题目链接
题目描述
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
示例 1:
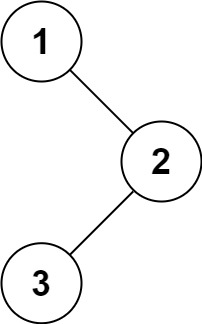
输入: root = [1,null,2,3]
输出: [1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入: root = []
输出: []
示例 3:
输入: root = [1]
输出: [1]
示例 4:
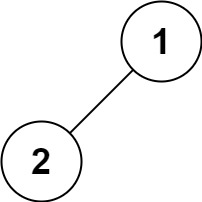
输入: root = [1,2]
输出: [2,1]
示例 5:
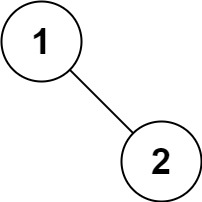
输入: root = [1,null,2]
输出: [1,2]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解题思路
方法一:递归
class Solution {public:void inorder(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res) {if (!root) {return;}inorder(root->left, res);res.push_back(root->val);inorder(root->right, res);}vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> res;inorder(root, res);return res;}};
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> ans;stack<TreeNode*> st;while(root!=nullptr||!st.empty()){// 先将当前结点和所有的左节点放入栈while(root){st.push(root);root = root->left;}// 此时将最左边节点取出root = st.top();st.pop();ans.push_back(root->val);// root指向最左边节点的右节点root = root->right;}return ans;}};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return res;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty() || root != null){
// 向左遍历,直到Null
while(root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
// root = stack.poll(); 等价
root = stack.pop();
// 当前节点没有左子树,记录值
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
}
- 时间复杂度 O(n)
-
方法三:morris
Morris 遍历算法是另一种遍历二叉树的方法,它能将非递归的中序遍历空间复杂度降为 O(1)。
Morris 遍历算法整体步骤如下(假设当前遍历到的节点为 x): 如果 x 无左孩子,先将 x 的值加入答案数组,再访问 x 的右孩子,即 x=x.right。
- 如果 x 有左孩子,则找到 x 左子树上最右的节点(即左子树中序遍历的最后一个节点,x 在中序遍历中的前驱节点),我们记为 predecessor。根据 predecessor 的右孩子是否为空,进行如下操作。
- 如果 predecessor 的右孩子为空,则将其右孩子指向 x,然后访问 x 的左孩子,即 x=x.left。
- 如果 predecessor 的右孩子不为空,则此时其右孩子指向 x,说明我们已经遍历完 x 的左子树,我们将 predecessor 的右孩子置空,将 x 的值加入答案数组,然后访问 xx 的右孩子,即 x=x.right。
- 重复上述操作,直至访问完整棵树
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
TreeNode *predecessor = nullptr;
while (root != nullptr) {
if (root->left != nullptr) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
// 也就是左子树中序遍历的最后一个节点
predecessor = root->left;
// predecessor->right != root说明 root的左子树已经遍历过了,并且最后一个节点
// 指向了root
while (predecessor->right != nullptr && predecessor->right != root) {
predecessor = predecessor->right;
}
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
// predecessor 的右指针指向 root,可以使左子树遍历完后开始遍历根节点和右子树
if (predecessor->right == nullptr) {
// root左子树最后一个节点指向root
predecessor->right = root;
// 开始遍历root左子树
root = root->left;
}
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
else {
// 遍历节点
res.push_back(root->val);
// 断开建立的连接
predecessor->right = nullptr;
// 开始遍历右子树
root = root->right;
}
}
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问根节点 和右子树
else {
res.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return res;
}
TreeNode tmp;
while(root != null){
if(root.left != null){
tmp = root.left;
while(tmp.right != null && tmp.right != root){
tmp = tmp.right;
}
if(tmp.right == root){
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
tmp.right = null;
}else{
tmp.right = root;
root = root.left;
}
}else{
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
- 时间复杂度 O(n)
- 空间复杂度 O(1)

