题目
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词的列表 wordDict,判定 s 是否可以被空格拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
说明:
- 拆分时可以重复使用字典中的单词。- 你可以假设字典中没有重复的单词。
示例 1:
输入: s = “leetcode”, wordDict = [“leet”, “code”] 输出: true 解释: 返回 true 因为 “leetcode” 可以被拆分成 “leet code”。
示例 2:**
输入: s = “applepenapple”, wordDict = [“apple”, “pen”] 输出: true 解释: 返回 true 因为 “applepenapple” 可以被拆分成 “apple pen apple”。 注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
示例 3:**
输入: s = “catsandog”, wordDict = [“cats”, “dog”, “sand”, “and”, “cat”] 输出: false
错误思路: map 查找效率O(1)
开始的思路是滑动窗口,把词典的单词放入map ,查找 [i,j) 区间的单词是否在map中,若在则滑动 i=jj在[0...s.length()] 中滑动,结束时 i=s.length 就会匹配成功 。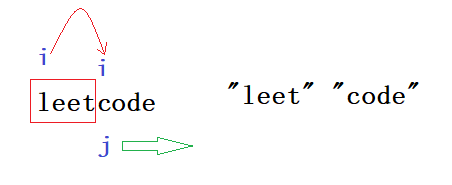
结果发现思路是错的:
**
aaaaaaa “aaa” “aaaa” 显然为True 但该思路会将其拆分为 aaa aaa a 最后一个不匹配
错误思路代码
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {int i,j;java.util.Hashtable<String,Integer>map=new java.util.Hashtable<>();for (String s1 : wordDict) {map.put(s1,1);}//入mapfor ( i = 0,j=1; j <= s.length(); j++) {if(map.containsKey(s.substring(i,j))) i=j;}return i==s.length();}
解题思路:动态规划
**
定义 表示字符串
前
个字符组成的字符串
是否能被空格拆分成若干个字典中出现的单词。
以 中的
做分割符,检查
和
- 检查**是否能够被空格拆分若干词典单词**
-  检查该字符串**是否在字典中出现**
先前已计算过 的结果,即
,若
也出现在字典,则
符合要求 。
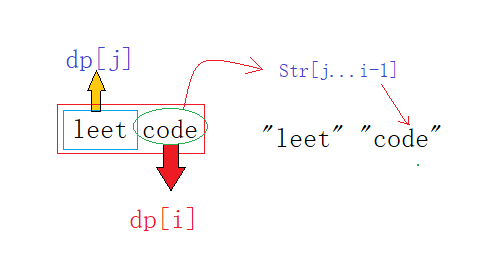
状态转移方程:
代码
官方代码
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
Set<String> wordDictSet = new HashSet(wordDict);//set存储字典
boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (dp[j] && wordDictSet.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
🦄效率优化
public class Demo {
static boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
HashMap<String,Integer> wordDictSet = new HashMap<>();
int minSize = Integer.MAX_VALUE, maxSize = 0;
for (String word: wordDict) {
wordDictSet.put(word,1);
if(word.length() < minSize) minSize = word.length();
if(word.length() > maxSize) maxSize = word.length();
}//单词存入map,并统计出最大长度和最小长度
boolean[]dp=new boolean[s.length()+1];
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); ++i) {
for (int j = Math.max(i - maxSize, 0); i - j >= minSize; ++j) {
if (dp[j] && wordDictSet.containsKey(s.substring(j, i))) {
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> wordDict=new ArrayList<>();
wordDict.add("leet");
wordDict.add("code");
System.out.println(wordBreak("leetcode",wordDict));
}
}
优化解释:
首先我们知道字典中的单词都是有长度的,假设所有单词长度集中在 6-12之间,那么我们可以知道当 j 做拆分的时候 的长度一但不在
6-12 之间定是不符合的。我们只需要集中判断 6-12 间的串即可。
![✍[LeetCode]dp139 单词拆分 - 图15](https://cdn.nlark.com/yuque/__latex/6fafc967abb0072f735dcaba5f470e5a.svg#card=math&code=%5Ctextbf%7Bdp%5Bi%5D%3Ddp%5Bj%5D%20%20%20and%20%20str%5B%20j%2Ci-1%20%5D%20%7Din%5C%20WordDict%5C%20%2C%5C%20%5C%200%20%5Cleq%20j%20%5Cleq%20i-1&height=20&width=432)

