Java 队列
Java 中的队列有很多,例如:ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue、PriorityQueue、DelayQueue、SynchronousQueue 等,那它们的作用是什么?又是如何分类的呢?
其实 Java 中的这些队列可以从不同的维度进行分类,例如可以从阻塞和非阻塞进行分类,也可以从有界和无界进行分类,从队列的功能上进行分类,例如:优先队列、普通队列、双端队列、延迟队列等。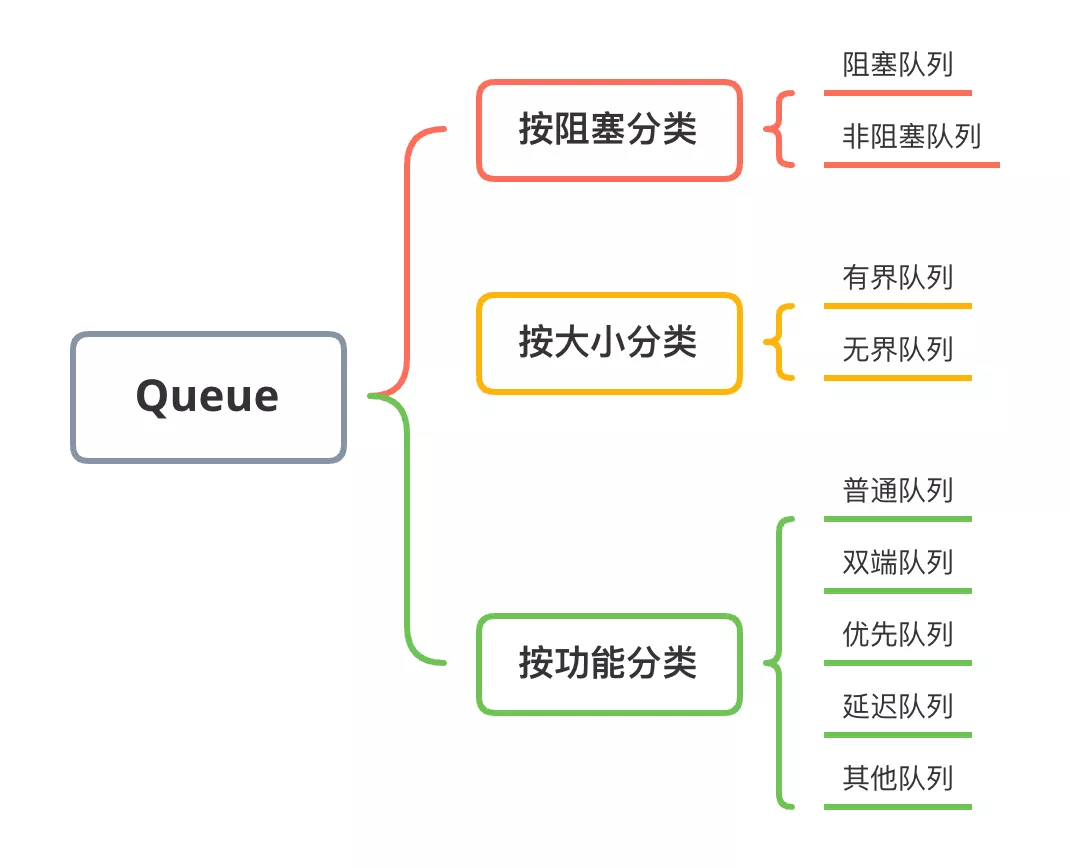
虽然重点是从功能上对队列进行解读,但其它分类也是 Java 中的重要概念,先来了解一下它们。
阻塞队列和非阻塞队列
阻塞队列(Blocking Queue)提供了可阻塞的 put 和 take 方法,它们与可定时的 offer 和 poll 是等价的。如果队列满了 put 方法会被阻塞等到有空间可用再将元素插入;如果队列是空的,那么 take 方法也会阻塞,直到有元素可用。当队列永远不会被充满时,put 方法和 take 方法就永远不会阻塞。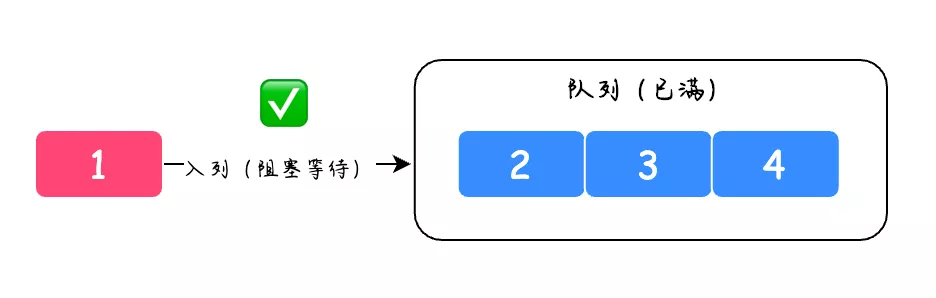
可以从队列的名称中知道此队列是否为阻塞队列,阻塞队列中包含 BlockingQueue 关键字,比如以下这些:
ArrayBlockingQueueLinkedBlockingQueuePriorityBlockingQueue-
阻塞队列功能演示
接下来来演示一下当阻塞队列的容量满了之后会怎样,示例代码如下:
import java.util.Date;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;public class BlockingTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 创建一个长度为 5 的阻塞队列ArrayBlockingQueue q1 = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 新创建一个线程执行入列new Thread(() -> {// 循环 10 次for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {q1.put(i);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(new Date() + " | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:" + q1.size());}System.out.println(new Date() + " | For End.");}).start();// 新创建一个线程执行出列new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {try {// 休眠 1SThread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (!q1.isEmpty()) {try {q1.take(); // 出列} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}).start();}}
以上代码的执行结果如下:
Mon Oct 19 20:16:12 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:1 Mon Oct 19 20:16:12 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:2 Mon Oct 19 20:16:12 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:3 Mon Oct 19 20:16:12 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:4 Mon Oct 19 20:16:12 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:5 Mon Oct 19 20:16:13 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:5 Mon Oct 19 20:16:14 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:5 Mon Oct 19 20:16:15 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:5 Mon Oct 19 20:16:16 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:5 Mon Oct 19 20:16:17 CST 2020 | ArrayBlockingQueue Size:5 Mon Oct 19 20:16:17 CST 2020 | For End.
从上述结果可以看出,当 ArrayBlockingQueue 队列满了之后就会进入阻塞,当过了 1 秒有元素从队列中移除之后,才会将新的元素入列。
非阻塞队列
非阻塞队列也就是普通队列,它的名字中不会包含 BlockingQueue 关键字,并且它不会包含 put 和 take 方法,当队列满之后如果还有新元素入列会直接返回错误,并不会阻塞的等待着添加元素,如下图所示: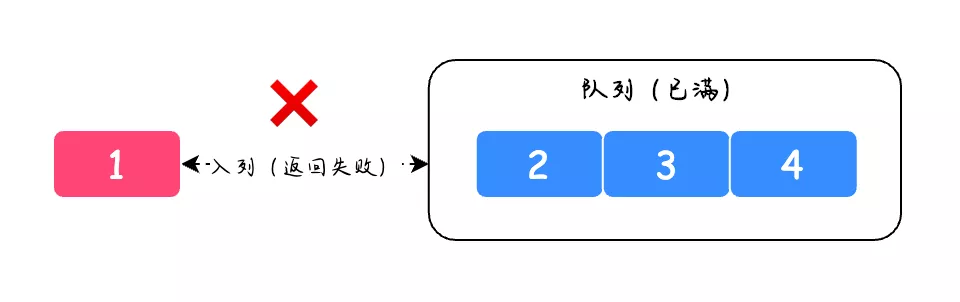
非阻塞队列的典型代表是 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 和 PriorityQueue。
有界队列和无界队列
有界队列
有界队列是指有固定大小的队列,比如设定了固定大小的 ArrayBlockingQueue,又或者大小为 0 的 SynchronousQueue。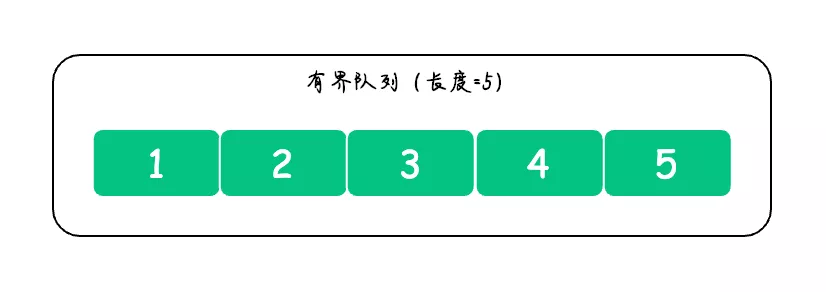
无界队列
无界队列指的是没有设置固定大小的队列,但其实如果没有设置固定大小也是有默认值的,只不过默认值是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,当然实际的使用中不会有这么大的容量(超过 Integer.MAX_VALUE),所以从使用者的角度来看相当于 “无界”的。
按功能分类
以功能来划分一下队列,它可以被分为:普通队列、优先队列、双端队列、延迟队列、其他队列等,接下来分别来看。
1.普通队列
普通队列(Queue)是指实现了先进先出的基本队列,例如 ArrayBlockingQueue 和 LinkedBlockingQueue,其中 ArrayBlockingQueue 是用数组实现的普通队列,如下图所示: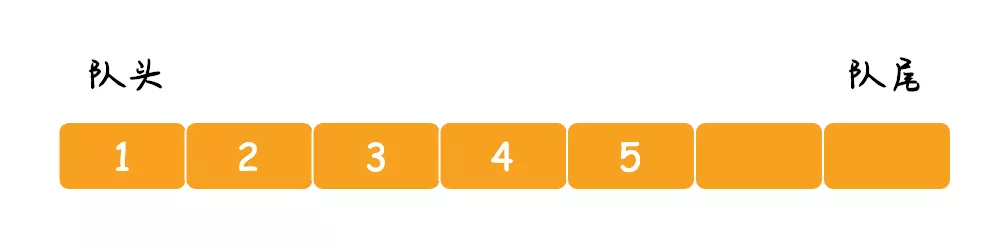
而 LinkedBlockingQueue 是使用链表实现的普通队列,如下图所示:
常用方法
普通队列中的常用方法有以下这些:
offer():添加元素,如果队列已满直接返回 false,队列未满则直接插入并返回 true;poll():删除并返回队头元素,当队列为空返回 null;add():添加元素,此方法是对 offer 方法的简单封装,如果队列已满,抛出 IllegalStateException 异常;remove():直接删除队头元素;put():添加元素,如果队列已经满,则会阻塞等待插入;take():删除并返回队头元素,当队列为空,则会阻塞等待;peek():查询队头元素,但不会进行删除;element():对 peek 方法进行简单封装,如果队头元素存在则取出并不删除,如果不存在抛出 NoSuchElementException 异常。 :::danger 注意:一般情况下**offer()**和**poll()**方法配合使用,**put()**和**take()**阻塞方法配合使用,**add()**和**remove()**方法会配合使用,程序中常用的是**offer()**和**poll()**方法,因此这两个方法比较友好,不会报错。 ::: 接下来以LinkedBlockingQueue为例,演示一下普通队列的使用:
以上代码的执行结果如下:import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;static class LinkedBlockingQueueTest {public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedBlockingQueue queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue();queue.offer("Hello");queue.offer("Java");queue.offer("Fcant");while (!queue.isEmpty()) {System.out.println(queue.poll());}}}
Hello Java Fcant
2.双端队列
双端队列(Deque)是指队列的头部和尾部都可以同时入队和出队的数据结构,如下图所示: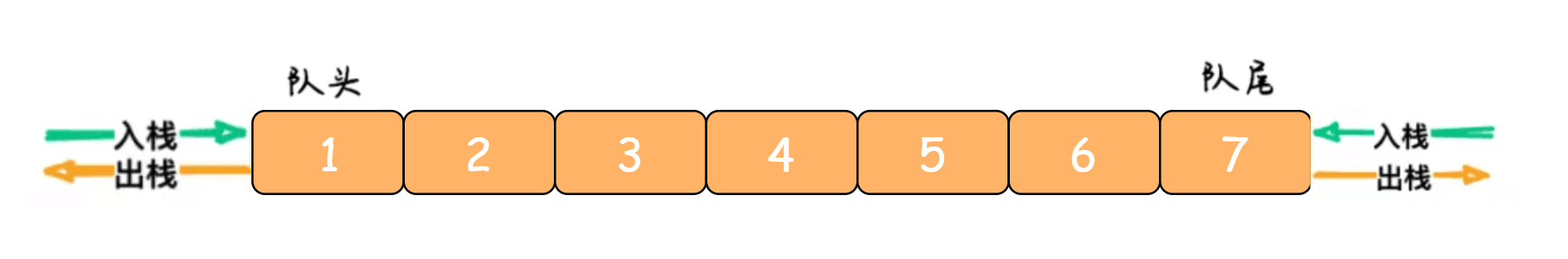
接下来演示一下双端队列 LinkedBlockingDeque 的使用:
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;/*** 双端队列示例*/static class LinkedBlockingDequeTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建一个双端队列LinkedBlockingDeque deque = new LinkedBlockingDeque();deque.offer("offer"); // 插入首个元素deque.offerFirst("offerFirst"); // 队头插入元素deque.offerLast("offerLast"); // 队尾插入元素while (!deque.isEmpty()) {// 从头遍历打印System.out.println(deque.poll());}}}
以上代码的执行结果如下:
offerFirst offer offerLast
3.优先队列
优先队列(PriorityQueue)是一种特殊的队列,它并不是先进先出的,而是优先级高的元素先出队。
优先队列是根据二叉堆实现的,二叉堆的数据结构如下图所示: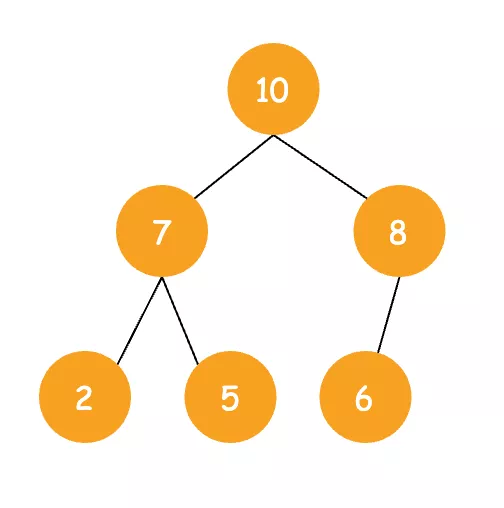
二叉堆分为两种类型:一种是最大堆一种是最小堆。以上展示的是最大堆,在最大堆中,任意一个父节点的值都大于等于它左右子节点的值。
因为优先队列是基于二叉堆实现的,因此它可以将优先级最好的元素先出队。
接下来演示一下优先队列的使用:
import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class PriorityQueueTest {// 自定义的实体类static class Viper {private int id; // idprivate String name; // 名称private int level; // 等级public Viper(int id, String name, int level) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.level = level;}public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getLevel() {return level;}public void setLevel(int level) {this.level = level;}}public static void main(String[] args) {PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(10, new Comparator<Viper>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Viper v1, Viper v2) {// 设置优先级规则(倒序,等级越高权限越大)return v2.getLevel() - v1.getLevel();}});// 构建实体类Viper v1 = new Viper(1, "Java", 1);Viper v2 = new Viper(2, "MySQL", 5);Viper v3 = new Viper(3, "Redis", 3);// 入列queue.offer(v1);queue.offer(v2);queue.offer(v3);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {// 遍历名称Viper item = (Viper) queue.poll();System.out.println("Name:" + item.getName() +" Level:" + item.getLevel());}}}
以上代码的执行结果如下:
Name:MySQL Level:5 Name:Redis Level:3 Name:Java Level:1
从上述结果可以看出,优先队列的出队是不考虑入队顺序的,它始终遵循的是优先级高的元素先出队。
4.延迟队列
延迟队列(DelayQueue)是基于优先队列 PriorityQueue 实现的,它可以看作是一种以时间为度量单位的优先的队列,当入队的元素到达指定的延迟时间之后方可出队。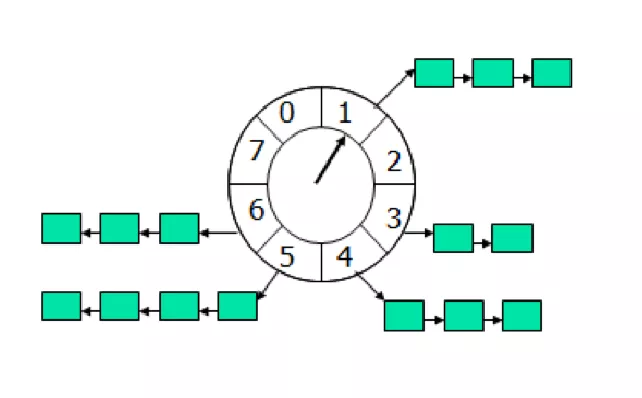
来演示一下延迟队列的使用:
import lombok.Getter;import lombok.Setter;import java.text.DateFormat;import java.util.Date;import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class CustomDelayQueue {// 延迟消息队列private static DelayQueue delayQueue = new DelayQueue();public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {producer(); // 调用生产者consumer(); // 调用消费者}// 生产者public static void producer() {// 添加消息delayQueue.put(new MyDelay(1000, "消息1"));delayQueue.put(new MyDelay(3000, "消息2"));}// 消费者public static void consumer() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println("开始执行时间:" +DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(new Date()));while (!delayQueue.isEmpty()) {System.out.println(delayQueue.take());}System.out.println("结束执行时间:" +DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(new Date()));}static class MyDelay implements Delayed {// 延迟截止时间(单位:毫秒)long delayTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// 借助 lombok 实现@Getter@Setterprivate String msg;/*** 初始化* @param delayTime 设置延迟执行时间* @param msg 执行的消息*/public MyDelay(long delayTime, String msg) {this.delayTime = (this.delayTime + delayTime);this.msg = msg;}// 获取剩余时间@Overridepublic long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {return unit.convert(delayTime - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}// 队列里元素的排序依据@Overridepublic int compareTo(Delayed o) {if (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) > o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {return 1;} else if (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) < o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {return -1;} else {return 0;}}@Overridepublic String toString() {return this.msg;}}}
以上代码的执行结果如下:
开始执行时间:2020-10-20 20:17:28 消息1 消息2 结束执行时间:2020-10-20 20:17:31
从上述结束执行时间和开始执行时间可以看出,消息 1 和消息 2 都正常实现了延迟执行的功能。
5.其他队列
在 Java 的队列中有一个比较特殊的队列 SynchronousQueue,它的特别之处在于它内部没有容器,每次进行 put() 数据后(添加数据),必须等待另一个线程拿走数据后才可以再次添加数据,它的使用示例如下:
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;public class SynchronousQueueTest {public static void main(String[] args) {SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();// 入队new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {try {System.out.println(new Date() + ",元素入队");queue.put("Data " + i);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}).start();// 出队new Thread(() -> {while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(new Date() + ",元素出队:" + queue.take());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}).start();}}
以上代码的执行结果如下:
Mon Oct 19 21:00:21 CST 2020,元素入队 Mon Oct 19 21:00:22 CST 2020,元素出队:Data 0 Mon Oct 19 21:00:22 CST 2020,元素入队 Mon Oct 19 21:00:23 CST 2020,元素出队:Data 1 Mon Oct 19 21:00:23 CST 2020,元素入队 Mon Oct 19 21:00:24 CST 2020,元素出队:Data 2
从上述结果可以看出,当有一个元素入队之后,只有等到另一个线程将元素出队之后,新的元素才能再次入队。
总结
Java 中的 5 种队列:普通队列、双端队列、优先队列、延迟队列、其他队列。其中普通队列的典型代表为 ArrayBlockingQueue 和 LinkedBlockingQueue,双端队列的代表为 LinkedBlockingDeque,优先队列的代表为 PriorityQueue,延迟队列的代表为 DelayQueue,最后还讲了内部没有容器的其他队列 SynchronousQueue。

