- 1、[LG] Pay Attention to MLPs
- 2、[CV] A Light Stage on Every Desk
- 3、[CV] Rethinking the Design Principles of Robust Vision Transformer
- 4、[CL] Representing Numbers in NLP: a Survey and a Vision
- 5、[CV] Divide and Contrast: Self-supervised Learning from Uncurated Data
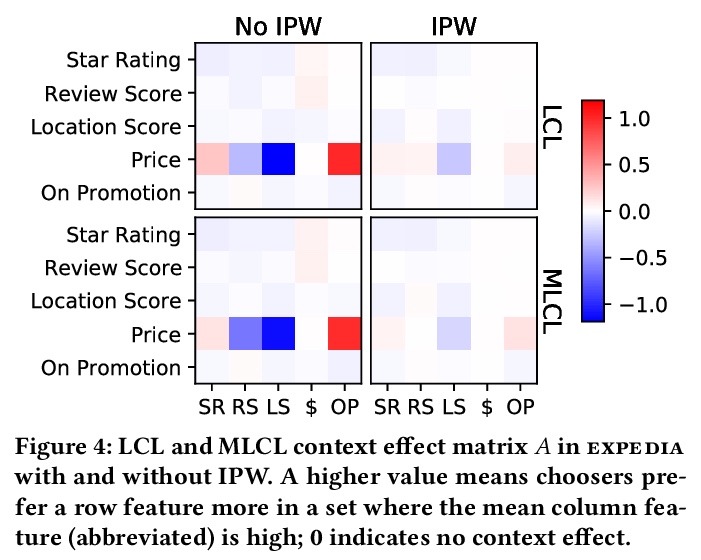
- [LG] Choice Set Confounding in Discrete Choice
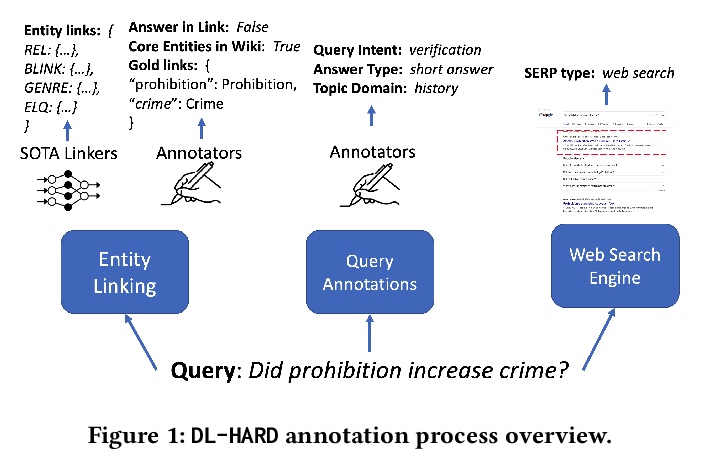
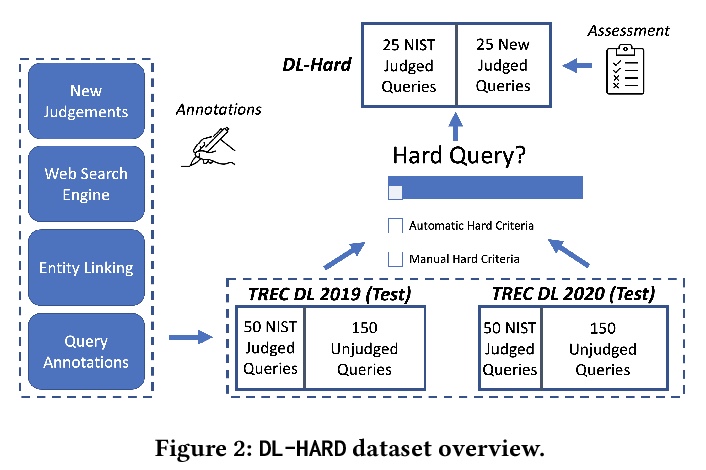
- [IR] How Deep is your Learning: the DL-HARD Annotated Deep Learning Dataset
- [RO] Manipulator-Independent Representations for Visual Imitation
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Pay Attention to MLPs
H Liu, Z Dai, D R. So, Q V. Le
[Google Research]
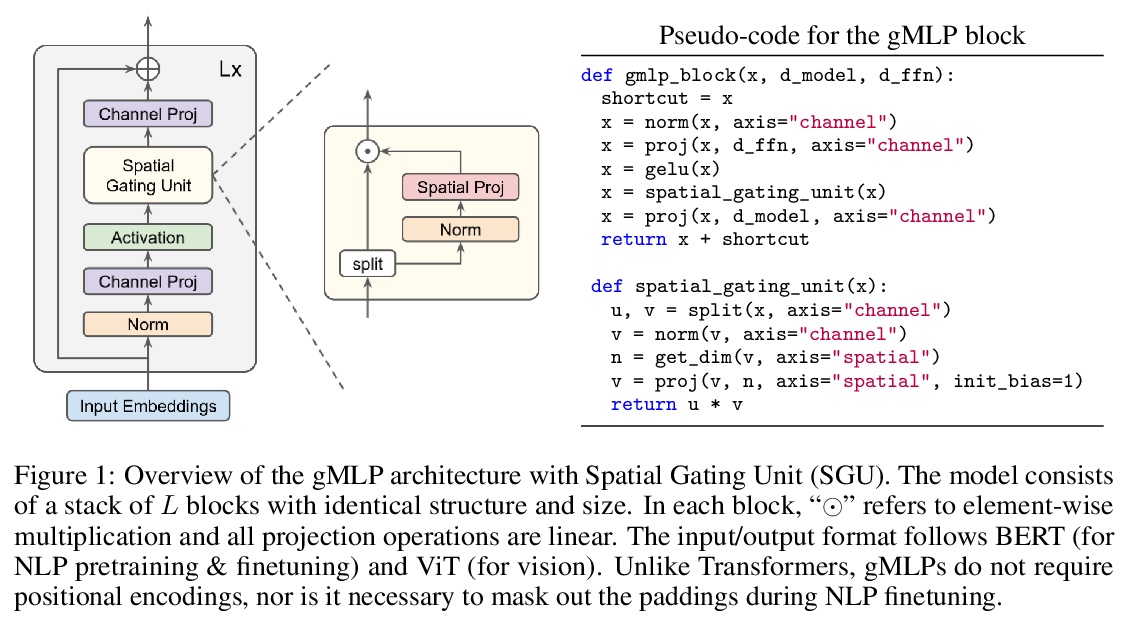
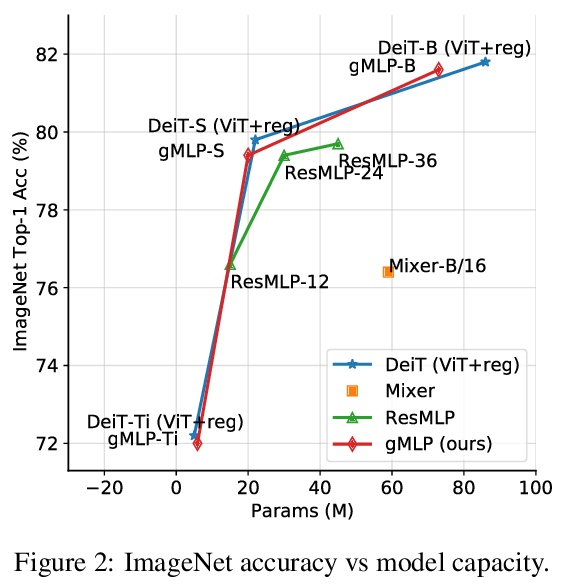
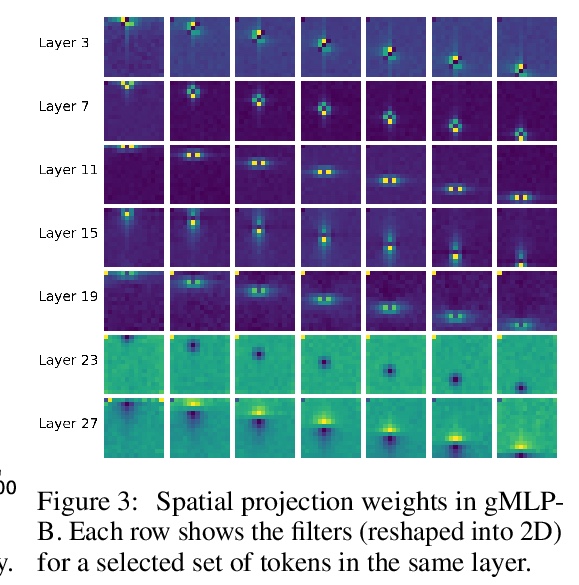
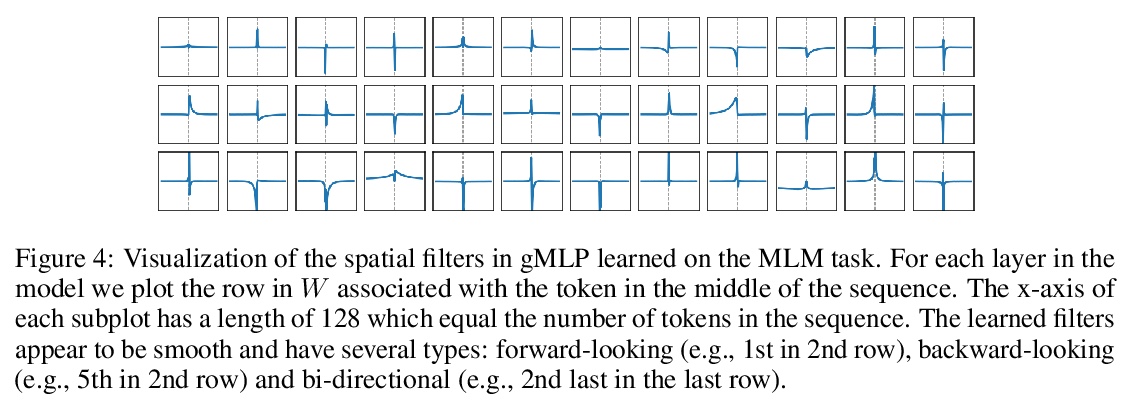
用非注意力多层感知器打败Transformer。Transformer是深度学习最重要的架构创新之一,在过去几年实现了许多突破。本文提出一种简单的无注意力网络架构——gMLP,完全基于门控多层感知器,由通道投影、空间投影和门控组成,在关键的语言和视觉应用中可以和Transformer一样表现出色。对比表明,对视觉Transformer来说自注意力并非那么关键,gMLP可以实现同样的准确性。对于BERT,gMLP模型在预训练的困惑度上与Transformer持平,在一些下游任务上表现更好。在gMLP表现较差的微调任务上,使gMLP模型大幅增大可以缩小与Transformer的差距。实验表明,在数据和计算量增加的情况下,gMLP可以和Transformers一样实现扩展。
Transformers have become one of the most important architectural innovations in deep learning and have enabled many breakthroughs over the past few years. Here we propose a simple attention-free network architecture, gMLP, based solely on MLPs with gating, and show that it can perform as well as Transformers in key language and vision applications. Our comparisons show that self-attention is not critical for Vision Transformers, as gMLP can achieve the same accuracy. For BERT, our model achieves parity with Transformers on pretraining perplexity and is better on some downstream tasks. On finetuning tasks where gMLP performs worse, making the gMLP model substantially larger can close the gap with Transformers. In general, our experiments show that gMLP can scale as well as Transformers over increased data and compute.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kg7P0qUKA
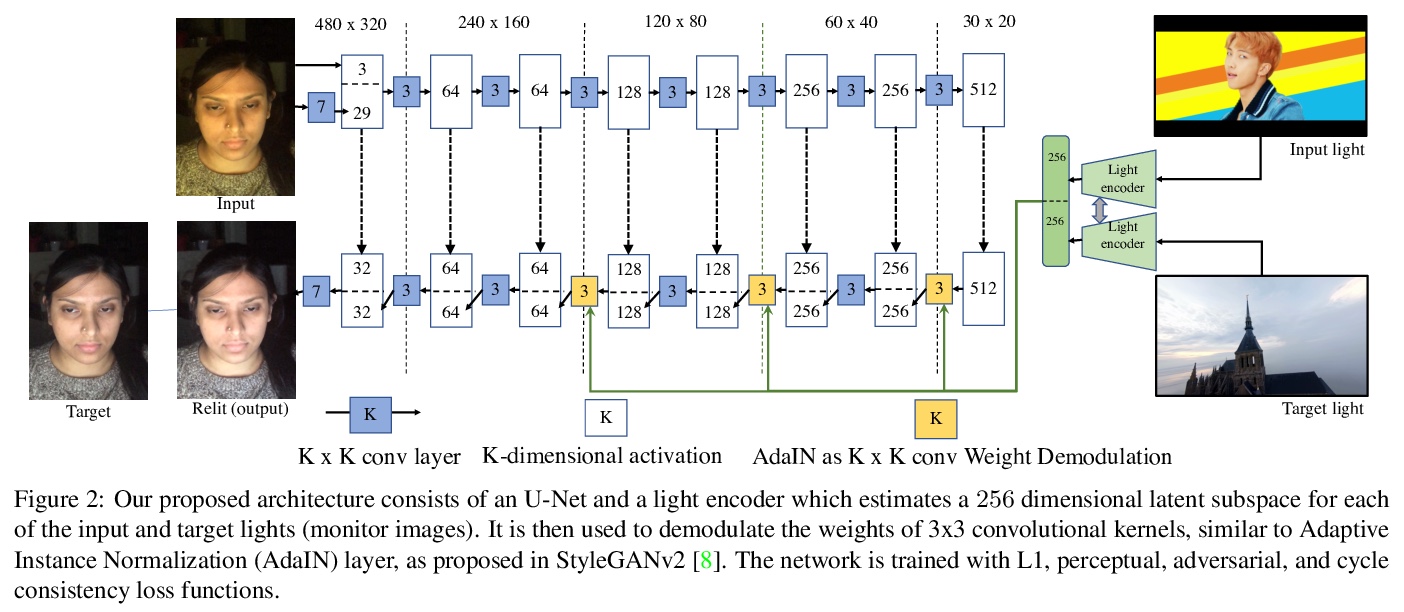
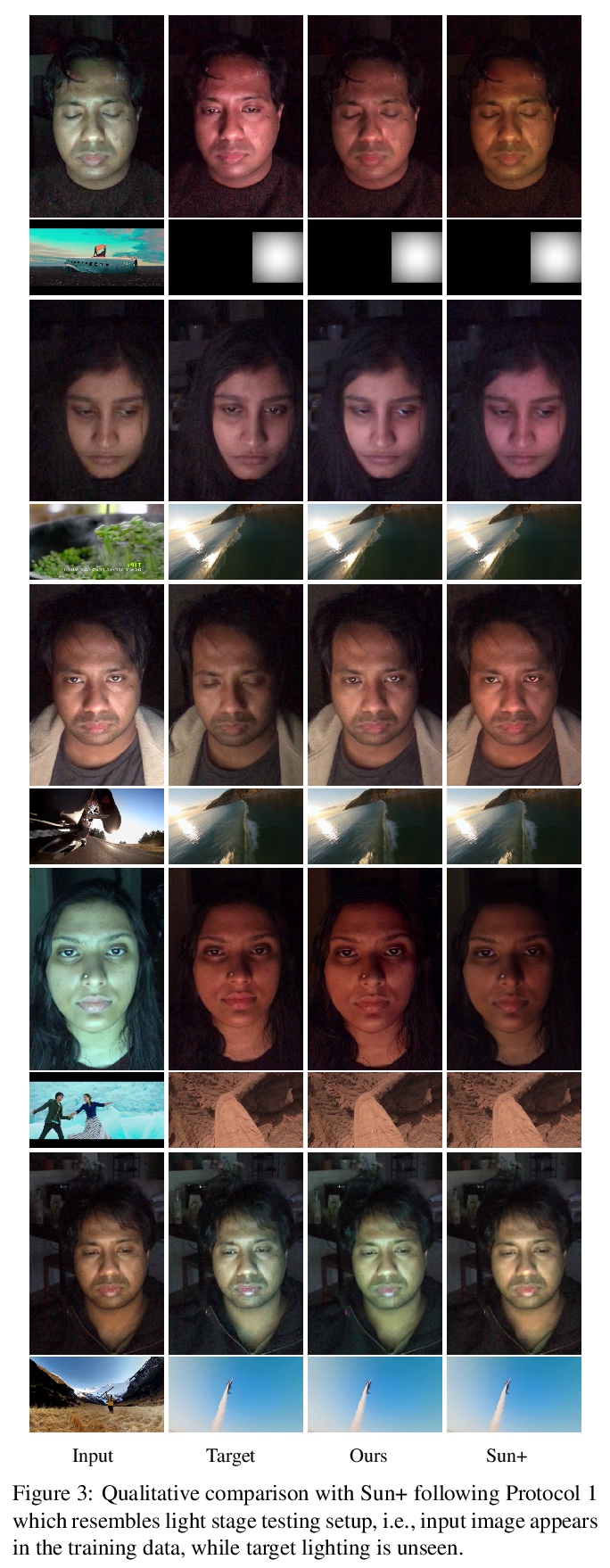
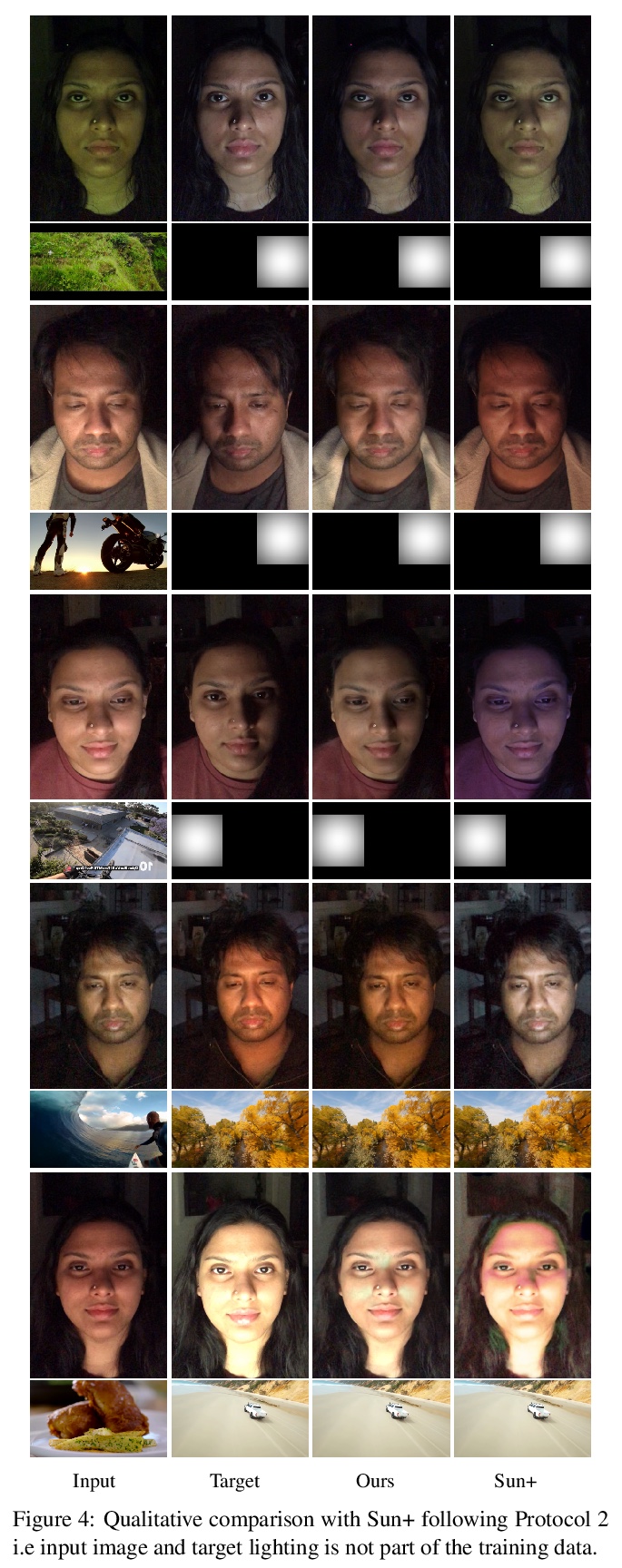
2、[CV] A Light Stage on Every Desk
S Sengupta, B Curless, I Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, S Seitz
[University of Washington]
用桌面显示器照明图片学习人脸重打光。人坐在电视或显示器前,他的脸会被随时变化的光线模式主动打亮。本文提出利用这种时变照明人脸进行学习,在任意新照明条件下对脸部进行重打光合成。现有的灯光台需要昂贵的、像房子一样大的球形捕捉架,世界上只有少数几个实验室才有,本文展示了如何从普通电视或桌面显示器获得有用数据。在用户观看YouTube视频或其他标准内容的图像上进行操作,而不是让用户承受令人不舒服的快速闪烁的灯光模式。在给定用户图像和显示器模式上训练一个深度网络,学习预测该用户在任意目标光照(显示器模式)下的图像。本方案易于部署,大大扩展了对光台数据和算法的访问。实验评估表明,该方法产生了现实的重打光结果。
Every time you sit in front of a TV or monitor, your face is actively illuminated by time-varying patterns of light. This paper proposes to use this time-varying illumination for synthetic relighting of your face with any new illumination condition. In doing so, we take inspiration from the light stage work of Debevec et al. [4], who first demonstrated the ability to relight people captured in a controlled lighting environment. Whereas existing light stages require expensive, room-scale spherical capture gantries and exist in only a few labs in the world, we demonstrate how to acquire useful data from a normal TV or desktop monitor. Instead of subjecting the user to uncomfortable rapidly flashing light patterns, we operate on images of the user watching a YouTube video or other standard content. We train a deep network on images plus monitor patterns of a given user and learn to predict images of that user under any target illumination (monitor pattern). Experimental evaluation shows that our method produces realistic relighting results. Video results are available at grail.cs.washington.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kg7VhgPlH

3、[CV] Rethinking the Design Principles of Robust Vision Transformer
X Mao, G Qi, Y Chen, X Li, S Ye, Y He, H Xue
[Alibaba Group & EPFL]
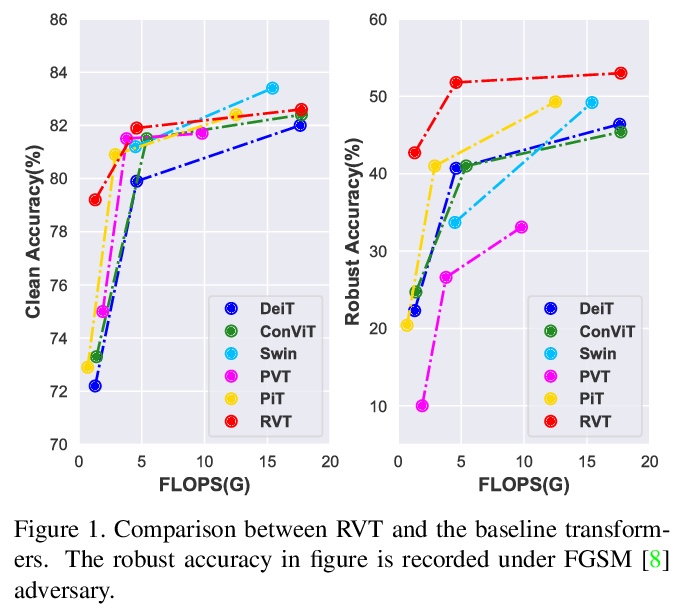
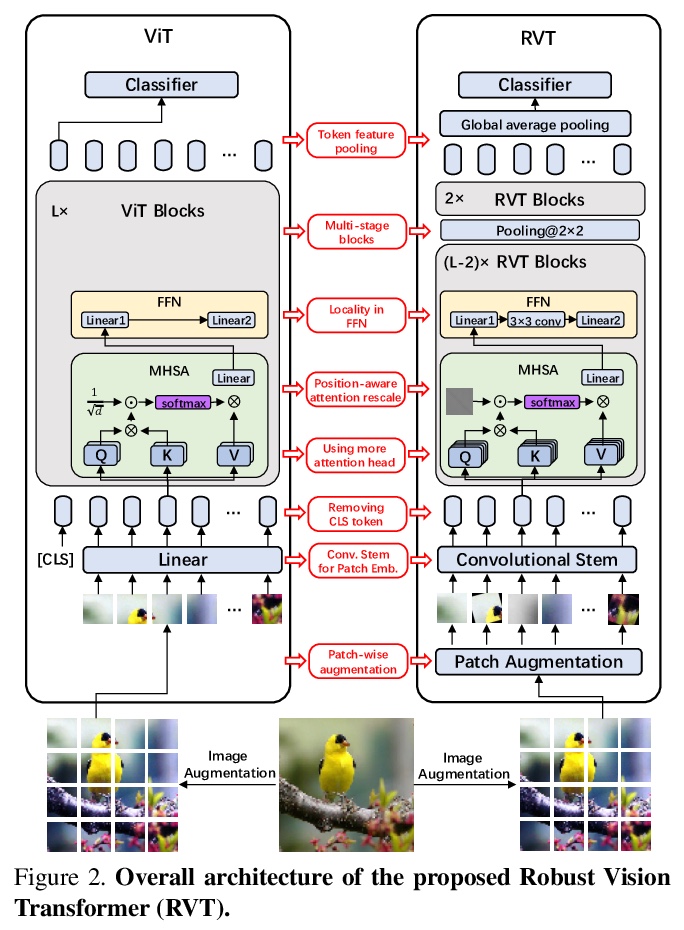
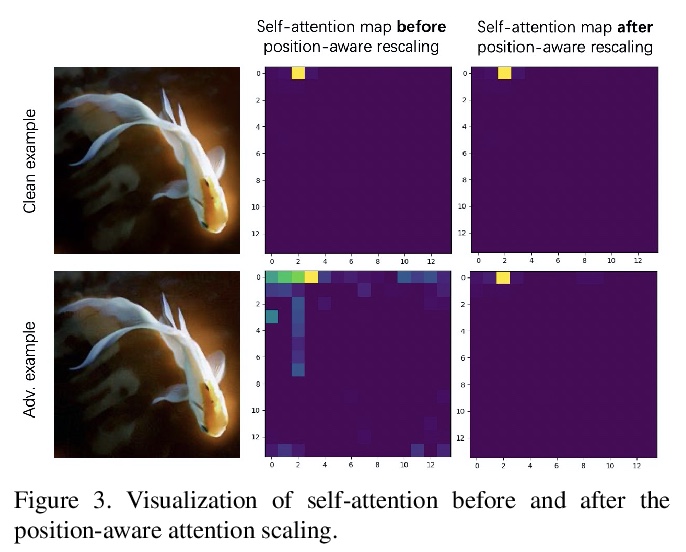
重新思考鲁棒视觉Transformer的设计原则。最近关于视觉Transformer(ViT)的研究进展表明,基于自注意力的网络,利用长程依赖建模能力,在大多数视觉任务中超过了传统卷积神经网络(CNN)。为进一步扩大计算机视觉的适用性,提出了许多改进的变体,通过考虑CNN的优势,即位置性、翻译不变性,重新设计Transformer架构,以获得更好的性能。然而,这些方法只考虑了模型的标准精度或计算成本。本文基于鲁棒性重新思考了ViT的设计原则,发现有些设计成分极大损害了ViT的鲁棒性和泛化能力,而有些则是有益的。通过结合鲁棒性设计组件,提出了鲁棒视觉Transformer(RVT),一种新的视觉Transformer,具有卓越的性能和强大的鲁棒性。进一步提出两种新的即插即用的技术,即位置感知注意力重构和图块式增强,来训练RVT。在ImageNet和六个鲁棒性基准上的实验结果表明,与以前的Transformer和最先进的CNN相比,RVT具有先进的鲁棒性和泛化能力。RVT-S*在包括ImageNet-C和ImageNet-Sketch在内的多个鲁棒性排行榜上也取得了第一名的成绩。
Recent advances on Vision Transformers (ViT) have shown that self-attention-based networks, which take advantage of long-range dependencies modeling ability, surpassed traditional convolution neural networks (CNNs) in most vision tasks. To further expand the applicability for computer vision, many improved variants are proposed to re-design the Transformer architecture by considering the superiority of CNNs, i.e., locality, translation invariance, for better performance. However, these methods only consider the standard accuracy or computation cost of the model. In this paper, we rethink the design principles of ViTs based on the robustness. We found some design components greatly harm the robustness and generalization ability of ViTs while some others are beneficial. By combining the robust design components, we propose Robust Vision Transformer (RVT). RVT is a new vision transformer, which has superior performance and strong robustness. We further propose two new plug-and-play techniques called position-aware attention rescaling and patch-wise augmentation to train our RVT. The experimental results on ImageNet and six robustness benchmarks show the advanced robustness and generalization ability of RVT compared with previous Transformers and state-of-the-art CNNs. Our RVT-S∗ also achieves Top-1 rank on multiple robustness leaderboards including ImageNet-C and ImageNet-Sketch.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kg7ZCvDv0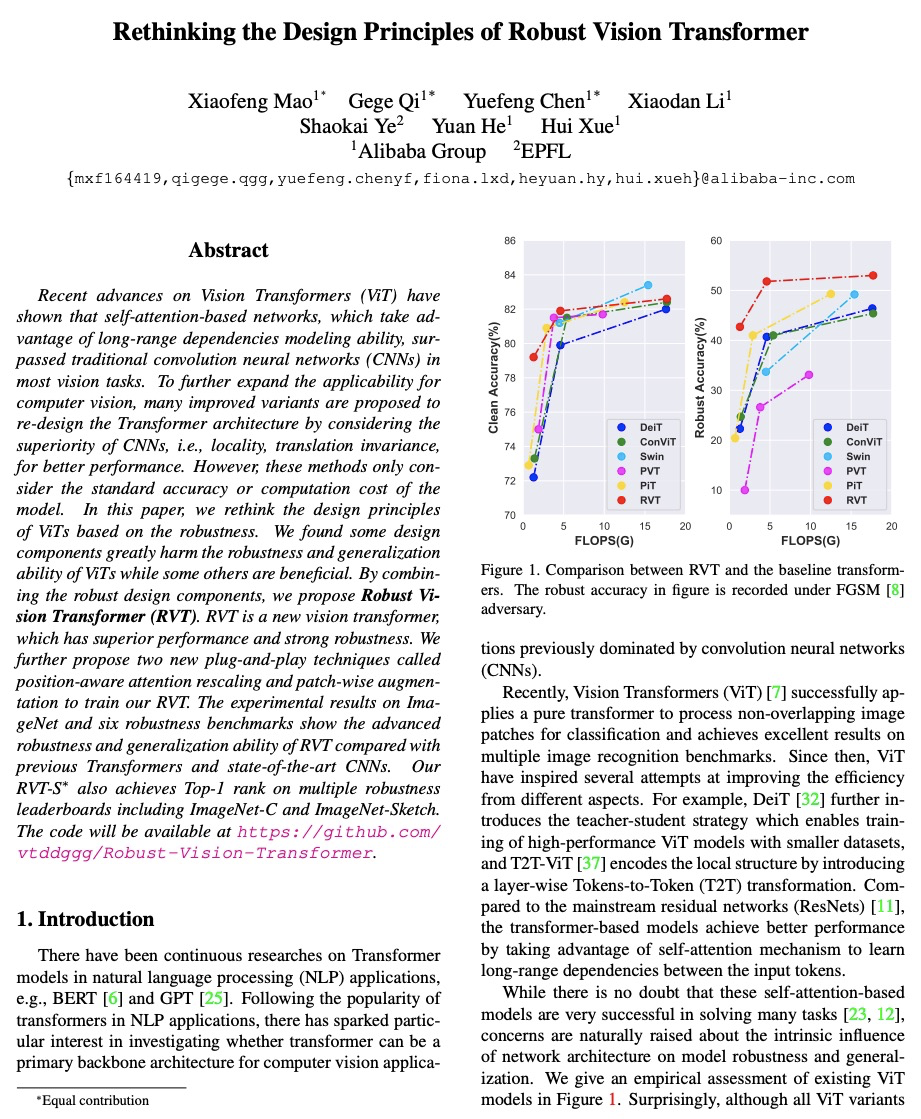
4、[CL] Representing Numbers in NLP: a Survey and a Vision
A Thawani, J Pujara, P A. Szekely, F Ilievski
[University of Southern California]
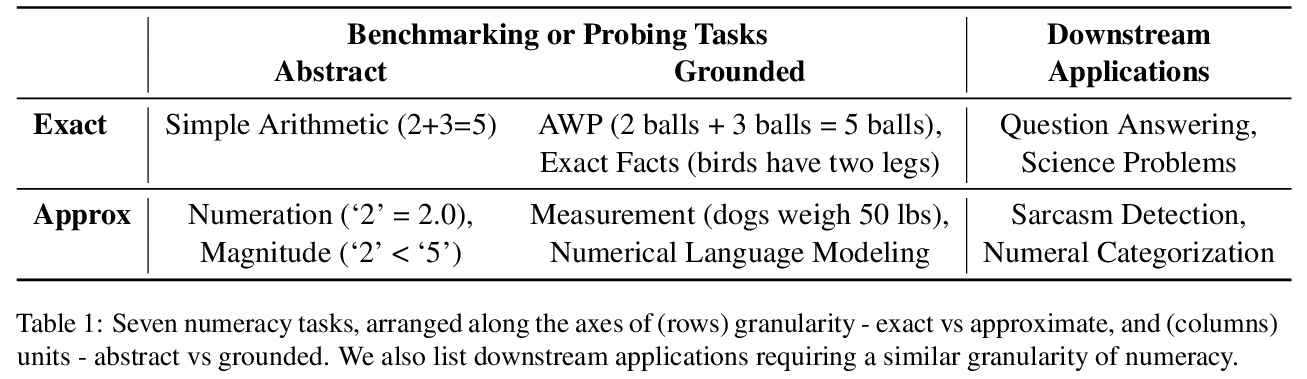
NLP数字表示综述。NLP系统很少对文本中的数字给予特别考虑。这与神经科学的共识形成鲜明对比,大脑中数字的表示方式与文字有很大差别。本文把最近NLP在数字方面的工作,整理成全面的任务和方法的分类,将算术的主观概念分解为7个子任务,沿两个维度进行梳理:颗粒度(精确与近似)和单位(抽象与具体),分析了之前发表的18个数字编码器/解码器所做的各种表示上的选择。讨论了在文本中表示数字的最佳实践,阐述了NLP中整体数字能力的愿景,包括设计权衡和统一的评估。从研究中得出两个主要结论:(1)默认的带有查找嵌入的子词分割的词表示,对数字来说显然不是最优的 (2)对整体解决数字问题所需的具体程度、覆盖范围和归纳偏差,还有几个有待解答的研究问题。
NLP systems rarely give special consideration to numbers found in text. This starkly contrasts with the consensus in neuroscience that, in the brain, numbers are represented differently from words. We arrange recent NLP work on numeracy into a comprehensive taxonomy of tasks and methods. We break down the subjective notion of numeracy into 7 subtasks, arranged along two dimensions: granularity (exact vs approximate) and units (abstract vs grounded). We analyze the myriad representational choices made by 18 previously published number encoders and decoders. We synthesize best practices for representing numbers in text and articulate a vision for holistic numeracy in NLP, comprised of design trade-offs and a unified evaluation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kg82Q0p6o
5、[CV] Divide and Contrast: Self-supervised Learning from Uncurated Data
Y Tian, O J. Henaff, A v d Oord
[MIT & DeepMind]
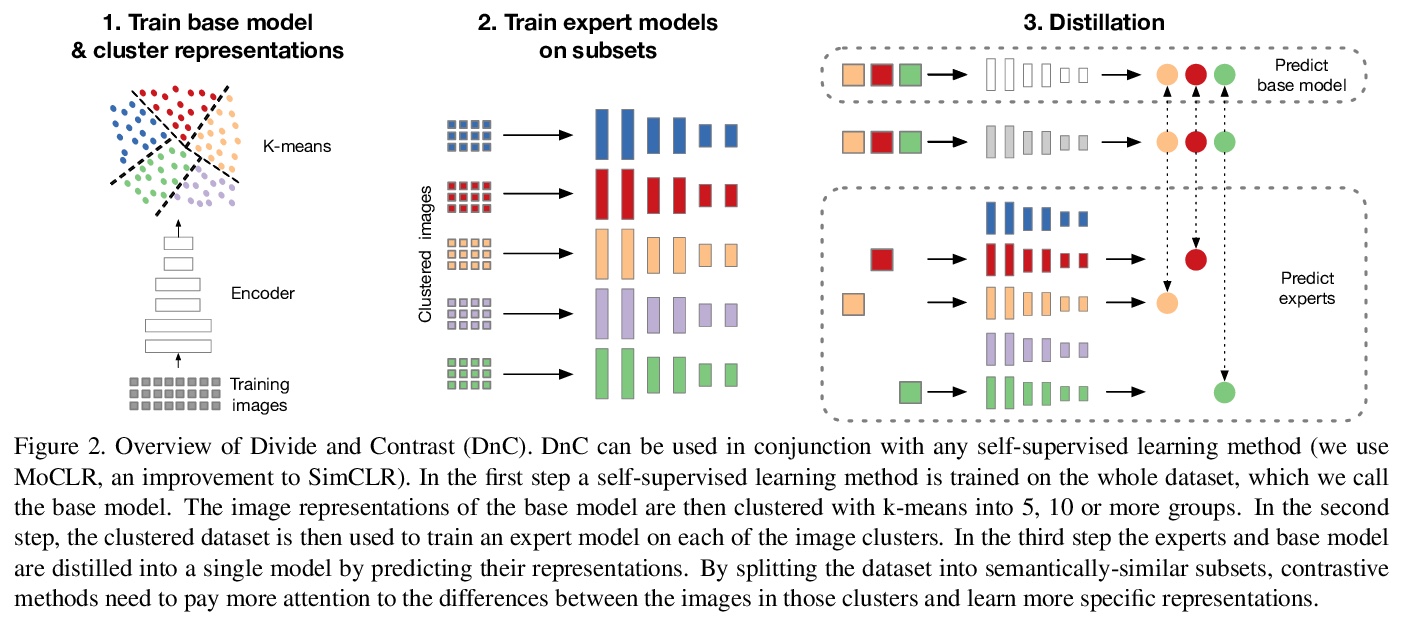
Divide and Contrast:未整理数据的自监督学习。自监督学习在利用大量无标签数据方面具有很好的前景,但迄今为止,其大部分进展仅限于精心策划的预训练数据,如ImageNet。本文探索了用更大的、没经过多少精心策划的图像数据集(如YFCC)进行对比学习的效果,发现所产生的表示质量确实存在很大差异。假设这种差距是由于图像类别分布的变化——更多样化和重尾——导致可学习的相关负样本减少。用一种新方法来测试该假设,Divide and Contrast (DnC),在对比学习和基于聚类的硬负面挖掘之间交替进行。在较少的数据集上进行预训练时,DnC极大提高了下游任务中自监督学习的性能,相对在经过整理的数据集上的先进水平具有竞争力。
Self-supervised learning holds promise in leveraging large amounts of unlabeled data, however much of its progress has thus far been limited to highly curated pretraining data such as ImageNet. We explore the effects of contrastive learning from larger, less-curated image datasets such as YFCC, and find there is indeed a large difference in the resulting representation quality. We hypothesize that this curation gap is due to a shift in the distribution of image classes—which is more diverse and heavytailed—resulting in less relevant negative samples to learn from. We test this hypothesis with a new approach, Divide and Contrast (DnC), which alternates between contrastive learning and clustering-based hard negative mining. When pretrained on less curated datasets, DnC greatly improves the performance of self-supervised learning on downstream tasks, while remaining competitive with the current stateof-the-art on curated datasets.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kg86eFfze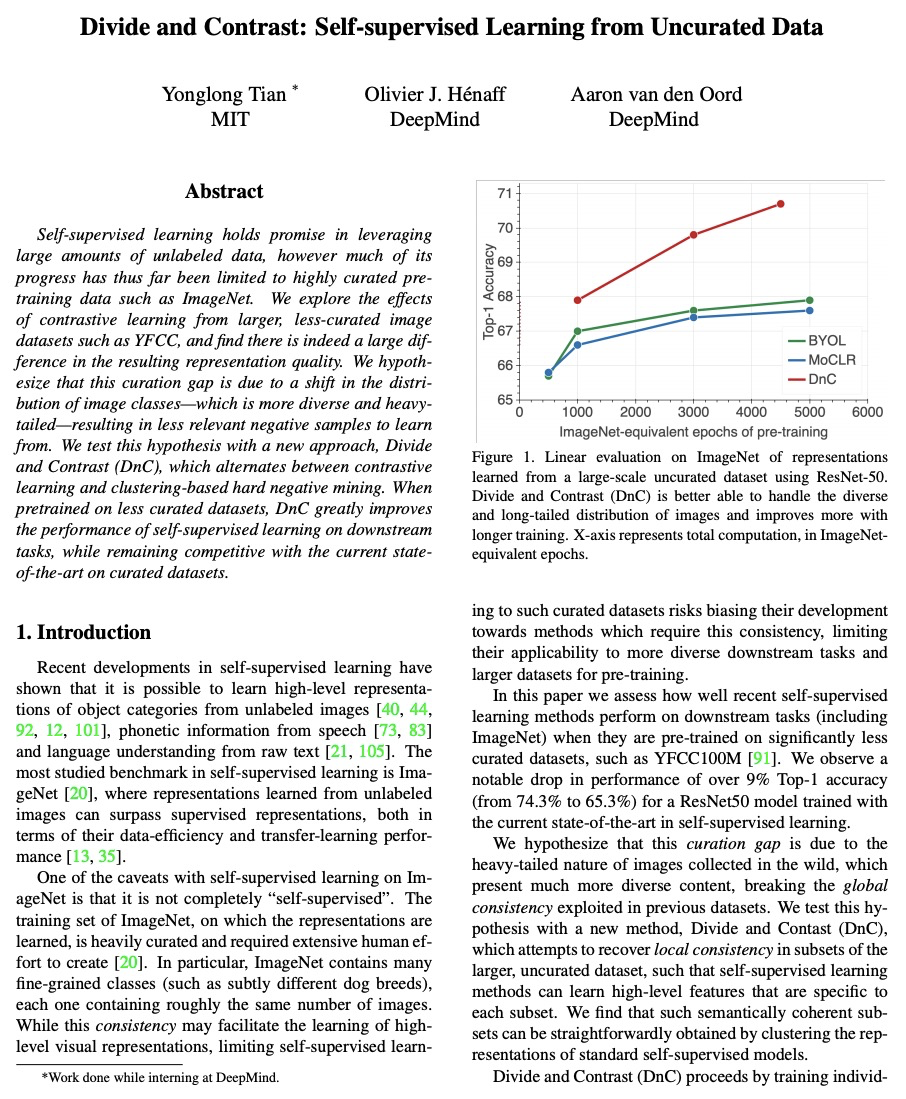
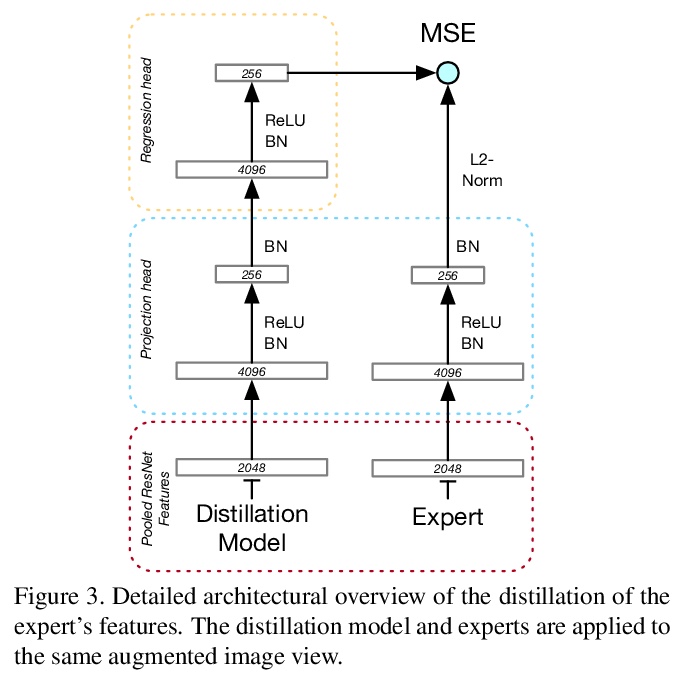

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[LG] Choice Set Confounding in Discrete Choice
偏好学习中离散选择的选择集混杂
K Tomlinson, J Ugander, A R. Benson
[Cornell University & Stanford University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kg8a4uhbb
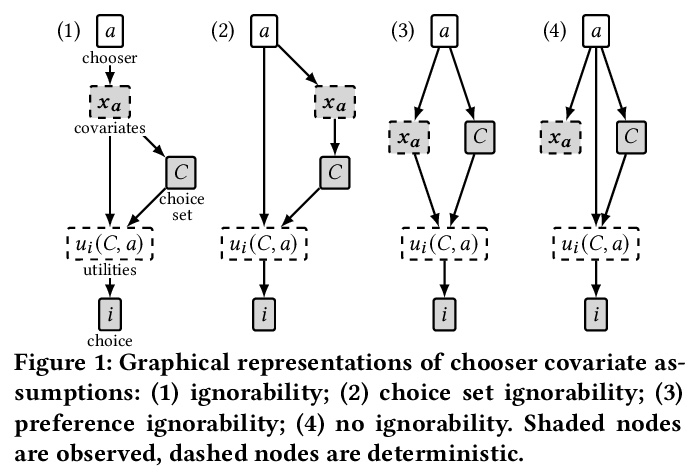
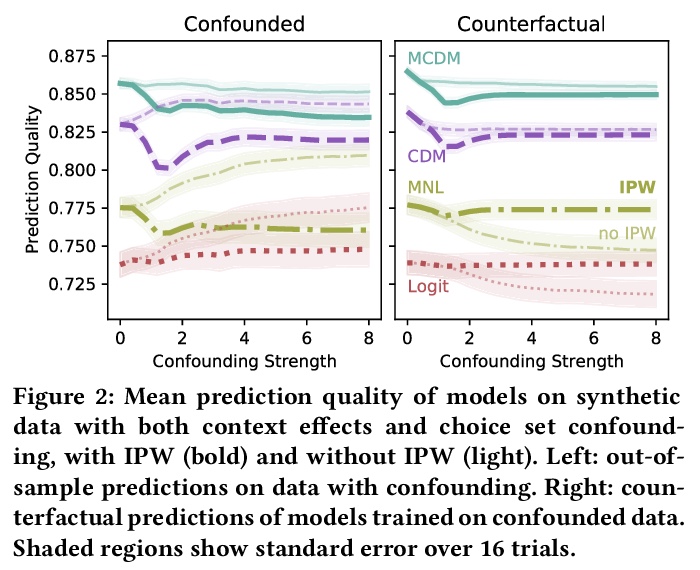
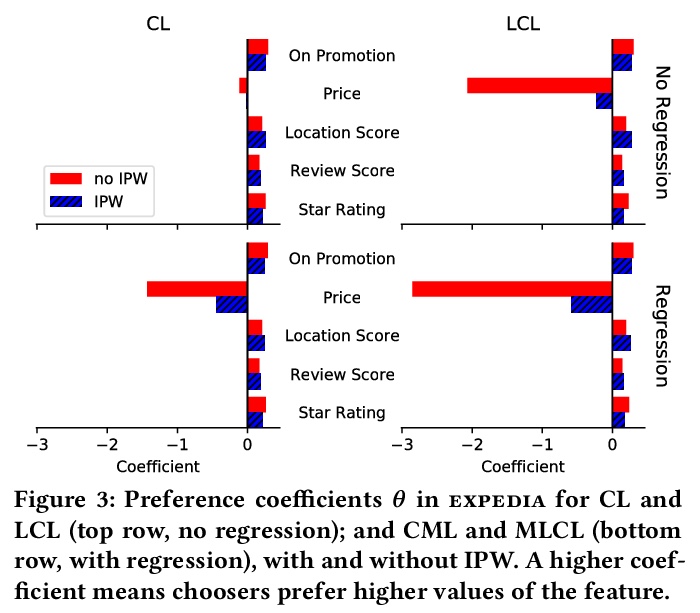
[IR] How Deep is your Learning: the DL-HARD Annotated Deep Learning Dataset
用于评估神经文档排序方法的DL-HARD标注数据集
I Mackie, J Dalton, A Yates
[University of Glasgow & Max Planck Institute for Informatics]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kg8bMkPVR
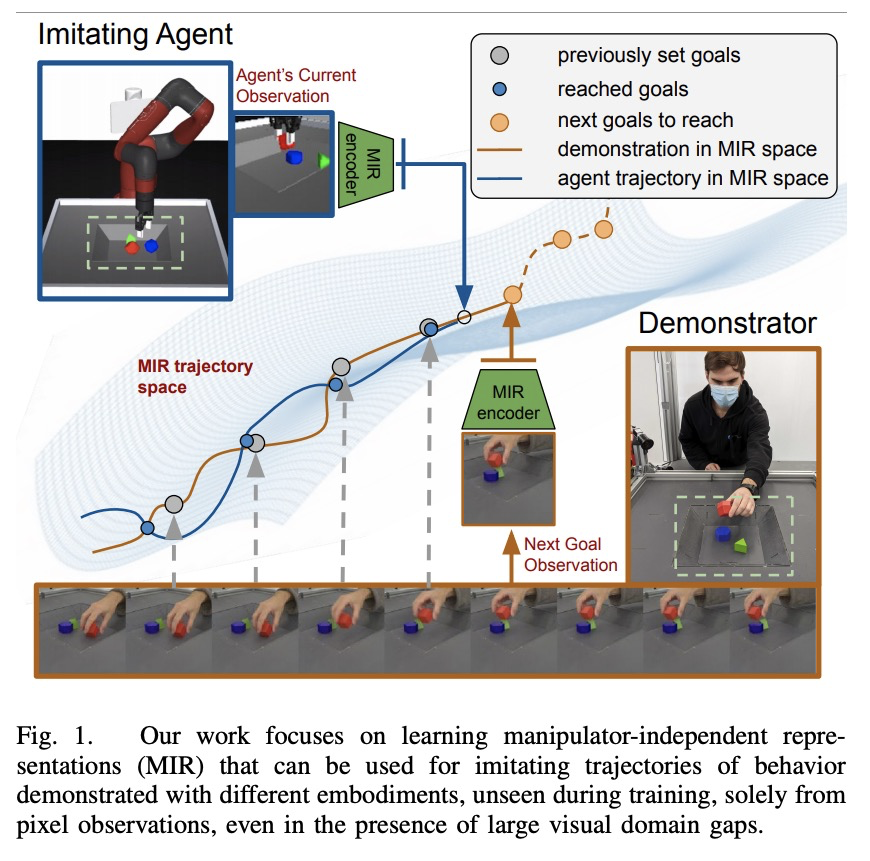
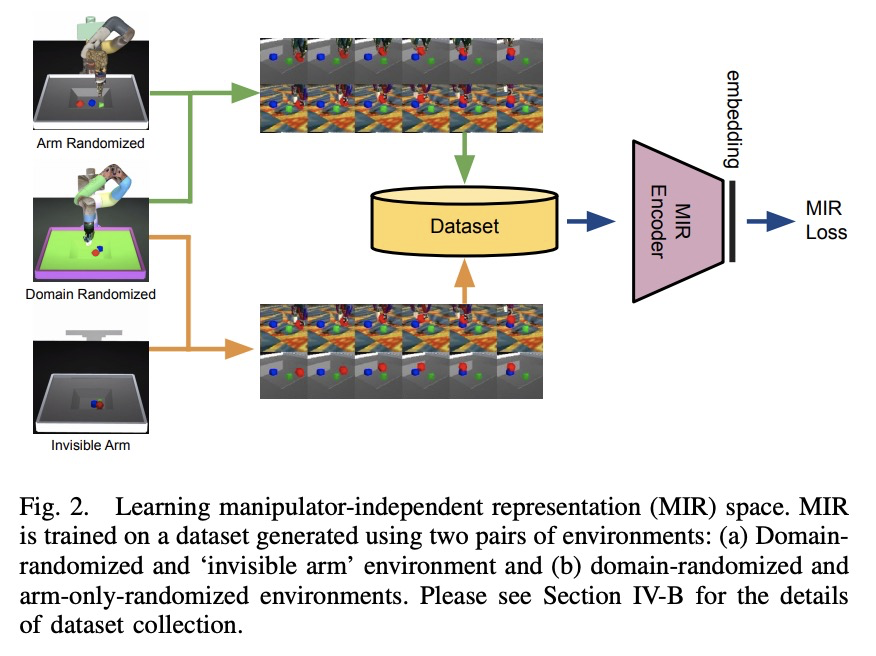
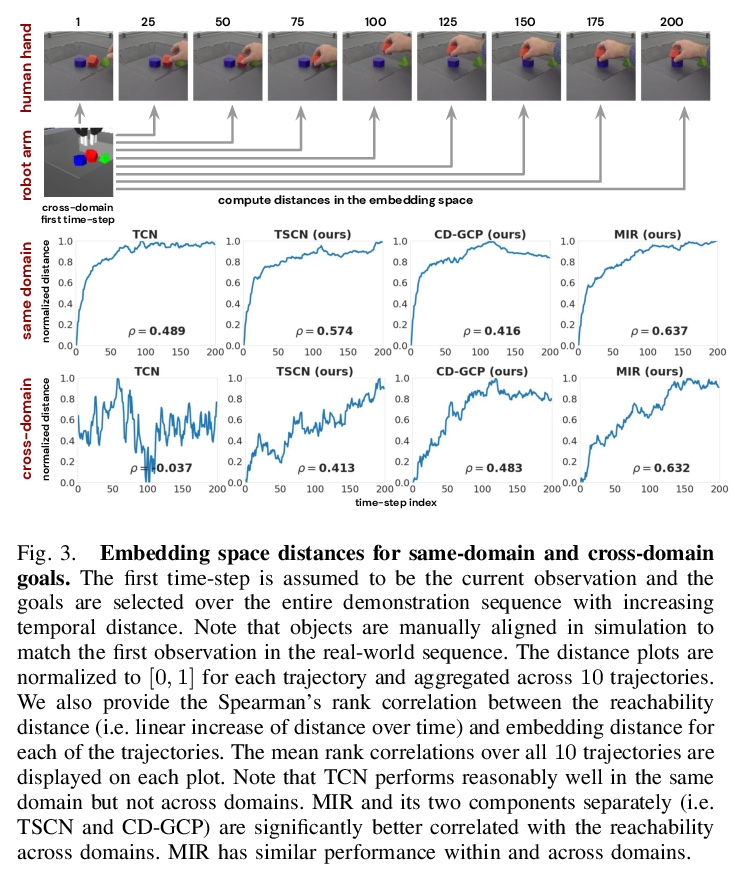
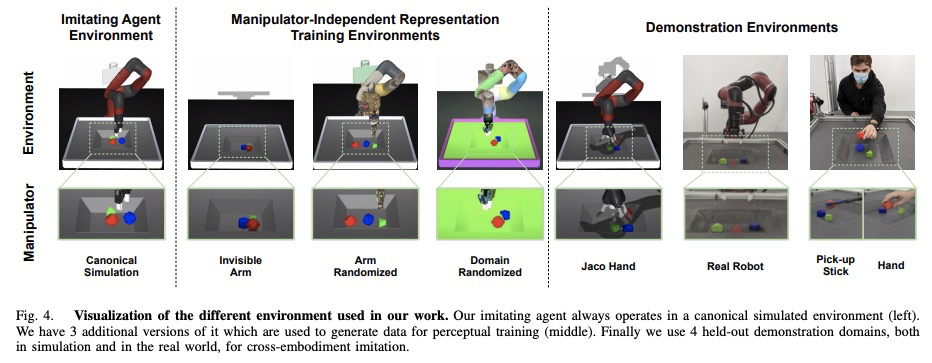
[RO] Manipulator-Independent Representations for Visual Imitation
面向视觉模仿的独立于操纵器的表示
Y Zhou, Y Aytar, K Bousmalis
[DeepMind]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kg8dO8at8