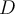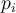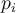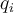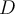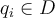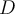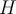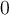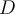Clustering tendency assessment determines whether a given data set has a non-random structure, which may lead to meaningful clusters.
- Assess if non-random structure exists in the data by measuring the probability that the data is generated by a uniform data distribution
- Test spatial randomness by statistical test: Hopkins Statistic 通过统计检验检验空间随机性:霍普金斯统计
- Given a dataset
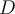 regarded as a sample of a random variable
regarded as a sample of a random variable 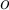 , determine how far away
, determine how far away 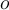 is from being uniformly distributed in the data space
is from being uniformly distributed in the data space - Sample
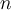 points,
points, 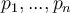 , uniformly from the range of
, uniformly from the range of 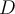 . For each
. For each 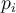 , find its nearest neighbour in
, find its nearest neighbour in  where
where 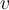 in
in 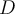
- Sample
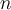 points,
points,  , uniformly from
, uniformly from 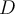 (
(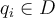 ). For each
). For each 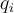 , find its nearest neighbour in
, find its nearest neighbour in 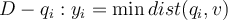 where
where 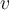 in
in  and
and 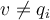
- Calculate the Hopkins Statistic:
- Given a dataset
- If [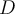](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=D) is uniformly distributed, [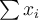](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=%5Csum%20x_i) and [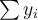](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=%5Csum%20y_i) will be close to each other and [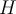](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=H) is close to 0.5.