其它名称:查询生成器(Query Builder),智能过滤器(Smart Filter),分段生成器(Segment Builder)。
一、问题总结
用户需要经常重复性地,基于一组自定义规则进行查询检索(或搜索查询)。
二、截图示例
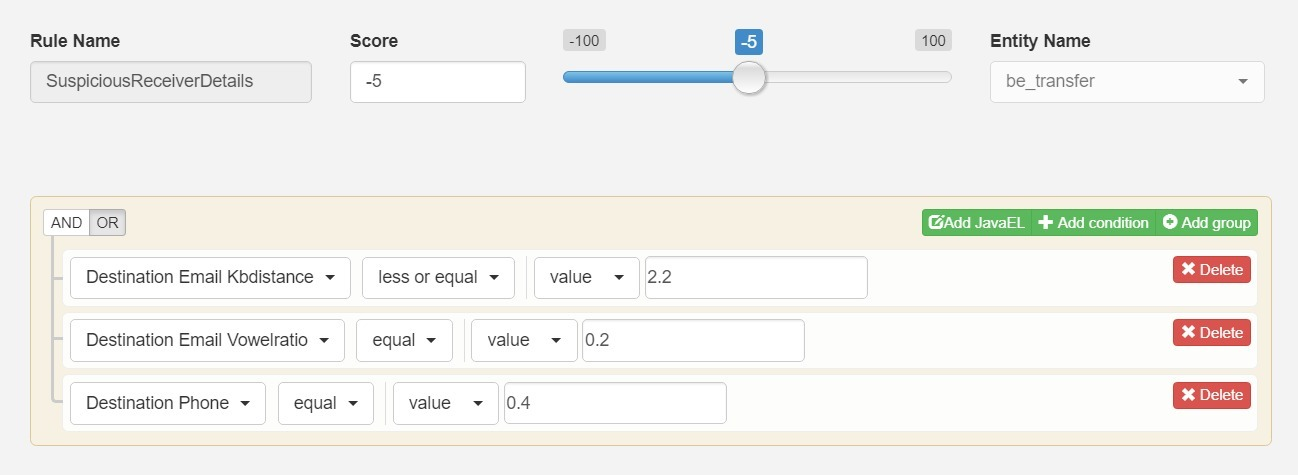
三、参考用法
- 用于基于多种条件进行检索查询。
- 用于保存片段内容(非静态选择内容)。
- 用于帮用户创建动态列表,固化所选规则集合,而不是固化实际检索结果。
- 用于当检索条件的类型不定、数量不定时。
- 如果用户输入单个文本内容即可找到需要的内容,不要使用本模式。
- 如果检索查询时每次都采用类型相同的变量,不要使用本模式。
四、解决方案
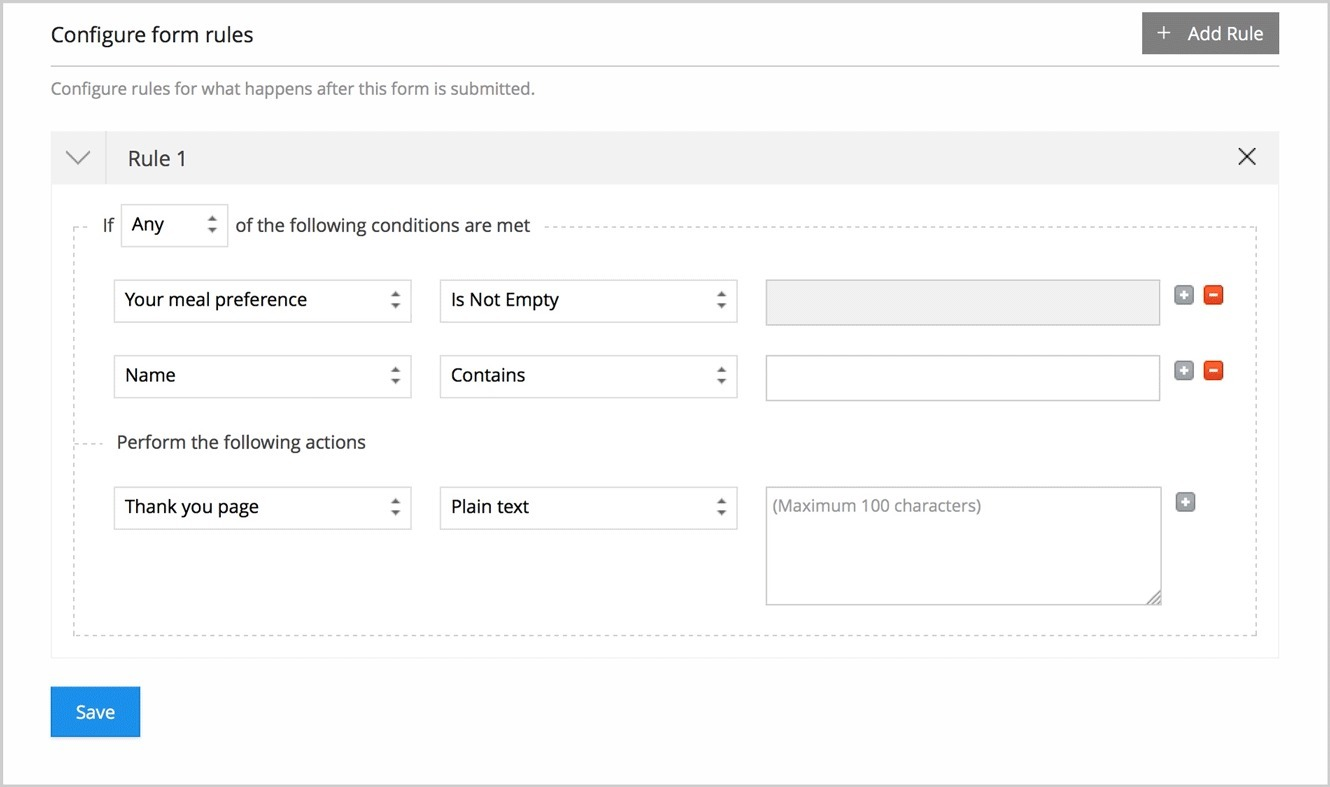
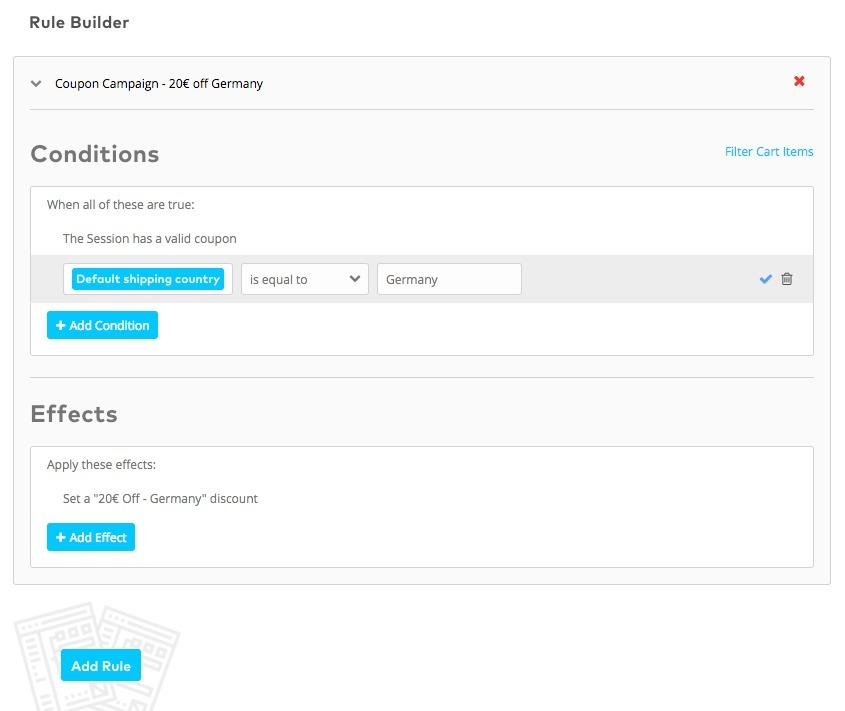
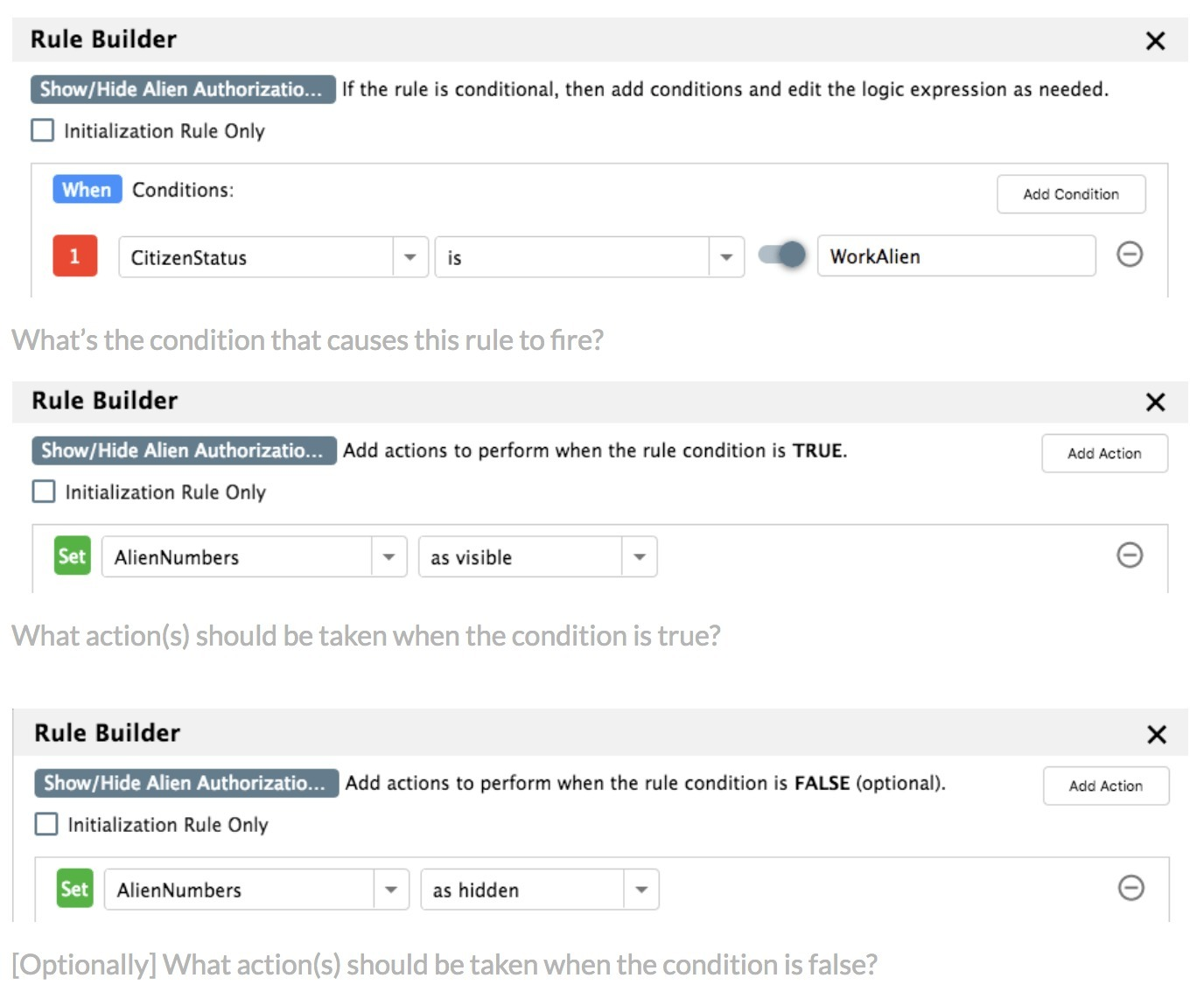
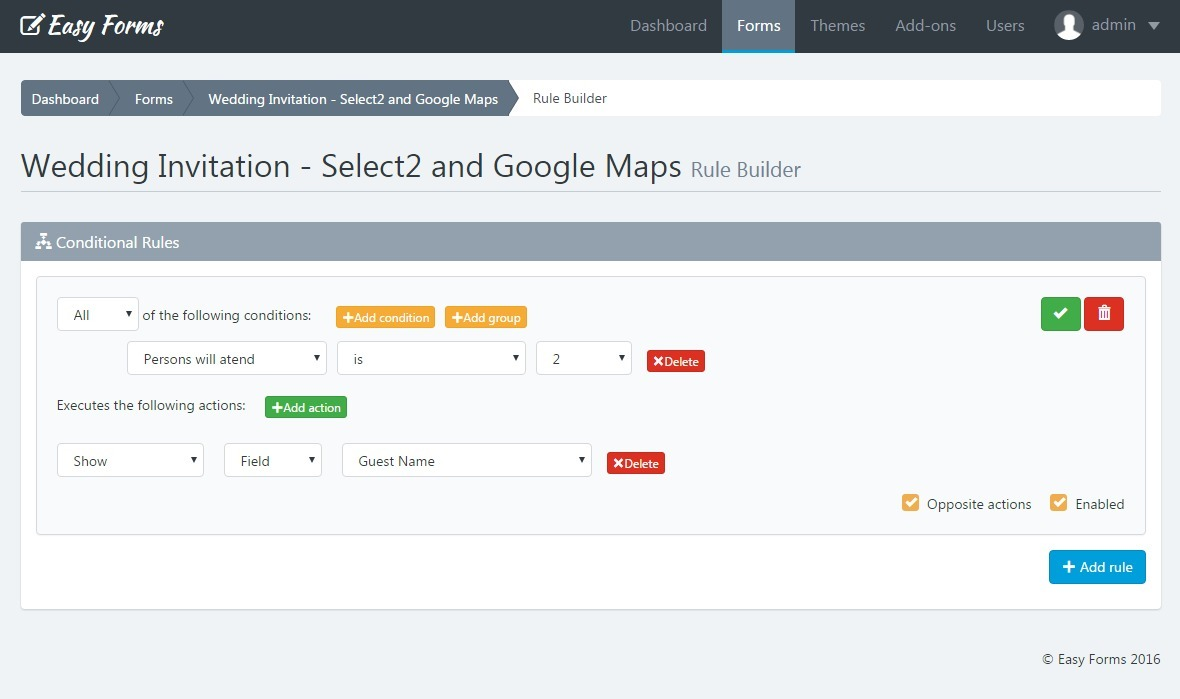
让用户创建动态规则列表,缩小数据集中的匹配结果。每个单独的行或框表示一条规则,所有规则竖直排列。
4.1 部分或全部
用户必须指定规则是必需的(and,与)还是可选的(or,或)。本模式的常见简化方法是提供一个选项,指定选择的规则需要全部满足还是满足任一规则即可。
一种更为细致的做法是,允许对每条规则都可以选择设置是必须满足(或必选)还是可选。
4.2 区别对待每类规则?
当用户选择想要(施加)的规则时,由这些规则得到的结果取决于在规则中输入的相关且有意义的信息。
这就是许多规则编辑器提供智能迷你表单的原因,这些表单形式取决于所选的规则类型。如果规则采用文本搜索,则「包含」、「不包含」、「匹配」或「不匹配」这样的选项是有意义的。其他规则可以是从动态列表中选择选项,或者提供数字或范围输入[6]。
4.3 添加和删除规则
规则编辑器中最厉害的功能是动态添加和删除规则。
添加规则按钮通常位于规则下方,添加和删除规则时其位置保持不变。该按钮也可以放在删除规则按钮旁边,这时添加的规则会插入到指定的规则下面。
删除规则功能通常放在规则所在行的前面或后面。
五、基本原理
用户使用规则编辑器构建检索条件时,对一到多个数据集中的内容进行检索查询。
由于数据集内容因时而变,因此活动规则返回的查询结果是动态的。当满足活动规则的条件、标准和值时,就会执行一组操作。可以将规则集分组为离散单元,配以条件逻辑,以构建复杂的规则条件[7]。
附录
[1] Use to save a segment rather than static selection
[2] Use to help users build dynamic lists, making the selected rules static rather than the actual search result
[3] Do not use when the type of search query requires the same types of variables to be chosen every single time.
[4] A more nuanced approach is to allow each rule to be a required match or just an optional match.
[5] As the user choses the kind of rule he or she wants to impose, those rules can have very different impacts on what corresponding data needs to be entered for the rule to give meaning.
[6] This is why many rule builders provide smart mini-forms that vary depending on what kind of rule is selected. One rule might impose a text search, wherein options like “contains”, “does not contain”, “matches”, or “do not match” make sense. Other rules could be to select an option from a dynamic list or to provide numeric- or range inputs.
[7] The results returned by an active rule can be dynamic in nature as its related datasets change over time. An active rule can trigger a set of actions to be performed when the conditions, criteria and values of the rule are met. Rules sets can be grouped into discrete units and linked together with condition logic to create highly complex rule conditions.
[8] 原文地址

