Testing a Function
unit test and test case
import unittestfrom name_function import get_formatted_nameclass NamesTestCase(unittest.TestCase):"""Tests for 'name_function.py'"""def test_first_last_name(self):"""Do names like 'Janis Joplin' work?"""formatted_name = get_formatted_name('janis', 'joplin')self.assertEqual(formatted_name, 'Janis Joplin')def test_first_middle_last_name(self):"""Do names like 'Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart' work?"""formatted_name = get_formatted_name('wolfgang', 'mozart', 'amadeus')self.assertEqual(formatted_name, 'Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart')if __name__ == '__main__':unittest.main()
- 使用单元测试编写测试用例可以用来自动测试,不用手动执行函数来测试
- 测试用例中每个以test_开头的函数都会自动执行
- 很多测试框架都会先导入测试文件再 运行。导入文件时,解释器将在导入的同时执行它。
if 代码块检查特殊变量 name ,这个变量是在程序执行时设置的。
如果这个文件作为主程序执行,变
量name 将被设置为’main‘ 。在这里,调用unittest.main() 来运
行测试用例。
如果这个文件被测试框架导入,变量name 的值将不 是’main‘ ,因此不会调用unittest.main() 。
Testing a Class
常用的assert methods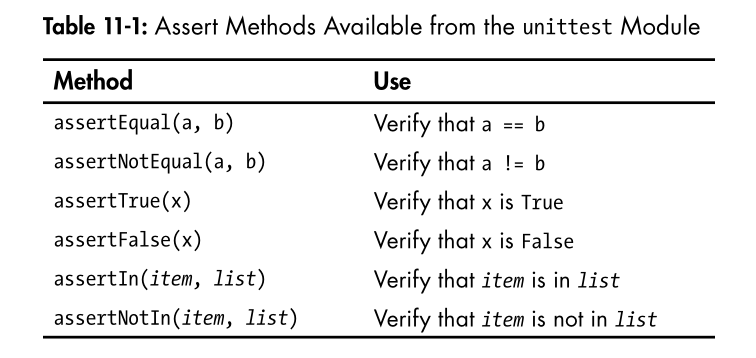
有一个class如下
class AnonymousSurvey:"""Collect anonymous answers to a survey question."""def __init__(self, question):"""Store a question, and prepare to store responses."""self.question = questionself.responses = []def show_question(self):"""Show the survey question."""print(self.question)def store_response(self, new_response):"""Store a single response to the survey."""self.responses.append(new_response)def show_results(self):"""Show all the responses that have been given."""print("Survey results:")for response in self.responses:print(f"- {response}")
编写测试
import unittestfrom survey import AnonymousSurveyclass TestAnonymousSurvey(unittest.TestCase):"""Tests for the class AnonymousSurvey"""def test_store_single_response(self):"""Test that a single response is stored"""question = "What language did you first learn to speak?"my_survey = AnonymousSurvey(question)my_survey.store_response('English')self.assertIn('English', my_survey.responses)def test_store_three_responses(self):"""Test that three individual responses are stored properly."""question = "What language did you first learn to speak?"my_survey = AnonymousSurvey(question)responses = ['English', 'Spanish', 'Mandarin']for response in responses:my_survey.store_response(response)for response in responses:self.assertIn(response, my_survey.responses)if __name__ == '__main__':unittest.main()
setUp()
- unittest.TestCase有一个setUp()方法,在setUp()内创建的对象,其他test_方法都能使用(必须加self.)
- Python在运行test_方法前会先运行setUp()方法(关键) ```python import unittest from survey import AnonymousSurvey
class TestAnonymousSurvey(unittest.TestCase): “””Tests for the class AnonymousSurvey”””
def setUp(self):"""Create a survey and a set of responses for use in all test methods."""question = "What language did you first learn to speak?"self.my_survey = AnonymousSurvey(question)self.responses = ['English', 'Spanish', 'Mandarin']def test_store_single_response(self):"""Test that a single response is stored"""self.my_survey.store_response(self.responses[0])self.assertIn('English', self.my_survey.responses)def test_store_three_responses(self):"""Test that three individual responses are stored properly."""for response in self.responses:self.my_survey.store_response(response)for response in self.responses:self.assertIn(response, self.my_survey.responses)
if name == ‘main‘: unittest.main() ``` When a test case is running, Python prints one character for each unit test as it is completed. A passing test prints a dot, a test that results in an error prints an E, and a test that results in a failed assertion prints an F.

