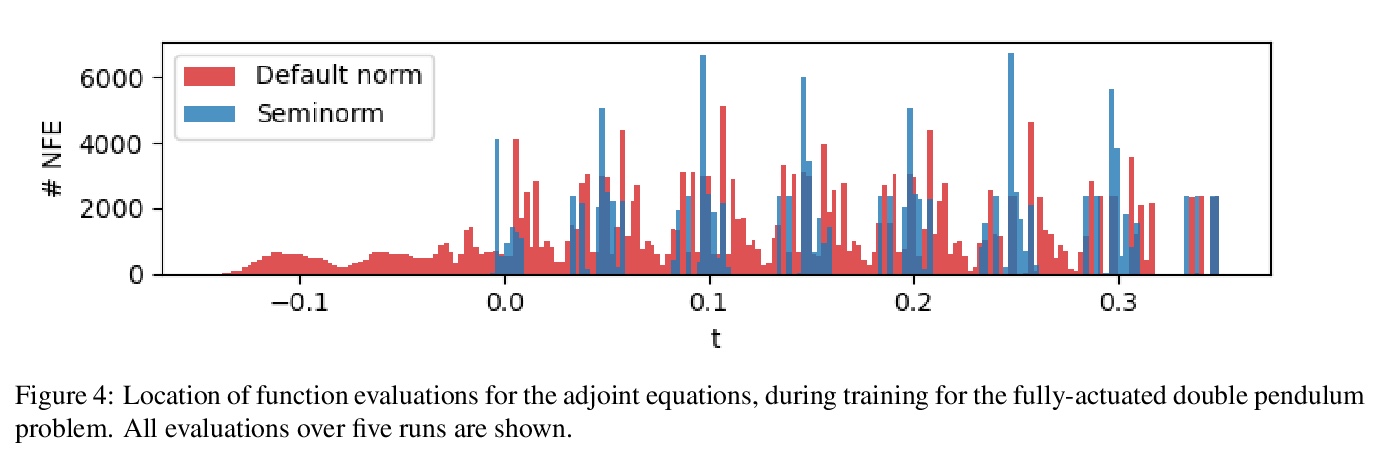
[LG] “Hey, that’s not an ODE”: Faster ODE Adjoints via Seminorms
通过半模实现更快的ODE联接
P Kidger, R T. Q. Chen, T Lyons
[University of Oxford & University of Toronto]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf4czqIMH
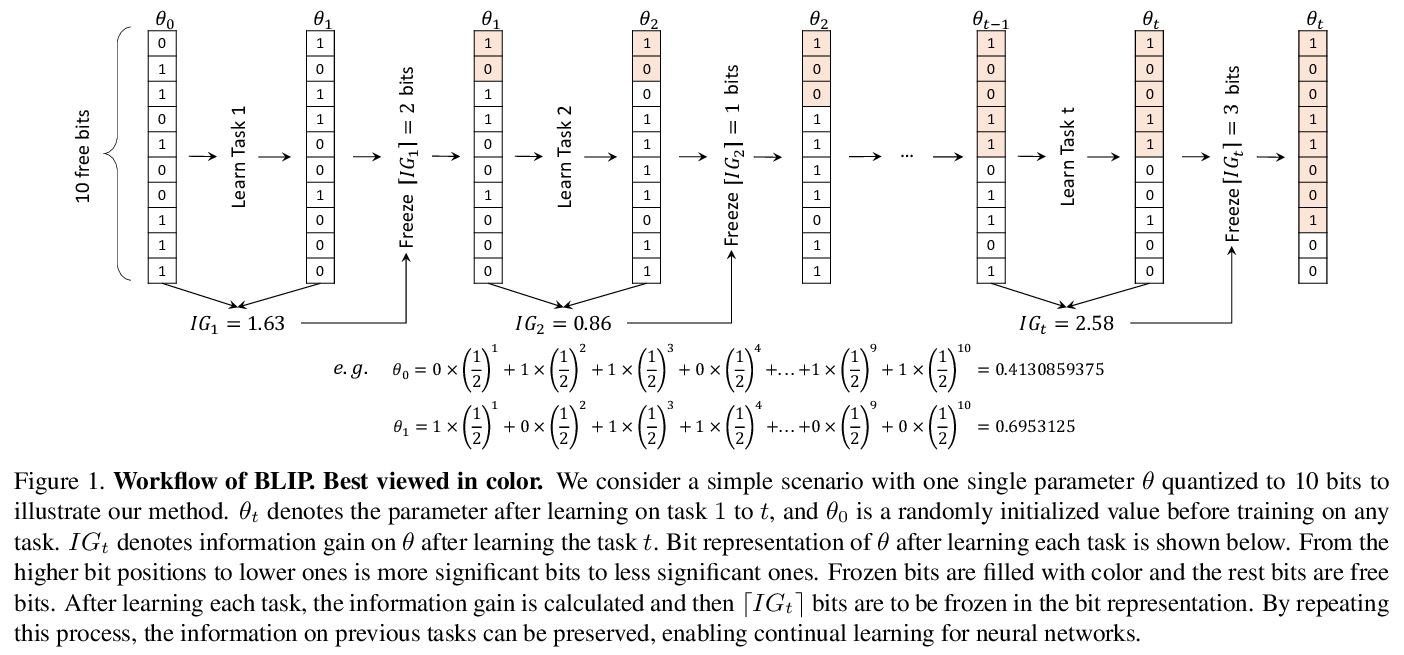
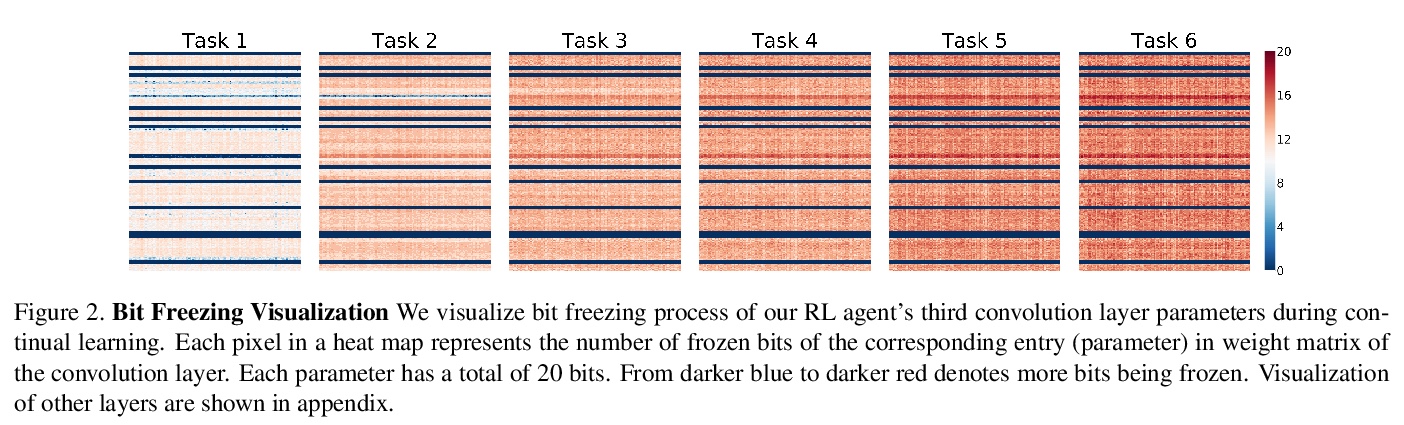
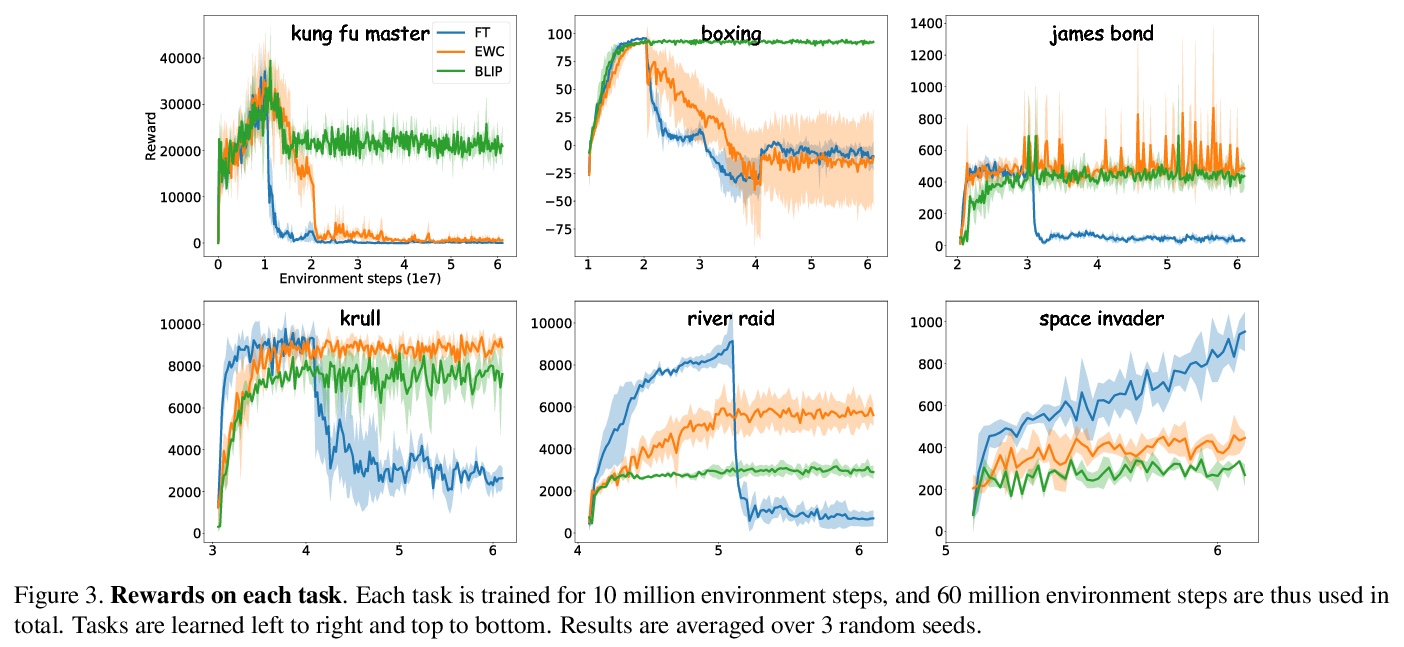
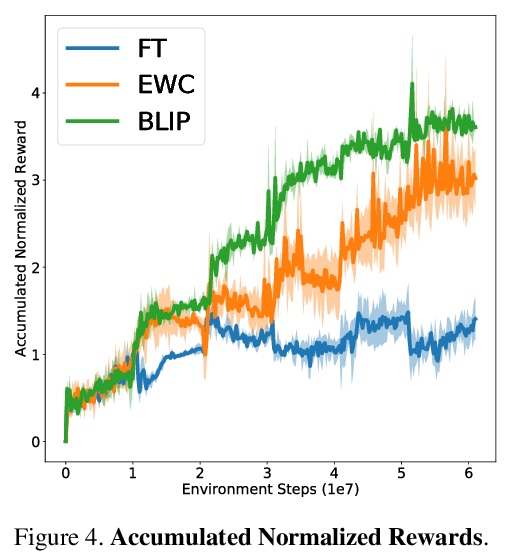
[LG] Continual Learning via Bit-Level Information Preserving
基于位级信息保留的持续学习
Y Shi, L Yuan, Y Chen, J Feng
[National University of Singapore & YITU Technology]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kf4gmEqBx