前言
在平时的 API 开发过程中,总会遇到一些错误异常没有捕捉到的情况。那有的小伙伴可能会想,这还不简单么,在 API 最外层加一个 try...catch 不就完事了。
这种方法简单粗暴。在每一个 API 入口,都去做 try...catch 吗?这样不是代码看起来非常丑陋。所以使用 AOP 来实现是最佳的选择。
Spring Boot 通过注解来实现全局异常处理的。
@ControllerAdvice 和 @ExceptionHandler
@ControllerAdvice相当于controller的切面,主要用于@ExceptionHandler,@InitBinder和@ModelAttribute,使注解标注的方法对每一个 controller 都起作用。默认对所有 controller 都起作用,当然也可以通过@ControllerAdvice注解中的一些属性选定符合条件的 controller 。@ExceptionHandler用于异常处理的注解,可以通过 value 指定处理哪种类型的异常还可以与@ResponseStatus搭配使用,处理特定的 http 错误。标记的方法入参与返回值都有很大的灵活性,具体可以看注释也可以在后边的深度探究。案例分析
通过全局异常处理的方式了解 Spring Boot 的全局异常处理。案例一
一般的异常处理,所有的API都需要有相同的异常结构。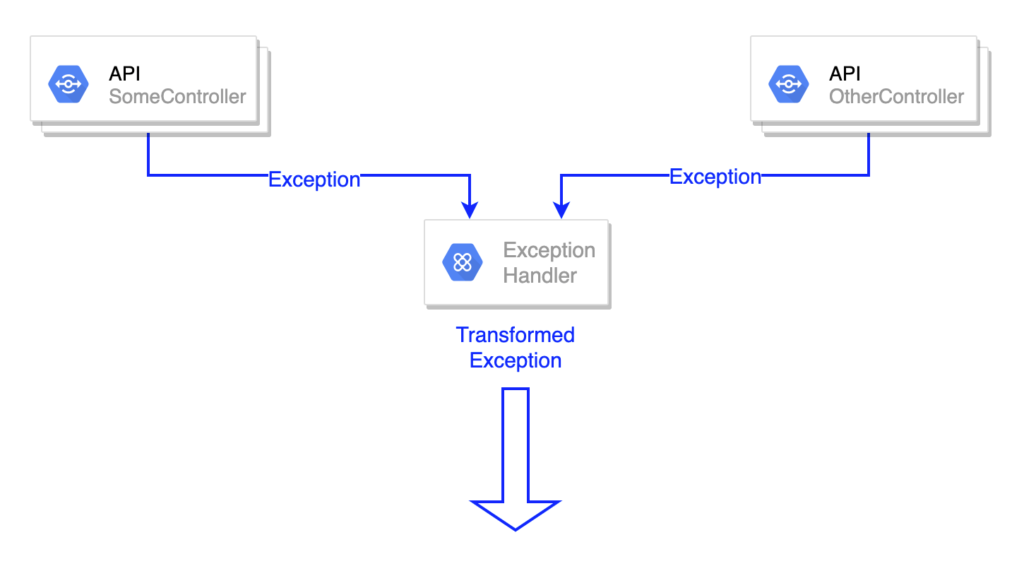
在这种情况下,实现是非常简单的,只需要创建GeneralExceptionHandler类,用@ControllerAdvice注解来注解它,并创建所需的@ExceptionHandler,它将处理所有由应用程序抛出的异常,如果它能找到匹配的@ExceptionHandler,它将相应地进行转换。@ControllerAdvicepublic class GeneralExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)protected ResponseEntity<Error> handleException(Exception ex) {MyError myError = MyError.builder().text(ex.getMessage()).code(ex.getErrorCode()).build();return new ResponseEntity(myError,HttpStatus.valueOf(ex.getErrorCode()));}}
案例二
有一个API,它需要有一个或多个异常以其他格式处理,与其他应用程序的 API 不同。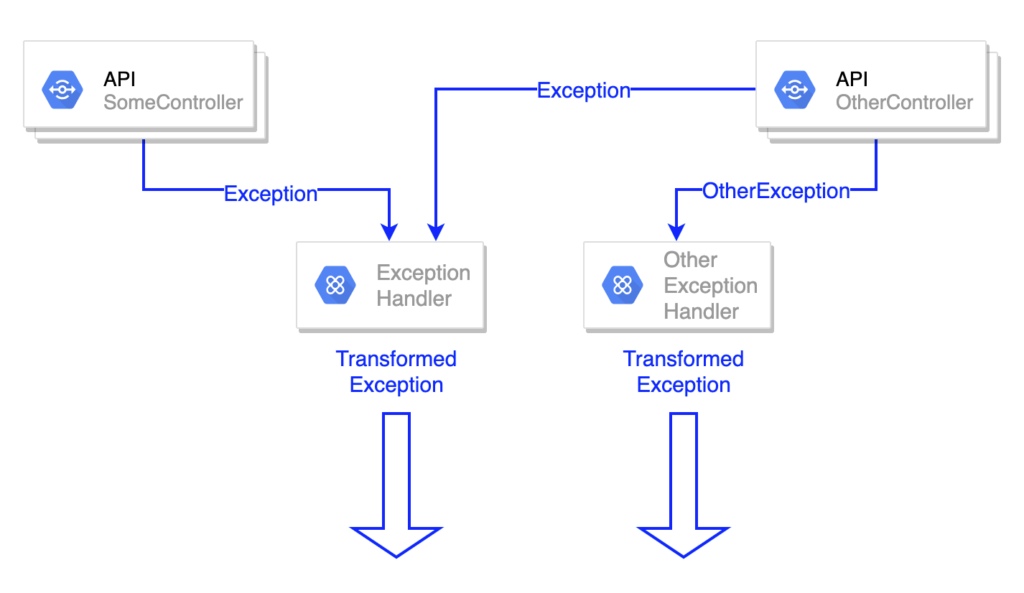
可以采取两种方式来实现这种情况。可以在OtherController内部添加@ExceptionHandler来处理OtherException,或者为OtherController创建新的@ControllerAdvice,以备在其他 API 中处理OtherException。
在OtherController中添加@ExceptionHandler来处理OtherException的代码示例。
只针对@RestController@RequestMapping("/other")public class OtherController {@ExceptionHandler(OtherException.class)protected ResponseEntity<Error> handleException(OtherException ex) {MyOtherError myOtherError = MyOtherError.builder().message(ex.getMessage()).origin("Other API").code(ex.getErrorCode()).build();return new ResponseEntity(myOtherError,HttpStatus.valueOf(ex.getErrorCode()));}}
OtherController控制器的@ControllerAdvice的代码示例@ControllerAdvice(assignableTypes = OtherController.class)public class OtherExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler(OtherException.class)protected ResponseEntity<Error> handleException(OtherException ex) {MyOtherError myOtherError = MyOtherError.builder().message(ex.getMessage()).origin("Other API").code(ex.getErrorCode()).build();return new ResponseEntity(myOtherError,HttpStatus.valueOf(ex.getErrorCode()));}}
案例三
与案例二类似,有一个 API 需要以不同于应用程序中其他 API 的方式对异常进行格式化,但这次所有的异常都需要进行不同的转换。
为了实现这个案例,将不得不使用两个@ControllerAdvice,并加上@Order注解的注意事项。因为现在需要告诉 Spring,在处理同一个异常时,哪个@ControllerAdvice的优先级更高。如果没有指定@Order,在启动时,其中一个处理程序将自动注册为更高的顺序,异常处理将变得不可预测。例如,如果使用mvn springboot:run任务启动一个应用程序,OtherExceptionHandler是主要的,但是当以jar形式启动时,GeneralExceptionHandler是主要的。@ControllerAdvicepublic class GeneralExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)protected ResponseEntity<Error> handleException(Exception ex) {MyError myError = MyError.builder().text(ex.getMessage()).code(ex.getErrorCode()).build();return new ResponseEntity(myError,HttpStatus.valueOf(ex.getErrorCode()));}}@ControllerAdvice(assignableTypes = OtherController.class)@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)public class OtherExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)protected ResponseEntity<Error> handleException(Exception ex) {MyError myError = MyError.builder().message(ex.getMessage()).origin("Other API").code(ex.getErrorCode()).build();return new ResponseEntity(myError,HttpStatus.valueOf(ex.getErrorCode()));}}
总结
经过上述的几个案例,应该已经能够轻松应对 Spring Boot 中大部分的全局异常处理的情况。
为什么不使用@RestControllerAdvice呢?如果是用的@RestControllerAdvice注解,它会将数据自动转换成JSON格式,不再需要ResponseEntity的处理来。这种与Controller和RestController类似,本质是一样的,所以在使用全局异常处理之后可以进行灵活的选择处理。

