
二叉堆数据结构
二叉堆是一种特殊的二叉树,它具有以下两个特性:
- 结构特性:它是一棵完全二叉树,表示树的每一层都有左侧和右侧子节点(除了最后一层的叶节点),并且最后一层的叶节点尽可能都是左侧子节点。
- 堆特性:二叉堆不是最小堆就是最大堆。最小堆允许你快速导出树的最小值,最大堆允许你快速导出数的最大值。
最大堆
父节点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值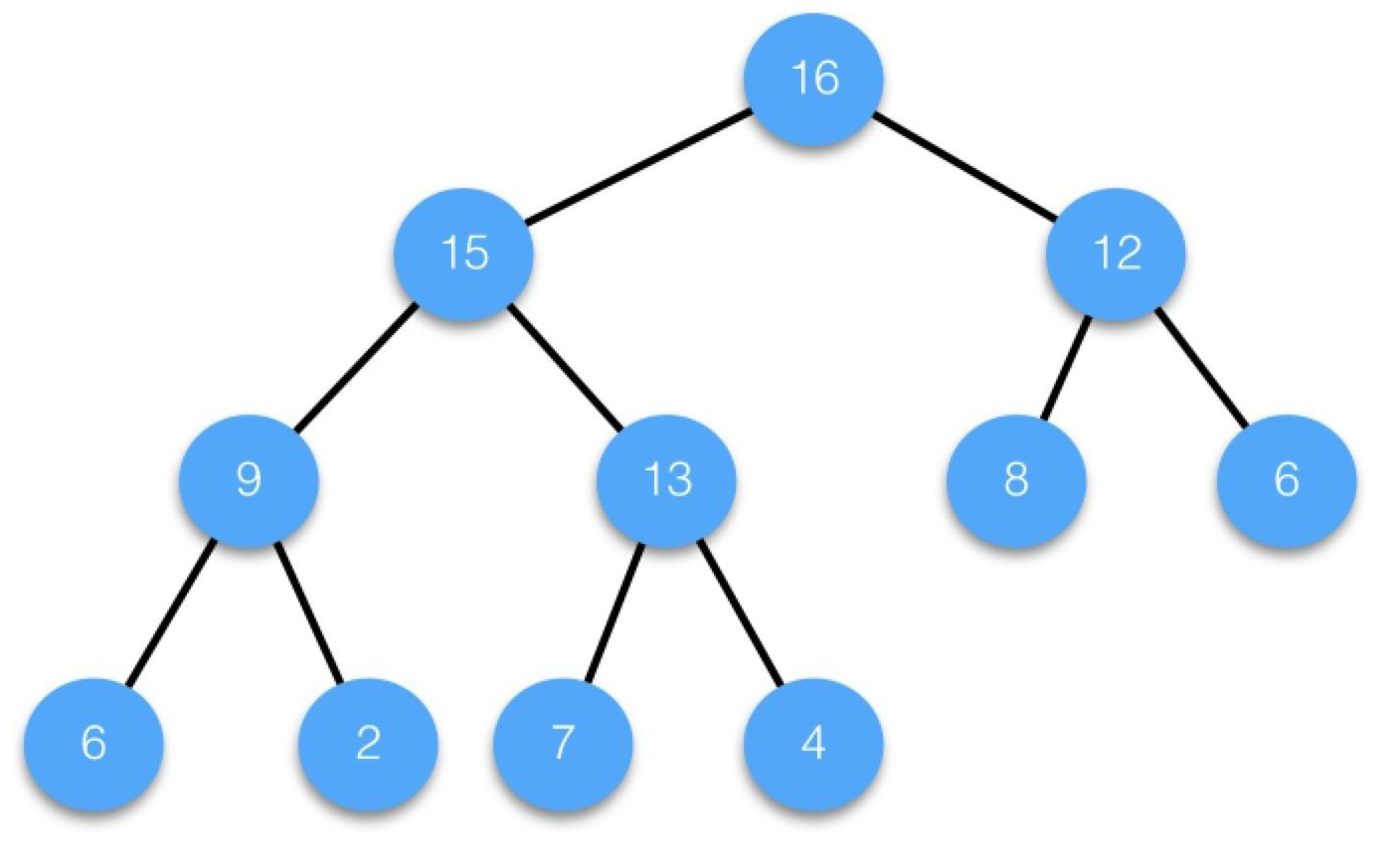
最小堆
父节点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值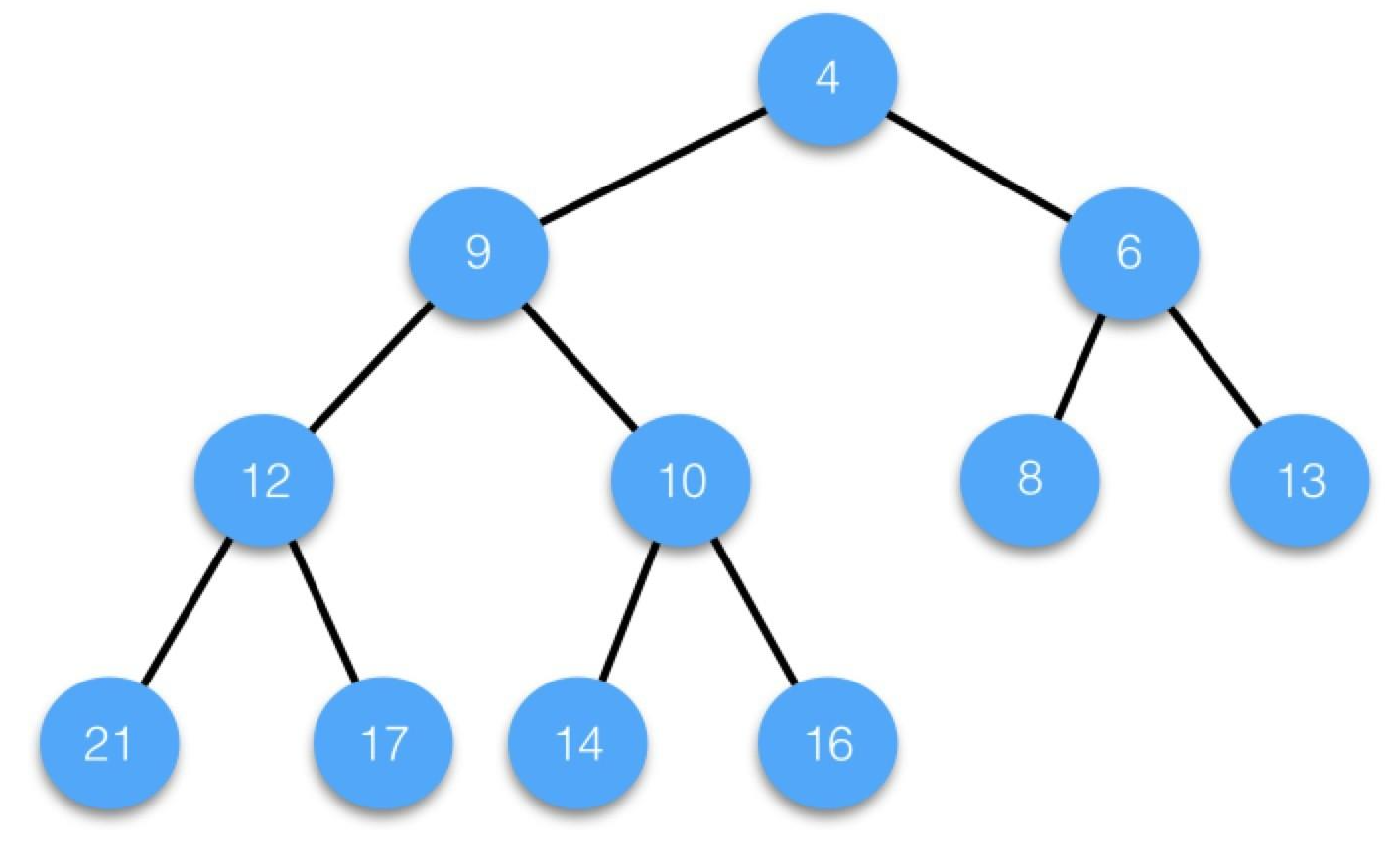
实现最小堆
创建最小堆类
在 constructor 构造函数中,定义 compareFn 函数来比较存储在数据结构中的值,使用数组来存储数据。
class MinHeap {constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {this.compareFn = compareFn;this.heap = [];}}
声明 Compare 常量
export const Compare = {LESS_THAN: -1,BIGGER_THAN: 1,EQUALS: 0};
创建 defaultCompare 函数
export function defaultCompare(a, b) {if (a === b) {return Compare.EQUALS;}return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;}
在本文中,我们使用数组来存储二叉堆的节点,因此我们可以通过 index 来获取二叉堆的节点。 对于给定位置 index 的节点:
- 它的左侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 1
- 它的右侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 2
- 它的父节点位置 (index - 1)/ 2
根据以上规则,我们来实现获取节点的方法。
getLeftIndex - 获取左侧子节点
getLeftIndex(index) {return (2 * index) + 1;}
getRightIndex - 获取右侧子节点
getRightIndex(index) {return (2 * index) + 2;}
getParentIndex - 获取父节点
getParentIndex(index) {if (index === 0) {return undefined;}return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);}
insert - 向堆中插入值
insert(value) {if (value != null) {const index = this.heap.length;// 将值插入到堆的底部叶节点(即数组的最后一个位置)this.heap.push(value);// 将插入的值和它的父节点进行交换,直到父节点小于这个插入的值this.siftUp(index);// 插入成功,返回 truereturn true;}// 插入失败,返回 falsereturn false;}
将值插入到堆的底部叶节点 (即数组的最后一个位置),然后执行 siftUp 方法,将插入的值和它的父节点进行交换,直到父节点小于这个插入的值。
siftUp - 上移操作
siftUp(index) {// 获取父节点的位置let parent = this.getParentIndex(index);while (index > 0 &&this.compareFn(this.heap[parent], this.heap[index]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {// 在最小堆中,如果插入的值小于它的父节点(或者在最大堆中比父节点大),将这个元素和父节点交换swap(this.heap, parent, index);// 交换节点位置index = parent;parent = this.getParentIndex(index);}}
swap 交换函数
function swap(array, a, b) {const temp = array[a];array[a] = array[b];array[b] = temp;}
在 swap 函数中,定义了一个 temp 变量来缓存要交换的第一个元素,然后,将第二个元素赋值到第一个元素的位置 array[a] = array[b]; ,最后,将缓存起来的第一个元素的值覆盖到第二个元素的值 array[b] = temp; 。
也可以使用 ES6 的数组结构语法实现 swap 函数:
const swap = (array, a, b) => [array[a], array[b]] = [array[b], array[a]];
size - 获取堆中数据的长度
size() {return this.heap.length;}
isEmpty - 判断堆是否为空
isEmpty() {return this.size() <= 0;}
clear - 清空堆
this.heap = [];
findMinimum - 查找堆中最小值
findMinimum() {return this.isEmpty() ? undefined : this.head[0];}
在最小堆中,最小值总是位于数组的第一个位置(堆的根节点)。在最大堆中,数组的第一个元素就是最大的值(堆的根节点),因此可以使用相同的代码获取最大堆的最大值。
extract - 导出堆中的最小值或最大值
extract() {// 堆为空,也就是没有值可以导出,返回 undefinedif (this.isEmpty()) {return undefined;}// 堆中只有一个值,直接移除并返回这个值if (this.size() === 1) {return this.heap.shift();}// 将需要移除的值缓存起来const removedValue = this.heap.shift();// 将堆的最后一个元素移动至根部this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();// 从根元素开始交换元素,直至堆的结构正常this.siftDown(0);return removedValue;}
移除最小值(最小堆) 或 最大值(最大堆),也就是要移除数组中的第一个元素 (堆的根节点)。在移除后,我们需要将堆的最后一个元素移动至根部并执行 siftDown 函数,将堆中的元素进行交换直至堆的结构正常。
siftDown - 下移操作
// 接收移除元素的位置作为参数siftDown(index) {let element = index;// 获取左侧子节点的位置const left = this.getLeftIndex(index);// 获取右侧子节点的位置const right = this.getRightIndex(index);// 获取堆的长度const size = this.size();// 如果元素 this.heap[element] 比它的左侧子节点要小,交换元素和它的左侧子节点if (left < size &&this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[left]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {element = left;}// 如果元素小于 this.heap[element] 小于它的右侧子节点,交换元素和它的右侧子节点if (right < size &&this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[right]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {element = right;}// 在找到最小子节点的位置后,校验它的值是否和 element 相同,不同,则进行交换if (index !== element) {swap(this.heap, index, element);this.siftDown(element);}}
heapify
heapify(array) {if (array) {this.heap = array;}const maxIndex = Math.floor(this.size() / 2) - 1;for (let i = 0; i <= maxIndex; i++) {this.siftDown(i);}return this.heap;}
getAsArray
getAsArray() {return this.heap;}
完整代码
export class MinHeap {constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {this.compareFn = compareFn;this.heap = [];}// 获取左侧子节点位置getLeftIndex(index) {return (2 * index) + 1;}// 获取右侧子节点位置getRightIndex(index) {return (2 * index) + 2;}// 获取父节点位置getParentIndex(index) {if (index === 0) {return undefined;}return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);}// 堆的大小size() {return this.heap.length;}// 是否为空堆isEmpty() {return this.size() <= 0;}// 清空堆clear() {this.heap = [];}// 查找堆的最小值、最大值findMinimum() {return this.isEmpty() ? undefined : this.heap[0];}// 向堆中插入值insert(value) {if (value != null) {const index = this.heap.length;this.heap.push(value);this.siftUp(index);return true;}return false;}// 下移操作siftDown(index) {let element = index;const left = this.getLeftIndex(index);const right = this.getRightIndex(index);const size = this.size();if (left < size &&this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[left]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {element = left;}if (right < size &&this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[right]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {element = right;}if (index !== element) {swap(this.heap, index, element);this.siftDown(element);}}// 节点上移操作siftUp(index) {let parent = this.getParentIndex(index);while (index > 0 &&this.compareFn(this.heap[parent], this.heap[index]) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {swap(this.heap, parent, index);index = parent;parent = this.getParentIndex(index);}}// 导出堆中的最小值或最大值extract() {if (this.isEmpty()) {return undefined;}if (this.size() === 1) {return this.heap.shift();}const removedValue = this.heap[0];this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();this.siftDown(0);return removedValue;}heapify(array) {if (array) {this.heap = array;}const maxIndex = Math.floor(this.size() / 2) - 1;for (let i = 0; i <= maxIndex; i++) {this.siftDown(i);}return this.heap;}getAsArray() {return this.heap;}}
实现最大堆
最大堆的实现和最小堆的实现是一模一样的,不同之处在于我们要把所有 > (大于) 的比较换成 < (小于) 的比较。
创建最大堆类
class MaxHeap extends MinHeap {constructor (compareFn = defaultCompare) {super(compareFn);this.compareFn = reverseCompare(compareFn);}}
我们通过继承 MinHeap 类来实现最大堆,并定义了一个 reverseCompare 函数进行反向比较,也就是不再对 a 和 b 进行比较,而是将 b 和 a 进行比较。
reverseCompare
function reverseCompare(compareFn) {return (a, b) => compareFn(b, a);}

