- 1、[CL] Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling
- 2、[CV] Neural Monocular 3D Human Motion Capture with Physical Awareness
- 3、[CV] Robust and Generalizable Visual Representation Learning via Random Convolutions
- 4、[CL] BERT memorisation and pitfalls in low-resource scenarios
- 5、[AI] One Model to Rule them All: Towards Zero-Shot Learning for Databases
- [CV] GridToPix: Training Embodied Agents with Minimal Supervision
- [CV] Curious Representation Learning for Embodied Intelligence
- [RO] Learning to drive from a world on rails
- [RO] Learning Visually Guided Latent Actions for Assistive Teleoperation
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CL] Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling
N Goyal, J Du, M Ott, G Anantharaman, A Conneau
[Facebook AI]
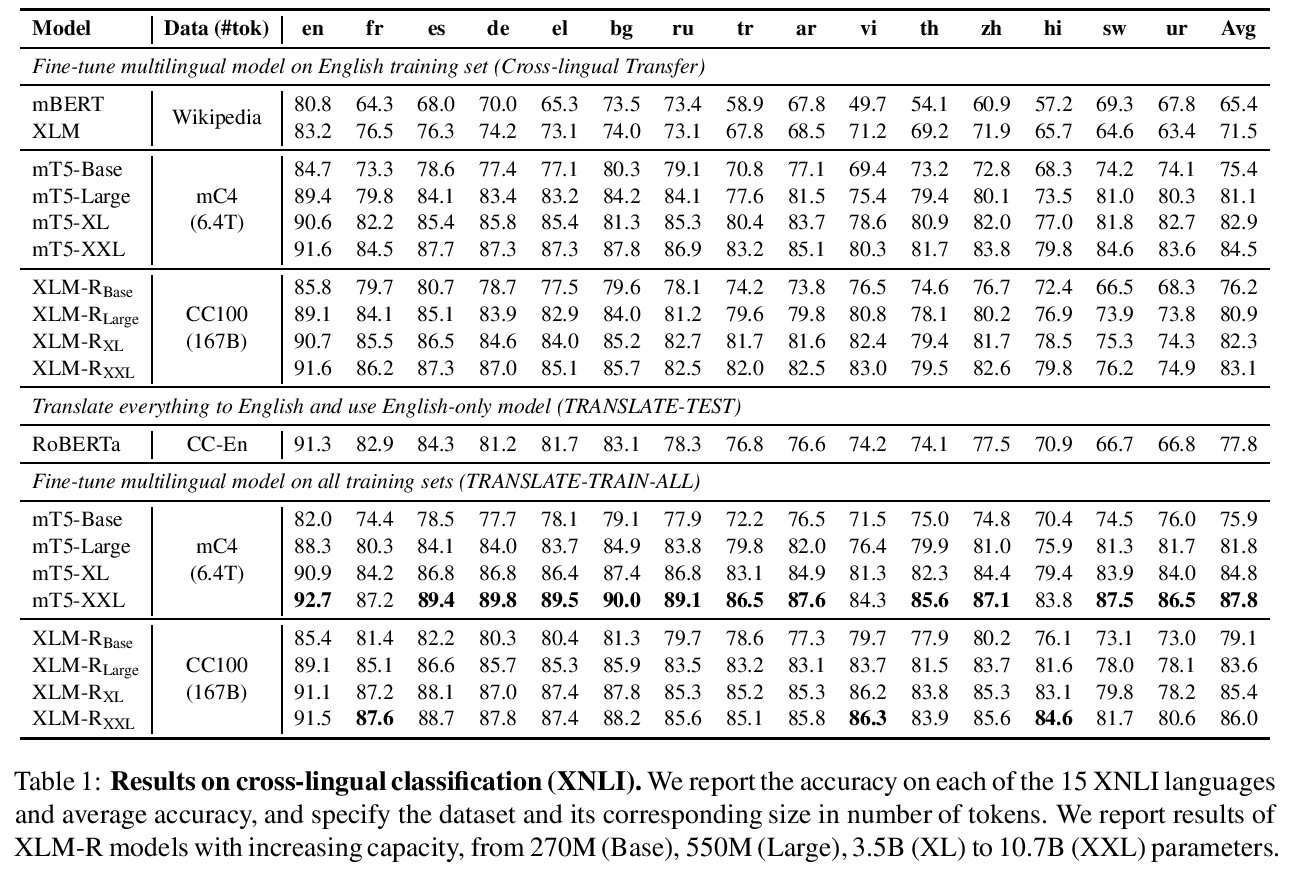
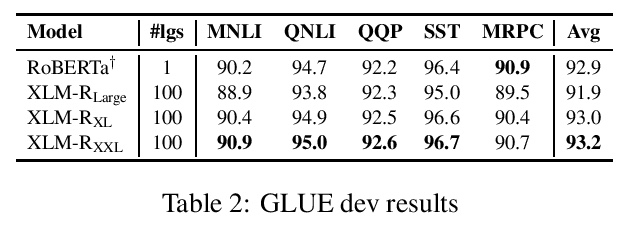
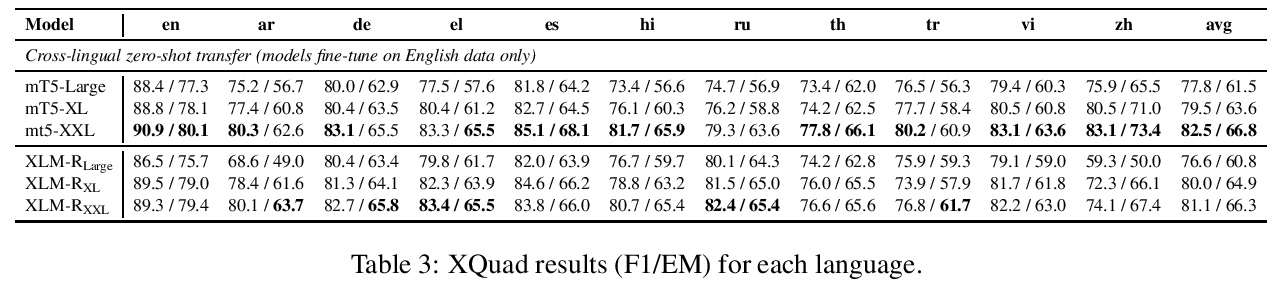
更大规模Transformer的多语种掩码语言建模。最近的工作证明了跨语种语言模型预训练对跨语言理解的有效性。本文提出两个更大的多语种掩码语言模型的结果,分别是XLM-RXL和XLM-RXXL,参数分别为35B和107B,在XNLI上的平均准确率比XLM-R高出1.8%和2.4%。模型在GLUE基准的几个英语任务上也比RoBERTa-Large模型平均高出0.3%,同时处理99种以上的语言。这表明具有较大容量的预训练模型可以在高资源语言上获得强大的性能,同时大大改善低资源语言。
Recent work has demonstrated the effectiveness of cross-lingual language model pretraining for cross-lingual understanding. In this study, we present the results of two larger multilingual masked language models, with 3.5B and 10.7B parameters. Our two new models dubbed XLM-RXL and XLM-RXXL outperform XLM-R by 1.8% and 2.4% average accuracy on XNLI. Our model also outperforms the RoBERTa-Large model on several English tasks of the GLUE benchmark by 0.3% on average while handling 99 more languages. This suggests pretrained models with larger capacity may obtain both strong performance on high-resource languages while greatly improving low-resource languages. We make our code and models publicly available.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdZMPkfHr
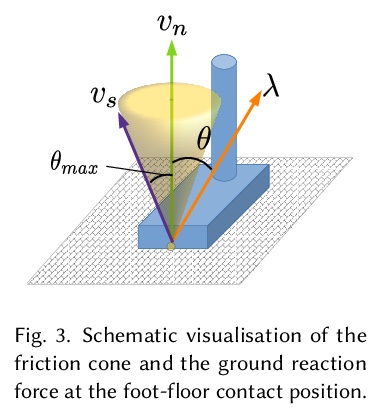
2、[CV] Neural Monocular 3D Human Motion Capture with Physical Awareness
S Shimada, V Golyanik, W Xu, P Pérez, C Theobalt
[Max Planck Institute for Informatics & Facebook Reality Labs & Valeo.ai]
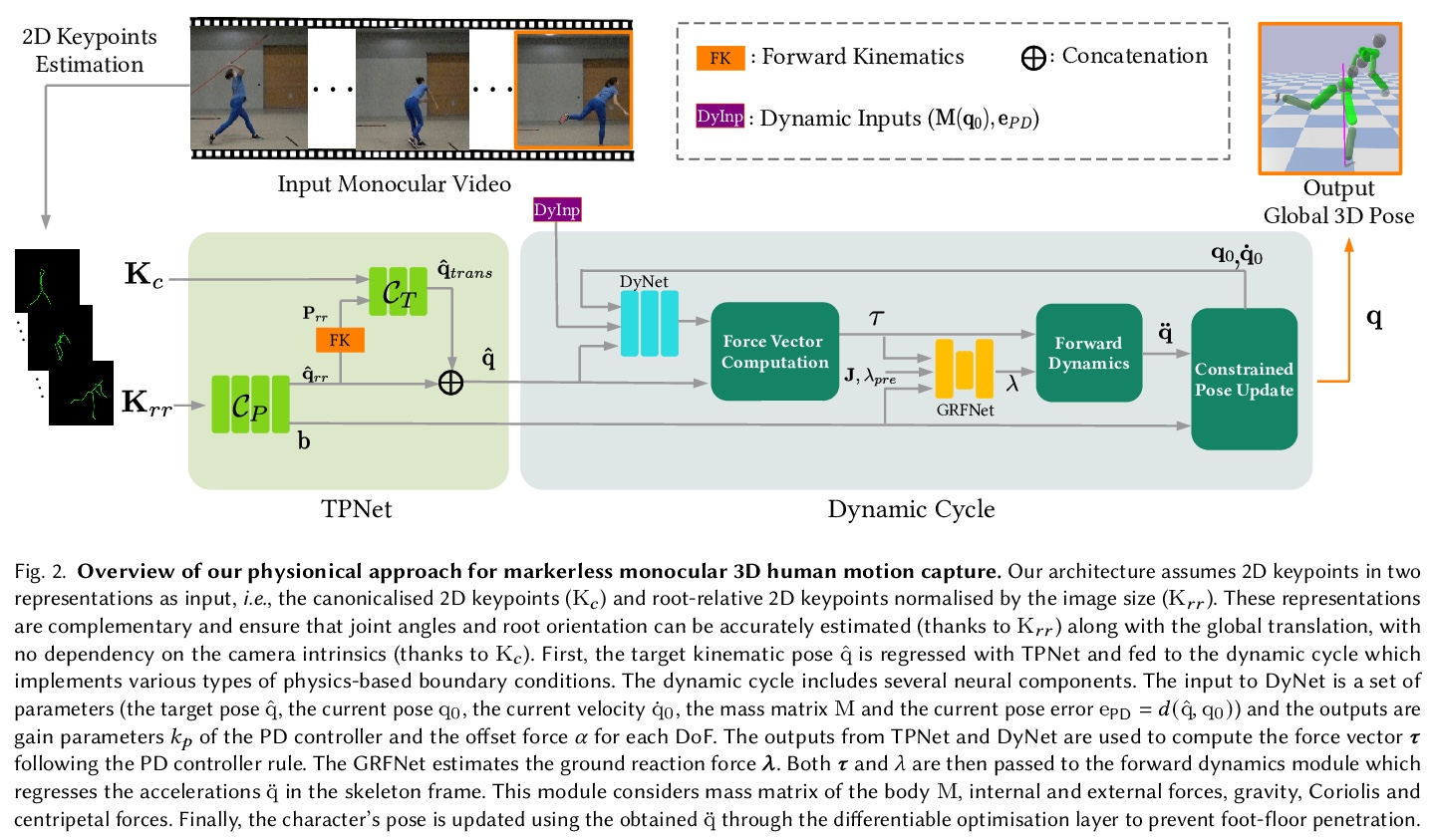
物理感知神经网络单目3D人体运动捕捉。提出了一种新的可训练系统,以实现物理上可信的无标记3D人体运动捕捉,在广泛的挑战性场景中取得了最先进的结果。与大多数人体运动捕捉的神经网络方法不同,所提出的physionical,具有对物理和环境限制的感知,以一种完全可微的方式结合了几个关键创新:1.比例-派生控制器,其增益由神经网络预测,即使快速运动情况下也能减少延迟;2.明确的刚体动力学模型;3.新的优化层,防止物理上不可信的脚底穿透作为一个硬约束条件。系统输入是二维联合关键点,以一种新的方式被规范化,在训练时和测试时减少对固有相机参数的依赖。3D标注不可用时,模型只使用2D标注进行微调。在各种具有挑战性的场景(包括新录制场景)中,能以交互式帧率产生平滑的、符合物理原理的3D运动,其优势在实际序列中尤其明显,这些序列与常见的3D姿态估计基准(如Human 3.6M和MPI-INF-3DHP)有很大不同。
We present a new trainable system for physically plausible markerless 3D human motion capture, which achieves state-of-the-art results in a broad range of challenging scenarios. Unlike most neural methods for human motion capture, our approach, which we dub physionical, is aware of physical and environmental constraints. It combines in a fully differentiable way several key innovations, i.e., 1. a proportional-derivative controller, with gains predicted by a neural network, that reduces delays even in the presence of fast motions, 2. an explicit rigid body dynamics model and 3. a novel optimisation layer that prevents physically implausible foot-floor penetration as a hard constraint. The inputs to our system are 2D joint keypoints, which are canonicalised in a novel way so as to reduce the dependency on intrinsic camera parameters — both at train and test time. This enables more accurate global translation estimation without generalisability loss. Our model can be finetuned only with 2D annotations when the 3D annotations are not available. It produces smooth and physically principled 3D motions in an interactive frame rate in a wide variety of challenging scenes, including newly recorded ones. Its advantages are especially noticeable on in-the-wild sequences that significantly differ from common 3D pose estimation benchmarks such as Human 3.6M and MPI-INF-3DHP. Qualitative results are available atthis http URL
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdZQM1xQ2

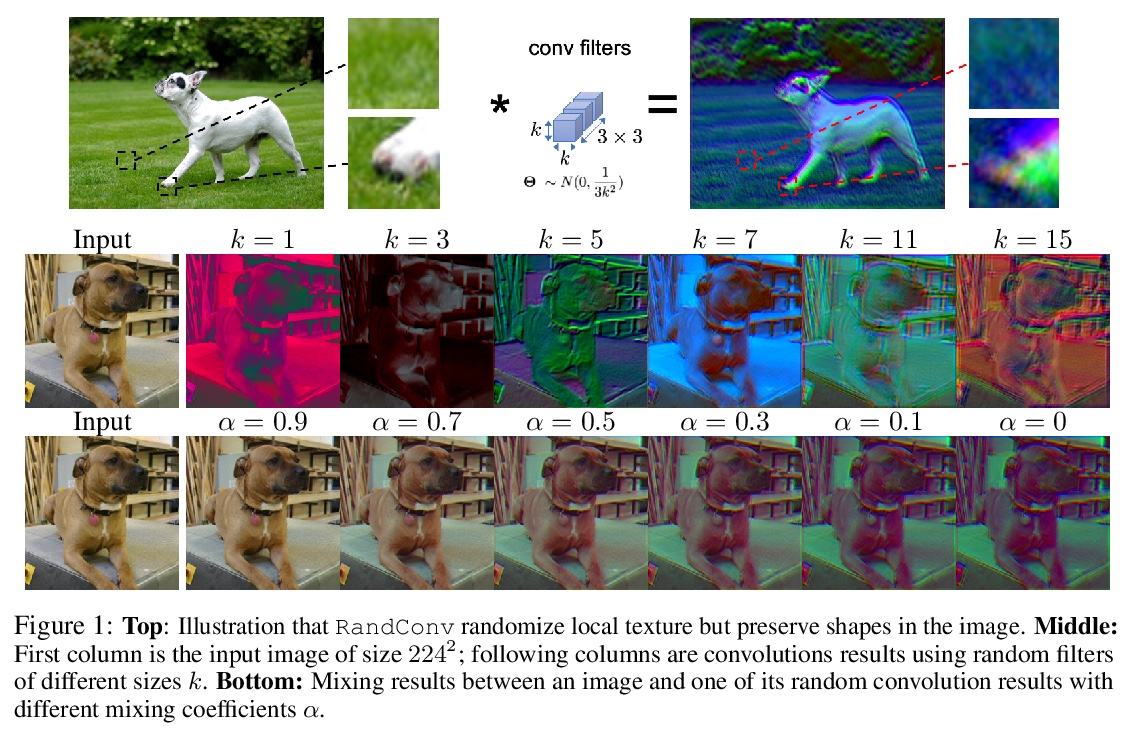
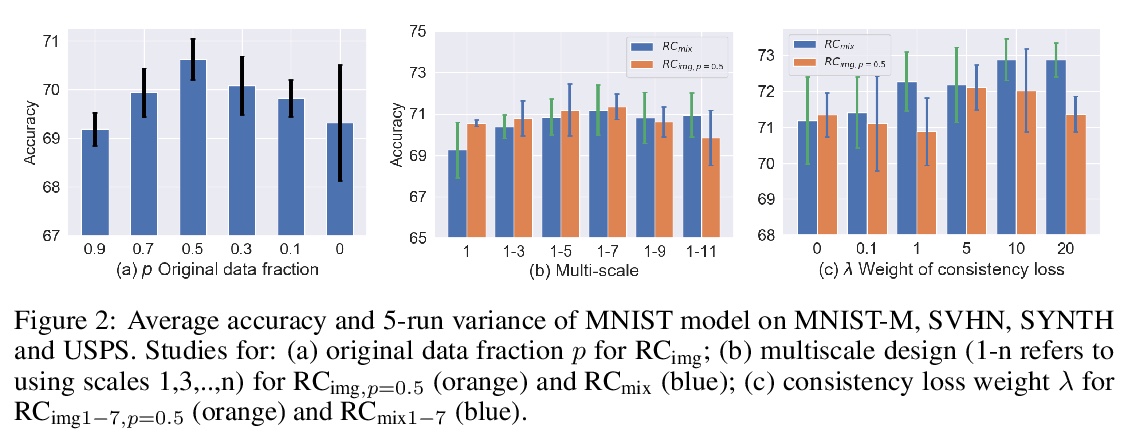
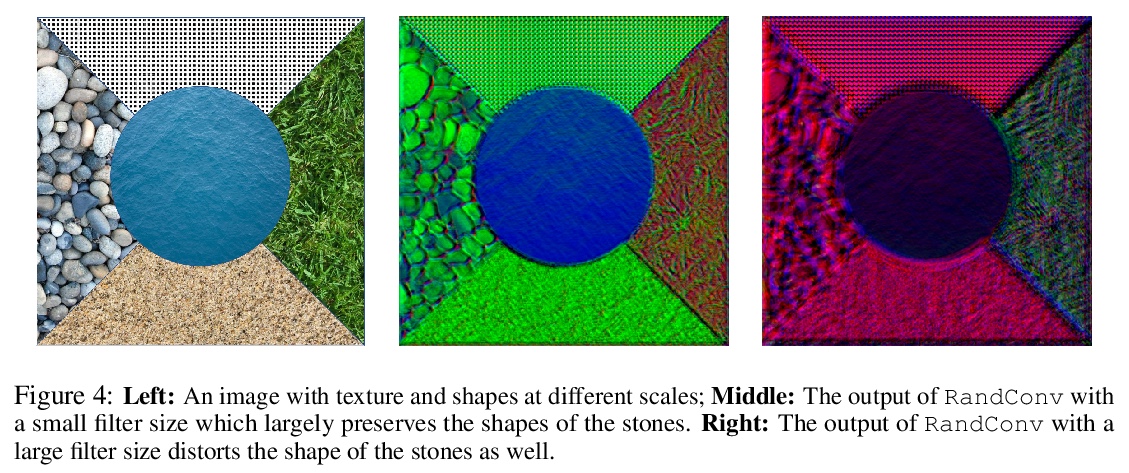
3、[CV] Robust and Generalizable Visual Representation Learning via Random Convolutions
Z Xu, D Liu, J Yang, C Raffel, M Niethammer
[University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill & Yale University]
基于随机卷积的鲁棒通用视觉表征学习。虽然在各种计算机视觉任务中取得了成功,但深度神经网络已被证明容易受到纹理风格变化和小扰动的影响,而人类对这些扰动是鲁棒的。用随机卷积作为数据增强,即RandConv,神经网络的鲁棒性可以得到大幅改善。随机卷积能近似保留形状,并扭曲局部纹理,一致性损失可以进一步加强纹理变化下的不变性,创造出无限多的具有类似全局形状但随机局部纹理的新域。本文探索用多尺度随机卷积的输出作为新图像,或者在训练期间将其与原始图像混合。将新方法训练的网络应用于未见域,可提高领域泛化基准性能,并可扩展到ImageNet。特别是在泛化到PACS中的草图域和ImageNet-Sketch这一具有挑战性任务,本方法以较大优势胜过最先进方法,还可通过提供一个更鲁棒的预训练的视觉表征使下游任务受益。
While successful for various computer vision tasks, deep neural networks have shown to be vulnerable to texture style shifts and small perturbations to which humans are robust. In this work, we show that the robustness of neural networks can be greatly improved through the use of random convolutions as data augmentation. Random convolutions are approximately shape-preserving and may distort local textures. Intuitively, randomized convolutions create an infinite number of new domains with similar global shapes but random local texture. Therefore, we explore using outputs of multi-scale random convolutions as new images or mixing them with the original images during training. When applying a network trained with our approach to unseen domains, our method consistently improves the performance on domain generalization benchmarks and is scalable to ImageNet. In particular, in the challenging scenario of generalizing to the sketch domain in PACS and to ImageNet-Sketch, our method outperforms state-of-art methods by a large margin. More interestingly, our method can benefit downstream tasks by providing a more robust pretrained visual representation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdZVCwf9F
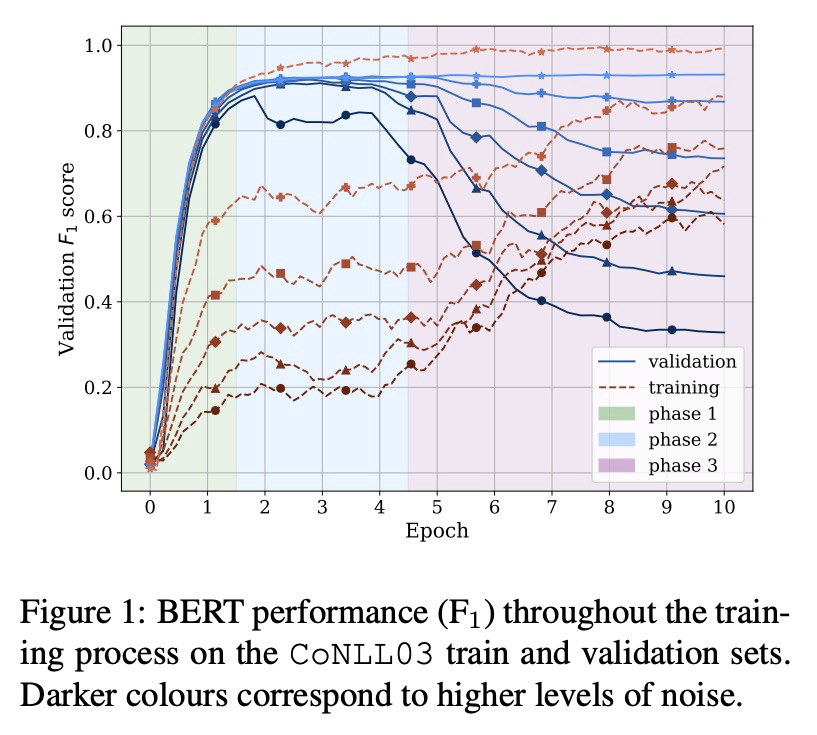
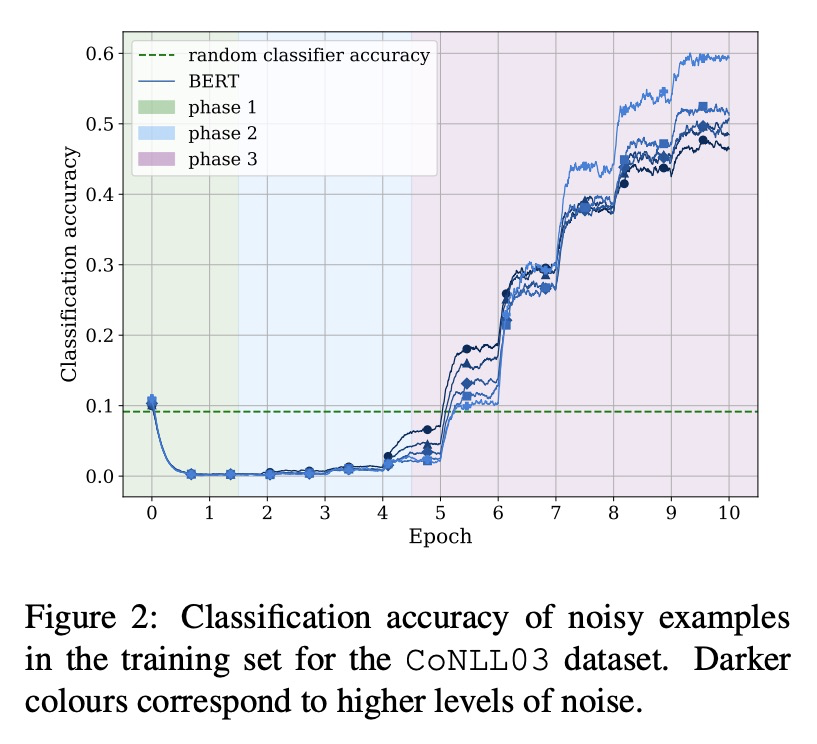
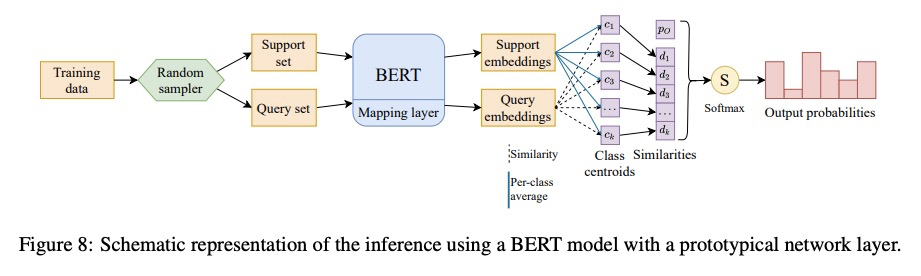
4、[CL] BERT memorisation and pitfalls in low-resource scenarios
M Tänzer, S Ruder, M Rei
[Imperial College London & DeepMind]
BERT在低资源情况下的记忆和缺陷。最先进的预训练模型已被证明能够记忆事实,并在有限训练数据量下表现良好。为更好地了解这些模型如何学习,本文研究了模型在嘈杂和低资源情况下的泛化和记忆能力,发现这些模型的训练几乎不受标签噪声影响,即使在极度嘈杂的数据集上也有可能达到接近最佳的表现,在低资源任务(如少样本学习和罕见实体识别)上测试时完全失败。为缓解这种局限性,提出一种基于BERT和原型网络的新型架构,以提高低资源命名实体识别任务的性能。
State-of-the-art pre-trained models have been shown to memorise facts and perform well with limited amounts of training data. To gain a better understanding of how these models learn, we study their generalisation and memorisation capabilities in noisy and low-resource scenarios. We find that the training of these models is almost unaffected by label noise and that it is possible to reach near-optimal performances even on extremely noisy datasets. Conversely, we also find that they completely fail when tested on low-resource tasks such as fewshot learning and rare entity recognition. To mitigate such limitations, we propose a novel architecture based on BERT and prototypical networks that improves performance in lowresource named entity recognition tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdZZvCnCt
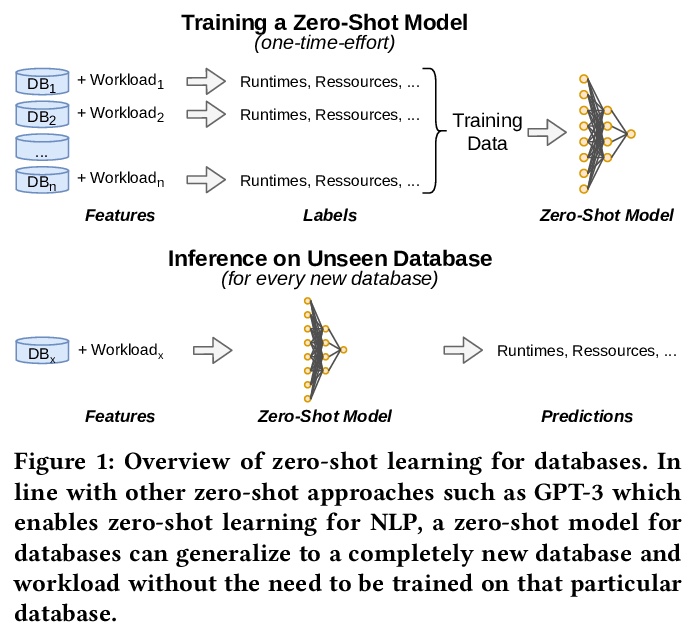
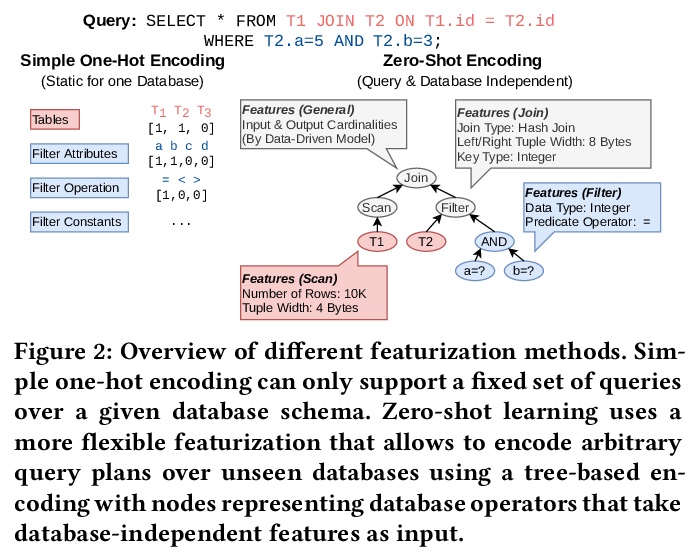
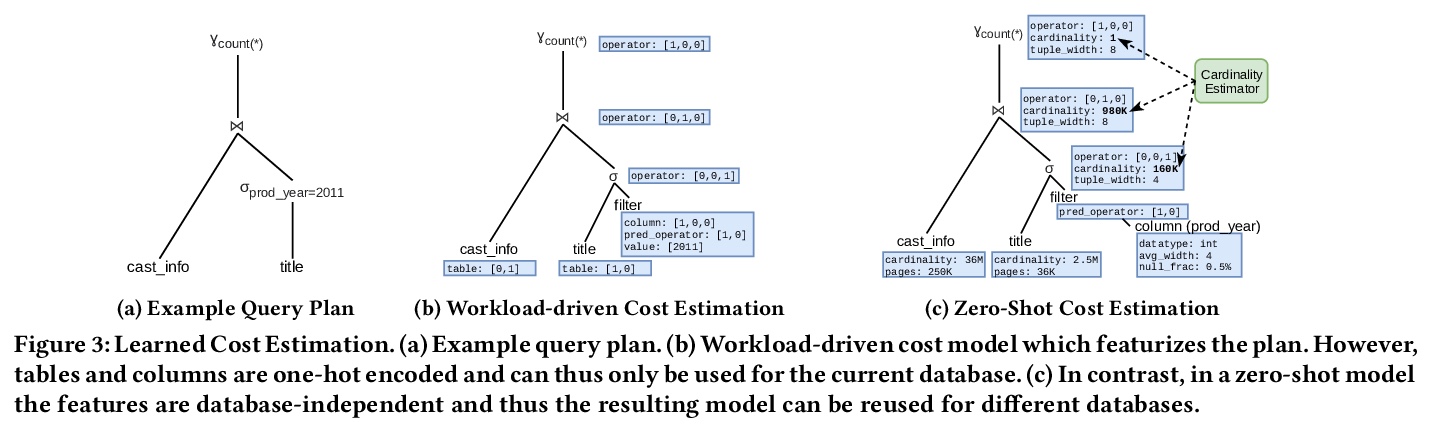
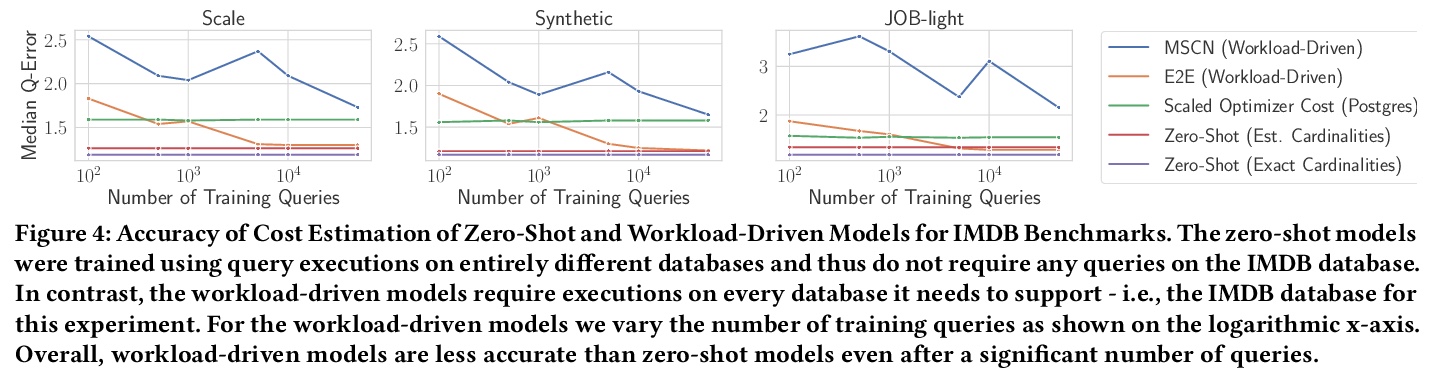
5、[AI] One Model to Rule them All: Towards Zero-Shot Learning for Databases
B Hilprecht, C Binnig
[TU Darmstadt]
数据库零样本学习。介绍了对所谓数据库零样本学习的看法,数据库零样本学习是一种新的数据库组件的学习方法,受GPT-3等模型迁移学习的最新进展的启发,无需训练新模型,即可支持新的数据库。展示了零样本学习对物理成本估计任务的可行性,提出了非常有希望的初步结果。讨论了与数据库零样本学习有关的核心挑战,提出一个路线图,将零样本学习扩展到成本估算以外的许多其他任务,甚至超越经典的数据库系统和工作负载。
In this paper, we present our vision of so called zero-shot learning for databases which is a new learning approach for database components. Zero-shot learning for databases is inspired by recent advances in transfer learning of models such as GPT-3 and can support a new database out-of-the box without the need to train a new model. As a first concrete contribution in this paper, we show the feasibility of zero-shot learning for the task of physical cost estimation and present very promising initial results. Moreover, as a second contribution we discuss the core challenges related to zero-shot learning for databases and present a roadmap to extend zero-shot learning towards many other tasks beyond cost estimation or even beyond classical database systems and workloads.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke024oM30
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
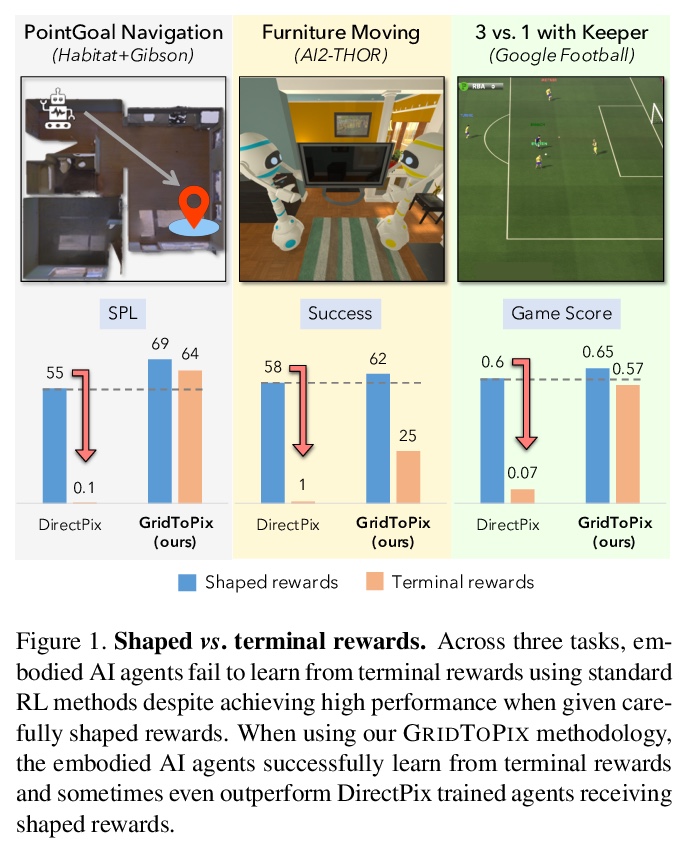
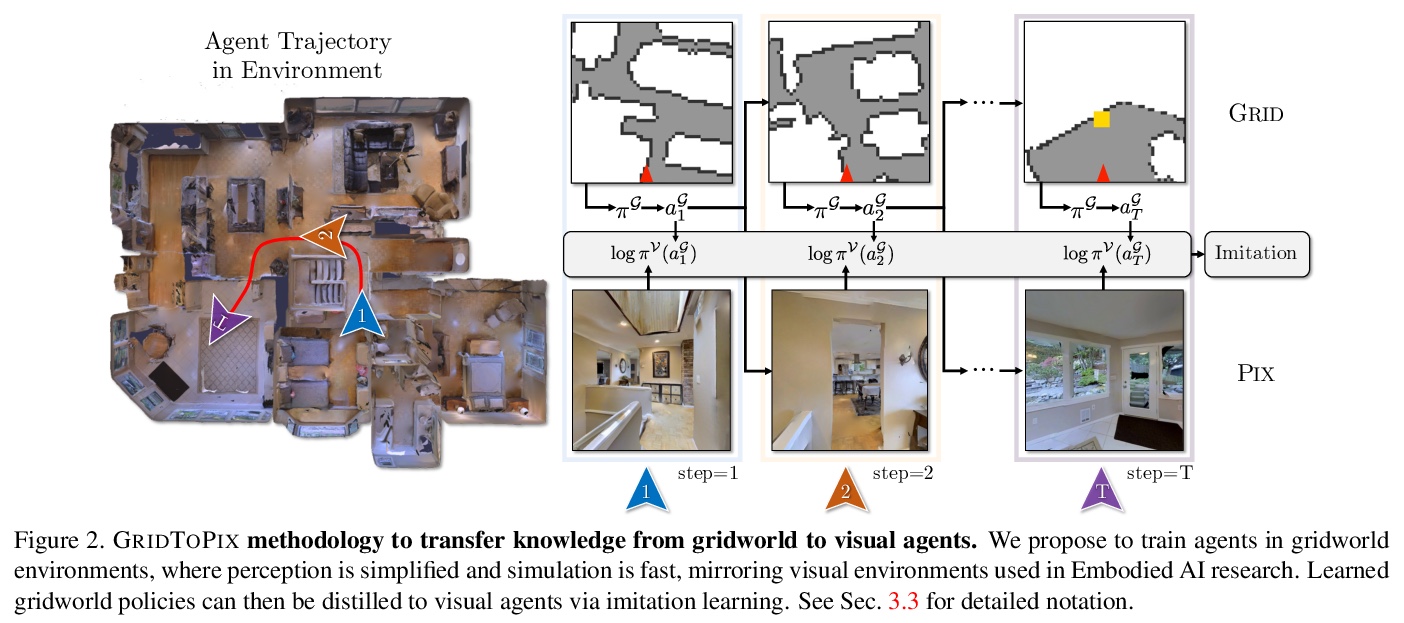
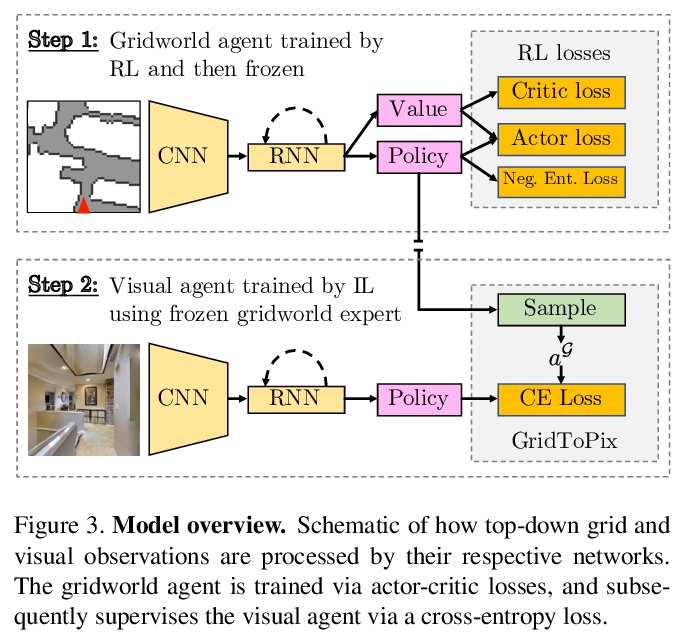
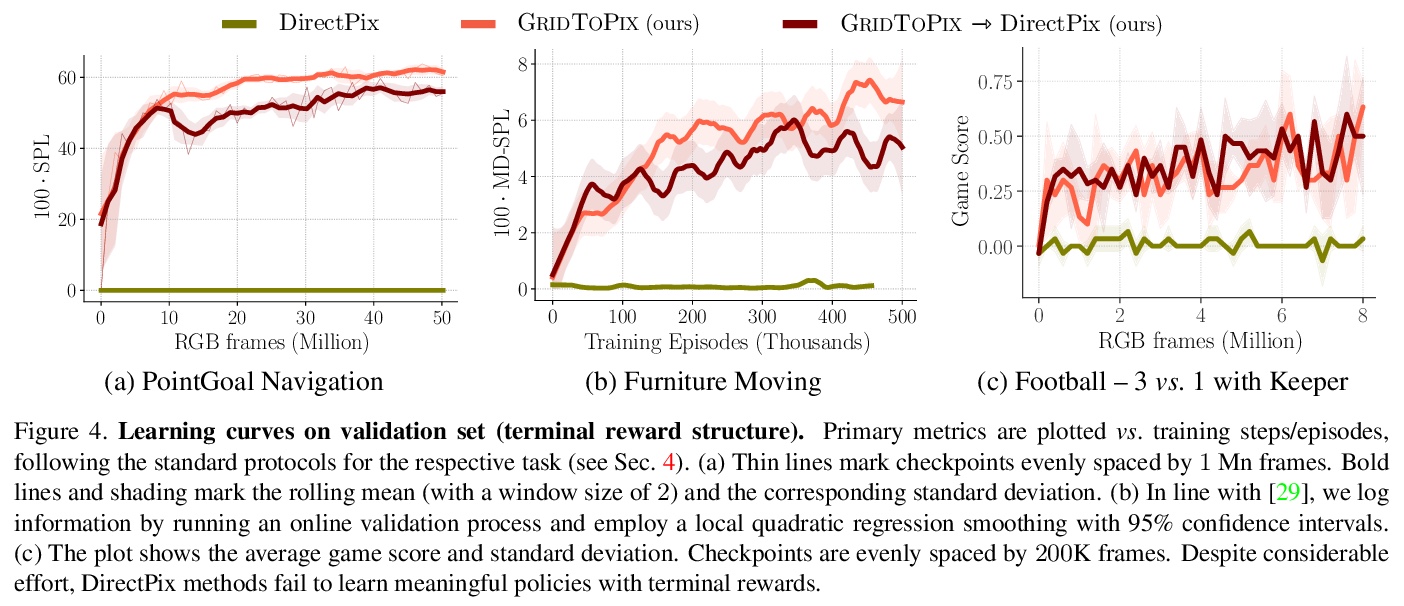
[CV] GridToPix: Training Embodied Agents with Minimal Supervision
GridToPix:用最小监督训练具身智能体
U Jain, I Liu, S Lazebnik, A Kembhavi, L Weihs, A Schwing
[University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign & Allen Institute for AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke04JgNAR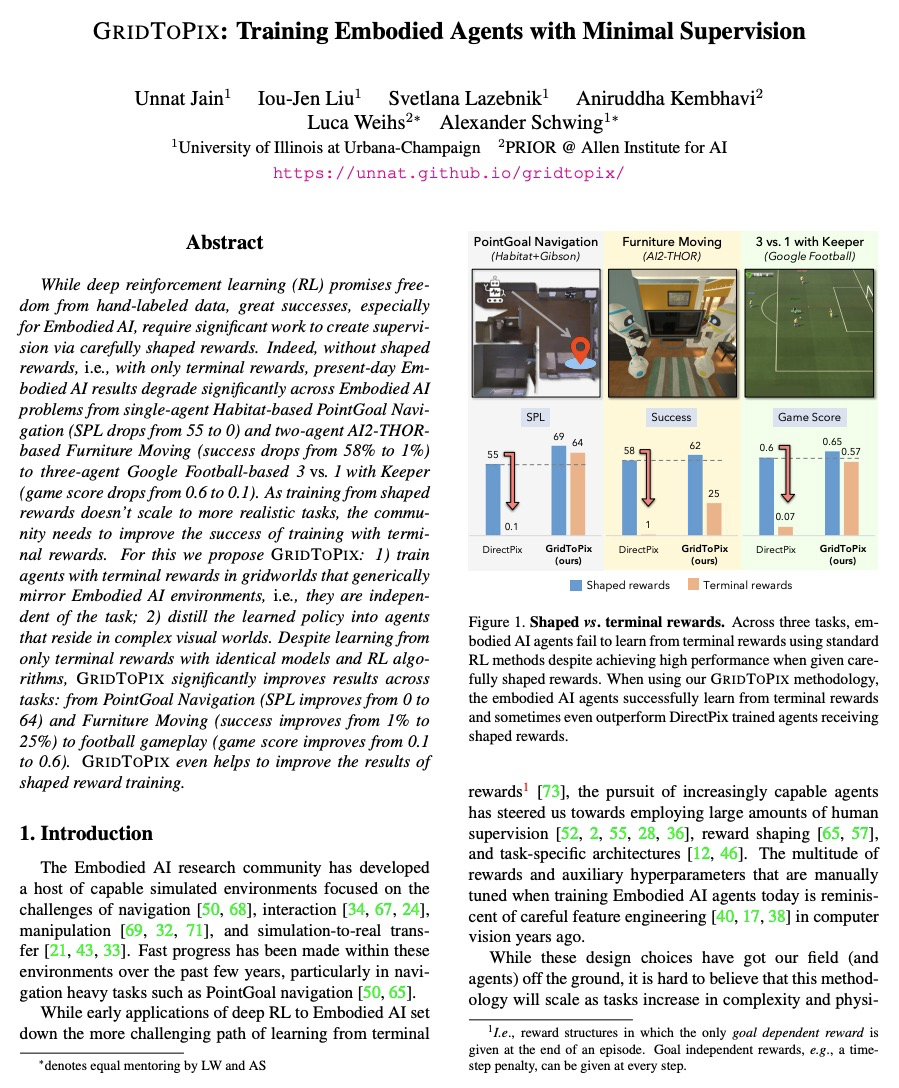
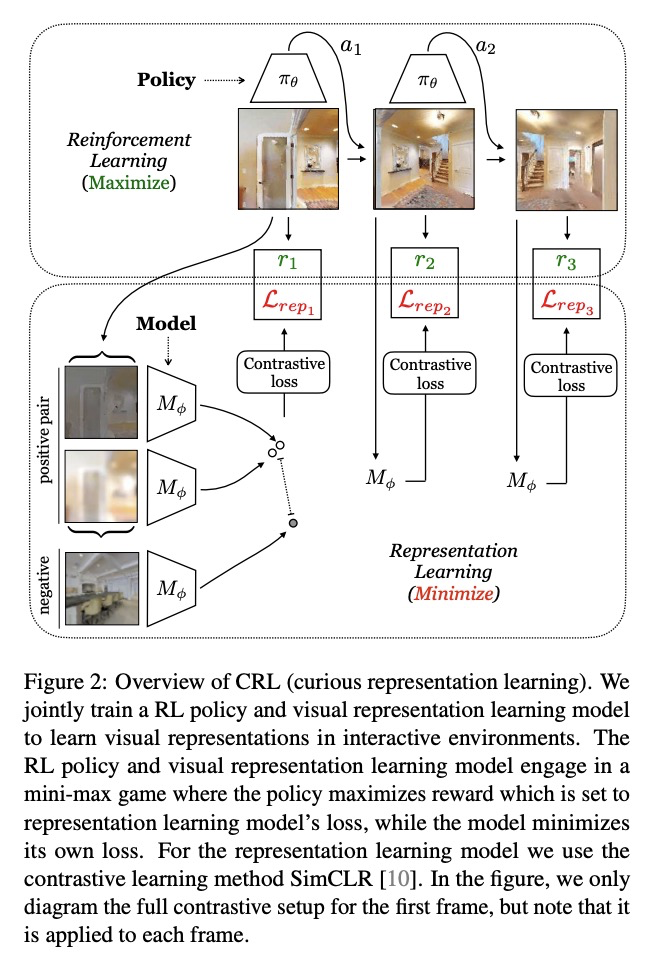
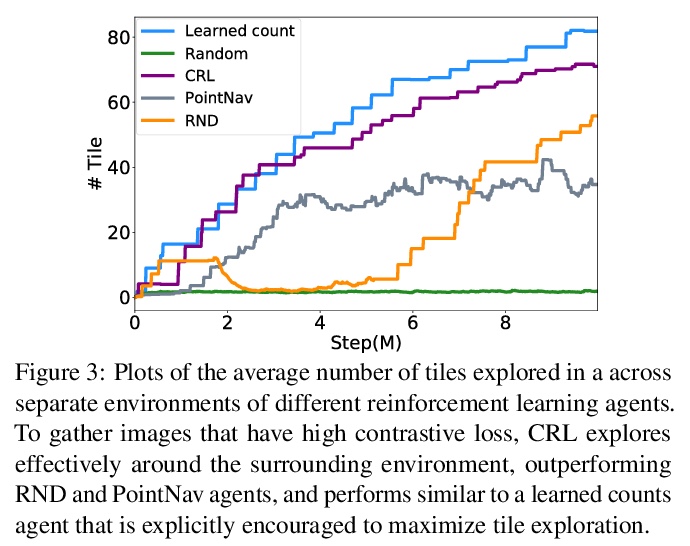
[CV] Curious Representation Learning for Embodied Intelligence
具身智能的好奇表征学习
Y Du, C Gan, P Isola
[MIT & MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke0aKqTEf

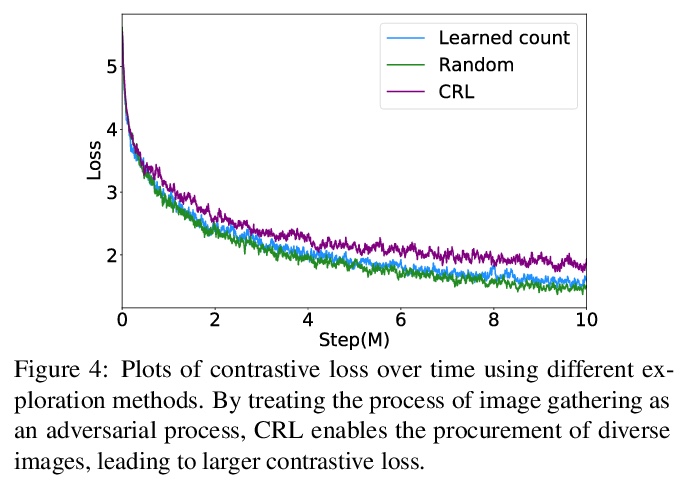
[RO] Learning to drive from a world on rails
轨道世界驾驶学习
D Chen, V Koltun, P Krähenbühl
[UT Austin & Intel Labs]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke0DZAi9W

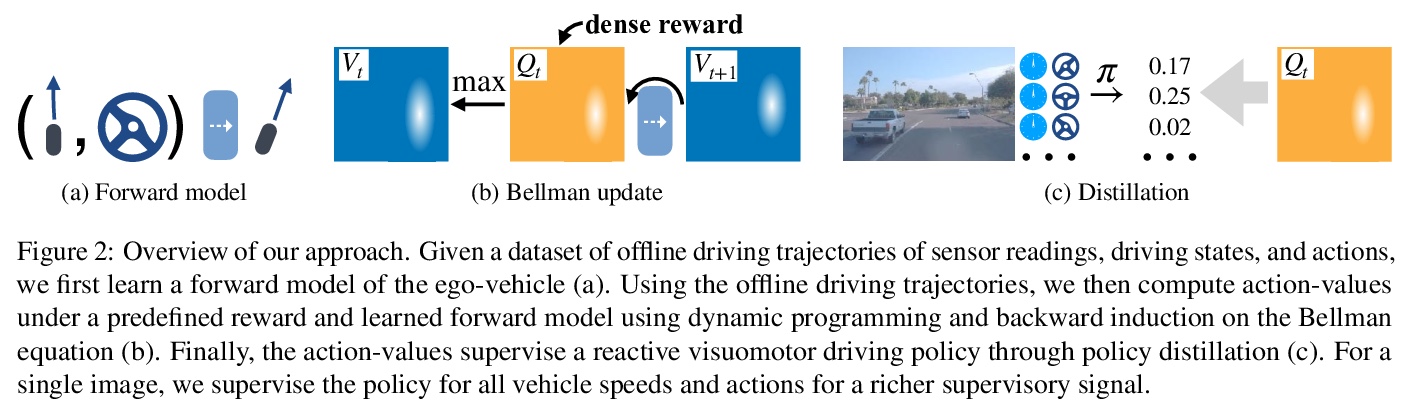
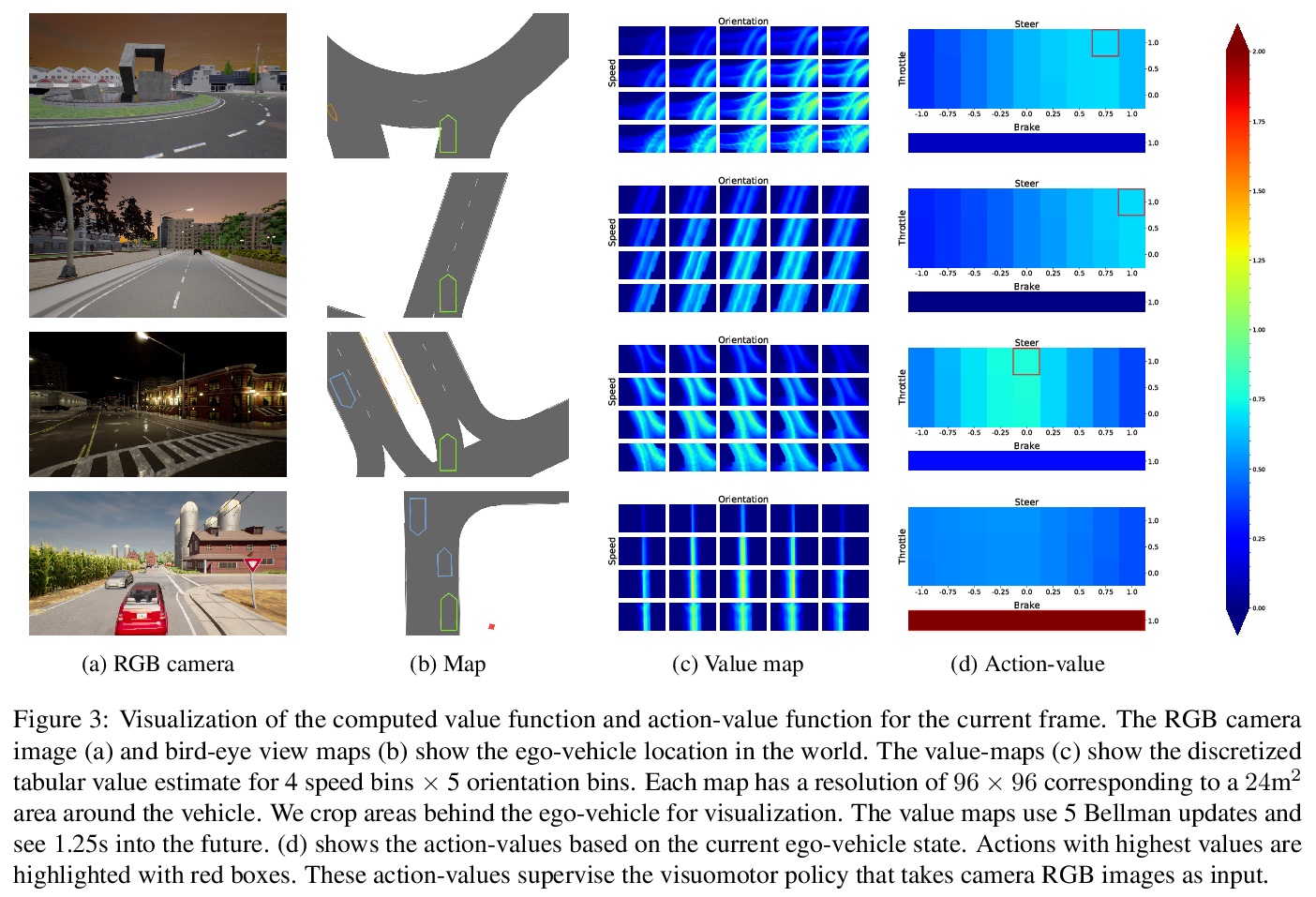

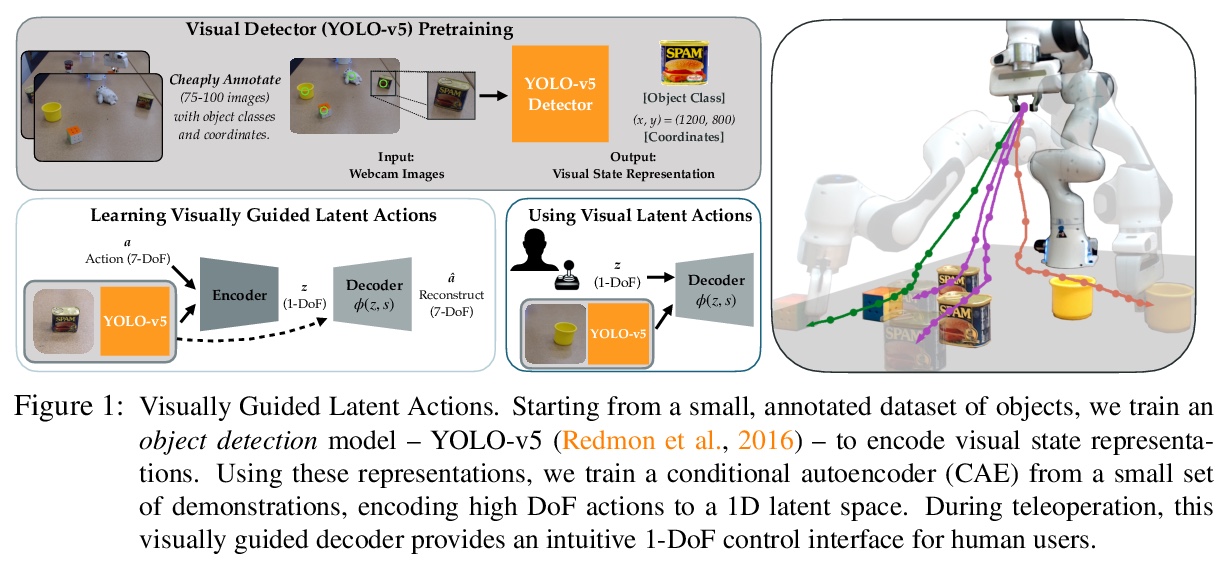
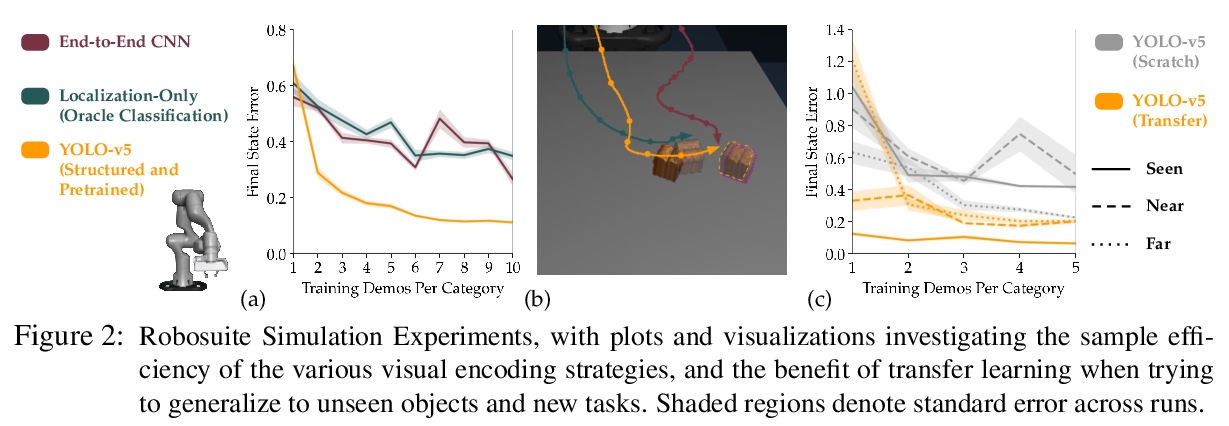
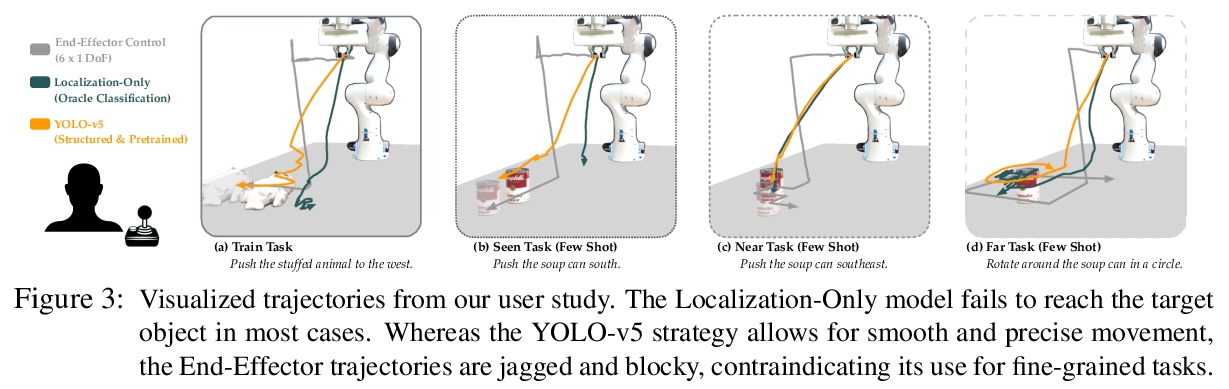
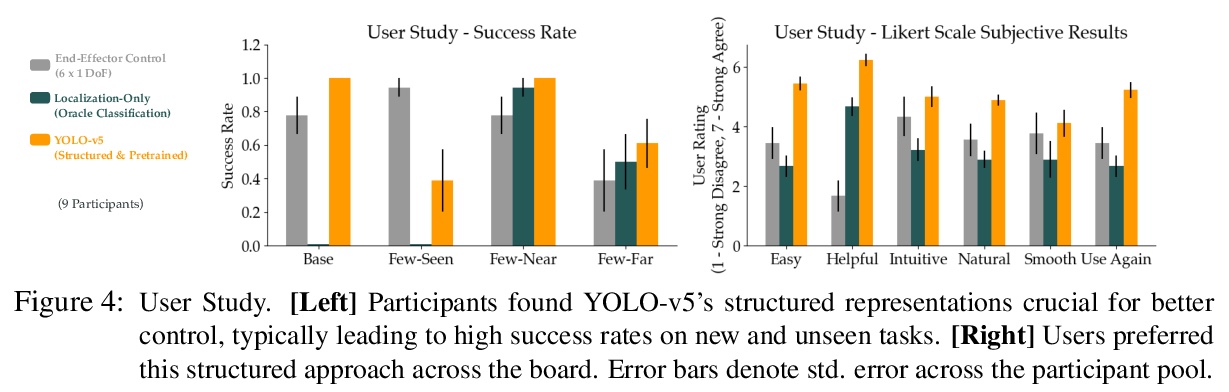
[RO] Learning Visually Guided Latent Actions for Assistive Teleoperation
辅助遥操作视觉引导潜动作学习
S Karamcheti, A J. Zhai, D P. Losey, D Sadigh
[Stanford University & California Institute of Technology & Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke0GgwcxQ