● Structured representations of knowledge 结构化的表示知识
● Very large ontologies in many domains, for example in the biomedical domain许多领域中非常大的本体,例如生物医学领域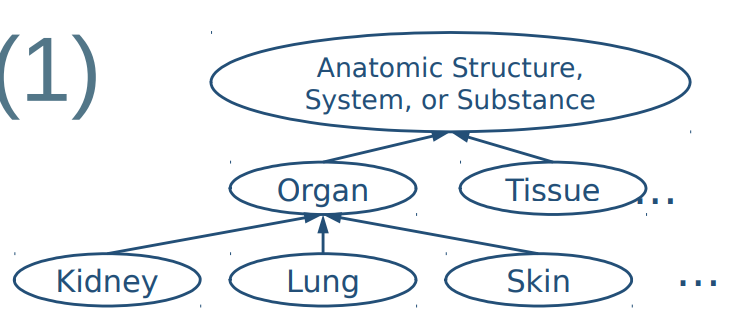

● Often multiple interrelated ontologies in a domain (e.g. anatomy) 通常在一个领域中有多个相互关联的本体(例如解剖学)
● We need to identify overlapping information between ontologies 我们需要识别本体之间的重叠信息
● Create mappings between ontologies 创建本体之间的映射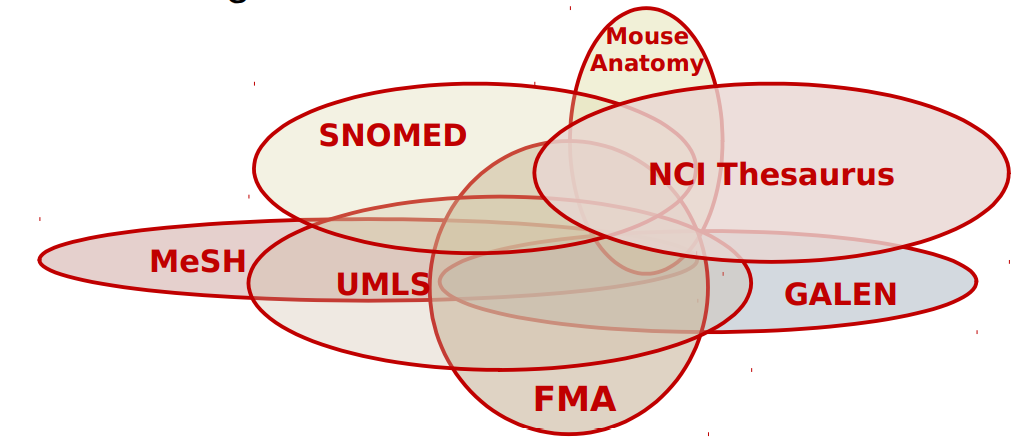
Ontology based annotations 基于本体的注释
● Standardised semantic descriptions of object properties 对象属性的标准化语义描述
● Applications: 应用
– Semantic search, navigation, etc.
- Functional analysis: Identification of significant characteristics of specific gene/proteins groups
–语义搜索、导航等。
-功能分析:确定特定基因/蛋白质组的显著特征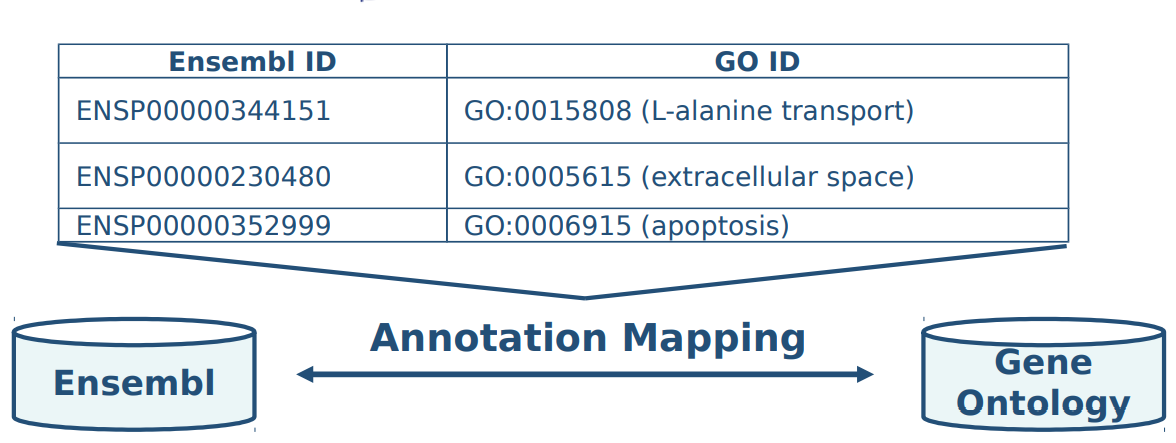
Ontology mappings and alignments 本体映射和对齐
● Overlapping ontologies allow the creation of mappings/alignments 重叠的本体允许创建映射/对齐
● Useful for data integration and analysis across sources 对跨来源的数据集成和分析有用
● Ontology mapping: Set of semantic correspondences between concepts of different ontologies 本体映射:不同本体的概念之间的一组语义对应
● Manual identification or (semi-) automatic matching approaches 手动识别或(半自动)匹配方法
● Use of mappings:
– Ontology merging (such as creation of an integrated cross-species anatomy ontology) 本体合并(例如创建集成的跨物种解剖学本体)
– Knowledge transfer (for example experiments for different species) 知识转移(例如不同物种的实验)
– Ontology curation (find missing ontology annotations)本体管理(查找缺失的本体注释)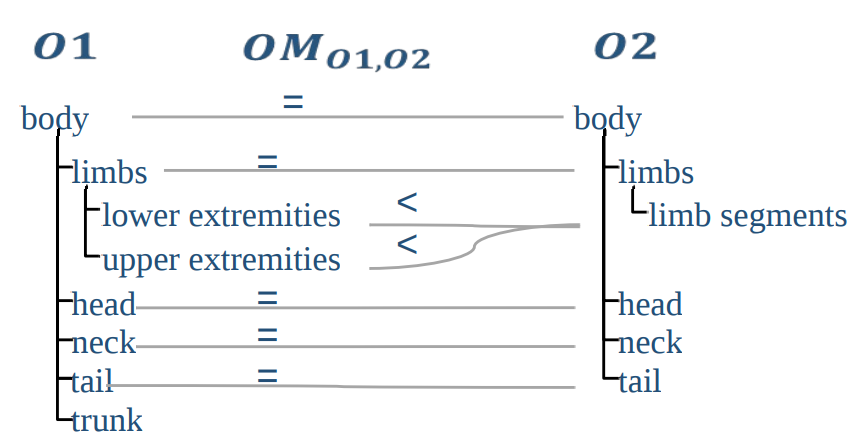
Evolution of ontology-based mappings 基于本体的映射演化
● Ontologies are not static! 本体不是静态的
● Research, new knowledge → Continuous changes 新的搜索和知识导致了持续变化
● Release of new versions 新版本的发布迭代
● Ontology changes: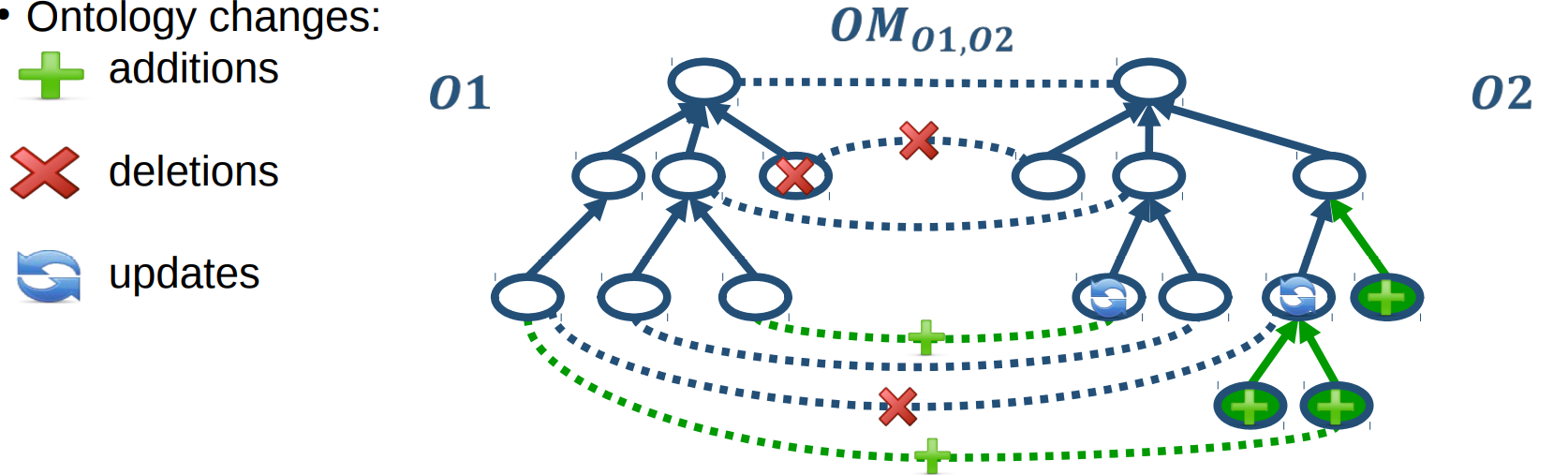
Ontology matching workflow 本体匹配工作流
● Manual creation of mappings between very large ontologies is too labor-intensive 非常大的本体之间的映射的手动创建过于耗费劳动力
● Semi-automatic generation of semantic correspondences: linguistic, structural, instance-based matching techniques (see lecture on schema matching, lecture 11) 语义对应的半自动生成:基于语言、结构和实例的匹配技术(参见第11讲模式匹配)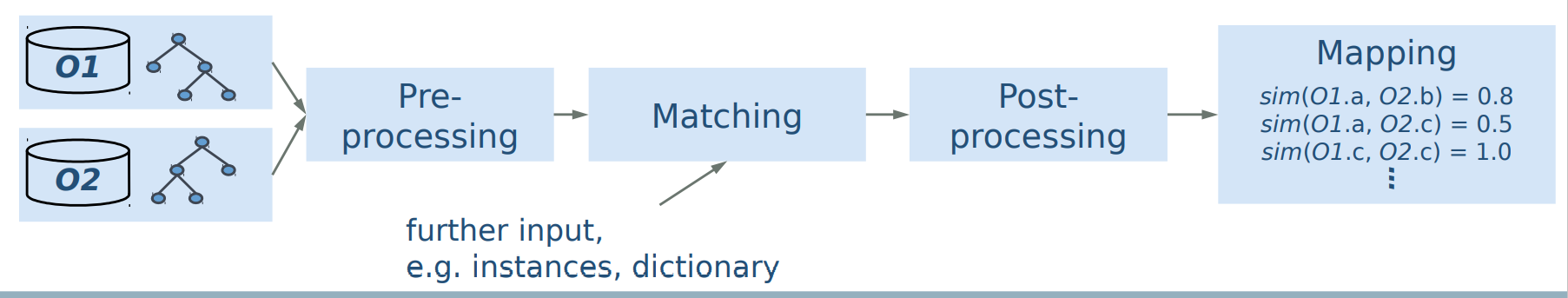
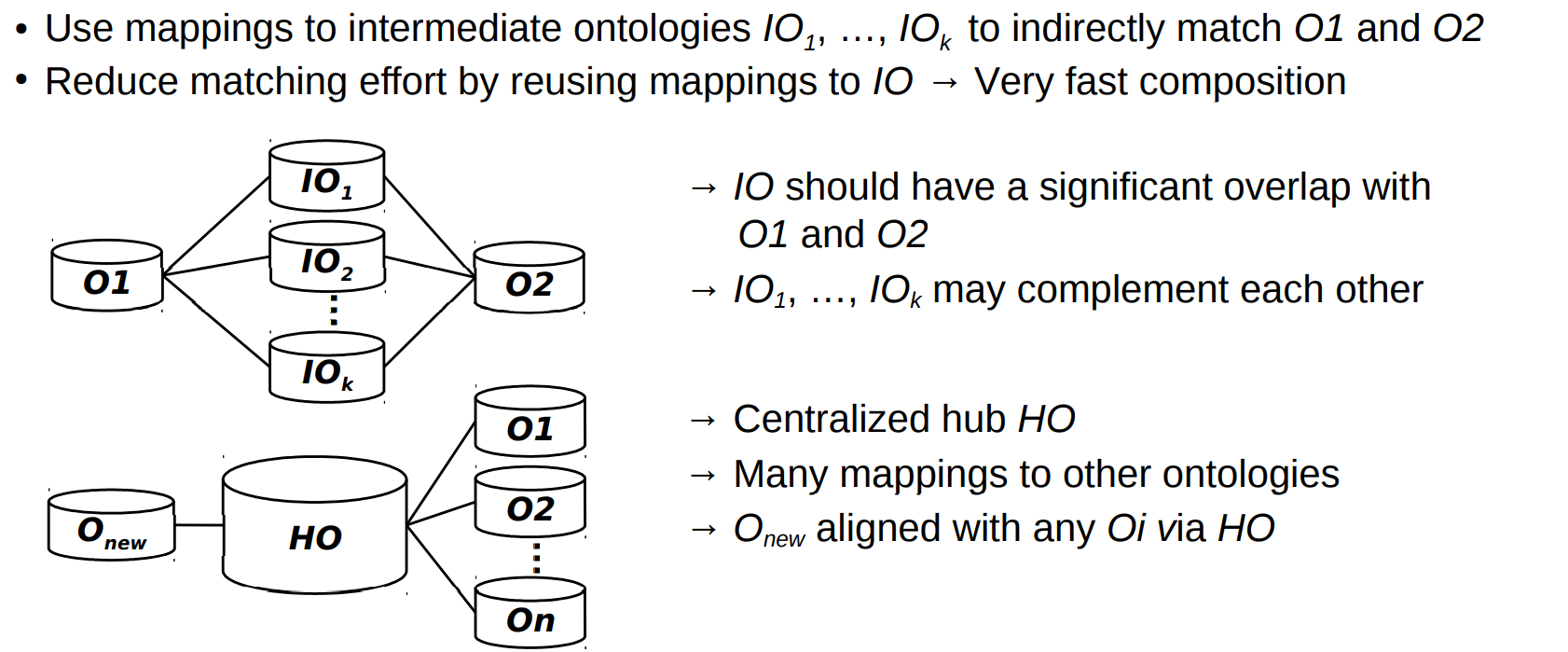
Mapping composition 地图构图
● Indirect composition-based matching 基于间接合成的匹配
● Via intermediate ontology (IO) or hub ontology (HO), synonym dictionary, etc. 通过中间本体(IO)或中枢本体(HO)、同义词词典等。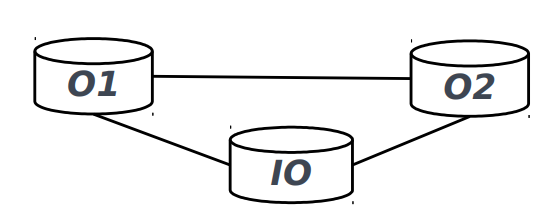
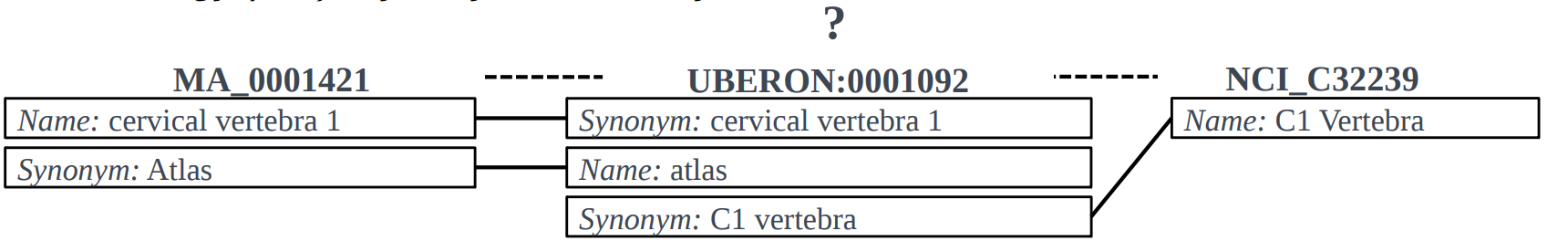
Indirect matching 间接匹配
Ontology evolution 本体进化
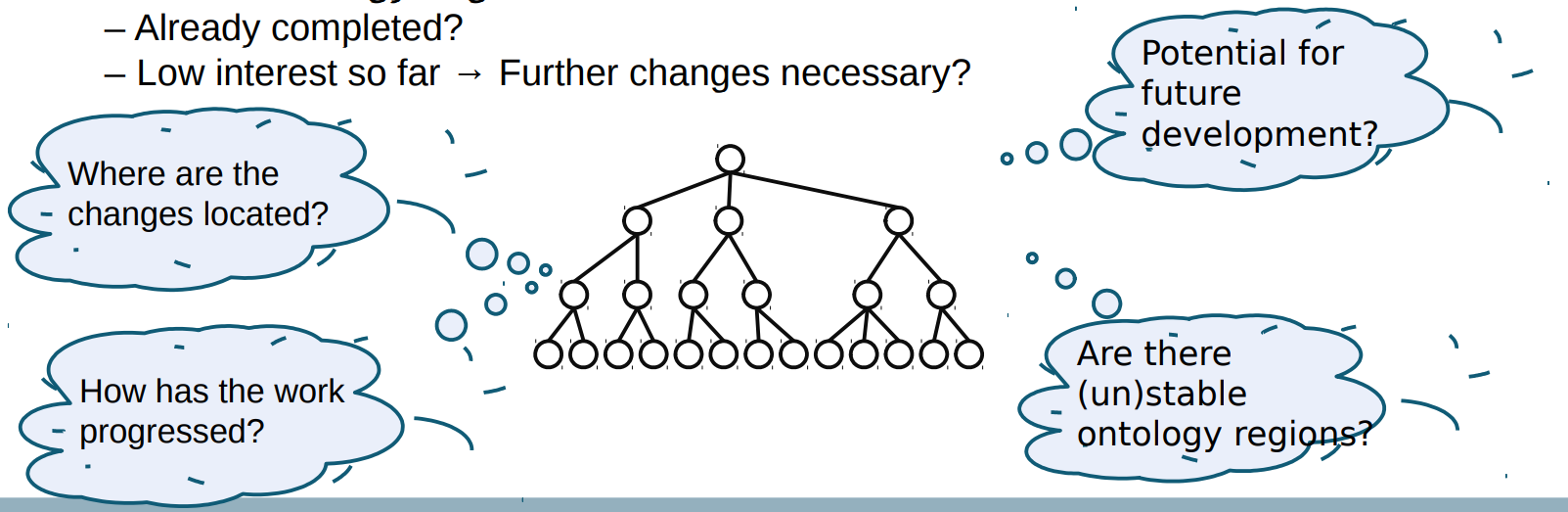
● Unstable ontology regions 不稳定的本体区域
– Many modifications → Focus of recent development 有很多调整→关注最近的变化
– Impact of changes on ontology-based algorithms or applications → Redo analyses? 变更对基于本体的算法或应用程序的影响→重做分析?
● Stable ontology regions 稳定的本体区域
– Already completed? 已经完成?
– Low interest so far → Further changes necessary? 目前为止改变较低→需要进一步修改吗?
Trend discovery 趋势发现
● Trend discovery based on sliding windows 基于滑动窗口的趋势发现
● Monitor region changes over long periods of time 长时间监控区域变化
– Ontology O, ontology region of interest OR 本体O和插入新信息的本体区域OR
– Time interval (t start , t end) 时间间隔(t开始,t结束)
– Sliding window of size ω 尺寸为ω的滑动窗口
– Step width Δ 步长δ
● Call region discovery algorithm within ω 叫做ω内的区域发现算法
– Collect change intensities for region of interest over time 收集感兴趣区域随时间的变化强度
Outlook and research directions 展望和研究方向
● Ontologies are becoming increasingly important 展望和研究方向
– In the life sciences (for example, conference series Data Integration in the Life Sciences – DILS) 在生命科学领域(例如,生命科学领域的会议系列数据集成–DILS)
– Knowledge-bases and the semantic Web 知识库和语义网
– Internet of Things 物联网
● Various research areas 各种研究领域
– Learning to match and map ontologies (semi-) automatically 学习匹配和映射本体(半自动)
– Mapping of dynamic ontologies 动态本体的映射
– Parallel algorithms for large-scale ontology matching, mapping and evolution大规模本体匹配、映射和进化的并行算法

