CSS Flex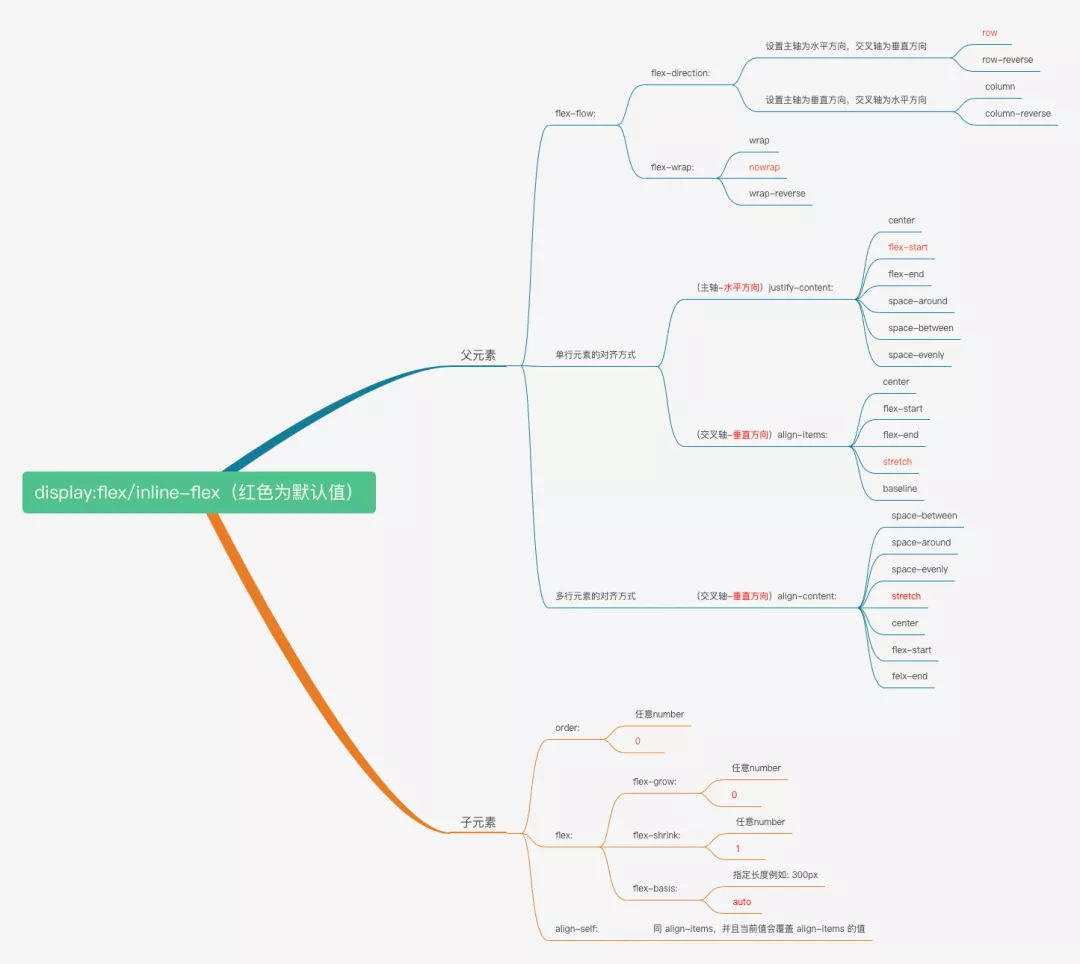
flex
下边按照上图的顺序来详细说明下每个属性的作用,并且参考 W3C 提到的代码结构:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><style>// 父元素.flex-container {display: flex;flex-direction: row;background-color: DodgerBlue;}// 子元素.flex-container > div {background-color: #f1f1f1;width: 100px;margin: 10px;text-align: center;line-height: 75px;font-size: 30px;}</style></head><body><div class="flex-container"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div></body></html>
flex
display: flex;
父元素变为 flex 布局,并且为 block 块级元素。
.flex-container {display: flex;background-color: DodgerBlue;margin: 10px;}.flex-container > div {background-color: #f1f1f1;margin: 10px;padding: 20px;font-size: 30px;}
<div class="flex-container"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div><div class="flex-container"><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div></div>

display: inline-flex;
父元素变为 flex 布局,并且是行内元素。
.flex-container {display: inline-flex;background-color: DodgerBlue;margin: 10px;}.flex-container > div {background-color: #f1f1f1;margin: 10px;padding: 20px;font-size: 30px;}
<div class="flex-container"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div><div class="flex-container"><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div></div>
flex-direction
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> flex-flow: -> flex-direction: -> row
row 为默认值
.flex-container {display: flex;flex-direction: row;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
在水平方向从左到右排列,同时决定了主轴为水平方向。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> flex-flow: -> flex-direction: -> row-reverse
.flex-container {display: flex;flex-direction: row-reverse;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
在水平方向从右到左排列,同时决定了主轴为水平方向。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> flex-flow: -> flex-direction: -> column
.flex-container {display: flex;flex-direction: column;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
在垂直方向从上到下排列,同时决定了主轴为垂直方向。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> flex-flow: -> flex-direction: -> column-reverse
.flex-container {display: flex;flex-direction: column-reverse;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
在垂直方向从下到上排列,同时决定了主轴为垂直方向。
下边为了简明,各属性都是默认主轴为水平方向进行举例
flex-wrap
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> flex-flow: ->flex-wrap: -> wrap
.flex-container {display: flex;flex-wrap: wrap;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
当空间不够的时候自动换行。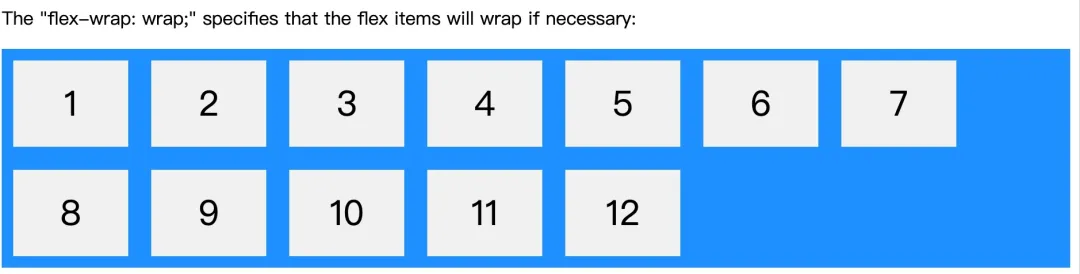
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> flex-flow: -> flex-direction: -> nowrap
nowrap 为默认值。
.flex-container {display: flex;flex-wrap: nowrap;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
当空间不够不进行换行,默认会进行压缩。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> flex-flow: -> flex-direction: -> wrap-reverse
.flex-container {display: flex;flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
在水平方向从左到右排列,同时使交叉轴的排列方向反向。
默认交叉轴是垂直方向,并且是从上到下。所以加了 wrap-reverse 就是从下到上了。
flex-flow
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> flex-flow:
上边介绍的 flex-direction 和 flex-wrap 可以合写为 flex-flow ,它们共同决定了主轴和交叉轴的排列方向,从左到右(从右到左)和从上到下(从下到上)的组合。
.flex-container {display: flex;flex-flow: row-reverse wrap-reverse;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
主轴为水平方向,row-reverse 从右到左,wrap-reverse 交叉轴从下到上。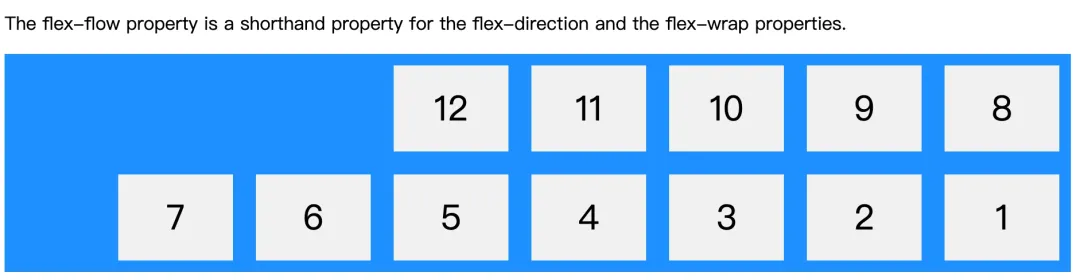
justify-content
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (主轴-默认水平方向)justify-content: -> center
.flex-container {display: flex;justify-content: center;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素居中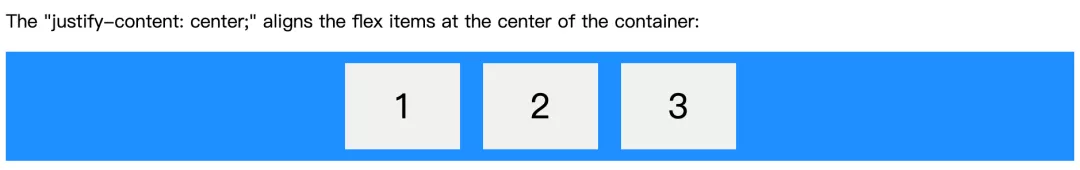
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (主轴-默认水平方向)justify-content: -> flex-start
.flex-container {display: flex;justify-content: flex-start;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素靠左对齐,并且 flex-start 为默认值。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (主轴-默认水平方向)justify-content: -> flex-end
.flex-container {display: flex;justify-content: flex-end;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素靠右对齐。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (主轴-默认水平方向)justify-content: -> space-around
.flex-container {display: flex;justify-content: space-around;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素均匀分布,元素之间的空白是两边的两倍。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (主轴-默认水平方向)justify-content: -> space-between
.flex-container {display: flex;justify-content: space-between;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素均匀分布,两边不留白。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (主轴-默认水平方向)justify-content: -> space-evenly
.flex-container {display: flex;justify-content: space-evenly;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
align-items
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-默认垂直方向)align-items: -> center
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 200px;align-items: center;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素垂直方向居中。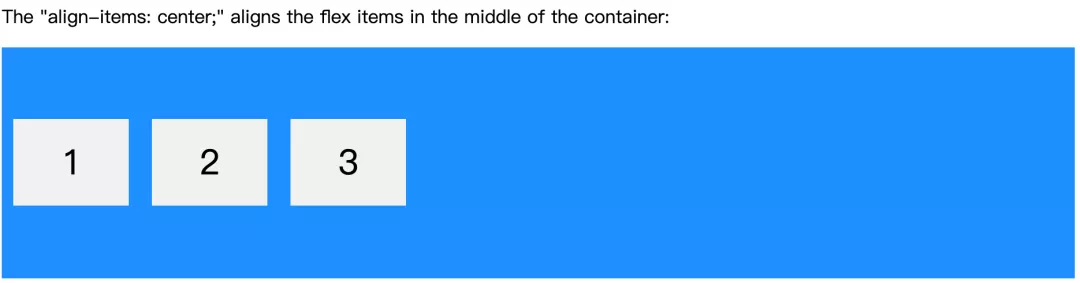
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-默认垂直方向)align-items: -> flex-start
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 200px;align-items: flex-start;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素垂直方向顶部。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-默认垂直方向)align-items: -> flex-end
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 200px;align-items: flex-end;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素垂直方向底部。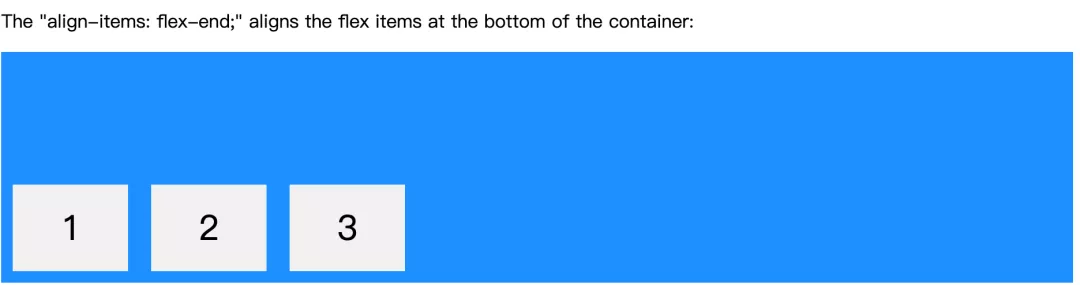
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-默认垂直方向)align-items: -> stretch
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 200px;align-items: stretch;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
子元素垂直方向拉伸,stretch 为默认值。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 单行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-默认垂直方向)align-items: -> baseline
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 200px;align-items: baseline;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
<div class="flex-container"><div><h1>1</h1></div><div><h6>2</h6></div><div><h3>3</h3></div><div><small>4</small></div></div>
当字体大小不一致的时候,根据字体的 baseline 对齐。
align-content
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 多行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-垂直方向)align-content: -> space-between
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 600px;flex-wrap: wrap;align-content: space-between;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
垂直方向,均匀分布,顶部底部没有空白。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 多行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-垂直方向)align-content: -> space-around
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 600px;flex-wrap: wrap;align-content: space-around;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
垂直方向,均匀分布,顶部底部有空白,是元素之前空白的一半。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 多行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-垂直方向)align-content: -> space-evenly
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 600px;flex-wrap: wrap;align-content: space-evenly;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
垂直方向,真均匀分布,空白全部相同。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 多行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-垂直方向)align-content: -> stretch
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 600px;flex-wrap: wrap;align-content: stretch;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
垂直拉伸占据空间剩余的空间,stretch 为默认值。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 多行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-垂直方向)align-content: -> flex-start
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 600px;flex-wrap: wrap;align-content: flex-start;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
垂直方向,顶部对齐。
display: flex/inline-flex -> 父元素 -> 多行元素的对齐方式 -> (交叉轴-垂直方向)align-content: -> flex-end
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 600px;flex-wrap: wrap;align-content: flex-end;background-color: DodgerBlue;}
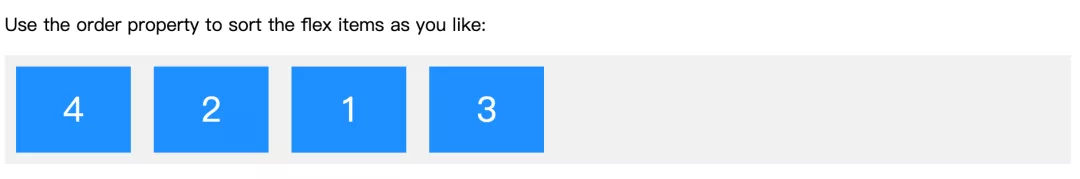
order
display: flex/inline-flex -> 子元素 -> order
.flex-container {display: flex;background-color: #f1f1f1;}
<div class="flex-container"><div style="order: 3">1</div><div style="order: 2">2</div><div style="order: 4">3</div><div style="order: 1">4</div></div>
flex-grow
display: flex/inline-flex -> 子元素 -> flex -> flex-grow
.flex-container {display: flex;background-color: #f1f1f1;}
<div class="flex-container"><div style="flex-grow: 1">1</div><div style="flex-grow: 1">2</div><div style="flex-grow: 8">3</div></div>
当有剩余空间时,是否进行拉伸,默认值 0 ,不拉伸。
有多个元素设置 flex-grow 的时候,值代表他们要增加的长度各自占额外空间的比例。
flex-shrink
display: flex/inline-flex -> 子元素 -> flex -> flex-shrink
.flex-container {display: flex;background-color: #f1f1f1;}.flex-container>div {background-color: DodgerBlue;color: white;width: 100px;margin: 10px;text-align: center;line-height: 75px;font-size: 30px;}
<div class="flex-container"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div style="flex-shrink: 0">3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div><div>7</div><div>8</div><div>9</div><div>10</div></div>
当空间不足时,是否进行压缩,默认值是 1,进行压缩,0 代表不压缩。
有多个元素设置 flex-shrink 的时候,值代表他们各自占要减少空间的比例。
flex-basis
display: flex/inline-flex -> 子元素 -> flex-> flex-basis
.flex-container {display: flex;background-color: #f1f1f1;}.flex-container>div {background-color: DodgerBlue;color: white;width: 100px;margin: 10px;text-align: center;line-height: 75px;font-size: 30px;}
<div class="flex-container"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div style="flex-basis:200px">3</div><div>4</div></div>
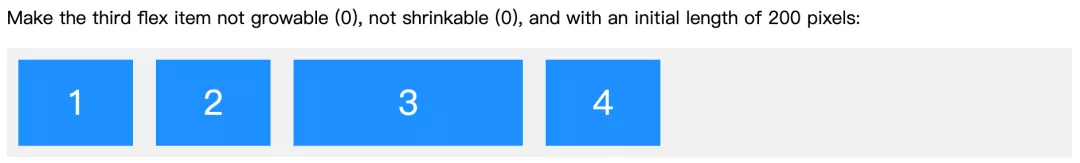
flex
display: flex/inline-flex -> 子元素 -> flex
flex-grow、 flex-shrink 、 flex-basis 三个属性的合并写法。
.flex-container {display: flex;background-color: #f1f1f1;}
<div class="flex-container"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div style="flex: 0 0 200px">3</div><div>4</div></div>
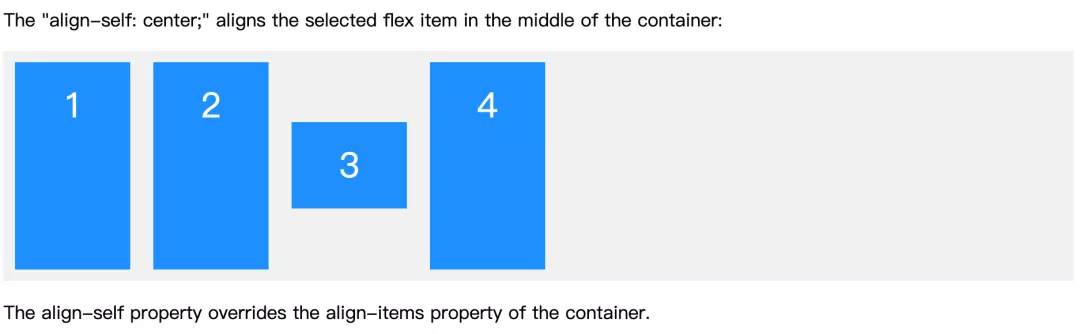
align-self
和 align-items 的属性相同,优先级更高,覆盖父元素的属性。
.flex-container {display: flex;height: 200px;background-color: #f1f1f1;}
<div class="flex-container"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div style="align-self: center">3</div><div>4</div></div>
默认是 stretch,3 元素将会居中。