Mybatis
Mybatis通过Mapper接口就能操作数据库的主要实现思想是:使用动态代理生成实现类,然后配合xml的映射文件中的SQL语句来实现对数据库的访问。
Mybatis编程模型
Mybatis是在iBatis上演变而来ORM框架,所以Mybatis最终会将代码转换成iBatis编程模型,而 Mybatis 代理阶段主要是将面向接口编程模型,通过动态代理转换成ibatis编程模型。
不直接使用iBatis编程模型的原因是为了解耦,从下面的两种示例可以看出,iBatis编程模型和配置文件耦合很严重。
面向接口编程模型
@Test// 面向接口编程模型public void quickStart() throws Exception {// 2.获取sqlSessiontry (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {initH2dbMybatis(sqlSession);// 3.获取对应mapperPersonMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(PersonMapper.class);JdkProxySourceClassUtil.writeClassToDisk(mapper.getClass().getSimpleName(), mapper.getClass());// 4.执行查询语句并返回结果Person person = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1L);System.out.println(person.toString());}}
ibatis编程模型
@Test// ibatis编程模型public void quickStartIBatis() throws Exception {// 2.获取sqlSessiontry (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {initH2dbMybatis(sqlSession);// ibatis编程模型(与配置文件耦合严重)Person person = sqlSession.selectOne("com.fcant.domain.mapper.PersonMapper.selectByPrimaryKey", 1L);System.out.println(person.toString());}}
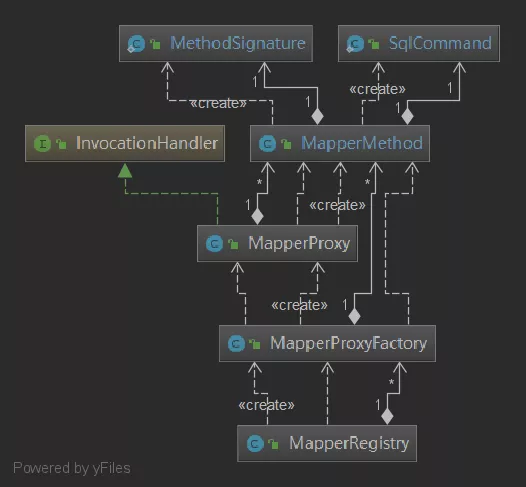
代理模块核心类
- MapperRegistry:Mapper接口动态代理工厂(MapperProxyFactory)的注册中心
- MapperProxyFactory:Mapper接口对应的动态代理工厂类。Mapper接口和MapperProxyFactory工厂类是一一对应关系
- MapperProxy:Mapper接口的增强器,它实现了
InvocationHandler接口,通过该增强的invoke方法实现了对数据库的访问 - MapperMethod:对insert, update, delete, select, flush节点方法的包装类,它通过
sqlSession来完成了对数据库的操作
代理初始化
加载Mapper接口到内存
在Mybatis 源码可以发现当配置文件解析完成的最后一步是调用org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace方法。该方法的主要作用是:根据 namespace 属性将Mapper接口的动态代理工厂(MapperProxyFactory)注册到 MapperRegistry 中。源码如下:
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {// 获取namespace属性(对应Mapper接口的全类名)String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();if (namespace != null) {Class<?> boundType = null;try {boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {//ignore, bound type is not required}if (boundType != null) {// 防止重复加载if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResourceconfiguration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);// 将Mapper接口的动态代理工厂注册到 MapperRegistry 中configuration.addMapper(boundType);}}}}
- 读取namespace属性,获取Mapper接口的全类名
- 根据全类名将Mapper接口加载到内存
- 判断是否重复加载Mapper接口
调用Mybatis 配置类(configuration)的addMapper方法,完成后续步骤
注册代理工厂类
org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#addMapper该方法直接回去调用org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry#addMapper方法完成注册。public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {// 必须是接口if (type.isInterface()) {if (hasMapper(type)) {// 防止重复注册throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");}boolean loadCompleted = false;try {// 根据接口类,创建MapperProxyFactory代理工厂类knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);parser.parse();loadCompleted = true;} finally {// 如果加载出现异常需要移除对应Mapperif (!loadCompleted) {knownMappers.remove(type);}}}}
判断加载类型是否是接口
- 重复注册校验,如果校验不通抛出
BindingException异常 - 根据接口类,创建MapperProxyFactory代理工厂类
-
获取代理对象
在Mybatis 源码中有如下代码,通过 sqlSession获取Mapper的代理对象:
PersonMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(PersonMapper.class);
getMapper 获取代理对象
sqlSession.getMapper(PersonMapper.class)最终调用的是org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry#getMapper方法,最后返回的是PersonMapper接口的代理对象,源码如下:public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {// 根据类型获取对应的代理工厂final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");}try {// 根据工厂类新建一个代理对象,并返回return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);} catch (Exception e) {throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);}}
根据类型获取对应的代理工厂
-
newInstance 创建代理对象
每一个Mapper接口对应一个MapperProxyFactory工厂类。MapperProxyFactory通过JDK动态代理创建代理对象,Mapper接口的代理对象是方法级别,所以每次访问数据库都需要新创建代理对象。源码如下:
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {// 使用JDK动态代理生成代理实例return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);}public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {// Mapper的增强器final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);return newInstance(mapperProxy);}
先获取Mapper对应增强器(MapperProxy)
-
代理类的反编译结果
import com.sun.proxy..Proxy8;import com.fcant.domain.model.Person;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;public final class $Proxy8 extends Proxy implements Proxy8 {private static Method m3;...public $Proxy8(InvocationHandler var1) throws {super(var1);}...public final Person selectByPrimaryKey(Long var1) throws {try {return (Person)super.h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[]{var1});} catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) {throw var3;} catch (Throwable var4) {throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);}}static {try {m3 = Class.forName("com.sun.proxy.$Proxy8").getMethod("selectByPrimaryKey", Class.forName("java.lang.Long"));} catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) {throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());}}}
从代理类的反编译结果来看,都是直接调用增强器的
invoke方法,进而实现对数据库的访问。执行代理
通过上诉反编译代理对象,可以发现所有对数据库的访问都是在增强器
org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy#invoke中实现的。执行增强器 MapperProxy
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {// 如果是Object本身的方法不增强if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);}// 判断是否是默认方法else if (method.isDefault()) {if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {return invokeDefaultMethodJava8(proxy, method, args);} else {return invokeDefaultMethodJava9(proxy, method, args);}}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}// 从缓存中获取MapperMethod对象final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);// 执行MapperMethodreturn mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}
如果是Object本身的方法不增强
- 判断是否是默认方法
- 从缓存中获取MapperMethod对象
- 执行MapperMethod
模型转换 MapperMethod
MapperMethod封装了Mapper接口中对应方法的信息(MethodSignature),以及对应的sql语句的信息(SqlCommand);它是mapper接口与映射配置文件中sql语句的桥梁;MapperMethod对象不记录任何状态信息,所以它可以在多个代理对象之间共享;
- SqlCommand :从configuration中获取方法的命名空间.方法名以及SQL语句的类型;
- MethodSignature:封装mapper接口方法的相关信息(入参,返回类型);
- ParamNameResolver:解析mapper接口方法中的入参;
在public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;// 根据SQL类型,调用不同方法。// 这里可以看出,操作数据库都是通过 sqlSession 来实现的switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT:// 根据方法返回值类型来确认调用sqlSession的哪个方法// 无返回值或者有结果处理器if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;}// 返回值是否为集合类型或数组else if (method.returnsMany()) {result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);}// 返回值是否为Mapelse if (method.returnsMap()) {result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);}// 返回值是否为游标类型else if (method.returnsCursor()) {result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);}// 查询单条记录else {// 参数解析Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);if (method.returnsOptional()&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {result = Optional.ofNullable(result);}}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());}if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");}return result;}private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {List<E> result;// 将方法参数转换成SqlCommand参数Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);if (method.hasRowBounds()) {// 获取分页参数RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);} else {result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);}// issue #510 Collections & arrays supportif (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {return convertToArray(result);} else {return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);}}return result;}
execute方法中完成了面向接口编程模型到iBatis编程模型的转换,转换过程如下:
- 通过
MapperMethod.SqlCommand. type+MapperMethod.MethodSignature.returnType来确定需要调用SqlSession中的那个方法 - 通过
MapperMethod.SqlCommand. name来找到需要执行方法的全类名 通过
MapperMethod.MethodSignature.paramNameResolver来转换需要传递的参数SqlSession
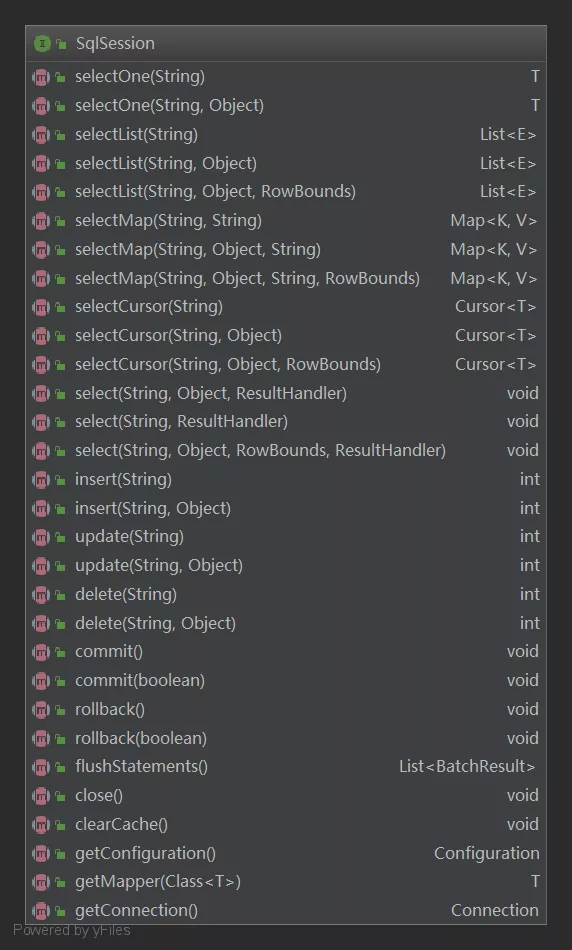
在Mybatis中SqlSession相当于一个门面,所有对数据库的操作都需要通过SqlSession接口,SqlSession中定义了所有对数据库的操作方法,如数据库读写命令、获取映射器、管理事务等,也是Mybatis中为数不多的有注释的类。
流程图
总结
通过上面的源码解析,可以发现Mybatis面向接口编程是通过JDK动态代理模式来实现的。主要执行流程是:
在映射文件初始化完成后,将对应的Mapper接口的代理工厂类
MapperProxyFactory注册到MapperRegistry- 每次操作数据库时,
sqlSession通过MapperProxyFactory获取Mapper接口的代理类 - 代理类通过增强器
MapperProxy调用XML映射文件中SQL节点的封装类MapperMethod - 通过
MapperMethod将Mybatis 面向接口的编程模型转换成iBatis编程模型(SqlSession模型) - 通过
SqlSession完成对数据库的操作