Spring Security过滤器链体系
在学习Spring Security的时候有没有下面这两个疑问:
- Spring Security的登录是怎么配置的?
- Spring Security的访问控制是什么机制?
SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration
上面两个疑问的答案就在配置类SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration中。可以按照下面这个思维导图去理解这个自动配置:
SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration为Spring Boot应用提供了一套默认的Spring Security配置。
这里的配置为:所有的请求都必须是认证用户发起的,同时开启表单登录功能以及Http Basic@Bean@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER)SecurityFilterChain defaultSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated().and().formLogin().and().httpBasic();return http.build();}
Authentication认证功能。访问/foo/bar时需要登录认证并且能够进行表单登录就是这个配置起作用了。这个是日常开发需要自定义的。这个SecurityFilterChain到底是什么呢?
从上面看得出SecurityFilterChainHttpSecurity就是一个构建类,它的使命就是构建出一个SecurityFilterChain:
当一个请求public interface SecurityFilterChain {// 当前请求是否匹配boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request);// 一揽子过滤器组成的有序过滤器链List<Filter> getFilters();}
HttpServletRequest进入SecurityFilterChain时,会通过matches方法来确定是否满足条件进入过滤器链。就好比VIP走的是VIP通道,享受的是VIP的一系列待遇;如果是普通用户,就走普通用户的通道并享受普通用户的待遇。 不管用户是哪种角色,都走的是一个过滤器链,一个应用中存在1-n个
不管用户是哪种角色,都走的是一个过滤器链,一个应用中存在1-n个SecurityFilterChain。那谁来管理多个SecurityFilterChain呢?
记住这个公式HttpSecurity->SecurityFilterChain。FilterChainProxyFilterChainProxy是一个GenericFilterBean(即使Servlet Filter又是Spring Bean),它管理了所有注入Spring IoC容器的SecurityFilterChain。刚接触Spring Security的时候是这样配置FilterChainProxy的:
根据不同的请求路径匹配走不同的<bean id="myfilterChainProxy" class="org.springframework.security.web.FilterChainProxy"><constructor-arg><util:list><security:filter-chain pattern="/do/not/filter*" filters="none"/><security:filter-chain pattern="/**" filters="filter1,filter2,filter3"/></util:list></constructor-arg></bean>
SecurityFilterChain。下面是示意图: 后面还会对遇到这个类,现在只需要明白上面这个图就行了。
后面还会对遇到这个类,现在只需要明白上面这个图就行了。
请注意:在同一过滤器链中不建议有多个FilterChainProxy实例,而且不应将其作为单纯的过滤器使用,它只应该承担管理SecurityFilterChain的功能。
Servlet 容器和Spring IoC容器之间的Filter生命周期并不匹配。为了让Spring IoC容器管理Filter的生命周期,DelegatingFilterProxyFilterChainProxy便交由Spring Web下的DelegatingFilterProxy来代理。而且FilterChainProxy不会在添加到应用程序上下文的任何过滤器Bean上调用标准Servlet过滤器生命周期方法,FilterChainProxy的生命周期方法会委托给DelegatingFilterProxy来执行。而DelegatingFilterProxy作为Spring IoC和Servlet的连接器存在。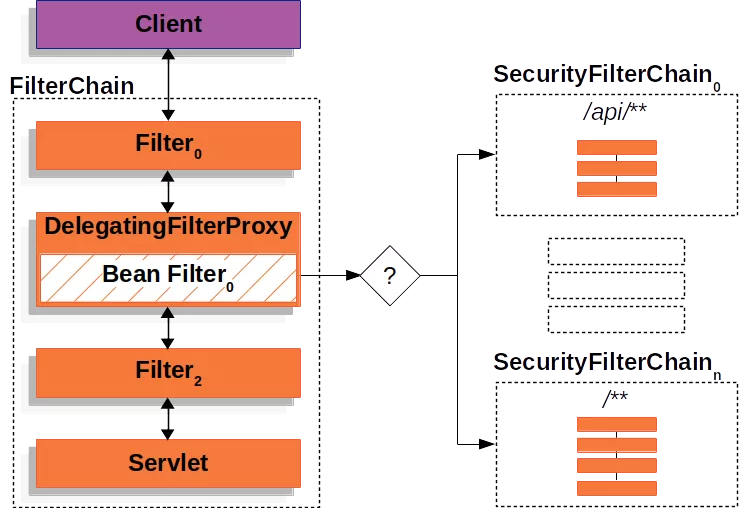
简单总结
上面的三个概念非常重要,涉及到Spring Security的整个过滤器链体系。Spring Security过滤器链匹配到特定的请求
如何拦截特定的请求
只有满足了SecurityFilterChain的match方法的请求才能被该SecurityFilterChain处理,那如何配置才能让一个SecurityFilterChain处理特定的路径呢?RequestMatcherHttpSecurity内置了RequestMatcher属性来处理路径匹配问题。RequestMatcher可总结为以下几大类: 使用Ant路径:
使用Ant路径:
如果配置了全局的Servlet Path的话,例如/v1,配置ant路径的话就要/v1/foo/**,使用MVC风格可以保持一致:httpSecurity.antMatcher("/foo/**");
另外MVC风格可以自动匹配后缀,例如/foo/hello可以匹配/foo/hello.do、/foo/hello.action 等等。另外也可以使用正则表达式来进行路径匹配:httpSecurity.mvcMatcher("/foo/**");
如果上面的都满足不了需要的话,可以通过httpSecurity.regexMatcher("/foo/.+");
HttpSecurity.requestMatcher方法自定义匹配规则;如果想匹配多个规则的话可以借助于HttpSecurity.requestMatchers方法来自由组合匹配规则,就像这样:
一旦配置了路径匹配规则的话,可以发现默认的表单登录404了,因为默认是/login,加了前缀后当然访问不到了。httpSecurity.requestMatchers(requestMatchers ->requestMatchers.mvcMatchers("/foo/**").antMatchers("/admin/*get"));
使用场景
比如后台管理系统和前端应用各自走不同的过滤器链,可以根据访问路径来配置各自的过滤器链。例如: ```java /**- Admin 过滤器链. *
- @param http the http
- @return the security filter chain
- @throws Exception the exception
/
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain adminSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.requestMatchers(requestMatchers -> requestMatchers.mvcMatchers(“/admin/*“))
}//todo 其它配置return http.build();
/**
- App 过滤器链. *
- @param http the http
- @return the security filter chain
- @throws Exception the exception / @Bean SecurityFilterChain appSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.requestMatchers(requestMatchers -> requestMatchers.mvcMatchers(“/app/*“)); //todo 其它配置 return http.build(); } ``` 另外也可以使用该特性降低不同规则URI之间的耦合性。

