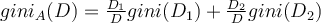Gini index is used in CART and IBM Intelligent miner decision tree learners
- All attributes are assumed nominal
If a data set 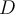 contains examples from
contains examples from 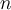 classes, gini index,
classes, gini index, 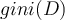 , measures the impurity of
, measures the impurity of 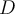 and is defined as
and is defined as
 where
where 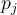 is the relative frequency of class
is the relative frequency of class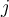 in
in 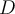
If a data set 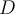 is split on attribute
is split on attribute 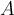 into two subsets
into two subsets 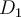 and
and 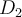 , the gini index
, the gini index 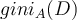 is defined as the size-weighted sum of the impurity of each partition:
is defined as the size-weighted sum of the impurity of each partition:
To split a node in the tree:
- Enumerate all the possible ways of splitting all the possible attributes
- The attribute split that provides the smallest gini(D) (i.e the greatest purity) is chosen to split the node 选择提供最小基尼系数(D)(即最大纯度)的属性分割来分割节点
Example (continued from previous)
D has 9 tuples in class buyscomputer = “yes” and 5 in “no”
Then 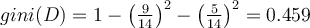
Now consider the attribute _income. Partition D into 10 objects in D1 with income in {low, medium} and 4 objects in D2 _with income in {high}
We have
[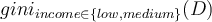 ](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=gini%7Bincome%20%5Cin%20%5C%7Blow%2C%20medium%5C%7D%7D%28D%29%20)
](https://wattlecourses.anu.edu.au/filter/tex/displaytex.php?texexp=gini%7Bincome%20%5Cin%20%5C%7Blow%2C%20medium%5C%7D%7D%28D%29%20)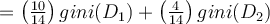
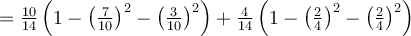
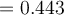

Similarly, gini{low,high} is 0.458; and gini{medium,high} is 0.450.
Thus, we split on the {low,medium} (and the other partition is {high}) since it has the lowest Gini index
When attributes are continuous or ordinal, the method for selecting the midpoint between each pair of adjacent values (described earlier) may be used.