题目
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交: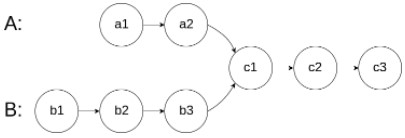
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须保持其原始结构 。
示例 1: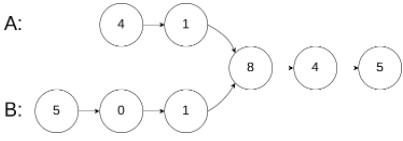
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3输出:Intersected at '8'解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2: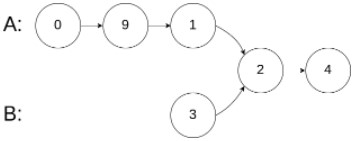
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1输出:Intersected at '2'解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3: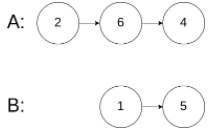
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2输出:null解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
listA中节点数目为mlistB中节点数目为n0 <= m, n <= 3 * 104- 1
<= Node.val <= 10^5 0 <= skipA <= m0 <= skipB <= n- 如果
listA和listB没有交点,intersectVal为0 - 如果
listA和listB有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
进阶:你能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
解题方法
双指针法
使用双指针分别计算两个链表的长度,随后将双指针重新移动至两个链表的头部,移动较长链表的指针使得两个指针末尾对齐。最后遍历链表寻找是否存在相交点。
时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(1)。
C++代码:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/class Solution {public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {int n_A = 0;int n_B = 0;ListNode* A = headA;ListNode* B = headB;while(A != NULL) {n_A++;A = A->next;}while(B != NULL) {n_B++;B = B->next;}A = headA;B = headB;if(n_A<n_B) {for(int i = 0; i<(n_B-n_A); i++) {B = B->next;}}else {for(int i = 0; i<(n_A-n_B); i++) {A = A->next;}}while(A != NULL) {if(A==B) return A;else {A = A->next;B = B->next;}}return NULL;}};
双指针法优化写法
无需计算两个链表的长度,将两个链表拼接即可实现循环中的末尾对齐
C++实现:
class Solution {public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {if (headA == nullptr || headB == nullptr) {return nullptr;}ListNode *pA = headA, *pB = headB;while (pA != pB) {pA = pA == nullptr ? headB : pA->next;pB = pB == nullptr ? headA : pB->next;}return pA;}};

