- 1、[CV] BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers
- 2、[LG] Controlling Neural Networks with Rule Representations
- 3、[LG] Self-Supervised Learning with Kernel Dependence Maximization
- 4、[LG] Learning Equivariant Energy Based Models with Equivariant Stein Variational Gradient Descent
- 5、[LG] Machine Learning Implicit Solvation for Molecular Dynamics
- [CL] Question Answering Infused Pre-training of General-Purpose Contextualized Representations
- [LG] Revisiting Model Stitching to Compare Neural Representations
- [CV] Dynamic Head: Unifying Object Detection Heads with Attentions
- [CL] Text Generation with Efficient (Soft) Q-Learning
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers
H Bao, L Dong, F Wei
[Microsoft Research]
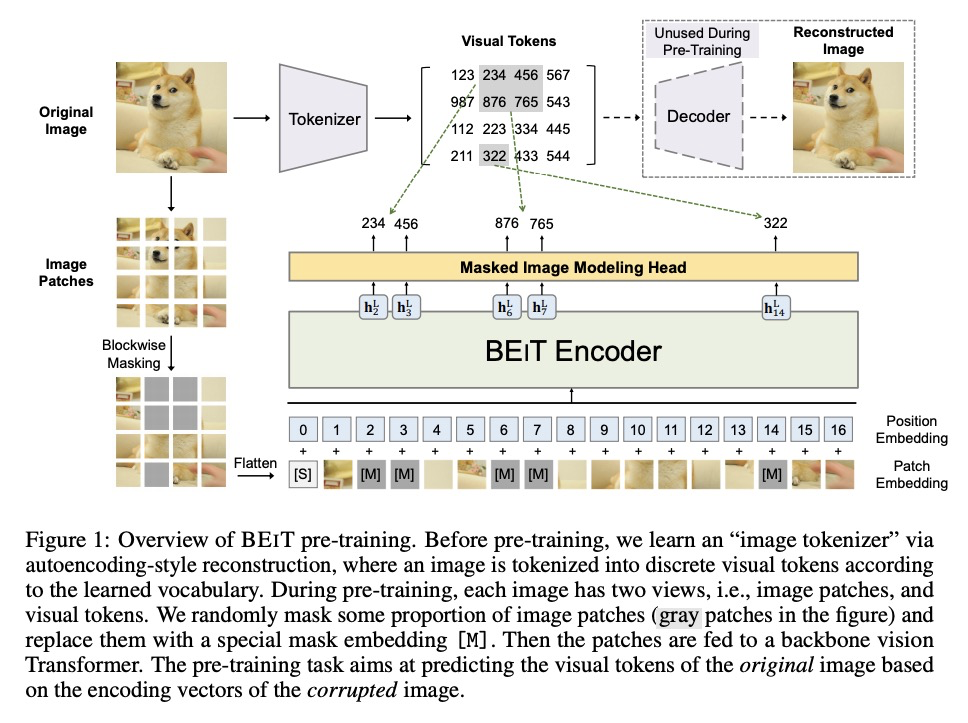
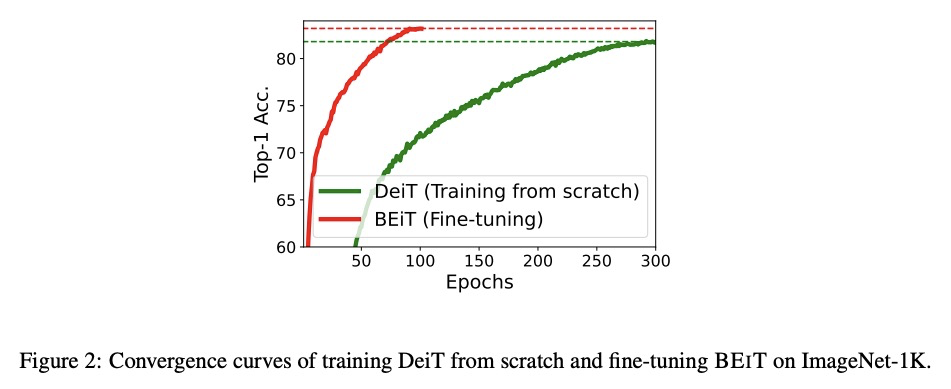
BEIT:图像Transformer的BERT预训练。本文提出一种自监督视觉表示模型BEIT——图像Transformer的双向编码器表示。受自然语言处理领域开发的BERT启发,本文提出一种掩蔽图像建模任务来预训练视觉Transformer。在预训练中,每张图像都有两种视图,即图块(如16×16像素),和视觉标记(离散标记)。将原始图像”标记化”为视觉标记,随机屏蔽一些图块,并将其送入骨干Transformer。预训练的目的,是根据被破坏的图块来恢复原始视觉标记。对BEIT进行预训练之后,通过在预训练编码器上添加任务层,直接对下游任务的模型参数进行微调。图像分类和语义分割的实验结果表明,该模型取得了与之前预训练方法有竞争力的结果。例如,基础规模的BEIT在ImageNet-1K上取得了83.2%的最高准确率,在相同设置下,大大超过了从零开始的DeiT训练(81.8%)。大规模的BEIT仅使用ImageNet-1K就获得了86.3%,甚至超过了在ImageNet-22K上进行有监督预训练的ViT-L(85.2%)。
We introduce a self-supervised vision representation model BEIT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder representation from Image Transformers. Following BERT (Devlin et al., 2019) developed in the natural language processing area, we propose a masked image modeling task to pretrain vision Transformers. Specifically, each image has two views in our pre-training, i.e, image patches (such as 16× 16 pixels), and visual tokens (i.e., discrete tokens). We first “tokenize” the original image into visual tokens. Then we randomly mask some image patches and fed them into the backbone Transformer. The pre-training objective is to recover the original visual tokens based on the corrupted image patches. After pre-training BEIT, we directly fine-tune the model parameters on downstream tasks by appending task layers upon the pretrained encoder. Experimental results on image classification and semantic segmentation show that our model achieves competitive results with previous pre-training methods. For example, base-size BEIT achieves 83.2% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K, significantly outperforming from-scratch DeiT training (81.8%; Touvron et al., 2020) with the same setup. Moreover, large-size BEIT obtains 86.3% only using ImageNet-1K, even outperforming ViT-L with supervised pre-training on ImageNet-22K (85.2%; Dosovitskiy et al., 2020).
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkxbEwaR8

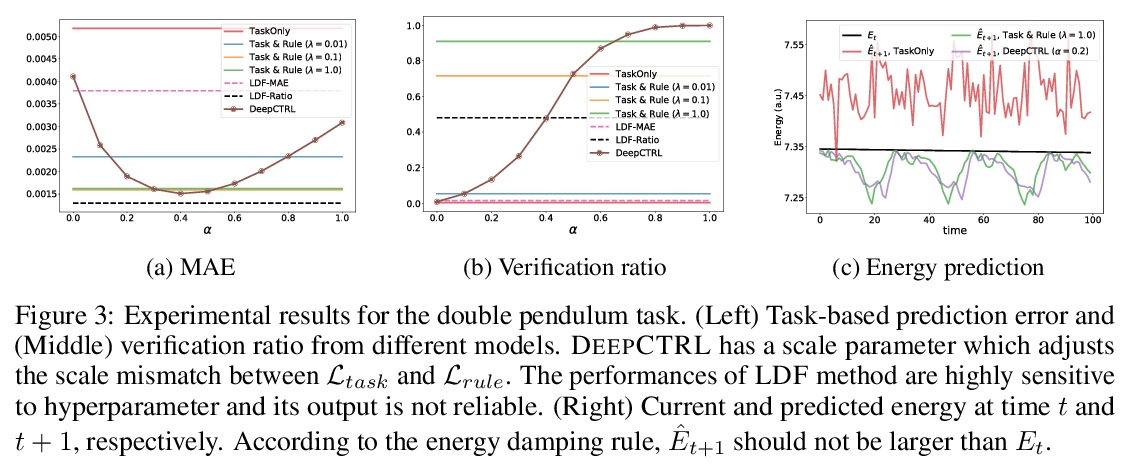
2、[LG] Controlling Neural Networks with Rule Representations
S Seo, S O. Arik, J Yoon, X Zhang, K Sohn, T Pfister
[Google Cloud AI]
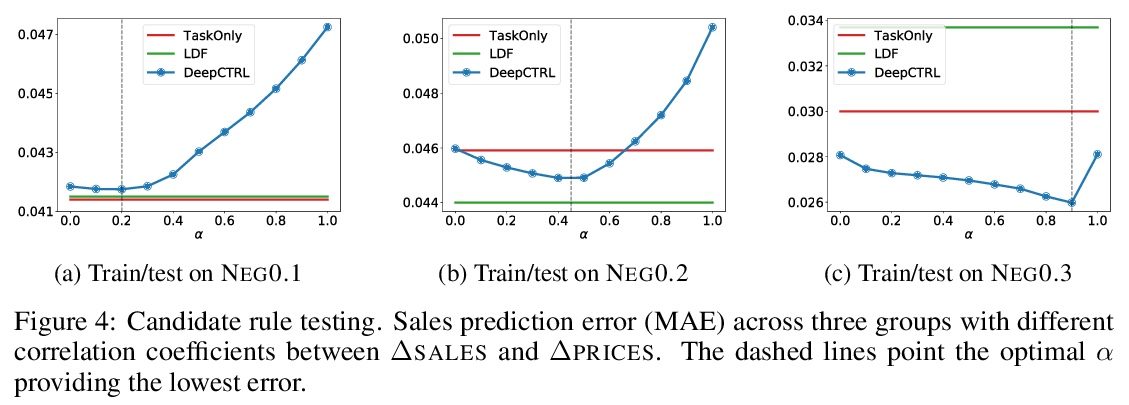
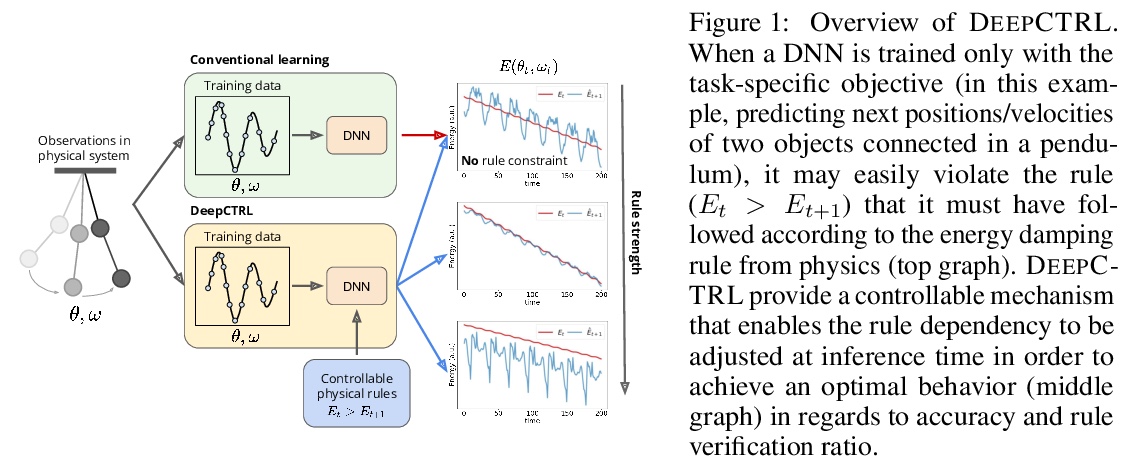
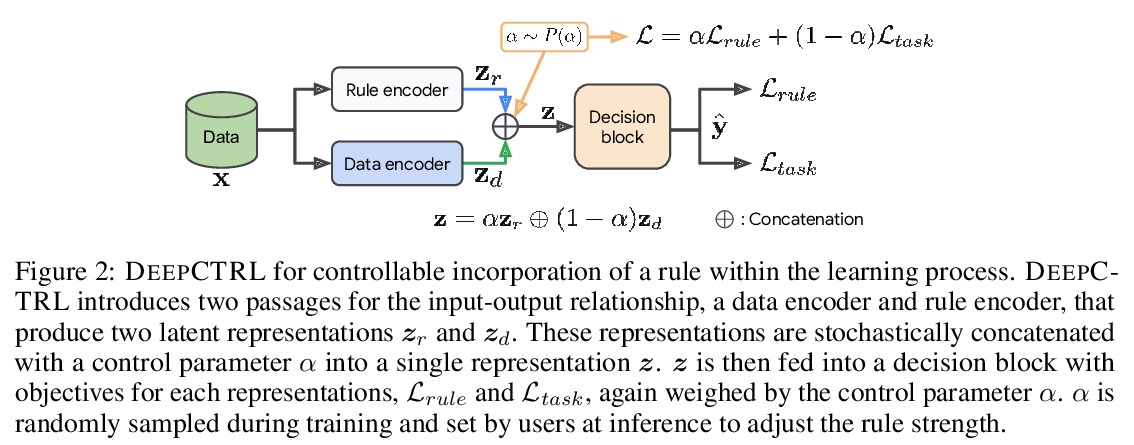
基于规则表示的神经网络控制。从规则中学习,对于构建可解释的、鲁棒的、可靠的深度神经网络至关重要。本文提出一种新的训练方法,将规则纳入深度网络学习,在推理时控制规则强度,无需重新训练。提出一种新的基于扰动的规则编码方法,将任意规则整合到有意义的表示中。具有可控规则表示的深度神经网络(DEEPCTRL)将规则编码器与基于规则的目标相结合,实现了决策的共享表示。DEEPCTRL对数据类型和模型结构是不可知的,可应用于任意类型的输入和输出的规则定义。DEEPCTRL的关键之处,在于不需要重新训练来适应规则强度——推理时,用户可根据准确度与规则验证率的理想操作点来调整它。DEEPCTRL与模型结构、数据类型和规则类型无关。在纳入规则至关重要的现实领域——如物理、零售和医疗——展示了DEEPCTRL在教授深度学习规则方面的有效性。DEEPCTRL通过大幅提高规则验证率,提高了训练好的模型的信任度和可靠性,同时在下游任务中也提供了准确度的提升。此外,DEEPCTRL还能实现新的用例,如对数据样本进行规则的假设测试,以及基于数据集之间共享规则的无监督适应。
We propose a novel training method to integrate rules into deep learning, in a way their strengths are controllable at inference. Deep Neural Networks with Controllable Rule Representations (DEEPCTRL) incorporates a rule encoder into the model coupled with a rule-based objective, enabling a shared representation for decision making. DEEPCTRL is agnostic to data type and model architecture. It can be applied to any kind of rule defined for inputs and outputs. The key aspect of DEEPCTRL is that it does not require retraining to adapt the rule strength – at inference, the user can adjust it based on the desired operation point on accuracy vs. rule verification ratio. In real-world domains where incorporating rules is critical – such as Physics, Retail and Healthcare – we show the effectiveness of DEEPCTRL in teaching rules for deep learning. DEEPCTRL improves the trust and reliability of the trained models by significantly increasing their rule verification ratio, while also providing accuracy gains at downstream tasks. Additionally, DEEPCTRL enables novel use cases such as hypothesis testing of the rules on data samples, and unsupervised adaptation based on shared rules between datasets.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkxgOyl9z

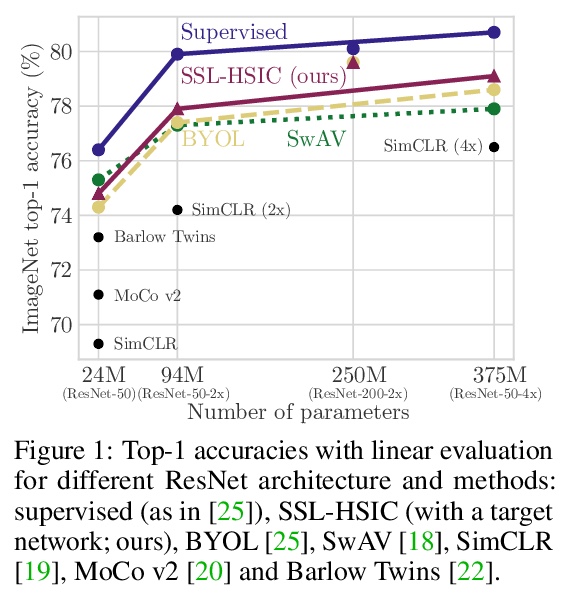
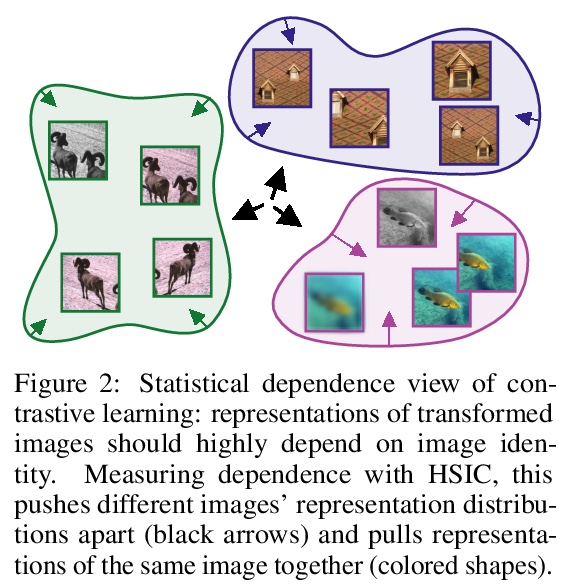
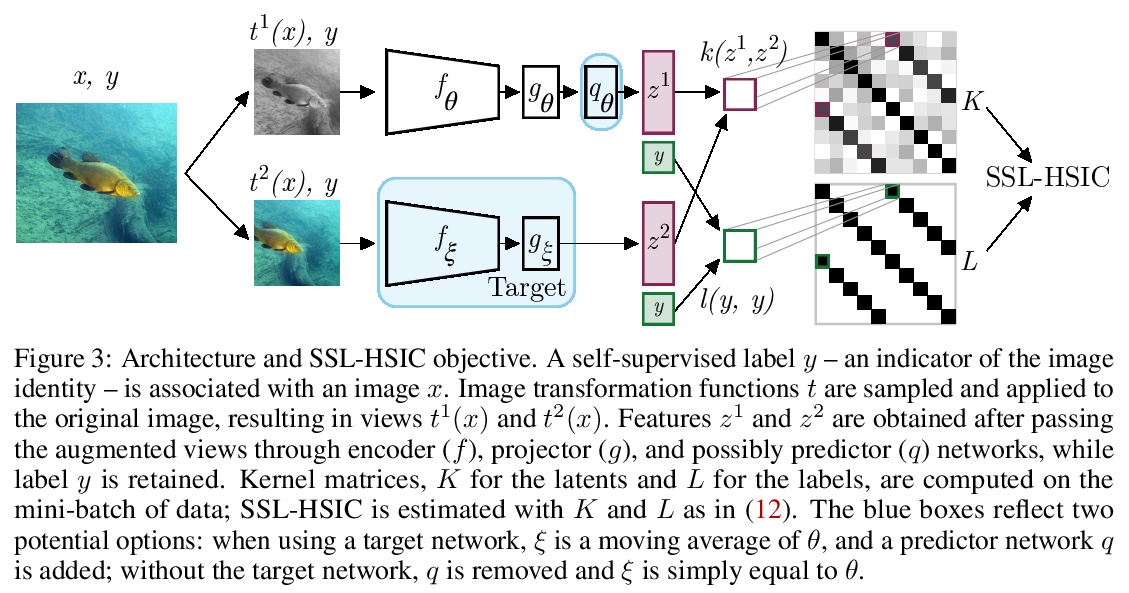
3、[LG] Self-Supervised Learning with Kernel Dependence Maximization
Y Li, R Pogodin, D J. Sutherland, A Gretton
[DeepMind & UCL & UBC]
基于核依赖最大化的自监督学习。从统计依赖的角度对图像表示进行自监督学习,提出了带有希尔伯特-施密特独立准则(SSL-HSIC)的自监督学习。SSL-HSIC最大限度提高了图像转换版本和图像特征之间的依赖性,同时使这些特征的核化方差最小。这个自监督学习框架产生了对InfoNCE的新的理解,它是不同变换之间互信息(MI)的变分下界。虽然已知MI本身有病态,可能会导致学习到无意义表征,但其约束的表现要好得多:它隐式地接近SSL-HSIC(有一个稍微不同的正则化器)。该方法也让我们了解了BYOL,因为SSL-HSIC也同样学习了样本的局部邻域。SSL-HSIC允许我们直接优化在时间上与批次大小呈线性关系的统计依赖性,而不需要限制性的数据假设或间接的互信息估计器。无论是否有目标网络的训练,SSL-HSIC在ImageNet上的标准线性评估、半监督学习和迁移到其他分类和视觉任务(如语义分割、深度估计和目标识别)方面与当前最先进的技术相当。
We approach self-supervised learning of image representations from a statistical dependence perspective, proposing Self-Supervised Learning with the HilbertSchmidt Independence Criterion (SSL-HSIC). SSL-HSIC maximizes dependence between representations of transformed versions of an image and the image identity, while minimizing the kernelized variance of those features. This self-supervised learning framework yields a new understanding of InfoNCE, a variational lower bound on the mutual information (MI) between different transformations. While the MI itself is known to have pathologies which can result in meaningless representations being learned, its bound is much better behaved: we show that it implicitly approximates SSL-HSIC (with a slightly different regularizer). Our approach also gives us insight into BYOL, since SSL-HSIC similarly learns local neighborhoods of samples. SSL-HSIC allows us to directly optimize statistical dependence in time linear in the batch size, without restrictive data assumptions or indirect mutual information estimators. Trained with or without a target network, SSL-HSIC matches the current state-of-the-art for standard linear evaluation on ImageNet [1], semi-supervised learning and transfer to other classification and vision tasks such as semantic segmentation, depth estimation and object recognition.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkxkZpt04
4、[LG] Learning Equivariant Energy Based Models with Equivariant Stein Variational Gradient Descent
P Jaini, L Holdijk, M Welling
[University of Amsterdam]
用等变斯坦变分梯度下降法学习等变基于能量模型。本文关注的是通过在概率模型中加入对称性,来有效采样和学习概率密度的问题。介绍了等变斯坦变分梯度下降算法——一种基于斯坦特性的等变采样方法,用于从具有对称性的密度中采样。等变SVGD通过等变核显式包含了密度中的对称性信息,这使得产生的采样器在采样复杂度和生成样本质量方面都很高效。定义了等变基于能量模型,来建模通过对比散度学习得到的不变密度。通过用等变SVGD来训练等变EBM,提出了改进和扩大基于能量模型训练的新方法。将这些等变基于能量模型用于图像数据集、多体粒子系统和分子结构生成的回归和分类任务中的联合密度建模。
We focus on the problem of efficient sampling and learning of probability densities by incorporating symmetries in probabilistic models. We first introduce Equivariant Stein Variational Gradient Descent algorithm – an equivariant sampling method based on Stein’s identity for sampling from densities with symmetries. Equivariant SVGD explicitly incorporates symmetry information in a density through equivariant kernels which makes the resultant sampler efficient both in terms of sample complexity and the quality of generated samples. Subsequently, we define equivariant energy based models to model invariant densities that are learned using contrastive divergence. By utilizing our equivariant SVGD for training equivariant EBMs, we propose new ways of improving and scaling up training of energy based models. We apply these equivariant energy models for modelling joint densities in regression and classification tasks for image datasets, many-body particle systems and molecular structure generation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkxrdkgqY
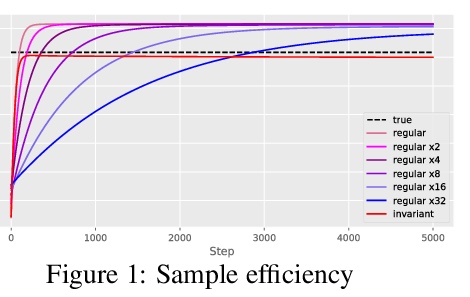
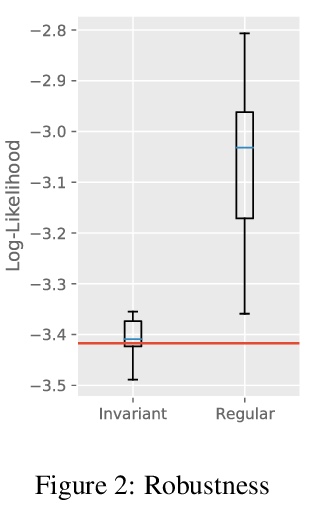
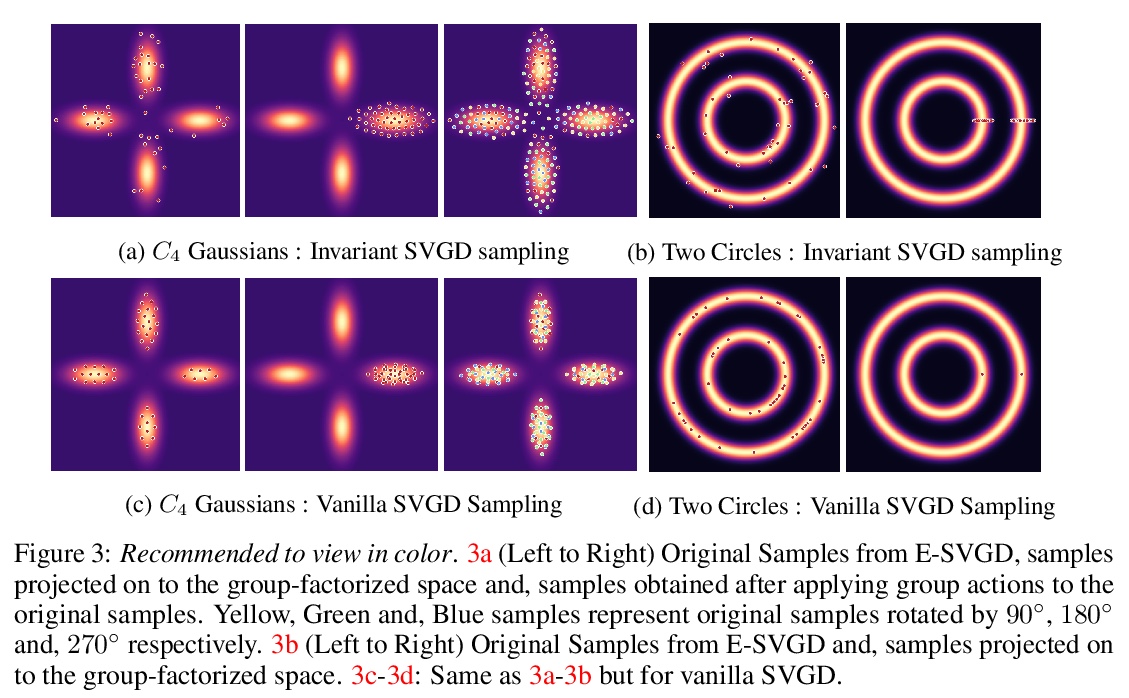
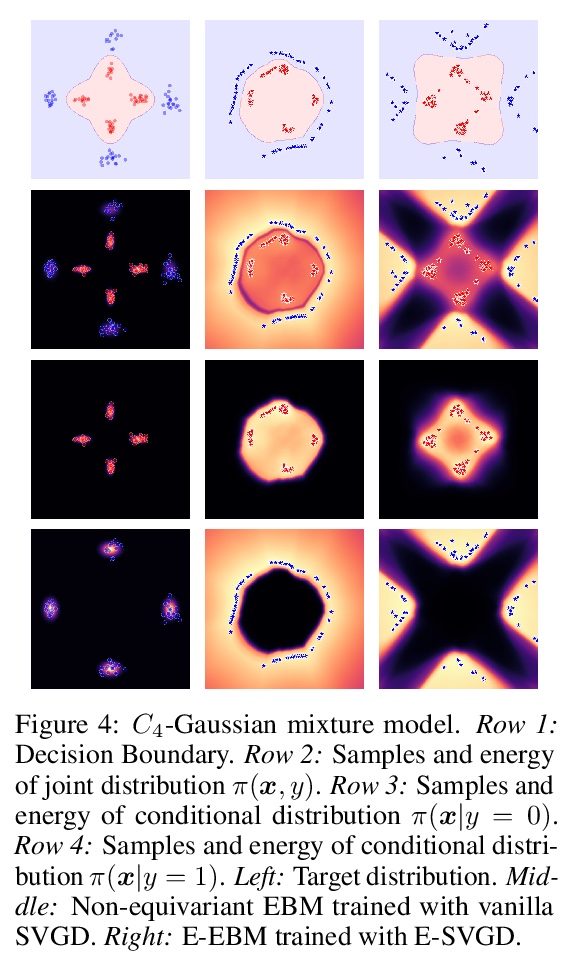
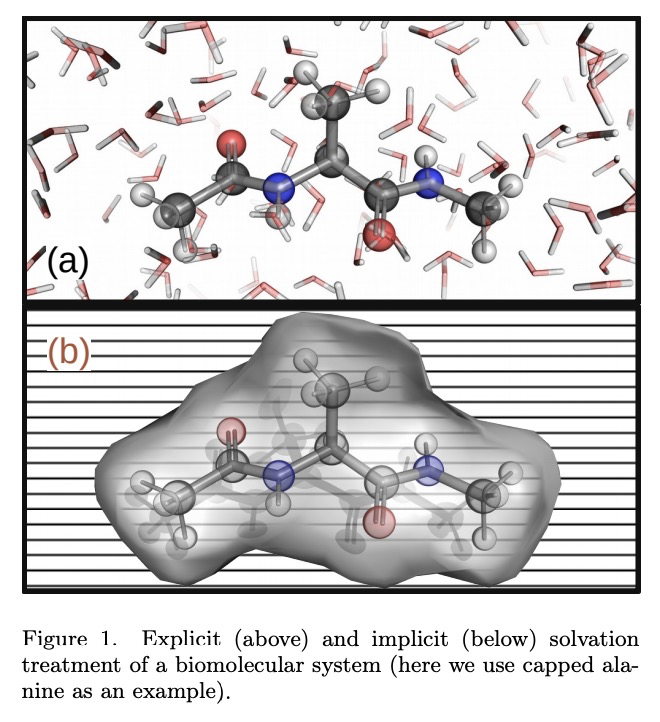
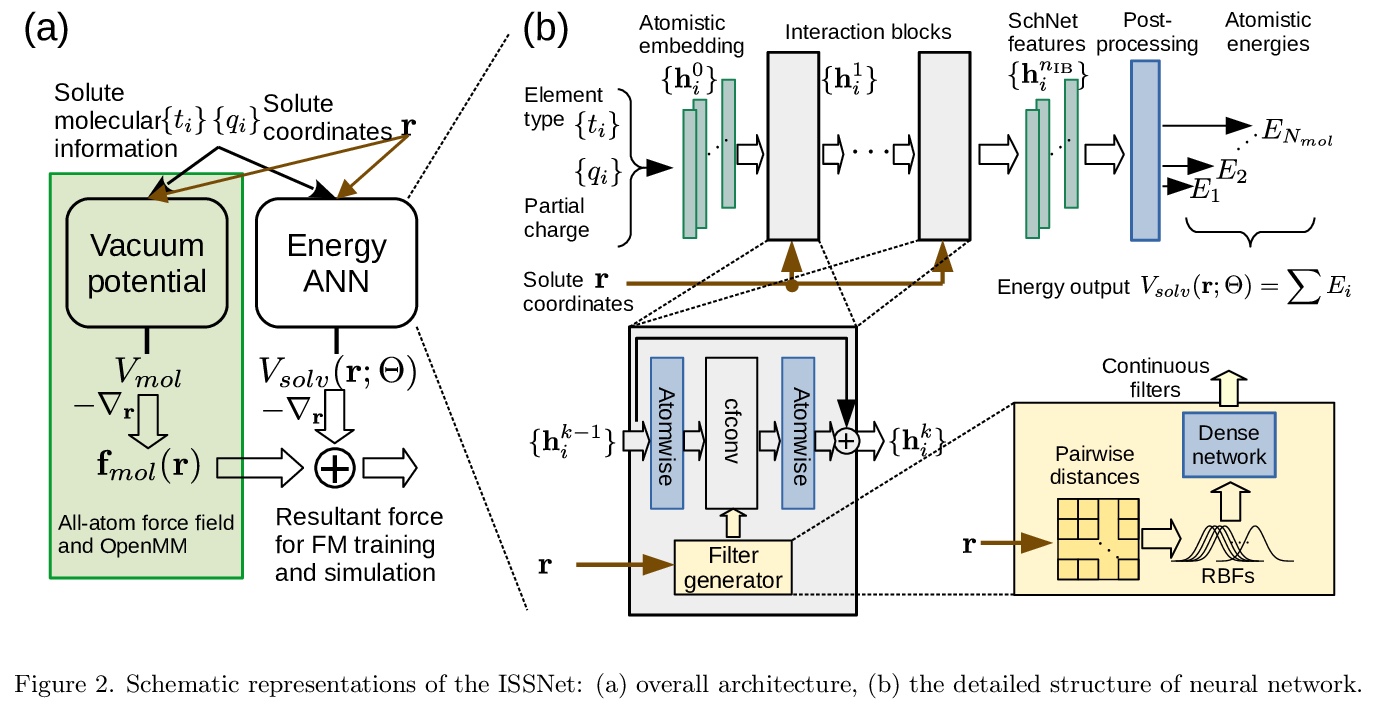
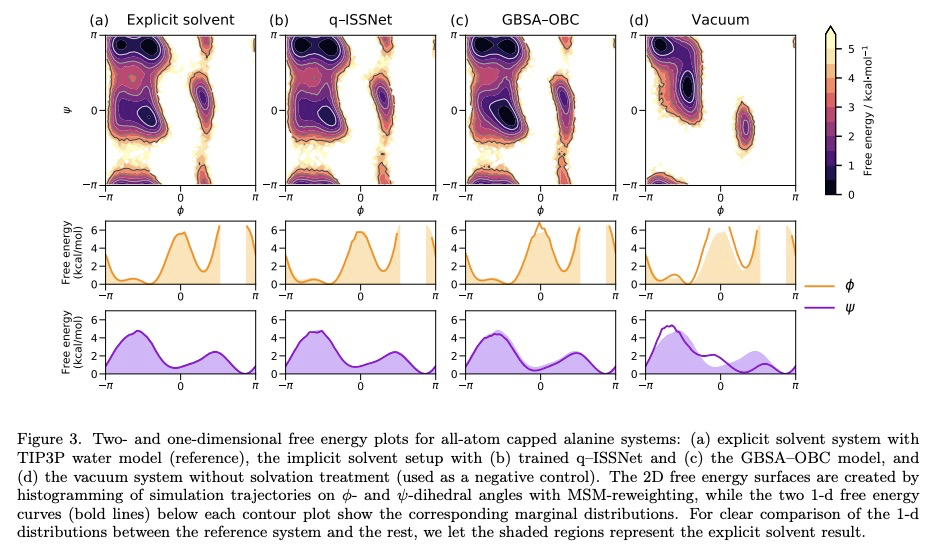
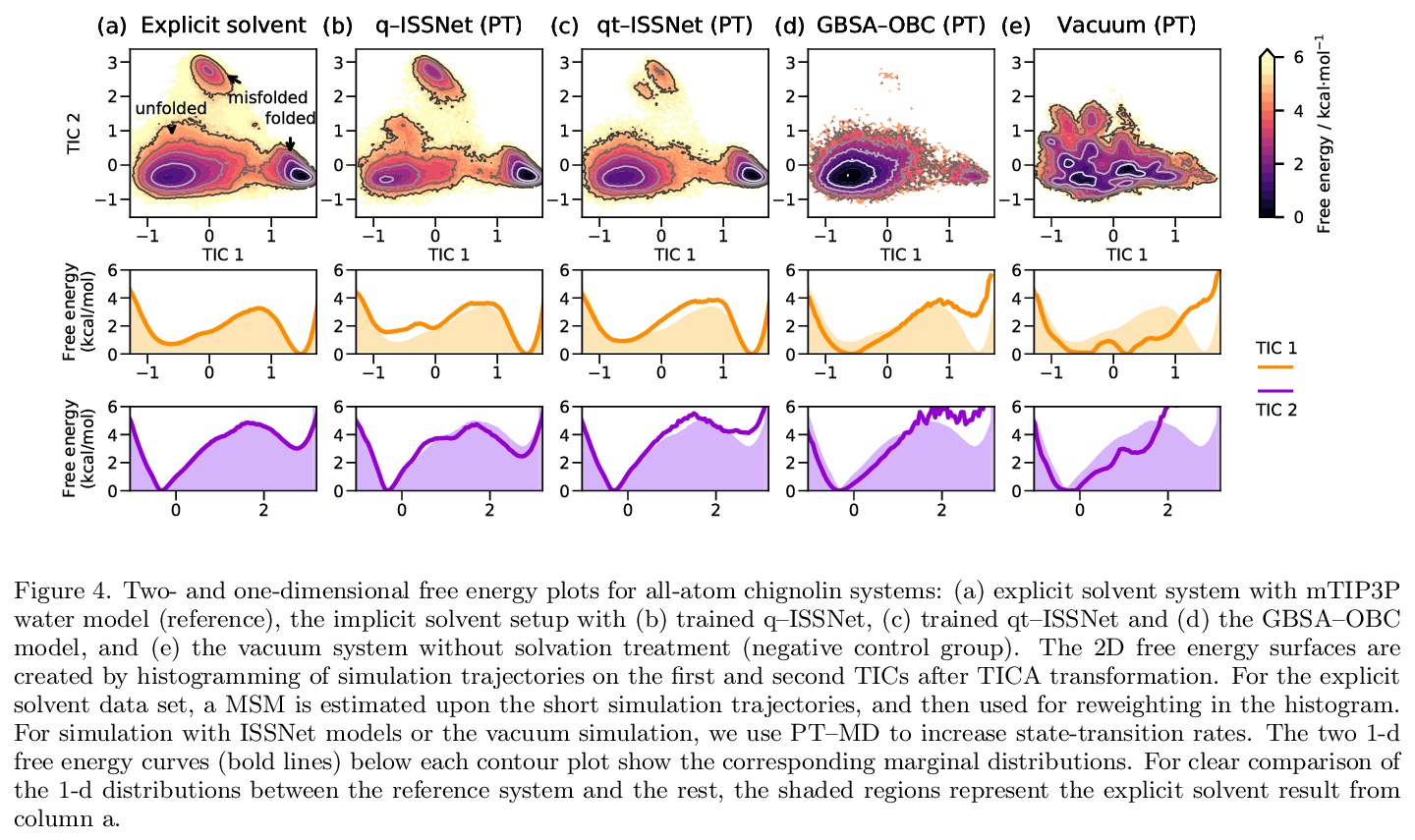
5、[LG] Machine Learning Implicit Solvation for Molecular Dynamics
Y Chen, A Krämer, N E. Charron, B E. Husic, C Clementi, F Noé
[Freie Universität & Rice University]
分子动力学的机器学习隐式求解。对生物分子溶剂环境进行精确建模,对于计算生物学和药物设计至关重要。为实现大系统的长模拟时间尺度,一种流行的方法是用隐性溶剂模型以均值场的方式纳入溶剂的影响。然而,现有的隐性溶剂模型面临的一个挑战是,与显性溶剂模型相比,往往缺乏准确性或某些物理特性,因为被忽视的溶剂分子的多体效应很难作为均值场建模。本文利用机器学习(ML)和多尺度粗粒化(CG)来学习隐性溶剂模型,可以在给定的训练数据下,以任意精度近似给定的显性溶剂模型的能量和热力学特性。继之前的ML-CG模型CGnet和CGSchnet之后,提出了ISSNet,一种图神经网络,用来建模平均力的隐性溶剂势。ISSNet可以从显性溶剂模拟数据中学习,很容易应用于MD模拟。比较了两个多肽系统在不同溶质处理下的溶质构象分布。结果表明,ISSNet模型在再现显性溶剂的小蛋白质系统的热力学方面可以胜过广泛使用的广义Born和表面积模型。新方法为利用机器学习的力量解决隐性溶剂问题奠定了基础,在硅研究和生物医学应用中,应用机器学习方法对溶剂效应进行精确建模具有潜在的好处。
Accurate modeling of the solvent environment for biological molecules is crucial for computational biology and drug design. A popular approach to achieve long simulation time scales for large system sizes is to incorporate the effect of the solvent in a mean-field fashion with implicit solvent models. However, a challenge with existing implicit solvent models is that they often lack accuracy or certain physical properties compared to explicit solvent models, as the many-body effects of the neglected solvent molecules is difficult to model as a mean field. Here, we leverage machine learning (ML) and multi-scale coarse graining (CG) in order to learn implicit solvent models that can approximate the energetic and thermodynamic properties of a given explicit solvent model with arbitrary accuracy, given enough training data. Following the previous ML—CG models CGnet and CGSchnet, we introduce ISSNet, a graph neural network, to model the implicit solvent potential of mean force. ISSNet can learn from explicit solvent simulation data and be readily applied to MD simulations. We compare the solute conformational distributions under different solvation treatments for two peptide systems. The results indicate that ISSNet models can outperform widely-used generalized Born and surface area models in reproducing the thermodynamics of small protein systems with respect to explicit solvent. The success of this novel method demonstrates the potential benefit of applying machine learning methods in accurate modeling of solvent effects for in silico research and biomedical applications.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kkxw8h9CK
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CL] Question Answering Infused Pre-training of General-Purpose Contextualized Representations
问答注入的通用上下文化表示预训练
R Jia, M Lewis, L Zettlemoyer
[Facebook AI Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkxAKC1ax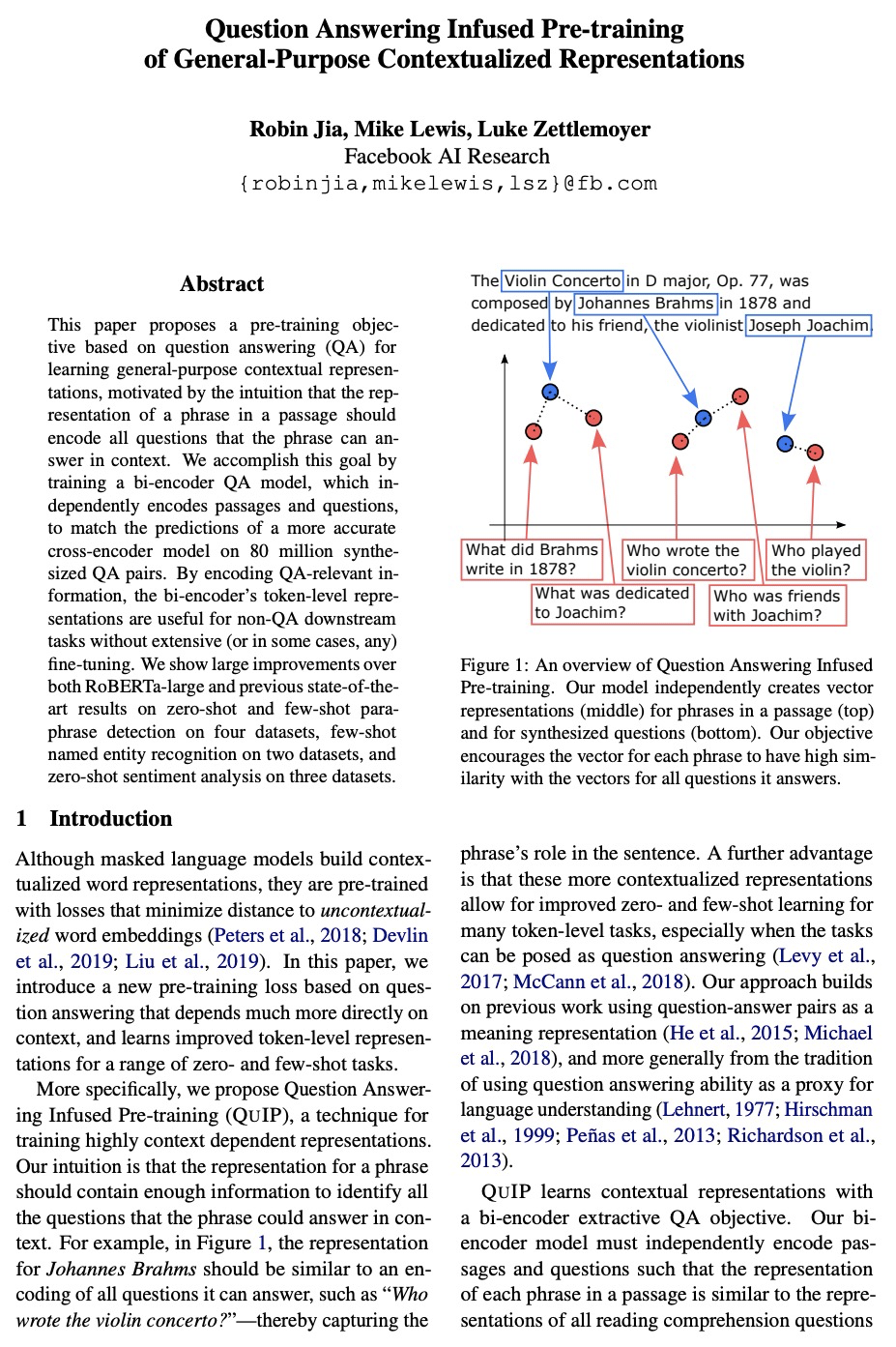
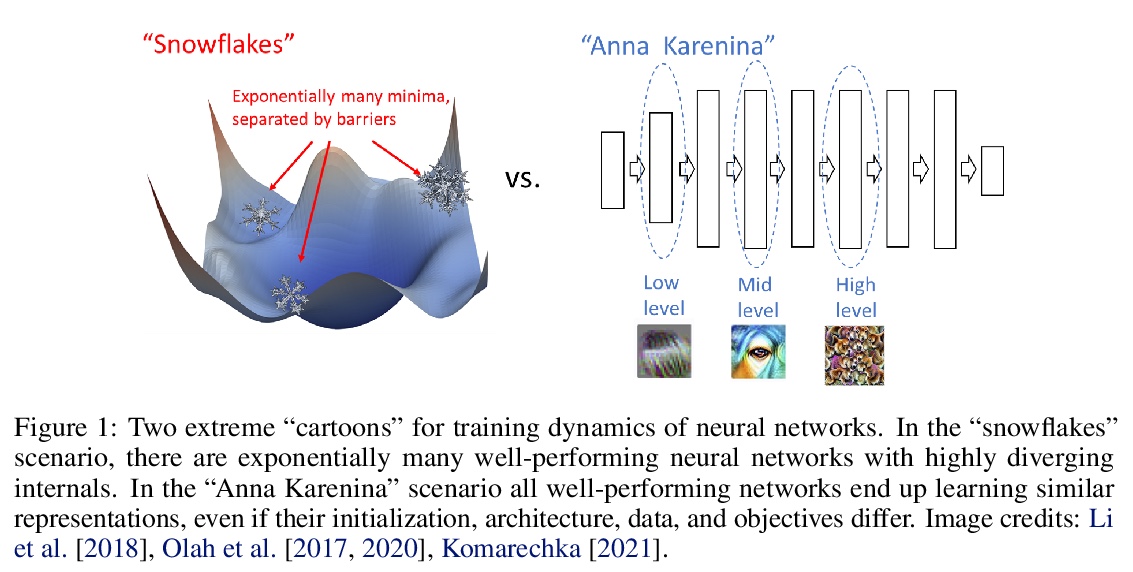
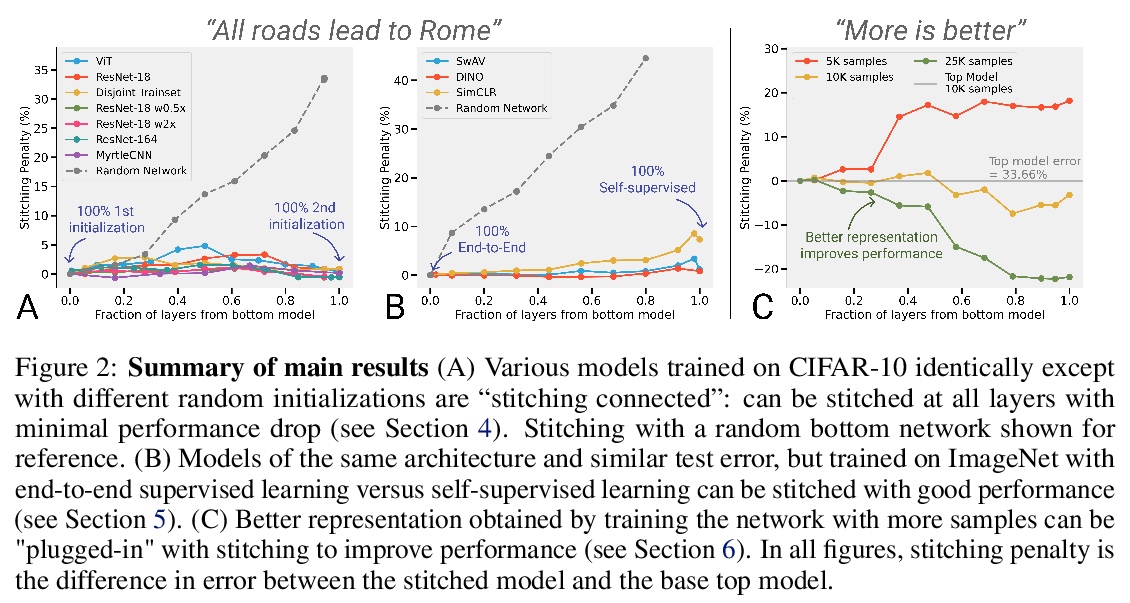
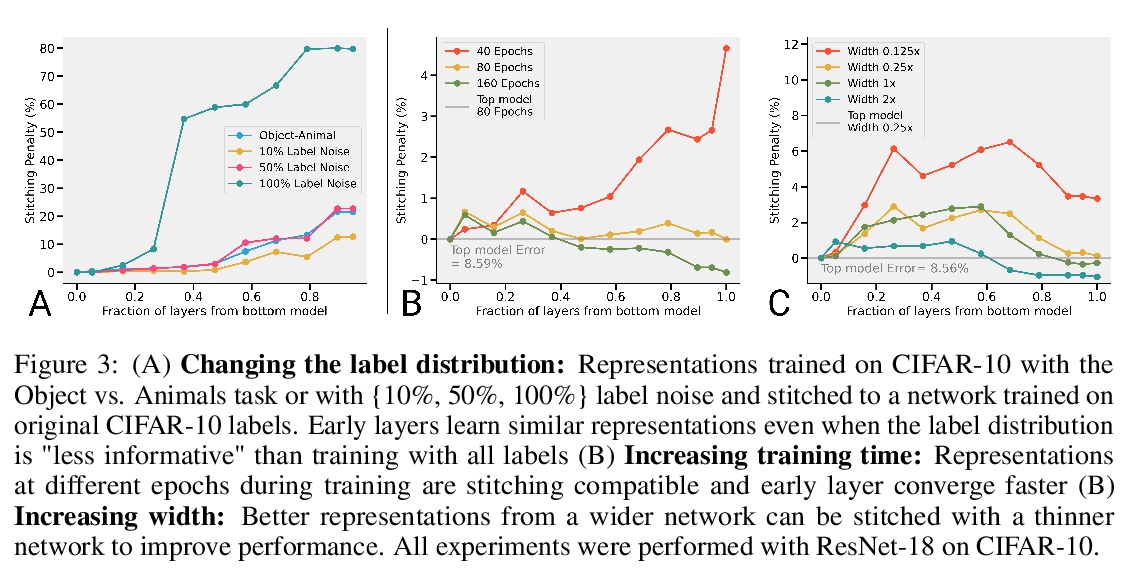
[LG] Revisiting Model Stitching to Compare Neural Representations
基于模型拼接的神经网络表示比较
Y Bansal, P Nakkiran, B Barak
[Harvard University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkxCQANwP
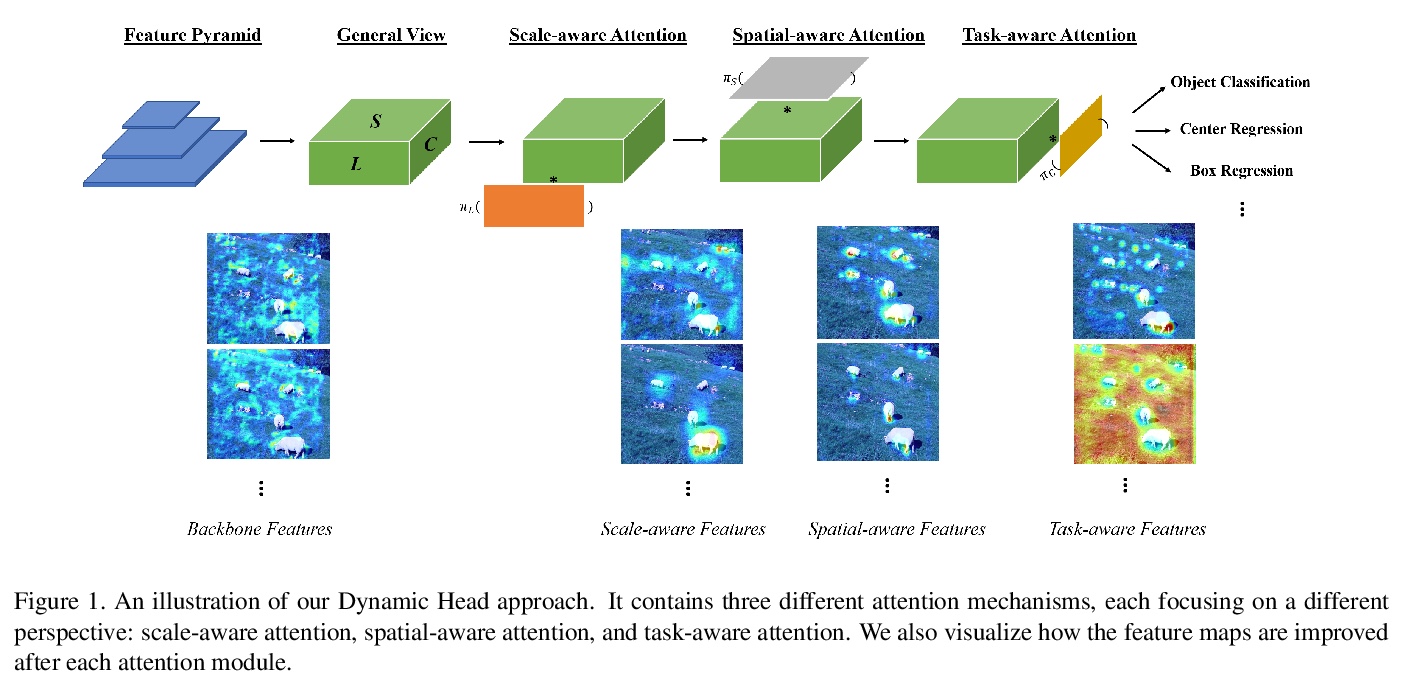
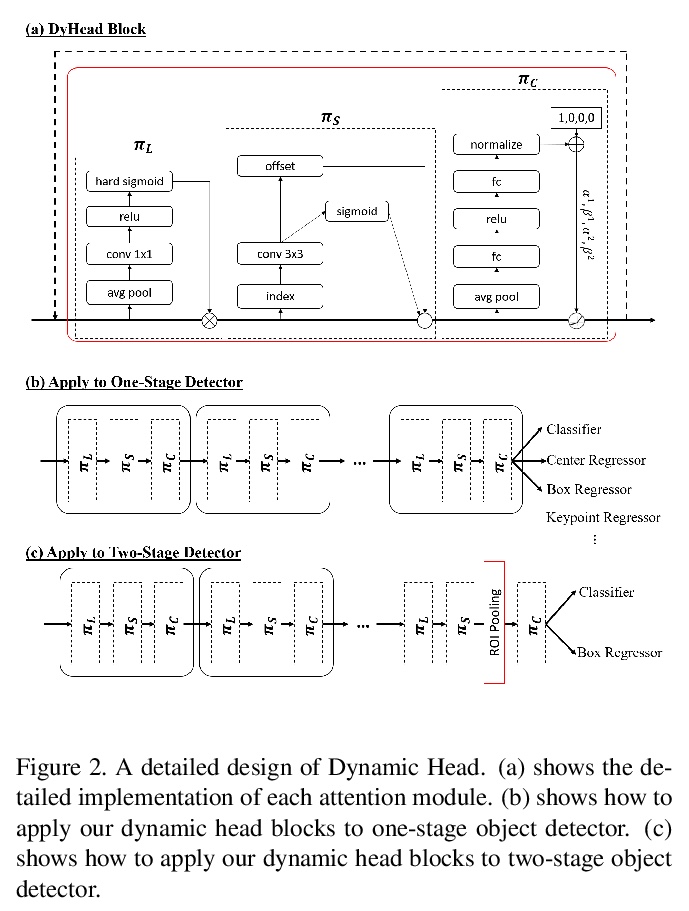
[CV] Dynamic Head: Unifying Object Detection Heads with Attentions
动态头:基于注意力的目标检测头
X Dai, Y Chen, B Xiao, D Chen, M Liu, L Yuan, L Zhang
[Microsoft]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkxECj18w

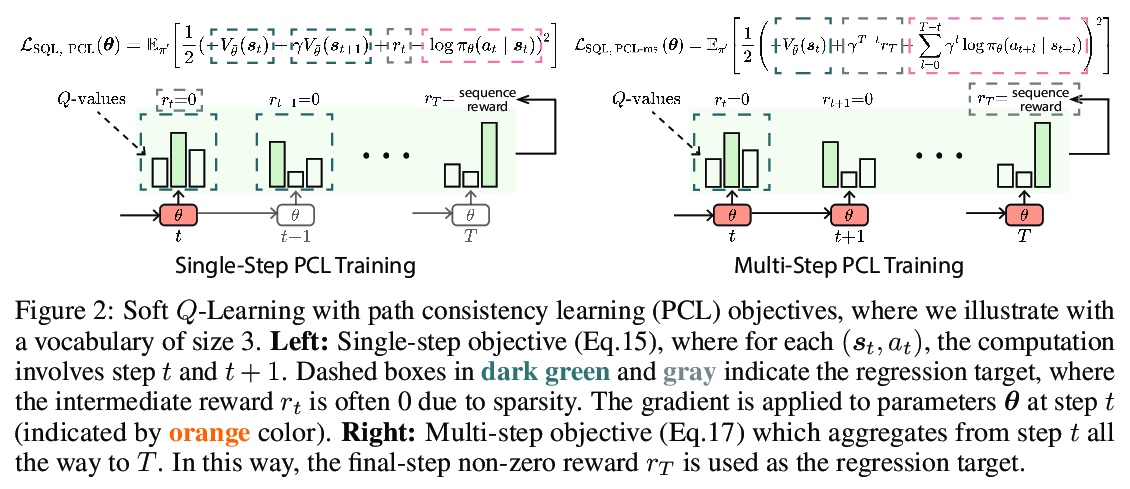
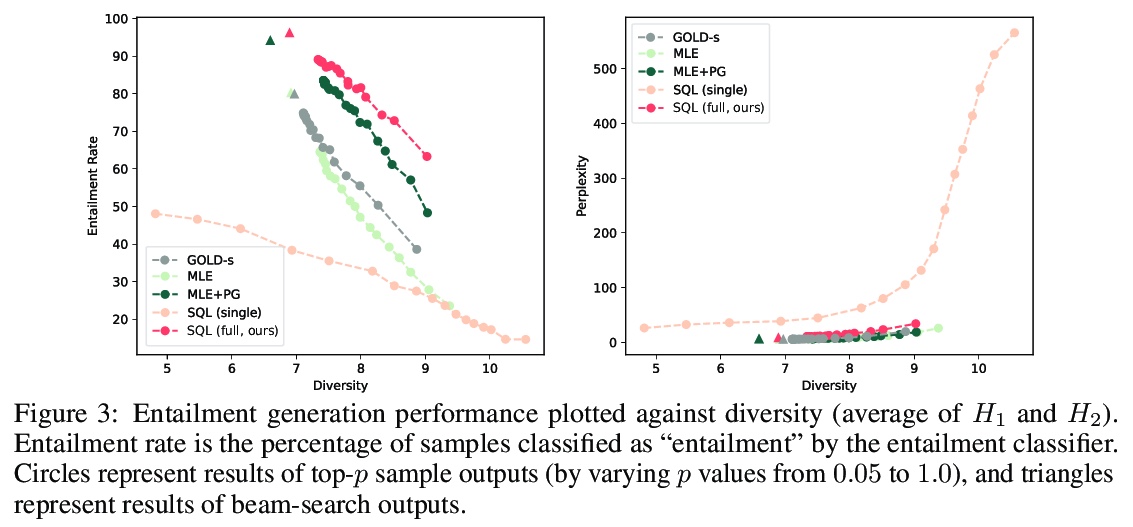
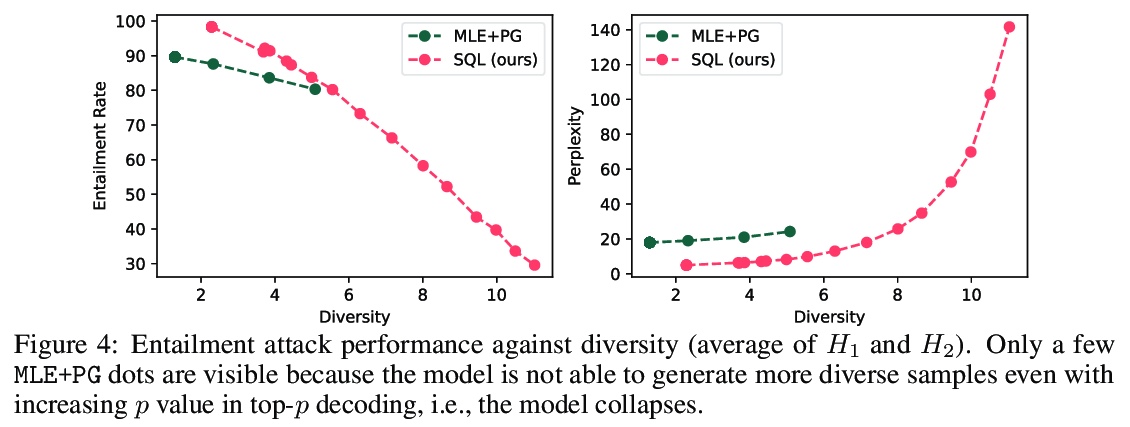
[CL] Text Generation with Efficient (Soft) Q-Learning
基于高效(软)Q-Learning的文本生成
H Guo, B Tan, Z Liu, E P. Xing, Z Hu
[CMU & UC San Diego]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkxGTwwsx