题目
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
- 节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
- 节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
注意:本题和 1038.从二叉搜索树到更大和树 相同
示例 1: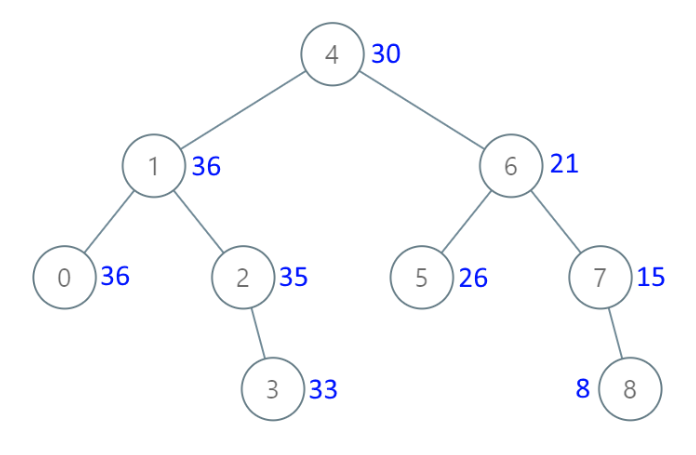
输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0,null,1]
输出:[1,null,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,0,2]
输出:[3,3,2]
示例 4:
输入:root = [3,2,4,1]
输出:[7,9,4,10]
提示:
- 树中的节点数介于
0和10^4之间。 - 每个节点的值介于
-10^4和10^4之间。 - 树中的所有值 互不相同 。
-
解题方法
反向中序遍历
采用迭代+栈维护未处理节点的方式,按照 右→中→左 的顺序遍历二叉树节点,记录大于当前节点的所有节点数值之和。
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)。
C++代码:/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) { int sum = 0; if(!root) return NULL; stack<TreeNode*> nodes; nodes.push(root); while(nodes.size()) { TreeNode* cur = nodes.top(); nodes.pop(); if(cur) { if(cur->left) nodes.push(cur->left); nodes.push(cur); nodes.push(NULL); if(cur->right) nodes.push(cur->right); } else { cur = nodes.top(); nodes.pop(); cur->val += sum; sum = cur->val; } } return root; } };递归
采用 DFS 反向中序遍历二叉树,记录上一个节点更新的数值,及大于当前元素的所有元素之和。
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
C++代码:/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { private: int sum = 0; public: void dfs(TreeNode* cur) { if(!cur) return; dfs(cur->right); cur->val += sum; sum = cur->val; dfs(cur->left); } TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root); return root; } };Morris 反向中序遍历
使用 Morris 遍历降低空间复杂度。
时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
C++代码:/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return NULL; int sum = 0; TreeNode* cur = root; TreeNode* mostleft; while(cur) { mostleft = cur->right; if(mostleft) { while(mostleft->left && mostleft->left!=cur) mostleft = mostleft->left; if(!mostleft->left) { mostleft->left = cur; cur = cur->right; } else { mostleft->left = NULL; cur->val += sum; sum = cur->val; cur = cur->left; } } else { cur->val += sum; sum = cur->val; cur = cur->left; } } return root; } };

