题目链接
题目描述
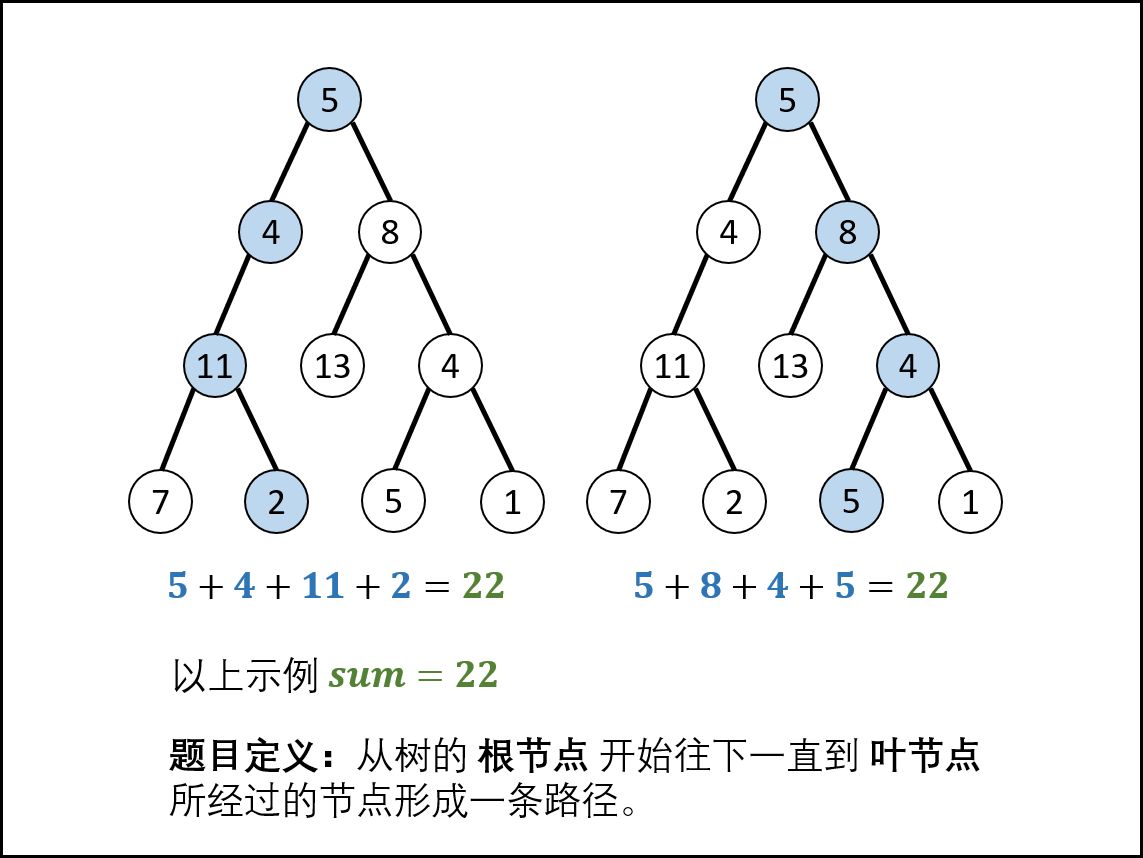
输入一颗二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
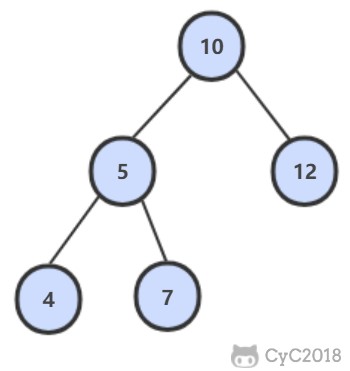
下图的二叉树有两条和为 22 的路径:10, 5, 7 和 10, 12
解题思路
回溯法(先序遍历 + 路径记录)
- 先序遍历: 按照 “根、左、右” 的顺序,遍历树的所有节点。
- 路径记录: 在先序遍历中,记录从根节点到当前节点的路径。当路径为 ① 根节点到叶节点形成的路径 且 ② 各节点值的和等于目标值 sum 时,将此路径加入结果列表。
算法流程:
**pathSum(root, sum)** 函数:
- 初始化: 结果列表
res,路径列表path。 - 返回值: 返回
res即可。
**recur(root, tar) **函数:
- 递推参数: 当前节点
root,当前目标值tar。 - 终止条件: 若节点
root为空,则直接返回。 - 递推工作:
- 路径更新: 将当前节点值
root.val加入路径path; - 目标值更新:
tar = tar - root.val(即目标值 tar 从 sum 减至 00 ); - 路径记录: 当 ①
root为叶节点 且 ② 路径和等于目标值 ,则将此路径path加入res。 - 先序遍历: 递归左 / 右子节点。
- 路径恢复: 向上回溯前,需要将当前节点从路径 path 中删除,即执行
path.pop()。
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}* };*/class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {if(root==NULL) return {};recur(root,sum);return res;}private:vector<vector<int>> res;vector<int> path;void recur(TreeNode* root,int sum){if(root==NULL) return;path.push_back(root->val);sum = sum - root->val;// 判断是否等于目标值if(sum==0&&root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL){res.push_back(path);// 下面可写可不写,不写下次递归也会停止。path.pop_back();return;}// 遍历左右子树recur(root->left,sum);recur(root->right,sum);// 回溯path.pop_back();}};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {
dfs(root, target);
return res;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int target){
if(root == null){
return;
}
target -= root.val;
path.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
if(target == 0){
// 需要重新创建一个list
res.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
}
// 回溯
path.remove(path.size()-1);
return;
}
dfs(root.left, target);
dfs(root.right, target);
// 回溯
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
- 时间复杂度 O(N) : N 为二叉树的节点数,先序遍历需要遍历所有节点。
- 空间复杂度 O(N) : 最差情况下,即树退化为链表时,path 存储所有树节点,使用 O(N) 额外空间。