- 1、[CV] You Only Learn One Representation: Unified Network for Multiple Tasks
- 2、[CL] Self-Attention Networks Can Process Bounded Hierarchical Languages
- 3、[LG] Revisiting Rainbow: Promoting more Insightful and Inclusive Deep Reinforcement Learning Research
- 4、[LG] Hyperparameter Selection for Imitation Learning
- 5、[LG] Boltzmann machines as two-dimensional tensor networks
- [CL] SUPERB: Speech processing Universal PERformance Benchmark
- [CL] DocSCAN: Unsupervised Text Classification via Learning from Neighbors
- [CV] Pushing it out of the Way: Interactive Visual Navigation
- [CV] AGORA: Avatars in Geography Optimized for Regression Analysis
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] You Only Learn One Representation: Unified Network for Multiple Tasks
C Wang, I Yeh, H M Liao
[Academia Sinica & Elan Microelectronics Corporation]
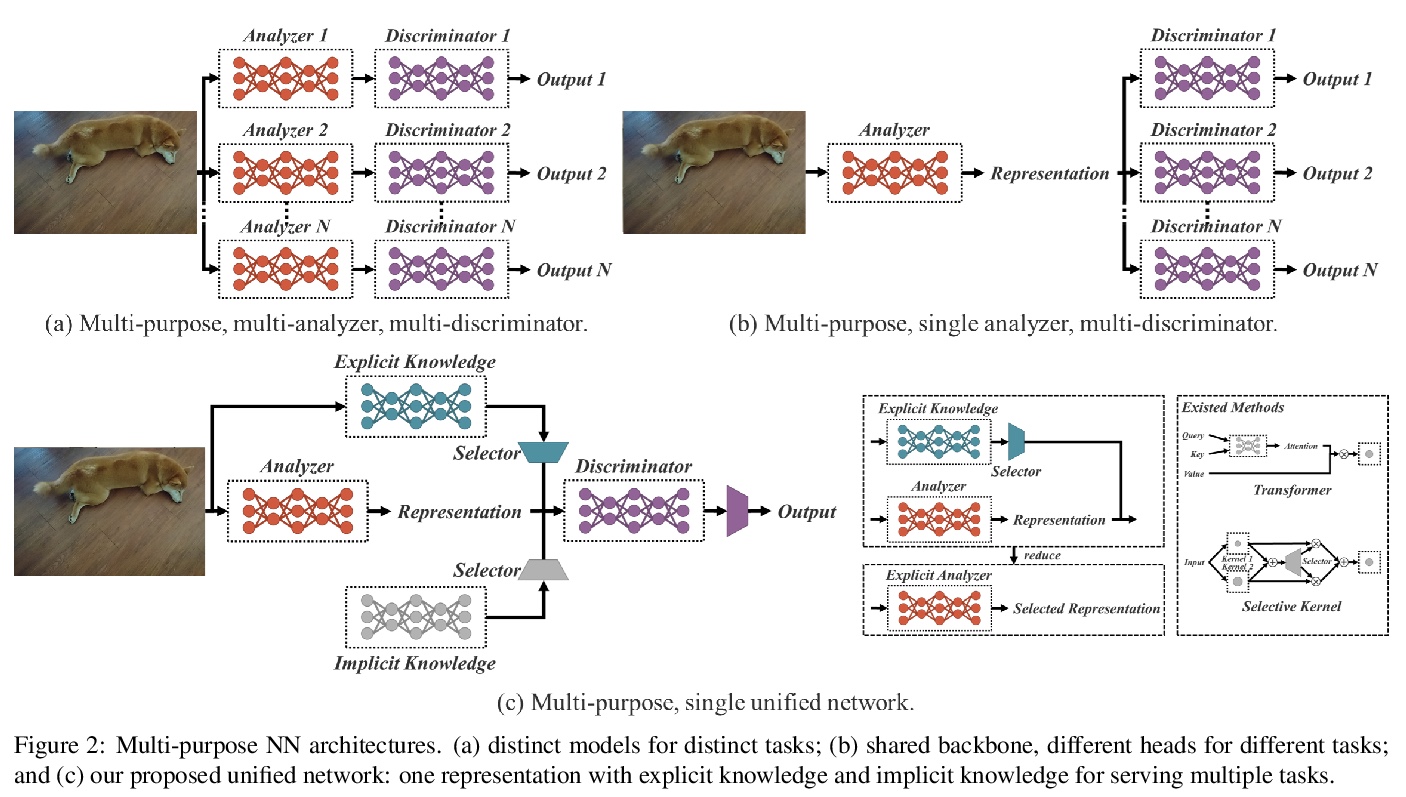
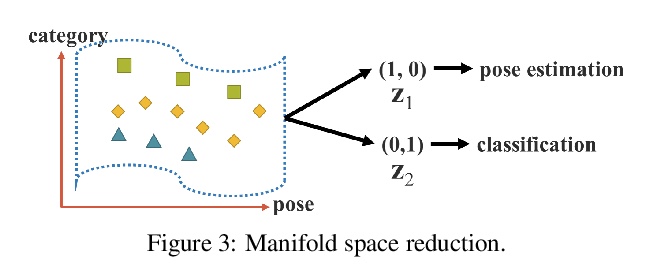
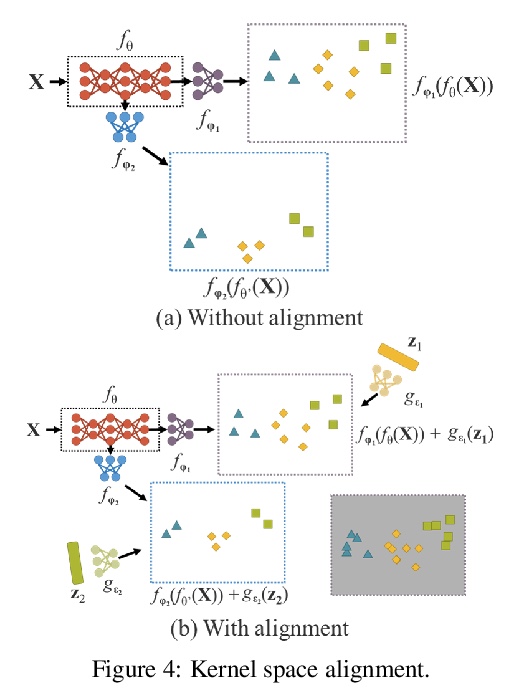
多任务统一网络。人们通过视觉、听觉、触觉以及历史经验,来”理解”这个世界。人类经验可通过正常学习(显性知识),也可以通过潜意识(隐性知识)来学习。这些通过正常学习或潜意识学到的经验,被编码并储存在大脑中。利用这些丰富的经验作为巨大的数据库,人类可有效处理数据,即使之前从未见过。本文提出一种统一网络,用来编码隐性知识和显性知识,就像人的大脑,可以从正常学习及潜意识中学习知识。统一网络可产生一种统一表示,同时为多种任务服务。可以在卷积神经网络中进行核空间对齐、预测细化和多任务学习。结果表明,当隐性知识被引入神经网络时,有利于所有任务的表现。进一步分析了从所提出的统一网络中学习到的隐性表征,其在捕捉不同任务的物理意义方面显示出巨大能力。
People “understand” the world via vision, hearing, tactile, and also the past experience. Human experience can be learned through normal learning (we call it explicit knowledge), or subconsciously (we call it implicit knowledge). These experiences learned through normal learning or subconsciously will be encoded and stored in the brain. Using these abundant experience as a huge database, human beings can effectively process data, even they were unseen beforehand. In this paper, we propose a unified network to encode implicit knowledge and explicit knowledge together, just like the human brain can learn knowledge from normal learning as well as subconsciousness learning. The unified network can generate a unified representation to simultaneously serve various tasks. We can perform kernel space alignment, prediction refinement, and multi-task learning in a convolutional neural network. The results demonstrate that when implicit knowledge is introduced into the neural network, it benefits the performance of all tasks. We further analyze the implicit representation learnt from the proposed unified network, and it shows great capability on catching the physical meaning of different tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhNCwuTsu

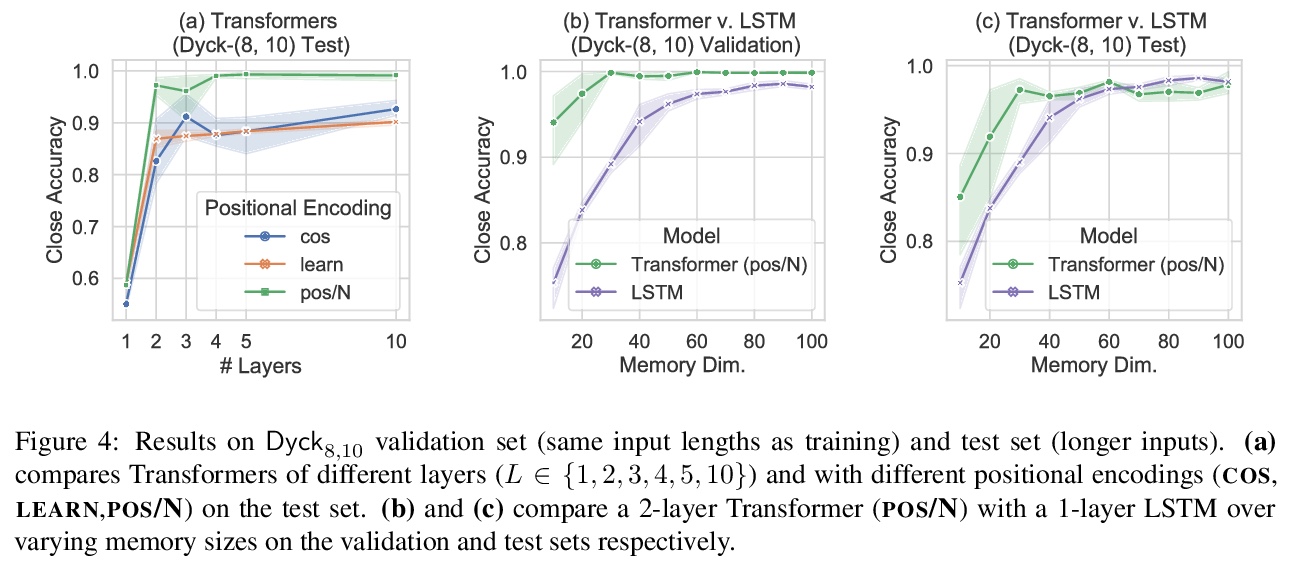
2、[CL] Self-Attention Networks Can Process Bounded Hierarchical Languages
S Yao, B Peng, C Papadimitriou, K Narasimhan
[Princeton University & Columbia University]
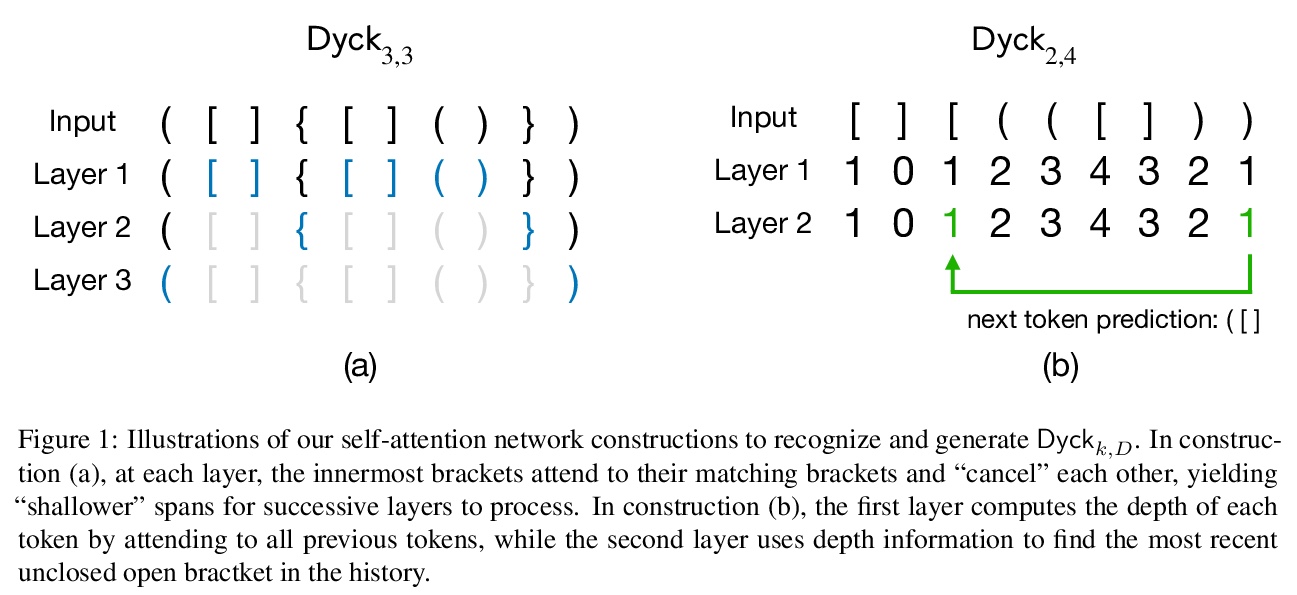
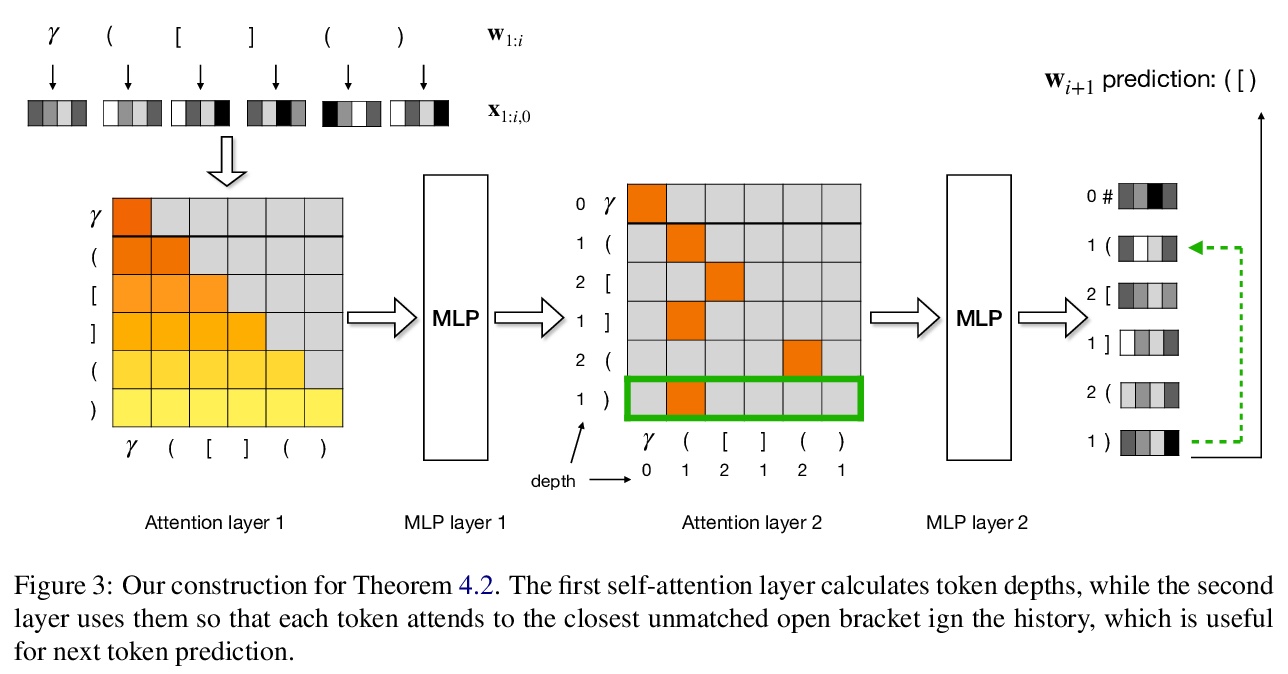
自注意力网络可处理有界层次语言。尽管自注意力网络在NLP中的表现令人印象深刻,但最近被证明在处理具有层次结构的形式语言方面有局限,例如Dyck**k,该语言由K类良好嵌套的括号组成。这表明自然语言可以用对于形式语言来说很弱的模型来近似,或者说自然语言中层次结构和递归的作用可能是有限的。自注意力网络可处理Dyckk,D,即深度以D为界的Dyckk子集,更好地捕捉自然语言的有界层次结构。构建了一个具有D+1层和O(log k)记忆大小(每层每标记)的硬注意力网络,能识别Dyckk,D,以及一个具有两层和O(log k)记忆大小的软注意力网络,能产生Dyckk,D。实验表明,在Dyckk,D**上训练的自注意力网络,能以近乎完美的精度泛化到更长的输入,同时也验证了自注意力网络相对递归网络的理论记忆优势。
Despite their impressive performance in NLP, self-attention networks were recently proved to be limited for processing formal languages with hierarchical structure, such as Dyckk, the language consisting of well-nested parentheses of k types. This suggested that natural language can be approximated well with models that are too weak for formal languages, or that the role of hierarchy and recursion in natural language might be limited. We qualify this implication by proving that self-attention networks can process Dyckk,D, the subset of Dyckk with depth bounded by D, which arguably better captures the bounded hierarchical structure of natural language. Specifically, we construct a hard-attention network with D + 1 layers and O(log k) memory size (per token per layer) that recognizes Dyckk,D, and a soft-attention network with two layers and O(log k) memory size that generates Dyckk,D. Experiments show that self-attention networks trained on Dyckk,D generalize to longer inputs with near-perfect accuracy, and also verify the theoretical memory advantage of self-attention networks over recurrent networks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhNGAvX2d

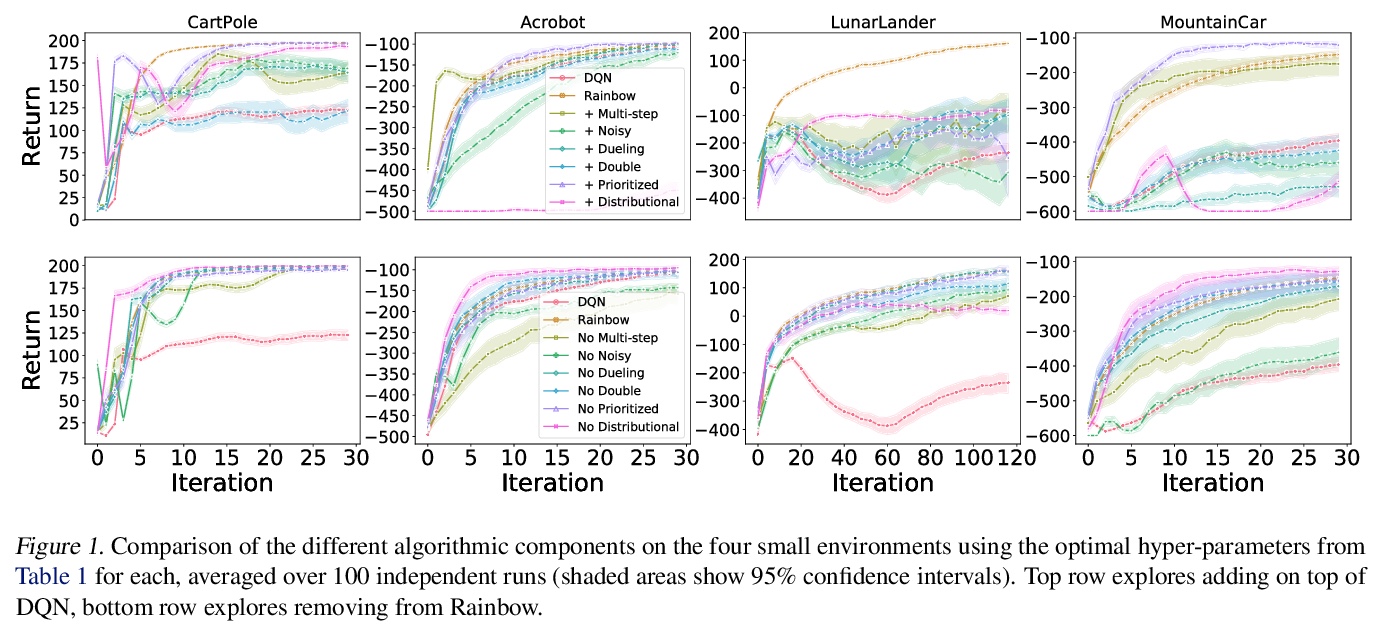
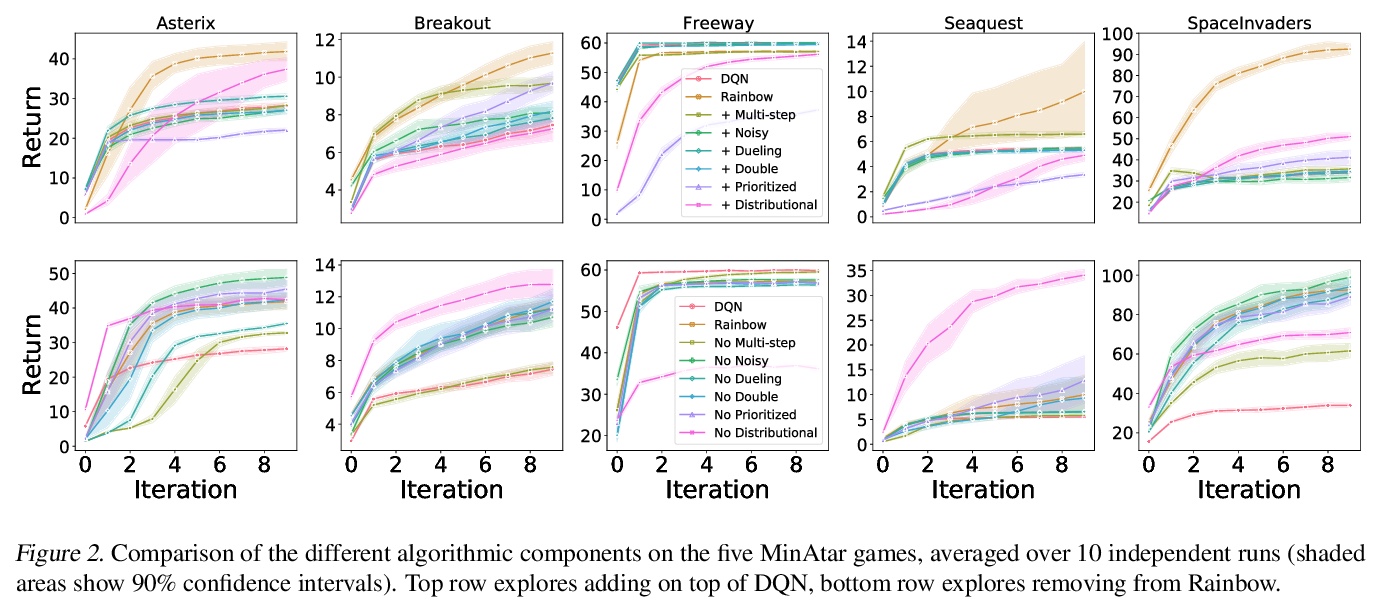
3、[LG] Revisiting Rainbow: Promoting more Insightful and Inclusive Deep Reinforcement Learning Research
J S. Obando-Ceron, P S Castro
[Google Research]
Rainbow的再研究:促进更有洞察力和包容性的深度强化学习研究。自DQN问世以来,绝大多数强化学习研究都集中在以深度神经网络为函数近似器的强化学习上。新方法通常是在一组现在已经成为标准的环境中进行评估,如Atari 2600游戏。虽然这些基准有助于评估的标准化,但它们的计算成本有一个不好的副作用,即扩大了那些有充足计算资源的人和没有计算资源的人之间的差距。本文认为,尽管社区强调大规模环境,但传统的小规模环境仍然可以产生有价值的科学见解,并可帮助降低欠发达社区的进入门槛。为证实该主张,从经验上重新研究了介绍Rainbow算法的论文,并对其算法提出了一些新见解。
Since the introduction of DQN, a vast majority of reinforcement learning research has focused on reinforcement learning with deep neural networks as function approximators. New methods are typically evaluated on a set of environments that have now become standard, such as Atari 2600 games. While these benchmarks help standardize evaluation, their computational cost has the unfortunate side effect of widening the gap between those with ample access to computational resources, and those without. In this work we argue that, despite the community’s emphasis on large-scale environments, the traditional small-scale environments can still yield valuable scientific insights and can help reduce the barriers to entry for underprivileged communities. To substantiate our claims, we empirically revisit the paper which introduced the Rainbow algorithm (Hessel et al., 2018) and present some new insights into the algorithms used by Rainbow.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhNMo8X4y


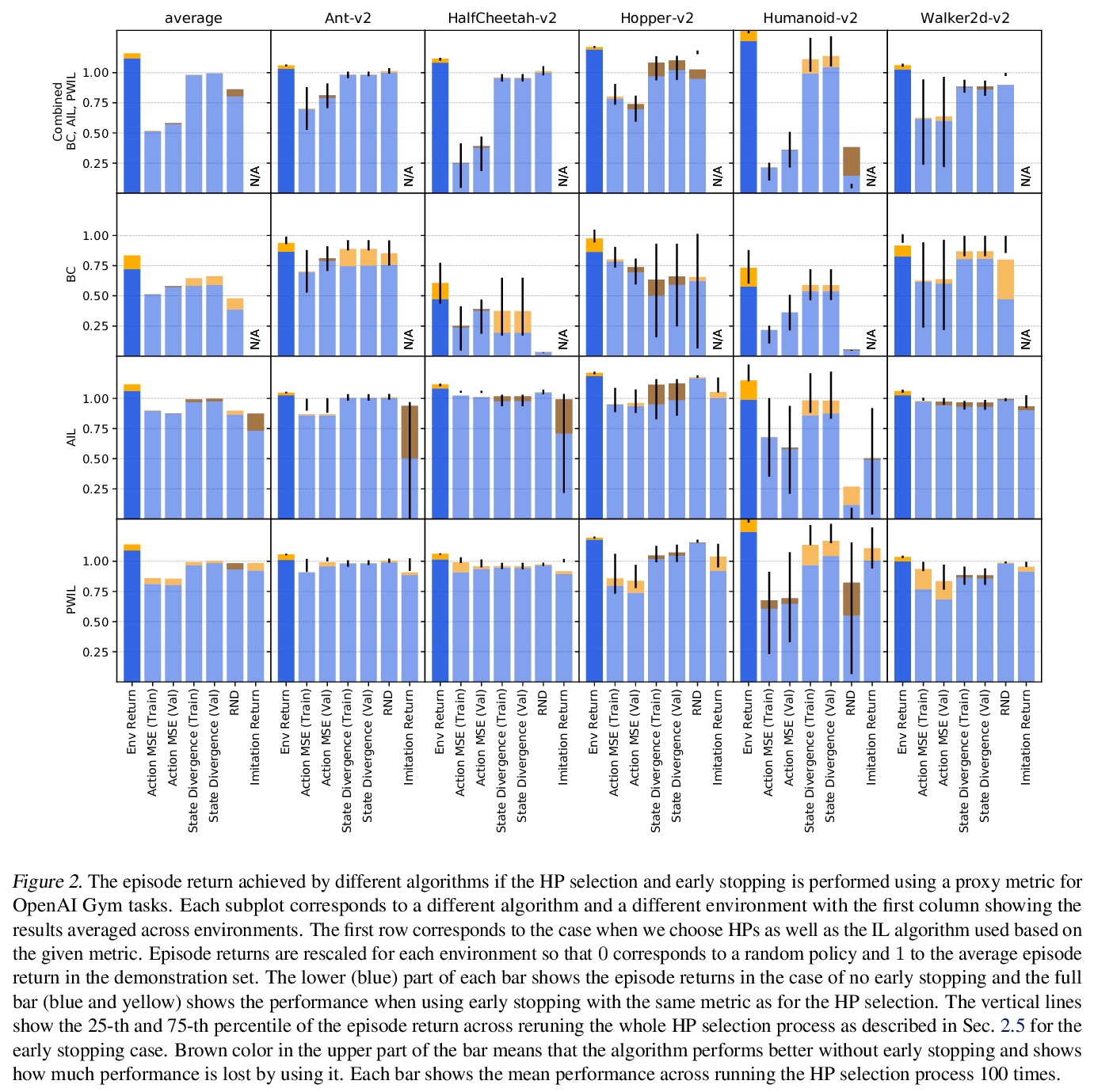
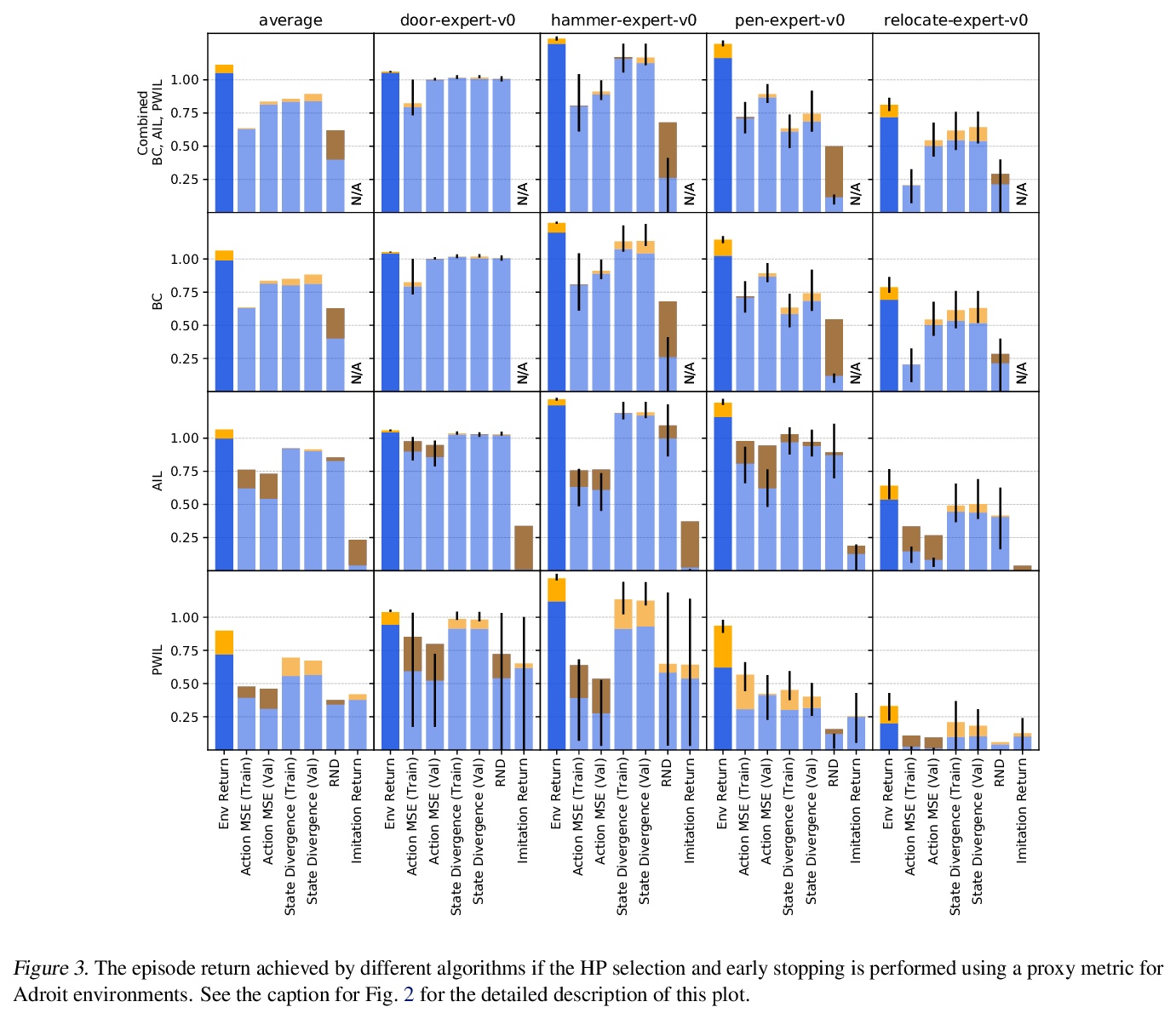
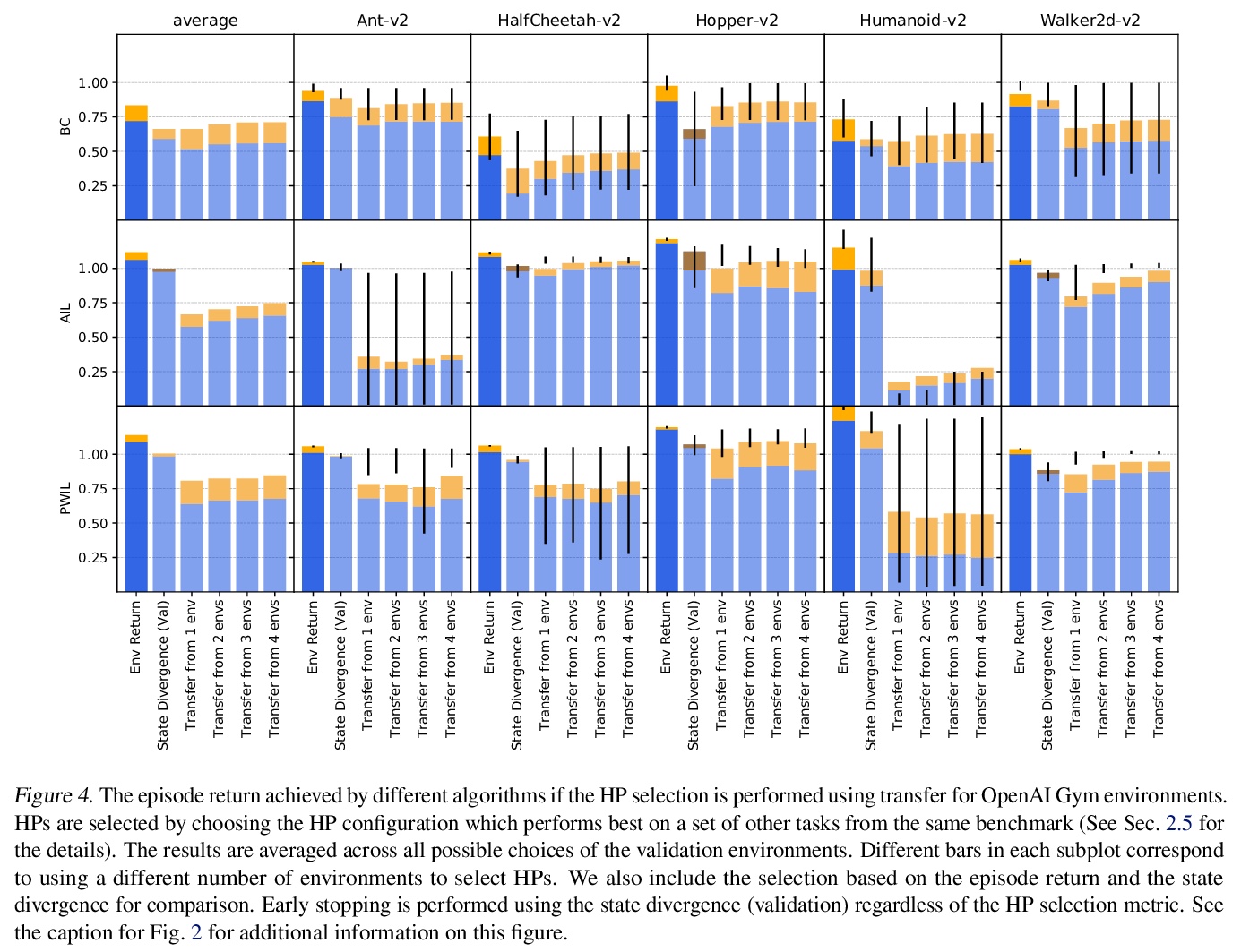
4、[LG] Hyperparameter Selection for Imitation Learning
L Hussenot, M Andrychowicz, D Vincent, R Dadashi, A Raichuk, L Stafiniak, S Girgin, R Marinier, N Momchev, S Ramos, M Orsini, O Bachem, M Geist, O Pietquin
[Google Research]
模仿学习超参数选择。本文讨论了在连续控制背景下为模仿学习算法调整超参数(HP)的问题,这种情况下,示范专家的基本奖励函数不能在所有时候被观察到。模仿学习的大量文献大多认为该奖励函数可用于超参数选择,但这并不是现实的情况。实际上,如果奖励函数可用,就能直接用于策略训练,就没有必要模仿了。为解决这个被忽视的问题,本文提出一些可能的外部奖励的代理。在一项广泛的实证研究中对它们进行了评估(9个环境中超过10000个智能体),并对超参数选择提出了实际建议。结果表明,虽然模仿学习算法对超参数选择很敏感,但通过奖励函数的代理,往往可以选择足够好的超参数。
We address the issue of tuning hyperparameters (HPs) for imitation learning algorithms in the context of continuous-control, when the underlying reward function of the demonstrating expert cannot be observed at any time. The vast literature in imitation learning mostly considers this reward function to be available for HP selection, but this is not a realistic setting. Indeed, would this reward function be available, it could then directly be used for policy training and imitation would not be necessary. To tackle this mostly ignored problem, we propose a number of possible proxies to the external reward. We evaluate them in an extensive empirical study (more than 10’000 agents across 9 environments) and make practical recommendations for selecting HPs. Our results show that while imitation learning algorithms are sensitive to HP choices, it is often possible to select good enough HPs through a proxy to the reward function.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhNRSchVH
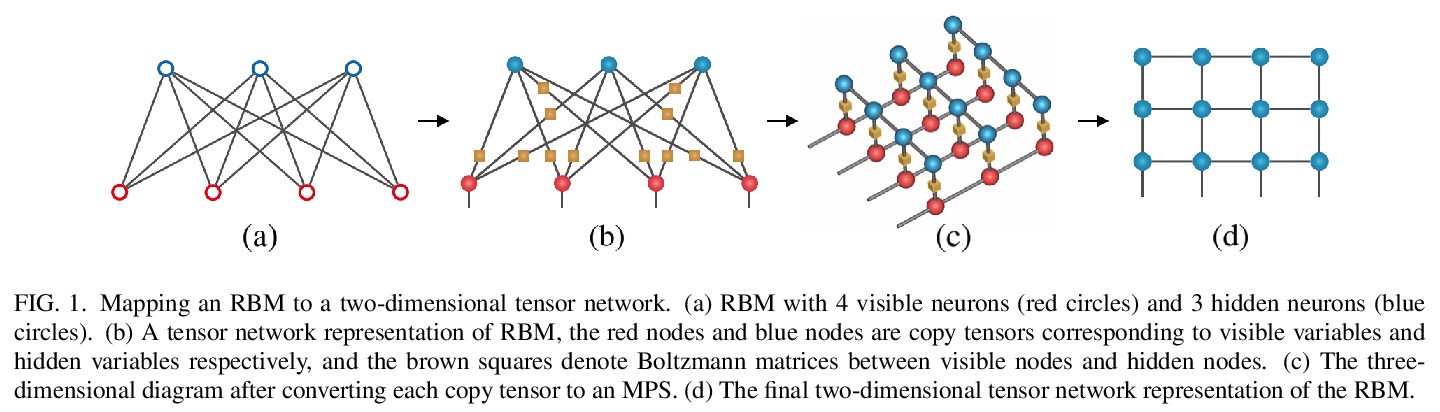
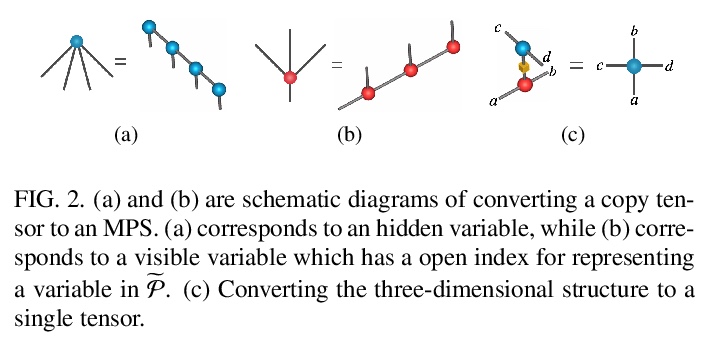
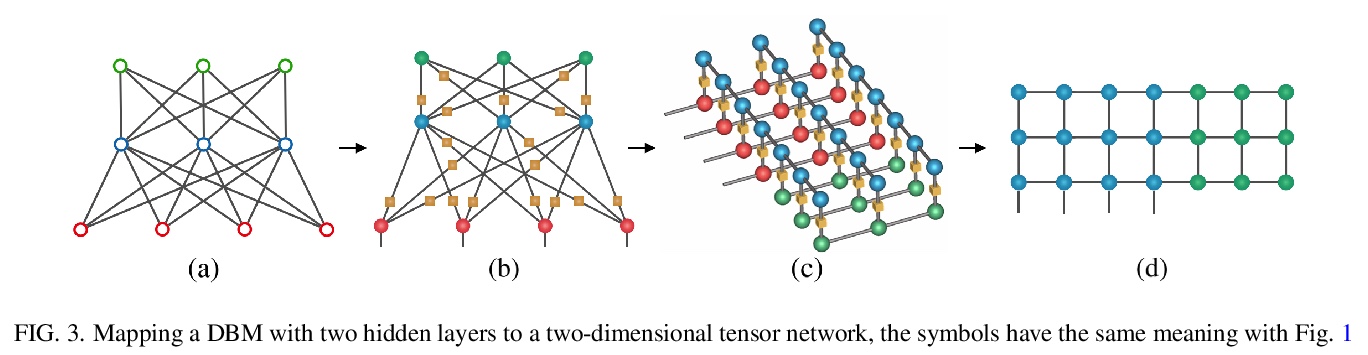
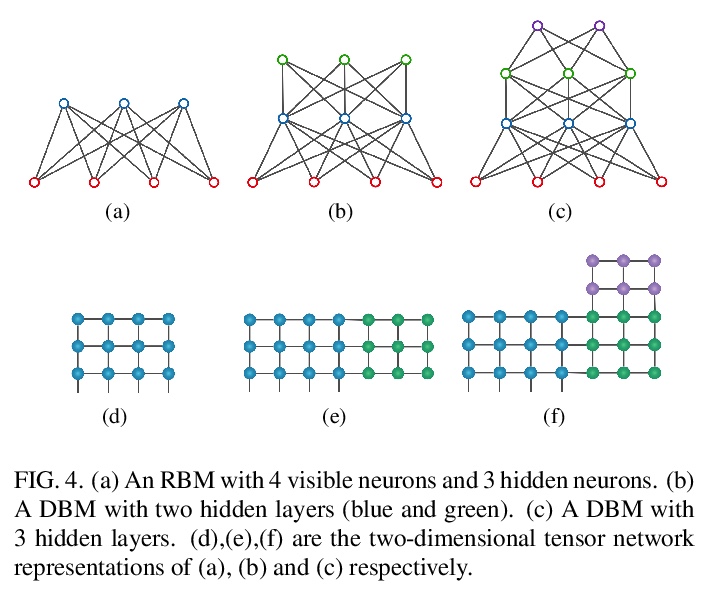
5、[LG] Boltzmann machines as two-dimensional tensor networks
S Li, F Pan, P Zhou, P Zhang
[Chinese Academy of Sciences]
作为二维张量网络的玻尔兹曼机。受限玻尔兹曼机(RBM)和深度玻尔兹曼机(DBM)是机器学习的重要模型,最近在量子多体物理学中发现了许多应用。本文表明,它们与张量网络之间存在着基本的联系。证明了任何RBM和DBM都可以精确地表示为一个二维张量网络。这种表示方法使人们了解到RBM和DBM利用张量网络的纠缠结构所具有的表达能力,也为RBM和DBM的计算配分函数提供了一种有效的张量网络收缩算法。通过数值实验,证明了所提出的算法在估计受限玻尔兹曼机和深度玻尔兹曼机的配分函数方面比最先进的机器学习方法要准确得多,并且在训练深度玻尔兹曼机的一般机器学习任务方面具有潜在的应用。
Restricted Boltzmann machines (RBM) and deep Boltzmann machines (DBM) are important models in machine learning, and recently found numerous applications in quantum many-body physics. We show that there are fundamental connections between them and tensor networks. In particular, we demonstrate that any RBM and DBM can be exactly represented as a two-dimensional tensor network. This representation gives an understanding of the expressive power of RBM and DBM using entanglement structures of the tensor networks, also provides an efficient tensor network contraction algorithm for the computing partition function of RBM and DBM. Using numerical experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed algorithm is much more accurate than the state-of-the-art machine learning methods in estimating the partition function of restricted Boltzmann machines and deep Boltzmann machines, and have potential applications in training deep Boltzmann machines for general machine learning tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhNWatMst
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
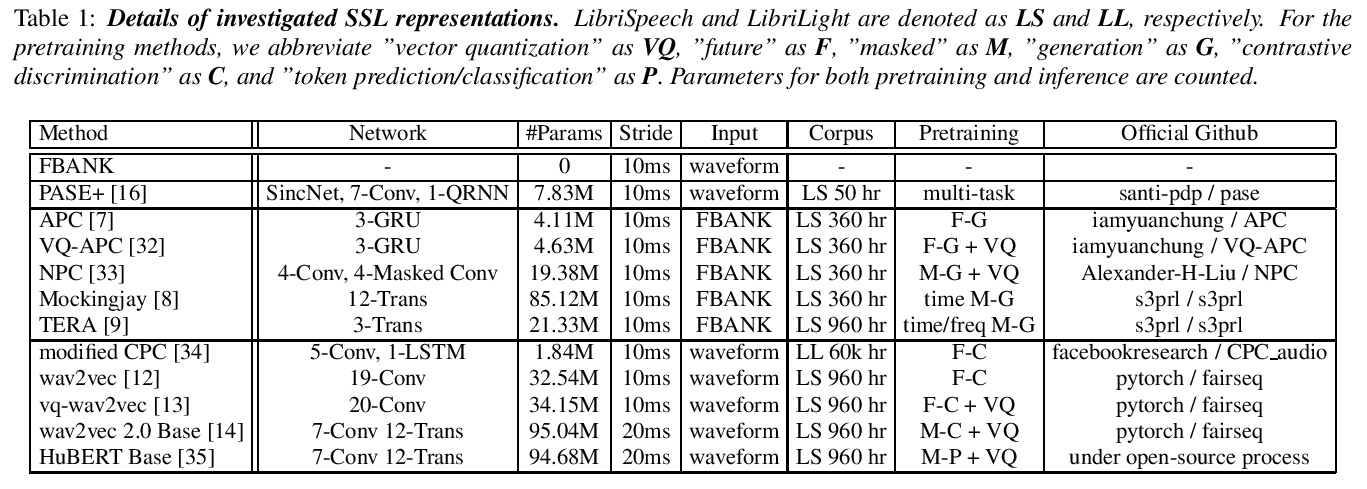
[CL] SUPERB: Speech processing Universal PERformance Benchmark
SUPERB:语音处理通用性能基准
S Yang, P Chi, Y Chuang, C J Lai, K Lakhotia, Y Y. Lin, A T. Liu, J Shi, X Chang, G Lin, T Huang, W Tseng, K Lee, D Liu, Z Huang, S Dong, S Li, S Watanabe, A Mohamed, H Lee
[National Taiwan University & MIT & Facebook AI Research & Johns Hopkins University & Amazon AI & CMU]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhNZ0ykm5
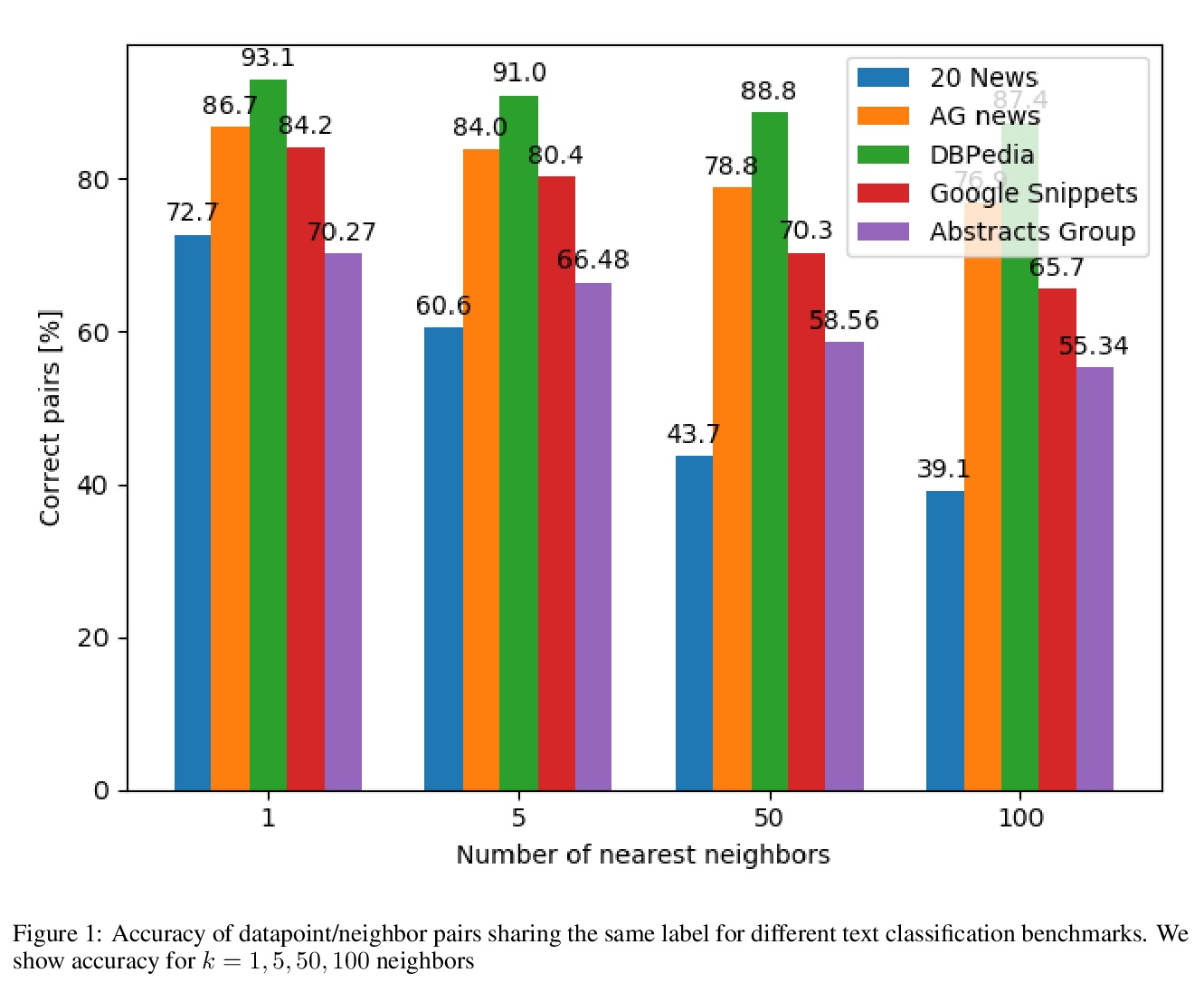
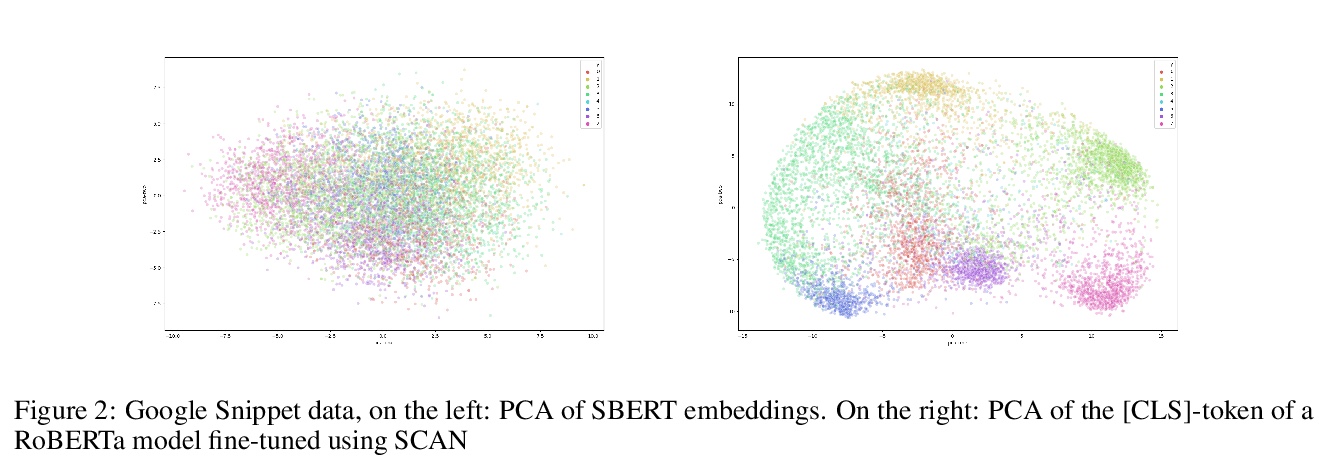
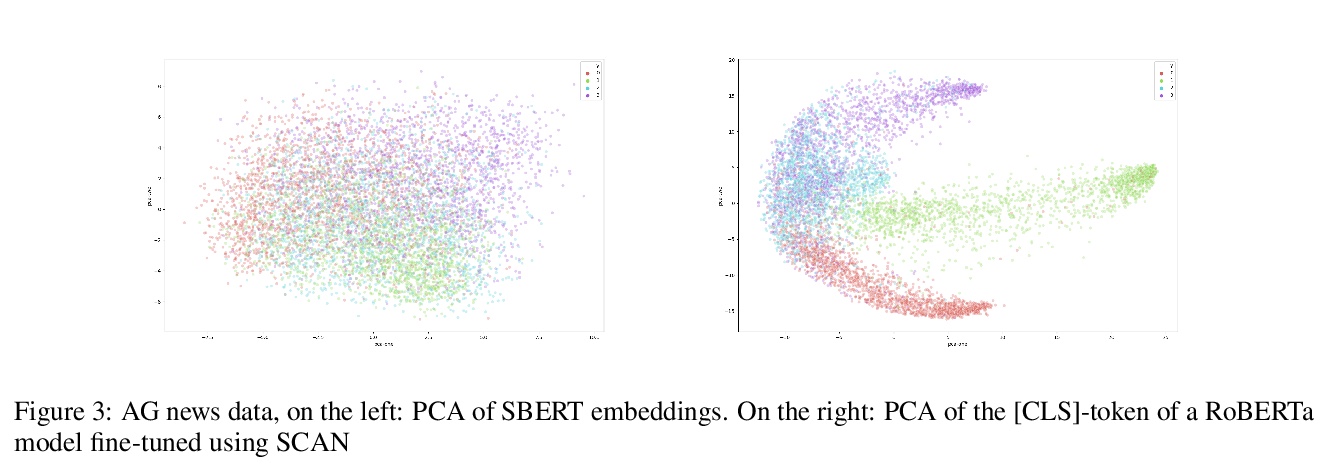
[CL] DocSCAN: Unsupervised Text Classification via Learning from Neighbors
DocSCAN:基于近邻学习的无监督文本分类
D Stammbach, E Ash
[ETH Zurich]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhO06gJsb
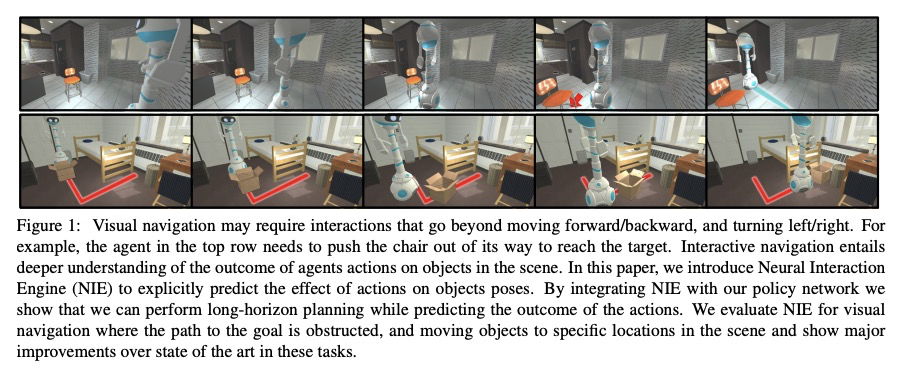
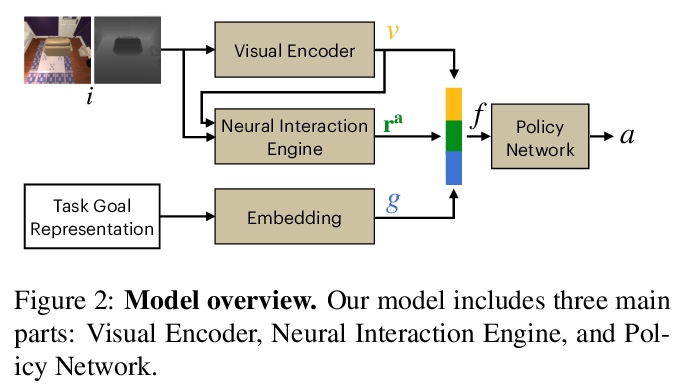
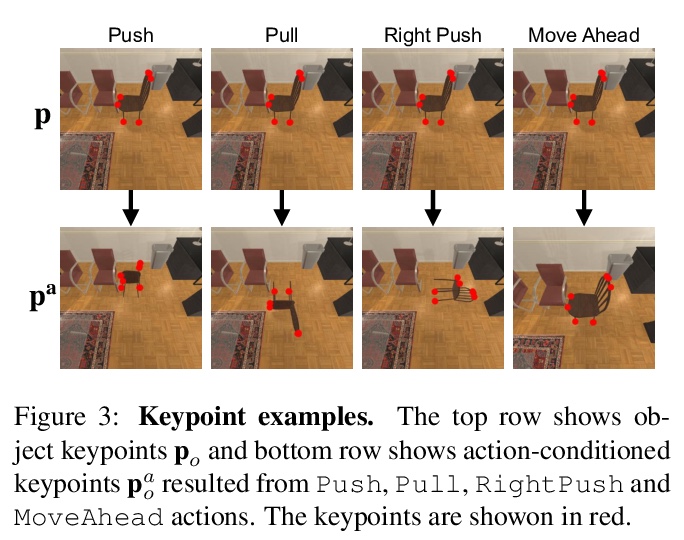
[CV] Pushing it out of the Way: Interactive Visual Navigation
交互式视觉导航
K Zeng, L Weihs, A Farhadi, R Mottaghi
[University of Washington & Allen Institute for AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhO2OmzsX
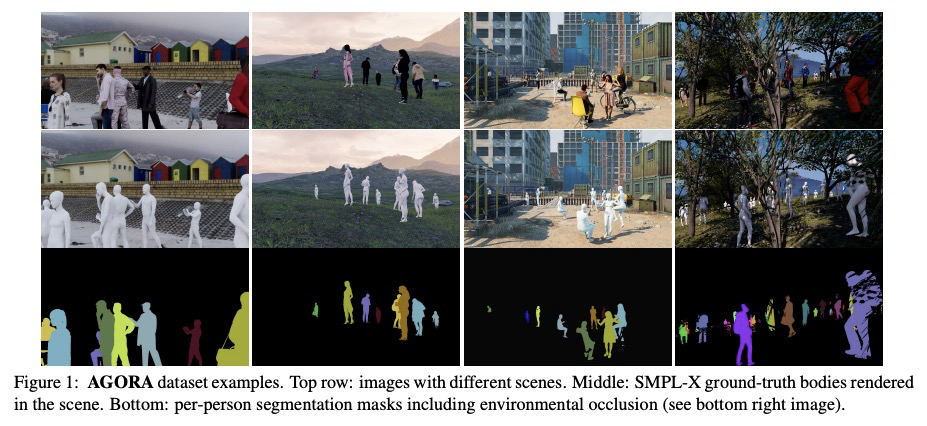
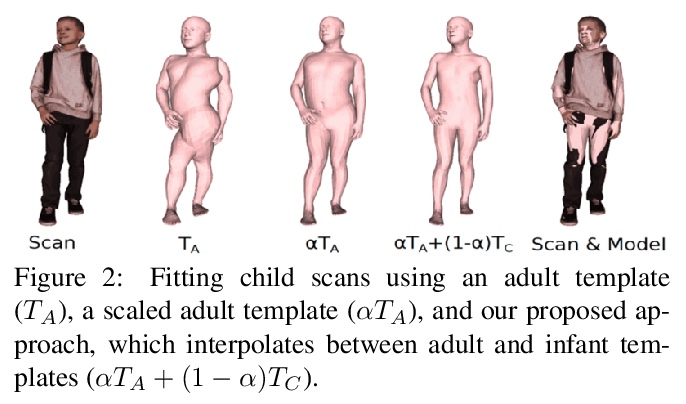
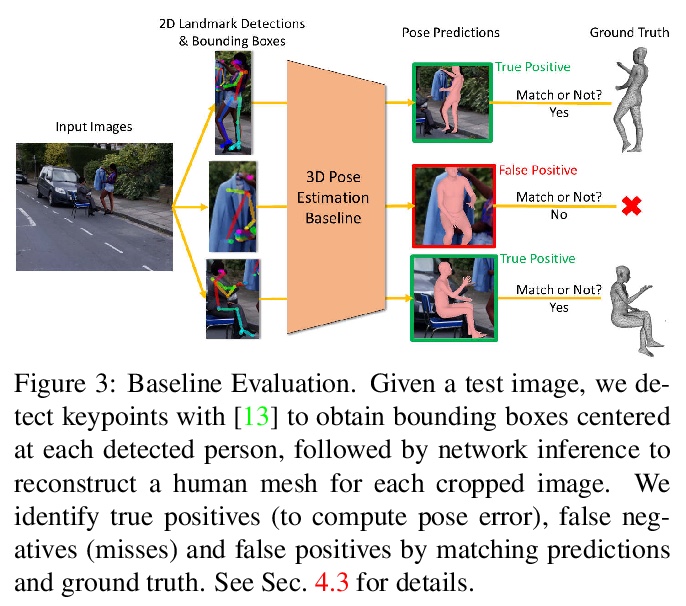
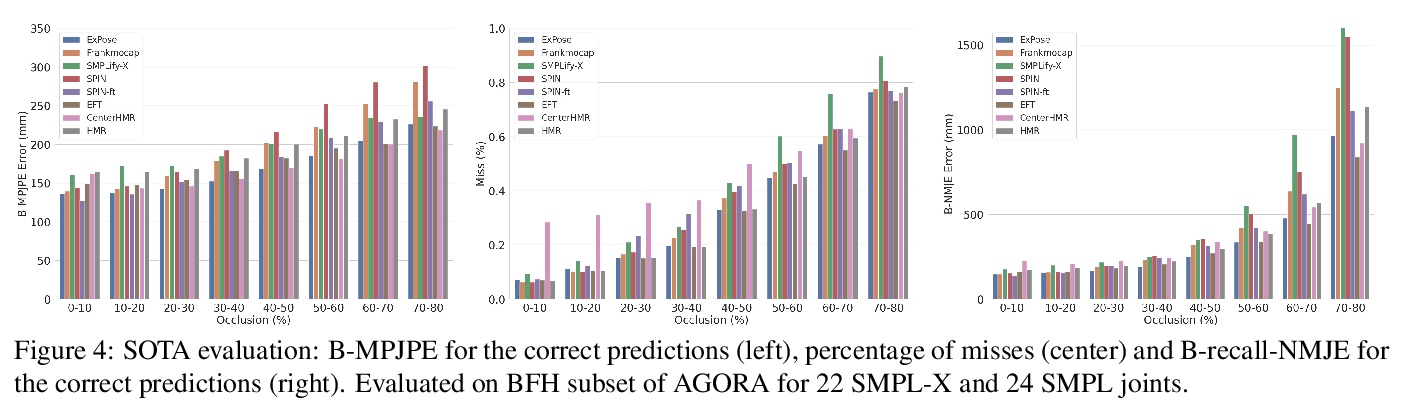
[CV] AGORA: Avatars in Geography Optimized for Regression Analysis
AGORA:3D场景人体姿态检测合成数据集
P Patel, C P. Huang, J Tesch, D T. Hoffmann, S Tripathi, M J. Black
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems & University of Freiburg]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhO4M9s11