题目链接
题目描述
解题思路
1. 使用递归
要逆序打印链表 1->2->3(3,2,1),可以先逆序打印链表 2->3(3,2),最后再打印第一个节点 1。而链表 2->3 可以看成一个新的链表,要逆序打印该链表可以继续使用求解函数,也就是在求解函数中调用自己,这就是递归函数。
/*** struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) :* val(x), next(NULL) {* }* };*/class Solution {public:vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {if(head==NULL)return {};vector<int> res;printList(head,res);return res;}void printList(ListNode* head,vector<int> &res){if(head==NULL)return;printList(head->next, res);res.push_back(head->val);}};
2. 使用头插法
头插法顾名思义是将节点插入到头部:在遍历原始链表时,将当前节点插入新链表的头部,使其成为第一个节点。
链表的操作需要维护后继关系,例如在某个节点 node1 之后插入一个节点 node2,我们可以通过修改后继关系来实现:
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
if(head==NULL)
return {};
vector<int> res;
while(head){
res.insert(res.begin(), head->val);
head = head->next;
}
return res;
}
};
为了能将一个节点插入头部,我们引入了一个叫头结点的辅助节点,该节点不存储值,只是为了方便进行插入操作。不要将头结点与第一个节点混起来,第一个节点是链表中第一个真正存储值的节点。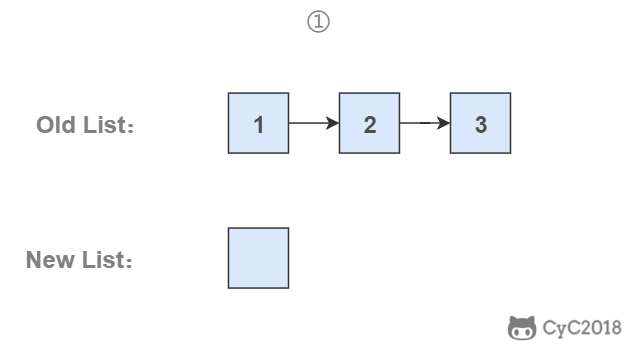
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> v;
if(head==nullptr)
return v;
vector<int>::iterator it;
while(head!=nullptr){
it = v.begin();
v.insert(it, head->val);
head = head->next;
}
return v;
}
};
3. 使用栈
栈具有后进先出的特点,在遍历链表时将值按顺序放入栈中,最后出栈的顺序即为逆序。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
stack<int> s;
vector<int> ret;
int temp;
while(head){
s.push(head->val);
head=head->next;
}
while(!s.empty()){
ret.push_back(s.top());
s.pop();
}
return ret;
}
};
4. 使用std::reverse()函数
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> ret;
while(head){
ret.push_back(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
std::reverse(ret.begin(),ret.end());
return ret;
}
};


