- 1、[AI] Why AI is Harder Than We Think
- 2、[LG] Bayesian Optimization is Superior to Random Search for Machine Learning Hyperparameter Tuning: Analysis of the Black-Box Optimization Challenge 2020
- 3、[LG] Outcome-Driven Reinforcement Learning via Variational Inference
- 4、[CL] A Replication Study of Dense Passage Retriever
- 5、[CV] Unsupervised 3D Shape Completion through GAN Inversion
- [CL] Visually grounded models of spoken language: A survey of datasets, architectures and evaluation techniques
- [CL] Extractive and Abstractive Explanations for Fact-Checking and Evaluation of News
- [CV] Rethinking BiSeNet For Real-time Semantic Segmentation
- [CV] BasicVSR++: Improving Video Super-Resolution with Enhanced Propagation and Alignment
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[AI] Why AI is Harder Than We Think
M Mitchell
[Santa Fe Institute]
为什么人工智能比我们想象的更难。自20世纪50年代开始,人工智能领域已经在乐观预测和大量投资(“人工智能的春天”)与失望、失去信心和缩减投资(“人工智能的寒冬”)之间循环了几次。如今人工智能突破的速度看似很快,但承诺已久的技术,如自动驾驶汽车、家政机器人和对话伴侣的开发,结果比许多人预期的要难得多。造成这些重复循环的一个原因是我们对智能本身的性质和复杂程度的理解有限。本文探讨了过度自信和对人工智能期望的失望之间的循环的原因,公众、媒体、甚至专家的过度乐观,可能源于我们谈论人工智能的方式以及我们对智能本质的直觉中的一些谬误,包括:沿着狭义人工智能的路径不断发展最后就能达到通用智能、对人来说好做的事对机器也容易反之也难、靠记忆实现智能的幻觉、智能全在大脑。理解这些谬误及其微妙的影响,可以指明如何创建更健壮、更值得信赖,甚至可能是更智能的人工智能系统。讨论了由这些谬误引发的开放性问题,包括赋予机器以人类常识这一古老的挑战。
Since its beginning in the 1950s, the field of artificial intelligence has cycled several times between periods of optimistic predictions and massive investment (“AI spring”) and periods of disappointment, loss of confidence, and reduced funding (“AI winter”). Even with today’s seemingly fast pace of AI breakthroughs, the development of long-promised technologies such as self-driving cars, housekeeping robots, and conversational companions has turned out to be much harder than many people expected. One reason for these repeating cycles is our limited understanding of the nature and complexity of intelligence itself. In this paper I describe four fallacies in common assumptions made by AI researchers, which can lead to overconfident predictions about the field. I conclude by discussing the open questions spurred by these fallacies, including the age-old challenge of imbuing machines with humanlike common sense.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5j27tlO
2、[LG] Bayesian Optimization is Superior to Random Search for Machine Learning Hyperparameter Tuning: Analysis of the Black-Box Optimization Challenge 2020
R Turner, D Eriksson, M McCourt, J Kiili, E Laaksonen, Z Xu, I Guyon
[Twitter & Facebook & SigOpt & Valohai & 4Paradigm & ChaLearn]
对机器学习超参调优来说贝叶斯优化要优于随机搜索:2020年黑盒优化挑战复盘。介绍了2020年NeurIPS 2020黑盒优化(BBO)挑战的结果和启示。该挑战强调了评估非微分优化器对调整机器学习模型超参数的重要性。这是第一个以机器学习为重点的黑盒优化挑战,基于在真实数据集上调优标准机器学习模型的(验证集)性能。这项比赛具有广泛的影响,因为黑盒优化(如贝叶斯优化)与几乎每个机器学习项目以及机器学习以外的许多应用中的超参调优有关。比赛结果决定性地证明了,贝叶斯优化相比随机搜索的好处。与随机搜索相比,顶尖的参赛者显示了超过100倍的样本效率提升。所有的顶尖团队都使用了某种形式的贝叶斯优化组合;热启动排行榜表明,即使是松散相关的问题,热启动也能产生巨大的性能收益;这项挑战为扩展提供了许多机会,以测试和推动黑盒优化的其他方面的界限。
This paper presents the results and insights from the black-box optimization (BBO) challenge at NeurIPS 2020 which ran from July-October, 2020. The challenge emphasized the importance of evaluating derivative-free optimizers for tuning the hyperparameters of machine learning models. This was the first black-box optimization challenge with a machine learning emphasis. It was based on tuning (validation set) performance of standard machine learning models on real datasets. This competition has widespread impact as black-box optimization (e.g., Bayesian optimization) is relevant for hyperparameter tuning in almost every machine learning project as well as many applications outside of machine learning. The final leaderboard was determined using the optimization performance on held-out (hidden) objective functions, where the optimizers ran without human intervention. Baselines were set using the default settings of several open-source black-box optimization packages as well as random search.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5sNgmuk



3、[LG] Outcome-Driven Reinforcement Learning via Variational Inference
T G. J. Rudner, V H. Pong, R McAllister, Y Gal, S Levine
[University of Oxford & UC Berkeley]
基于变分推理结果驱动的强化学习。虽然强化学习算法提供了自动获取最优策略的方法,但这种方法的实际应用需要一些设计决策,如手动设计奖励函数,不仅要定义任务,还要提供足够的塑造来完善它。本文讨论了一种强化学习的新观点,将其重塑为推断实现预期结果的行动的问题,而不是奖励最大化的问题。为了解决由此产生的以结果为导向的推理问题,建立了一个新的变分推理公式,以推导出一个形态良好的奖励函数,该函数可直接从环境交互中学习。从相应的变分目标中,还推导出一个新的概率贝尔曼备份算子,用来开发解决目标导向任务的非策略性算法。通过经验证明,这种方法消除了设计奖励函数的需要,并导致了有效的目标导向行为。
While reinforcement learning algorithms provide automated acquisition of optimal policies, practical application of such methods requires a number of design decisions, such as manually designing reward functions that not only define the task, but also provide sufficient shaping to accomplish it. In this paper, we discuss a new perspective on reinforcement learning, recasting it as the problem of inferring actions that achieve desired outcomes, rather than a problem of maximizing rewards. To solve the resulting outcome-directed inference problem, we establish a novel variational inference formulation that allows us to derive a well-shaped reward function which can be learned directly from environment interactions. From the corresponding variational objective, we also derive a new probabilistic Bellman backup operator reminiscent of the standard Bellman backup operator and use it to develop an off-policy algorithm to solve goal-directed tasks. We empirically demonstrate that this method eliminates the need to design reward functions and leads to effective goal-directed behaviors.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5yB9Rv7



4、[CL] A Replication Study of Dense Passage Retriever
X Ma, K Sun, R Pradeep, J Lin
[University of Waterloo]
密集段落检索器的复现性研究。用习得密集表示进行文本检索,最近成为用稀疏词袋表征的”传统”文本检索的一个有希望的替代方案。最近一项备受关注的工作是用于端到端开放域问答的密集段落检索器(DPR)技术。本文提出对这项工作的复现性研究,从原作提供的模型开始,采用Pyserini IR工具包和PyGaggle神经文本排名库中的独立实现,实验结果在很大程度上验证了原论文的描述,另外得出两个重要发现,有助于更好地理解DPR:原作似乎低估了BM25基线的有效性,因此也低估了密集稀疏混合检索的结果;通过纳入来自检索器的证据和改进的答案跨度评分技术,能用与原作完全相同的模型来提高端到端问答效率。
Text retrieval using learned dense representations has recently emerged as a promising alternative to “traditional” text retrieval using sparse bag-of-words representations. One recent work that has garnered much attention is the dense passage retriever (DPR) technique proposed by Karpukhin et al. (2020) for end-to-end open-domain question answering. We present a replication study of this work, starting with model checkpoints provided by the authors, but otherwise from an independent implementation in our group’s Pyserini IR toolkit and PyGaggle neural text ranking library. Although our experimental results largely verify the claims of the original paper, we arrived at two important additional findings that contribute to a better understanding of DPR: First, it appears that the original authors under-report the effectiveness of the BM25 baseline and hence also dense—sparse hybrid retrieval results. Second, by incorporating evidence from the retriever and an improved answer span scoring technique, we are able to improve end-to-end question answering effectiveness using exactly the same models as in the original work.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5CwDSdx

5、[CV] Unsupervised 3D Shape Completion through GAN Inversion
J Zhang, X Chen, Z Cai, L Pan, H Zhao, S Yi, C K Yeo, B Dai, C C Loy
[Nanyang Technological University & SenseTime Research]
基于GAN逆映射的无监督3D形状补全。大多数3D形状补全方法在很大程度上依赖于部分完整形状对并以全监督方式进行学习。尽管它们在域内数据上的表现令人印象深刻,但泛化到其他形式的部分形状或现实世界的部分扫描时,由于域的差距,往往无法获得令人满意的结果。与之前的全监督方法相比,本文提出了ShapeInversion,将生成对抗网络(GAN)逆映射引入到形状补全中。ShapeInversion使用一个在完整形状上预训练的GAN,搜索一个潜码,该代码给出一个完整形状,能最好地重建给定的部分输入。通过这种方式,ShapeInversion不再需要成对的训练数据,能纳入训练好的生成模型中捕获的丰富先验。在ShapeNet基准上,ShapeInversion优于SOTA无监督方法,可与用配对数据学习的有监督方法相媲美,还展示了显著的泛化能力,对现实世界的扫描和各种形式的部分输入以及不完整程度给出了鲁棒的结果。由于预训练GAN的参与,ShapeInversion自然地实现了一系列额外的能力,例如为一个模糊的部分输入产生多个有效的完整形状,以及形状操作和内插。
Most 3D shape completion approaches rely heavily on partial-complete shape pairs and learn in a fully supervised manner. Despite their impressive performances on in-domain data, when generalizing to partial shapes in other forms or real-world partial scans, they often obtain unsatisfactory results due to domain gaps. In contrast to previous fully supervised approaches, in this paper we present ShapeInversion, which introduces Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) inversion to shape completion for the first time. ShapeInversion uses a GAN pre-trained on complete shapes by searching for a latent code that gives a complete shape that best reconstructs the given partial input. In this way, ShapeInversion no longer needs paired training data, and is capable of incorporating the rich prior captured in a well-trained generative model. On the ShapeNet benchmark, the proposed ShapeInversion outperforms the SOTA unsupervised method, and is comparable with supervised methods that are learned using paired data. It also demonstrates remarkable generalization ability, giving robust results for real-world scans and partial inputs of various forms and incompleteness levels. Importantly, ShapeInversion naturally enables a series of additional abilities thanks to the involvement of a pre-trained GAN, such as producing multiple valid complete shapes for an ambiguous partial input, as well as shape manipulation and interpolation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5H79cv2




另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CL] Visually grounded models of spoken language: A survey of datasets, architectures and evaluation techniques
口语的视觉基础模型:数据集、结构和评价综述
G Chrupała
[Tilburg University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5L5AwRS




[CL] Extractive and Abstractive Explanations for Fact-Checking and Evaluation of News
新闻事实核查与评价的抽取式和抽象式解释
A Kazemi, Z Li, V Pérez-Rosas, R Mihalcea
[University of Michigan]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5MtlwAl


[CV] Rethinking BiSeNet For Real-time Semantic Segmentation
BiSeNet实时语义分割的反思
M Fan, S Lai, J Huang, X Wei, Z Chai, J Luo, X Wei
[Meituan]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5OdvyTi




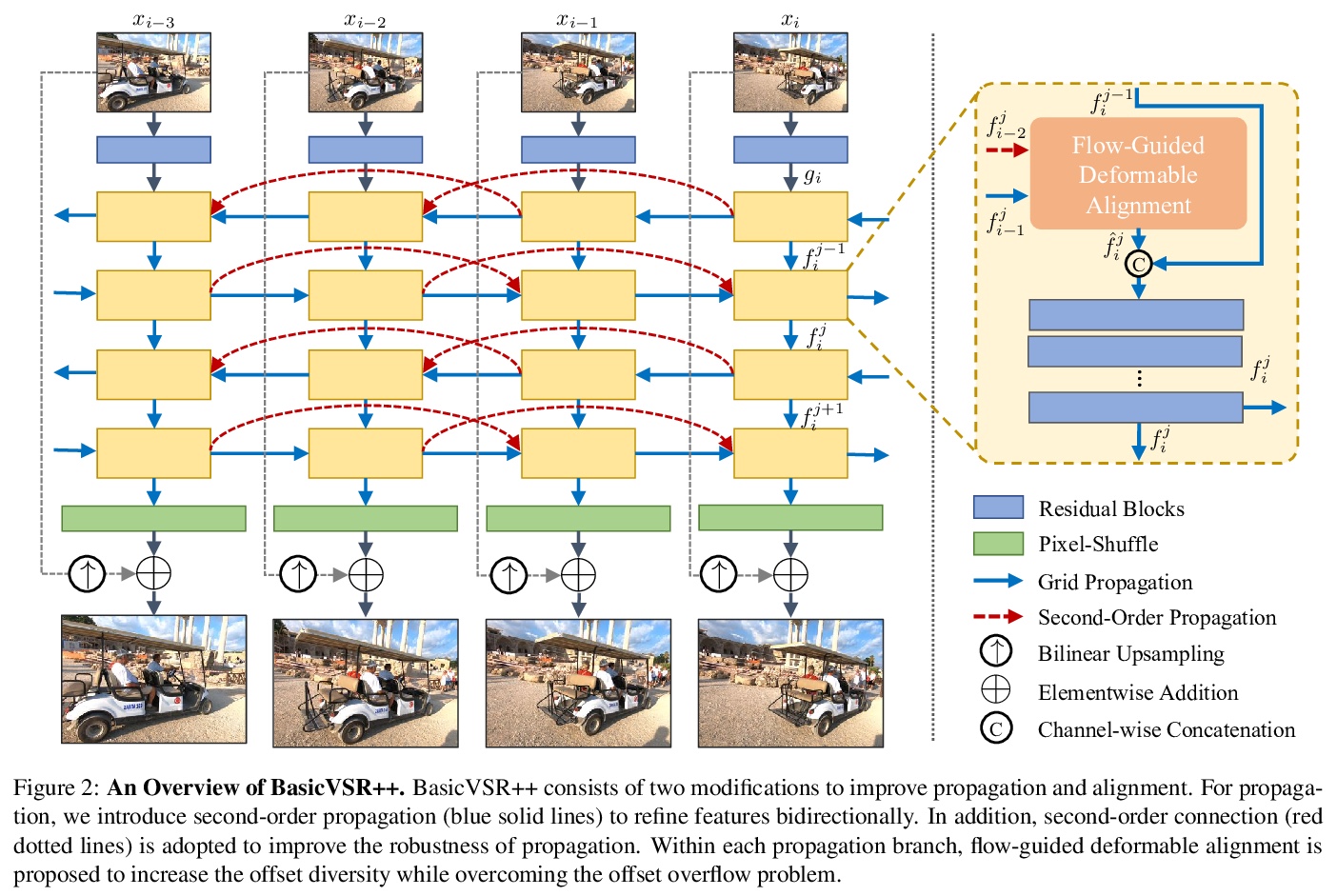
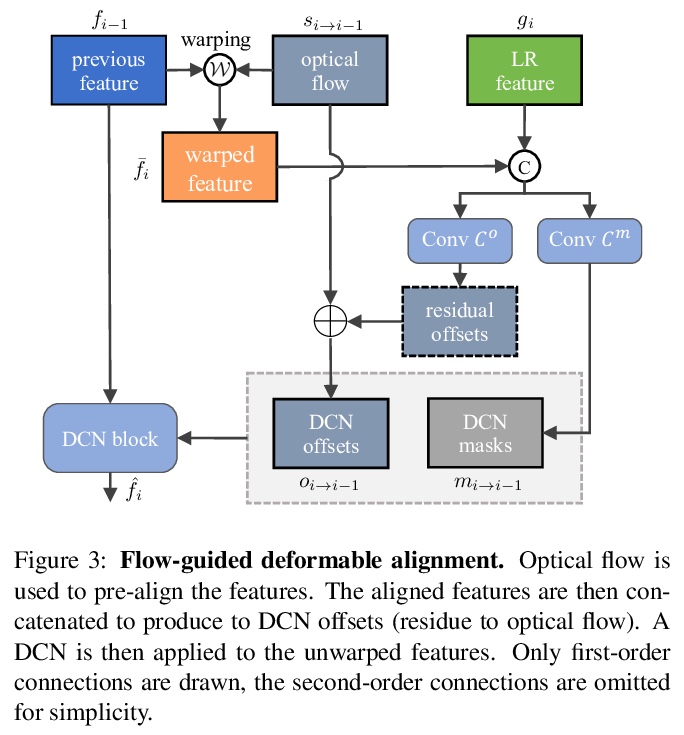
[CV] BasicVSR++: Improving Video Super-Resolution with Enhanced Propagation and Alignment
BasicVSR++:通过增强传播与对齐改善视频超分辨率
K C.K. Chan, S Zhou, X Xu, C C Loy
[Nanyang Technological University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kd5PM75cO