题目链接
题目描述
单词数组 words 的 有效编码 由任意助记字符串 s 和下标数组 indices 组成,且满足:
words.length == indices.length- 助记字符串
s以'#'字符结尾 - 对于每个下标
indices[i],s的一个从indices[i]开始、到下一个'#'字符结束(但不包括'#')的 子字符串 恰好与words[i]相等
给你一个单词数组 words ,返回成功对 words 进行编码的最小助记字符串 s 的长度 。
示例 1:
输入: words = [“time”, “me”, “bell”]
输出: 10
解释: 一组有效编码为 s = "time#bell#" 和 indices = [0, 2, 5] 。
words[0] = “time” ,s 开始于 indices[0] = 0 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”
words[1] = “me” ,s 开始于 indices[1] = 2 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”
words[2] = “bell” ,s 开始于 indices[2] = 5 到下一个 ‘#’ 结束的子字符串,如加粗部分所示 “time#bell#”
示例 2:
输入: words = [“t”]
输出: 2
解释: 一组有效编码为 s = “t#” 和 indices = [0] 。
提示:
1 <= words.length <= 20001 <= words[i].length <= 7-
解题思路
方法一:排序 + 前缀树
思路
如方法一所说,目标就是保留所有不是其他单词后缀的单词。
算法
去找到是否不同的单词具有相同的后缀,我们可以将其反序之后插入字典树中。例如,我们有 “time” 和 “me”,可以将 “emit” 和 “em” 插入字典树中。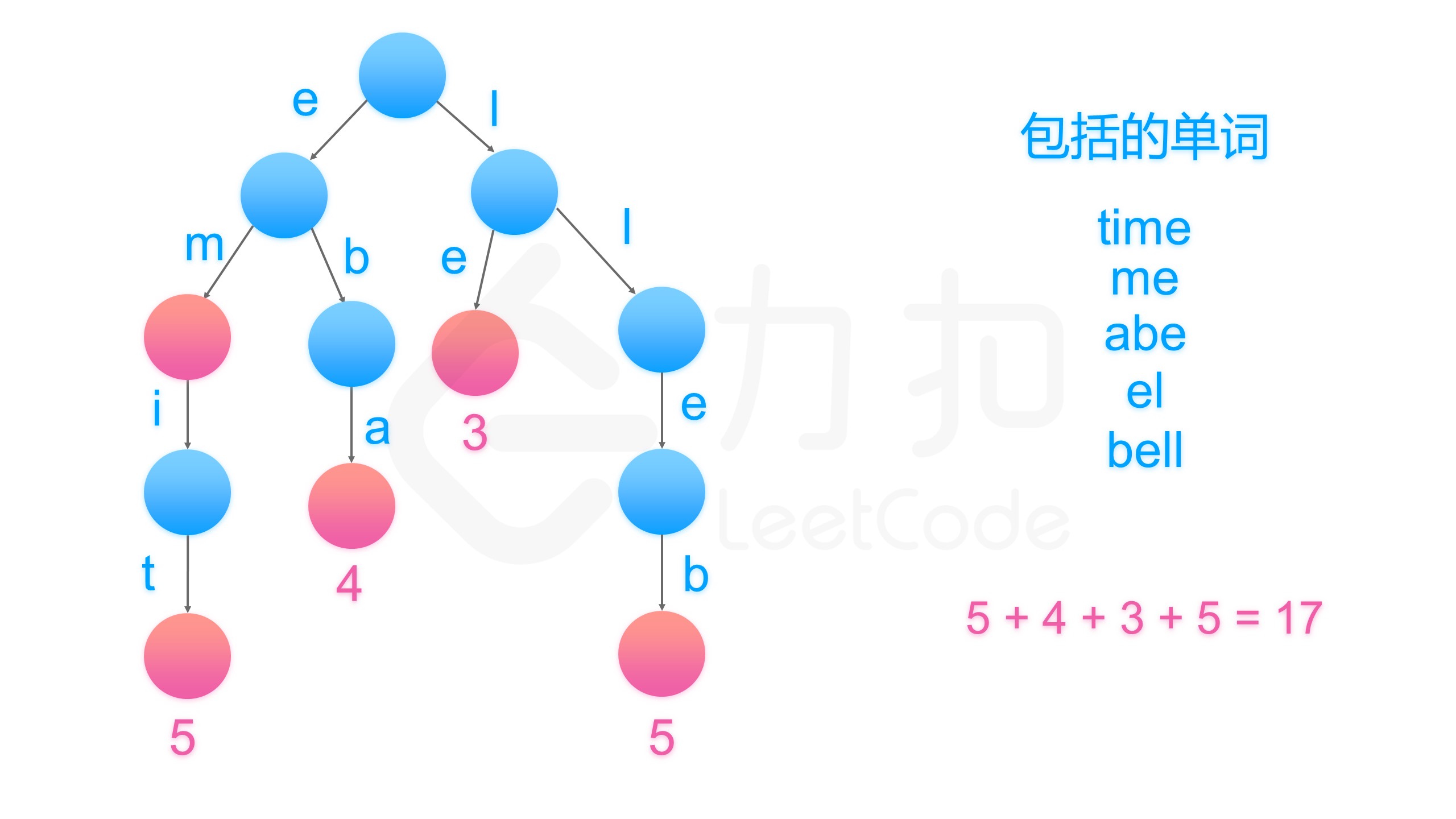
然后,字典树的叶子节点(没有孩子的节点)就代表没有后缀的单词,统计叶子节点代表的单词长度加一的和即为我们要的答案。class Solution {public int minimumLengthEncoding(String[] words) {Trie trie = new Trie();Map<Trie, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for(int i = 0; i < words.length; ++i){Trie cur = trie;// 向下探索for(int j = words[i].length() - 1; j >= 0; --j){cur = cur.get(words[i].charAt(j));}// 记录当前单词最后一个节点下一层节点个数// 如果下层节点个数为 0,则这是最后一层map.put(cur, i);}int res = 0;for(Trie t : map.keySet()){// 如果下层节点个数为 0,则这是最后一层if(t.count == 0){// 单词长度加一个 '#'res += words[map.get(t)].length() + 1;}}return res;}}class Trie {private Trie[] childen;int count; // 下一层节点个数public Trie() {childen = new Trie[26];count = 0; // 下一层节点个数默认为 0}public Trie get(char c) {int index = c - 'a';if(childen[index] == null){childen[index] = new Trie();// 下一层节点个数加一++count;}return childen[index];}}
时间复杂度 O(n)
- 空间复杂度 O(n)

