原文地址:DeepCut: Joint Subset Partition and Labeling for Multi Person Pose Estimation 作者信息:Leonid Pishchulin, Bernt Schiele
We propose an approach that jointly solves the tasks of detection and pose estimation: it infers the number of persons in a scene, identifies occluded body parts, and disambiguates body parts between people in close proximity of each other. __This joint formulation is in contrast to previous strategies, that address the problem by first detecting people and subsequently estimating their body pose.
多人人体姿态估计相对于单人人体姿态估计而言,是更加具有现实意义的。多人人体姿态估计的一些挑战:(1)人体遮挡问题;(2)人体检测框区域的重叠问题;(3)人体数量的未知等。一些采用先检测人体,后进行关节点检测的方法对于一些 Person 高度重叠的情况是非常不合适的,因为这种方式容许了同一个关节点被分配给多人。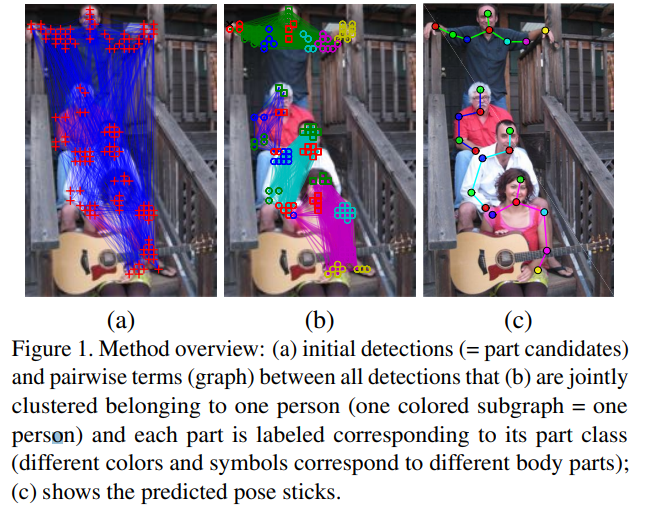
方法:首先检测出所有的关节点;然后关节点聚类;最后得到检测结果。
作者对问题的描述
The goal of this formulation is to state three problems jointly: 1. The selection of a subset of body parts from a set D of body part candidates, estimated from an image as described in Section 4 and depicted as nodes of a graph in Fig. 1(a). 2. The labeling of each selected body part with one of C body part classes, e.g., “arm”, “leg”, “torso”, as depicted in Fig. 1(c). 3. The partitioning of body parts that belong to the same person, as depicted in Fig. 1(b).
在完成关键点检测之后,将会得到很多的初始关节点,这些关节点是未知所属关系,未知关节点类别的。作者利用这些关节点产生密集图(dense graph),之后的工作即是从这个图中进行真实关节点的筛选、关节点类别的确定、关节点聚类(隐含了人数信息)等操作。这里翻译记录了作者来描述这个问题的方式。
作者采用三元组 进行描述,其中的
都是二进制随机变量:
其中 表示产生的关节点集合,
表示关节点类别集合,
表示排序组合中的
中取 2。作者对变量取值做如下规定:
表示节点
属于类别
;
表示节点
和节点
属于同一人;
是一个辅助变量:
,当
,那么节点
属于类别
,节点
属于类别
,并且两个节点属于同一个人。
感觉这是标签设计过程???
四个不等式约束: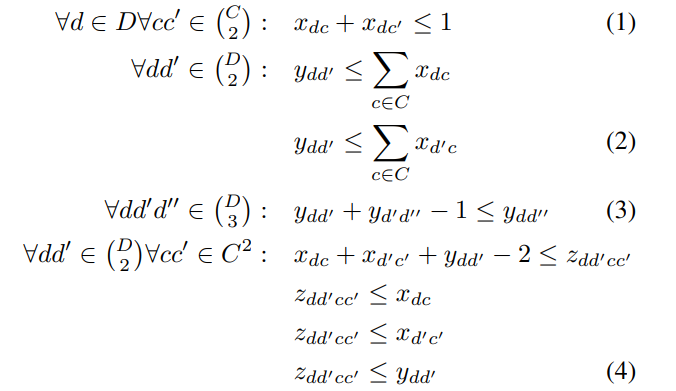
不等式(1)确保每个关节点最多属于一类,如果它不属于任何一类,那么它将被 Suppress;不等式(2)确保没被抑制的关节点不会和被抑制的关节点分为一类(即 ,基本前提是,两个关节点都没有被抑制;被抑制的关节点之间无分类);不等式(3)保证关节点所属关系的传递性,即
;不等式(4)确保辅助变量
的定义被满足。
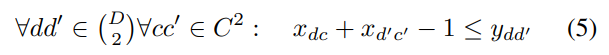
不等式(5)仅仅适用于单人情况。
这样的话,就得到了优化问题中的不等式约束;由于都是线性约束(仿射函数,既凸又凹),所以如果目标函数是凸函数可以利用凸优化的方式进行结果。(离散的优化问题,往往是比较麻烦的)凸优化问题的好处:局部最优解即是全局最优解。
目标函数
对于每对 ,
表示关节点
属于类别
的概率。对于每个
以及每个
,记
表示条件概率:在给定
和
属于类别
以及
的条件下,
和
属于同一个人的概率。当
时,
are the pairwise terms in a graphical model of the human body. 这样的表示方式是一个全连接的方式,所有预测的关节点之间都有连接。当
时,
表示
属于同一个人,同一个关节点的概率。
这种表示的特点:
- 防止一个关节点被分配给多个人;
- 表达里面本身就包含了,NMS 问题(多个关节点去表示同一个关节点);
The optimization problem that we call the subset partition and labeling problem is the ILP that minimizes over the set of feasible solutions
那么优化目标为: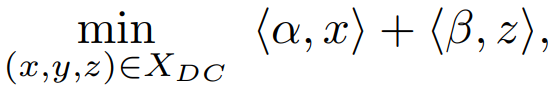
表示定义如下: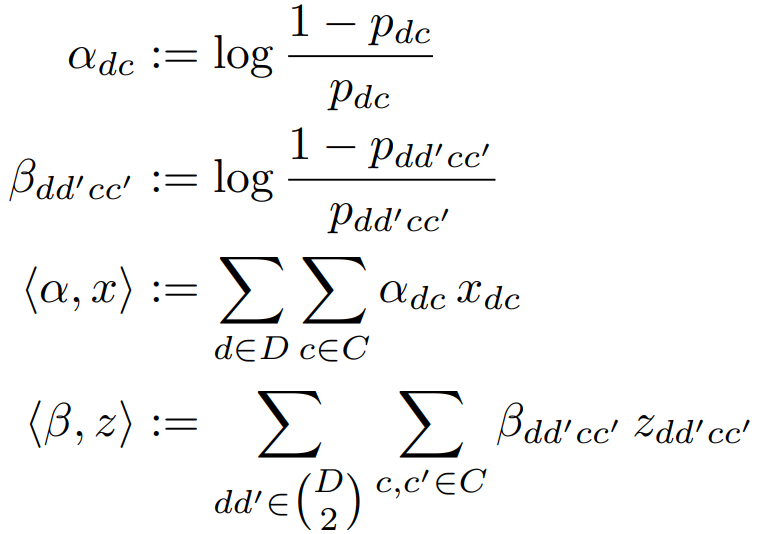
ILP问题:整数线性规划 完全没有明白,这些公式的含义,5555…… -_-,继续往下看 我的理解:“其中的概率值由网络预测输出,而其中的
则表示最优的分配关系。(不是简单的 Max 选择)”
Pairwise Probabilities
定义 pairwise features for the variable
。每一个被检测出来的关节点
都包括:标签概率特征
,位置信息
,尺寸
以及 Bounding box
坐标。给定两个被检测的关节点
,以及它们对应的特征
和
,对于
定义 two sets 的辅助变量:一个针对
的情况,另一个针对
的情况。这些特征能够捕获大致的 kinematic 相关性以及 appearance similarity between body parts.
当 时:对于同一个人的同一个关节点的不同检测结果应该要靠得很近。定义:
,其中
通过引入二次和指数形式来增强上述特征:
当 时:
定义辅助变量 分别表示两个关节点的欧几里得距离和角度(?)对于
的联合分布,作者没有直接利用
,而是采用一种后验概率:
作为 pairwise feature for
to encode the geometric relations between the body part class
and
. 更具体地来说:假设
,那么:
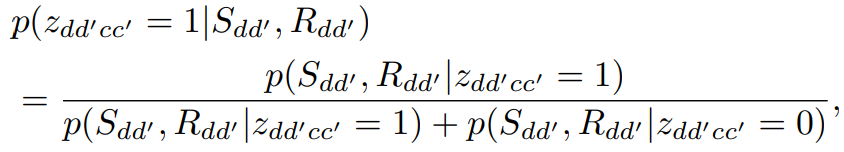
其中 通过 conducting a normalized 2D histogram(通过统计训练样本得到) of
and
获得;
也是通过类似的方式得到。作者在实验中也尝试了 encoding the appearance into the pairwise feature;具体方式:将 CNN-based part detectors 的输出
连接在前面的特征后面。最后的 pairwise feature 就是:
.
这里讲的是
是如何得到的。也即是说,通过上面的步骤,我们就得到了两两关节点之间的一个关系(联合特征),通过这种关系,我们来进行对应的估计。估计的内容:在两种情况下讨论,两个关节点属于同一个人的概率。
概率估计
需要估计的概率:(1) For every pair of detection and part classes, namely for any ,估计
表示关节点
属于类别
的概率;(关节点的类别概率)(2)For every combination of two distinct detections and two body part classes, namely for any
以及任意的
,我们估计概率
of
属于相同的人,并且
属于类别
,
属于类别
.
Learning. 给定特征 和高斯先验
,logistic 模型为:
,其中
参数通过 ML 方法进行估计。
ML:Maximum Likelihood Estimation,极大似然估计
Inference. 给定两个检测 ,系数
for
,
for
are obtained by the previous formulas. 系数
for
具有如下形式:
模型参数 通过 logistic regression 得到。
通过前面的特征,以及 logistic 模型就可以在给定两两联合特征
的条件下来估计两个关节点属于同一个节点的概率,该概率可以用
来表示。最后就可以得到
的值。由于其中的
是通过
得到的,该值可以直接由检测器输出。到此,我们就确定了
以及
,那么对上面的优化问题进行求解,得到最优的
就可以解决所有问题了。(将检测问题转为优化问题,方法有很多参数需要统计计算,感觉还是比较麻烦的。关节点分配,分类问题采用了传统的方法。)
身体关节检测器
作者采用修改后的 Fast R-CNN 作为关节点检测器。事实上 FR-CNN 是用于目标检测的,这里作者将其用来做关节点检测:以检测框的中心作为关节点的坐标。
作者利用关节点检测器提取了大量的关节点,之后将其转为优化问题来解决关节点的分配问题,以及关节点的类别问题。(后面那些公式可能还有些没有明白,之后再看几遍,顺便了解一下代码实现)不过 Graph 倒是个有用的东西。之后顺便去学习了解一下图割相关的知识!

