SpringBoot配置静态资源目录
使用Spring Boot 默认配置静态资源
- 默认配置的
/**映射到项目中src/main/resources/目录下的文件夹 /static、/public、/resources、/META-INF/resources,application.properties文件默认配置:
SpringBoot默认对/**的访问可以直接访问四个目录下的文件:#静态资源访问路径spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/**#静态资源映射路径spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/
- classpath:/public/
- classpath:/resources/
- classpath:/static/
- classpath:/META-INFO/resouces/
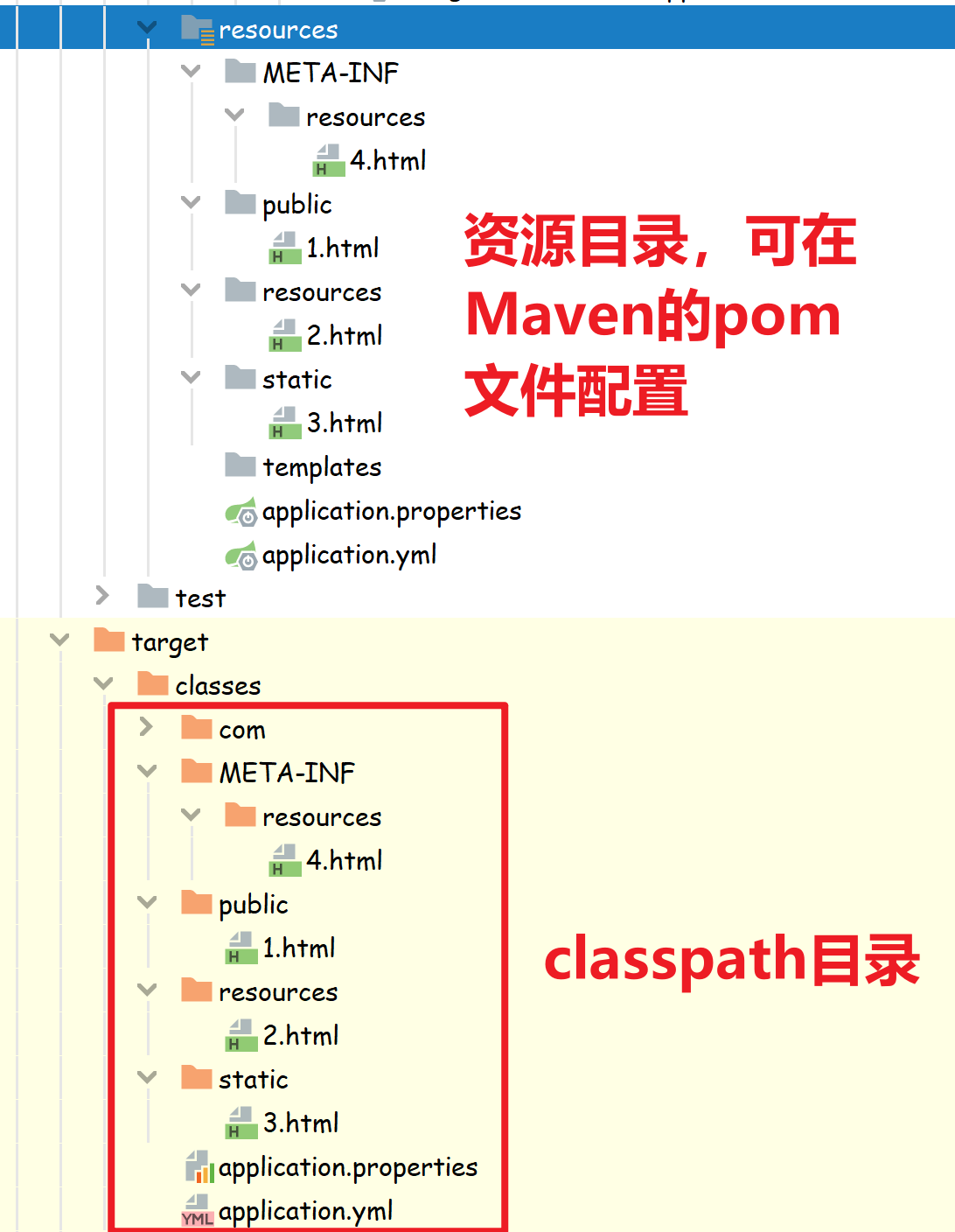
注意蓝色条下的资源文件夹resources与类路径下的文件夹classpath:/resources是不同的,蓝色条下的resources代表的是该目录下的文件为资源文件,在打包的时候会将该目录下的文件全部打包的类路径下,这个名称是可以改的,在pom.xml指定资源目录即可:
<resources><resource><directory>src/main/resources</directory></resource></resources>
而类路径下的resources是SpringBoot默认的静态资源文件夹之一,和public、static以及MEAT-INF/resources的功能相同。现在重启Spring boot就可以通过:
- http://localhost:8080/1.html
- http://localhost:8080/2.html
- http://localhost:8080/3.html
- http://localhost:8080/4.html
四个URL访问到四个目录下的静态资源了。
直接在application.yml中配置自定义的静态资源目录
spring:mvc:static-path-pattern: /image/**resources:static-locations: classpath:/images/
static-path-pattern:访问模式,默认为/**,多个可以逗号分隔static-locations:资源目录,多个目录逗号分隔,默认资源目录为classpath:/META-INF/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/
:::tips
注意,这个配置会覆盖SpringBoot默认的静态资源目录,例如如果按示例中配置,则无法再访问static、public、resources等目录下的资源了。
:::
- 目录优先级:/META-INF/resources > /resources > /static > /public
自定义静态资源目录:通过实现接口
现在就来自定义一个静态资源目录,定义一个images的目录来存放图片,所有/image/**的路径都会访问images目录下的资源:WebMvcConfigurer重写addResourceHandlers
增加配置类MyWebMvcConfigurer```java import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration public class MyWebMvcConfigurer implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { registry.addResourceHandler(“/image/**”).addResourceLocations(“classpath:/image/“); } }
这段代码应该比较简单,`@Configuration` 标识一个配置类。<br />`WebMvcConfigurerAdapter`是Spring提供的一个配置mvc的适配器,里面有很多配置的方法,`addResourceHandlers`就是专门处理静态资源的方法<a name="L7USa"></a>### 将静态资源通过流直接返回给前端在maven工程的resources的根目录下建立一个html的目录,然后把html文件放在该目录下,并且规定任何访问路径以/static/开头的即访问该目录下的静态资源,其实现如下:```java@Controllerpublic class StaticResourceController {@RequestMapping("/static/**")public void getHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {String uri = request.getRequestURI();String[] arr = uri.split("static/");String resourceName = "index.html";if (arr.length > 1) {resourceName = arr[1];}String url = StaticResourceController.class.getResource("/").getPath() +"html/" + resourceName;try {FileReader reader = new FileReader(new File(url));BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();String line = br.readLine();while (line != null) {sb.append(line);line = br.readLine();}response.getOutputStream().write(sb.toString().getBytes());response.flushBuffer();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
其实现过程很简单,就是先从路径中分离出来资源uri,然后从static目录下读取文件,并输出到前端。
因为只做简单演示,所以这里只处理了文本类型的文件,图片文件可以做类似的处理。当然,在实际中肯定不会这么做,Spring Boot 也肯定有更好的解决办法。
不过这个办法虽然有点笨,但确是最本质的东西,无论框架如何方便的处理了这类问题,但是抛开框架,依然要能够熟练的写出一个web项目,只有知道其实现原理,才会在遇到问题时能得心应手。
SpringBoot静态资源路径获取方式
方式一
String path = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader().getResource("").getPath();
方式二
ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("static/icon.png");InputStream inputStream = classPathResource.getInputStream();
直接获取,无需配置静态目录;
相比上一种方式,这种方法不会在linux或者jar上失效!
总结
方式二的静态资源获取方式要优于第一种。

