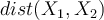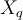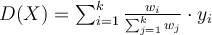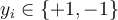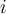- kNN classifiers are based on learning by analogy
- A training tuple described by _n _attributes represents a point in the n-dimensional space
- All training tuples are stored in an n-dimensional space
- Given a tuple of unknown class or unknown target value, KNN classifier searches k nearest neighbours of the unknown tuple.
Two ways of classifying the unknown tuple in kNN
- Discrete method (discrete-valued method)
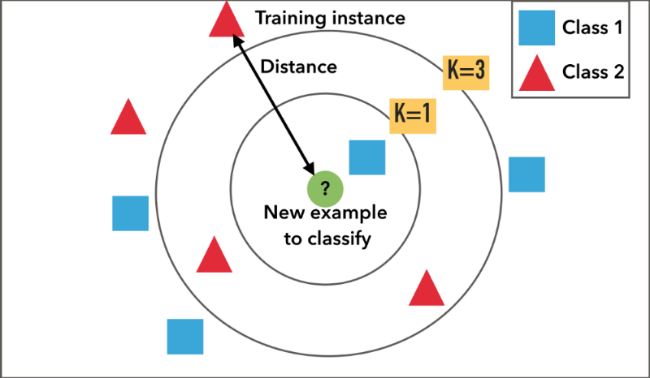
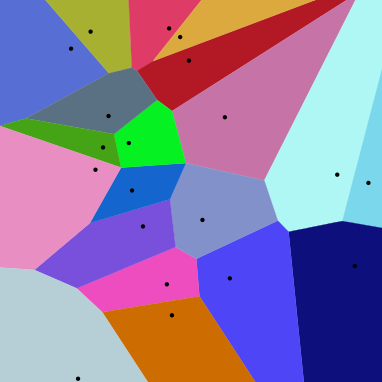
- k-NN returns the most common value among the k training examples nearest to [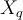](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=X_q) (test tuple)- Decision function:- [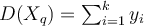](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=D%28X_q%29%20%3D%20%5Csum_%7Bi%3D1%7D%5E%7Bk%7D%20y_i)- where [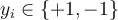](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=y_i%20%5Cin%20%5C%7B%2B1%2C%20-1%5C%7D) is the class of [](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=i)th nearest neighbour- If [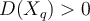](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=D%28X_q%29%20%3E%200) then [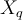](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=X_q) is positive class otherwise negative class- Voronoi diagram: the decision surface induced by 1-NN for a typical set of training examples
- Continuous method (real-valued prediction):
Characteristics of KNN
- Robust to noisy data by averaging k-nearest neighbours
- Extremely slow when classifying test tuples
- With
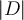 training tuples,
training tuples, 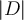 comparisons are required to find k-nearest neighbourhood
comparisons are required to find k-nearest neighbourhood - For example, SVM only requires
 comparisons where
comparisons where 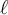 is the number of support vectors
is the number of support vectors - Partial distance method:
- Compute a distance on a subset of n attributes.
- If the distance exceeds a threshold, further distance computation will be halted
- Otherwise keep computing the distance on the remaining attributes
- Compute a distance on a subset of n attributes.
- With
部分距离方法:
计算n个属性子集上的距离。
如果距离超过一个阈值,进一步的距离计算将停止
否则,继续计算其余属性的距离