题目
小偷又发现了一个新的可行窃的地区。这个地区只有一个入口,我们称之为 root 。
除了 root 之外,每栋房子有且只有一个“父“房子与之相连。一番侦察之后,聪明的小偷意识到“这个地方的所有房屋的排列类似于一棵二叉树”。 如果 两个直接相连的房子在同一天晚上被打劫 ,房屋将自动报警。
给定二叉树的 root 。返回 在不触动警报的情况下 ,小偷能够盗取的最高金额 。
示例 1: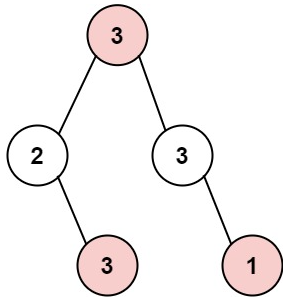
输入: root = [3,2,3,null,3,null,1]输出: 7解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 3 + 3 + 1 = 7
示例 2: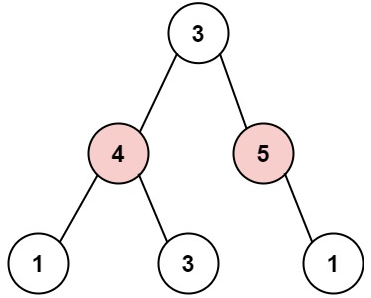
输入: root = [3,4,5,1,3,null,1]
输出: 9
解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 4 + 5 = 9
提示:
- 树的节点数在
[1, 10^4]范围内 0 <= Node.val <= 10^4解题方法
递归+记忆搜索
每一个节点的数值计算有两种情况:考虑子节点 和 不考虑子节点。对二叉树采用后序遍历的方式进行遍历,并使用哈希表记录已经遍历过的节点对应数值。
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(logn)
C++代码: ```cpp /**- Definition for a binary tree node.
- struct TreeNode {
- int val;
- TreeNode *left;
- TreeNode *right;
- TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
- TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
- TreeNode(int x, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
- }; / class Solution { private: unordered_map<TreeNode, int> recored;
public: int rob(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return 0; if(!root->left && !root->right) return root->val; if(recored[root]) return recored[root]; int val1 = root->val; if(root->left) val1 += rob(root->left->left) + rob(root->left->right); if(root->right) val1 += rob(root->right->left) + rob(root->right->right); int val2 = rob(root->left) + rob(root->right); recored[root] = max(val1, val2); return recored[root]; } };
<a name="GkETV"></a>
## 动态规划
使用动态数组`dp[0], dp[1]`描述当前节点不偷和偷分别能获得的最大收获。对于二叉树的遍历由于当前节点需要根据子节点的结果进行判断,因此采用后序遍历。终止条件为遍历至空节点时返回`{0, 0}`。<br />时间复杂度`O(n)`,空间复杂度`O(logn)`<br />**C++代码:**
```cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> dfs(TreeNode* cur) {
if(!cur) return vector<int>{0, 0};
vector<int> left = dfs(cur->left);
vector<int> right = dfs(cur->right);
int val0 = max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1]);
int val1 = cur->val + left[0] + right[0];
return vector<int>{val0, val1};
}
public:
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result = dfs(root);
return max(result[0], result[1]);
}
};

