- 1、[LG] Embodied Intelligence via Learning and Evolution
- 2、[AS] Speech Recognition by Simply Fine-tuning BERT
- 3、[CL] Pitfalls of Static Language Modelling
- 4、[AS] Towards Natural and Controllable Cross-Lingual Voice Conversion Based on Neural TTS Model and Phonetic Posteriorgram
- 5、[LG] Fast Concept Mapping: The Emergence of Human Abilities in Artificial Neural Networks when Learning Embodied and Self-Supervised
- [AP] Simulation-Based Decision Making in the NFL using NFLSimulatoR
- [LG] Variance Penalized On-Policy and Off-Policy Actor-Critic
- [LG] Melon Playlist Dataset: a public dataset for audio-based playlist generation and music tagging
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[LG] Embodied Intelligence via Learning and Evolution
A Gupta, S Savarese, S Ganguli, L Fei-Fei
[Stanford University]
基于学习和进化的具身智能。提出了深度进化强化学习(DERL),一种新的计算框架,可进化出不同的智能体形态,在复杂环境中仅使用低水平的自我中心感觉信息来学习具有挑战性的运动和操纵任务。利用DERL,证明了环境复杂性、形态智能和控制的可学习性之间的关系:首先,环境复杂性促进了形态智能的进化,可用形态促进新任务学习的能力来量化。其次,进化快速选择学习速度较快的形态,从而使早期祖先一生中较晚学会的行为在其后代一生中较早表现出来。在复杂环境中学习和进化的智能体中,这一结果构成了长期以来猜想的形态学鲍德温效应的首次证明。第三,实验表明,鲍德温效应和形态智能的出现都有一个机理基础,即通过物理上更稳定、能量效率更高的形态的进化,促进学习和控制。
The intertwined processes of learning and evolution in complex environmental niches have resulted in a remarkable diversity of morphological forms. Moreover, many aspects of animal intelligence are deeply embodied in these evolved morphologies. However, the principles governing relations between environmental complexity, evolved morphology, and the learnability of intelligent control, remain elusive, partially due to the substantial challenge of performing large-scale in silico experiments on evolution and learning. We introduce Deep Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning (DERL): a novel computational framework which can evolve diverse agent morphologies to learn challenging locomotion and manipulation tasks in complex environments using only low level egocentric sensory information. Leveraging DERL we demonstrate several relations between environmental complexity, morphological intelligence and the learnability of control. First, environmental complexity fosters the evolution of morphological intelligence as quantified by the ability of a morphology to facilitate the learning of novel tasks. Second, evolution rapidly selects morphologies that learn faster, thereby enabling behaviors learned late in the lifetime of early ancestors to be expressed early in the lifetime of their descendants. In agents that learn and evolve in complex environments, this result constitutes the first demonstration of a long-conjectured morphological Baldwin effect. Third, our experiments suggest a mechanistic basis for both the Baldwin effect and the emergence of morphological intelligence through the evolution of morphologies that are more physically stable and energy efficient, and can therefore facilitate learning and control.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K0t3Z3ccR


2、[AS] Speech Recognition by Simply Fine-tuning BERT
W Huang, C Wu, S Luo, K Chen, H Wang, T Toda
[Nagoya University, Japan & Academia Sinica]
基于简单微调BERT的语音识别。提出一种简单的自动语音识别方法BERT-ASR,简单地对预训练BERT模型进行微调,将ASR表述为一个分类问题,其目标是在给定声学语音信号和历史词的情况下,正确分类下一个词。给定一个历史语境序列,一个强大的语言可以缩小可能的选择范围,语音信号可以作为一个简单线索。与传统自动语音识别系统从头开始训练强大的声学模型不同,通过简单微调BERT模型就可实现语音识别。在普通话AISHELL-1数据集上展示了所提出想法的有效性。
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K0t9HjF4q



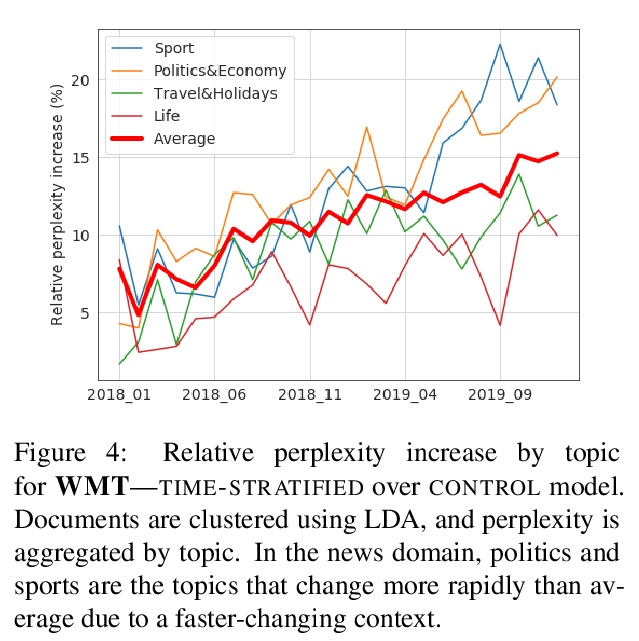
3、[CL] Pitfalls of Static Language Modelling
A Lazaridou, A Kuncoro, E Gribovskaya, D Agrawal, A Liska, T Terzi, M Gimenez, C d M d’Autume, S Ruder, D Yogatama, K Cao, T Kocisky, S Young, P Blunsom
[DeepMind]
静态语言建模的陷阱。系统评价了当前的语言模型在基于过去预测未来的现实设置中,在多大程度上具有泛化能力。现行的语言建模评价范式,即从重叠时段中提取训练和评价集,对模型泛化的评价过于乐观。实验表明,最先进的Transformer模型预测在其训练时段之外的未来语句的现实设置中表现更差。单独增加模型大小,并不能解决时间上的泛化问题;能不断用新信息更新知识的模型,确实可以减缓随时间推移而退化的速度。时间分层是一种现实的评价设置,能在真正未见的数据上评价模型,可对模型的分布外泛化进行更公平的评价。一个更现实的动态语言建模基准,可用来衡量进展,并最终鼓励开发能处理非稳定文本数据并保持与世界同步的模型。
Our world is open-ended, non-stationary and constantly evolving; thus what we talk about and how we talk about it changes over time. This inherent dynamic nature of language comes in stark contrast to the current static language modelling paradigm, which constructs training and evaluation sets from overlapping time periods. Despite recent progress, we demonstrate that state-of-the-art Transformer models perform worse in the realistic setup of predicting future utterances from beyond their training period — a consistent pattern across three datasets from two domains. We find that, while increasing model size alone — a key driver behind recent progress — does not provide a solution for the temporal generalization problem, having models that continually update their knowledge with new information can indeed slow down the degradation over time. Hence, given the compilation of ever-larger language modelling training datasets, combined with the growing list of language-model-based NLP applications that require up-to-date knowledge about the world, we argue that now is the right time to rethink our static language modelling evaluation protocol, and develop adaptive language models that can remain up-to-date with respect to our ever-changing and non-stationary world.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K0tdnboJc


4、[AS] Towards Natural and Controllable Cross-Lingual Voice Conversion Based on Neural TTS Model and Phonetic Posteriorgram
S Zhao, H Wang, T H Nguyen, B Ma
[Alibaba Group]
基于神经网络TTS模型和音素后验概率的自然可控跨语言语音转换。提出了基于神经网络FastSpeech TTS模型和LPCNet声码器的高质量跨语言语音转换框架。提出用音素后验概率和归一化对数尺度基频来克服不同语言之间显著的语音和节律的不匹配。充分利用所提出的有效特征表示和先进的合成器和声码器,所提出的FastSpeech-VC仅用单语言语料就能产生高质量的转换语音和良好的说话人相似性。FastSpeech-VC还具有可控性,可平滑地调整语音速率,大大加快了音频生成速度,只需有限数据就能适应说话人。
Cross-lingual voice conversion (VC) is an important and challenging problem due to significant mismatches of the phonetic set and the speech prosody of different languages. In this paper, we build upon the neural text-to-speech (TTS) model, i.e., FastSpeech, and LPCNet neural vocoder to design a new cross-lingual VC framework named FastSpeech-VC. We address the mismatches of the phonetic set and the speech prosody by applying Phonetic PosteriorGrams (PPGs), which have been proved to bridge across speaker and language boundaries. Moreover, we add normalized logarithm-scale fundamental frequency (Log-F0) to further compensate for the prosodic mismatches and significantly improve naturalness. Our experiments on English and Mandarin languages demonstrate that with only mono-lingual corpus, the proposed FastSpeech-VC can achieve high quality converted speech with mean opinion score (MOS) close to the professional records while maintaining good speaker similarity. Compared to the baselines using Tacotron2 and Transformer TTS models, the FastSpeech-VC can achieve controllable converted speech rate and much faster inference speed. More importantly, the FastSpeech-VC can easily be adapted to a speaker with limited training utterances.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K0tmvmc32

5、[LG] Fast Concept Mapping: The Emergence of Human Abilities in Artificial Neural Networks when Learning Embodied and Self-Supervised
V Clay, P König, G Pipa, K Kühnberger
[University of Osnabrück]
快速概念图:人工神经网络具身和自监督学习时人类能力的出现。引入一种设置,智能体通过自监督探索在模拟世界中学习,通过与世界的交互学习到的表征,来关联语义概念。提出了快速概念映射方法,用神经元的相关发射模式来定义和检测语义概念。这种关联只要需要极少的标注样本,类似于在人类中观察到的一种叫做快速映射的现象。提出了一个可行的策略,用于学习概念,不需要太多的监督,通过与世界的单纯互动,可以学习环境的有意义的表征。
Most artificial neural networks used for object detection and recognition are trained in a fully supervised setup. This is not only very resource consuming as it requires large data sets of labeled examples but also very different from how humans learn. We introduce a setup in which an artificial agent first learns in a simulated world through self-supervised exploration. Following this, the representations learned through interaction with the world can be used to associate semantic concepts such as different types of doors. To do this, we use a method we call fast concept mapping which uses correlated firing patterns of neurons to define and detect semantic concepts. This association works instantaneous with very few labeled examples, similar to what we observe in humans in a phenomenon called fast mapping. Strikingly, this method already identifies objects with as little as one labeled example which highlights the quality of the encoding learned self-supervised through embodiment using curiosity-driven exploration. It therefor presents a feasible strategy for learning concepts without much supervision and shows that through pure interaction with the world meaningful representations of an environment can be learned.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K0tsB1MIe




另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[AP] Simulation-Based Decision Making in the NFL using NFLSimulatoR
用NFLSimulatoR实现基于仿真的国家橄榄球联盟决策
B Williams, W Palmquist, R Elmore
[University of Denver]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K0tkOoRY4


[LG] Variance Penalized On-Policy and Off-Policy Actor-Critic
On-Policy和Off-Policy Actor-Critic的方差惩罚
A Jain, G Patil, A Jain, K Khetarpal, D Precup
[McGill University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K0txyfY07


[LG] Melon Playlist Dataset: a public dataset for audio-based playlist generation and music tagging
Melon播放列表数据集:面向音频播放列表生成和音乐标记的公开数据集
A Ferraro, Y Kim, S Lee, B Kim, N Jo, S Lim, S Lim, J Jang, S Kim, X Serra, D Bogdanov
[Universitat Pompeu Fabra & Kakao Corp]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K0tAzCvVv



