- 1、InputStream转化为String
- 1、使用
InputStreamReader和StringBuilder(JDK) - 2、使用
inputStream.read()andStringBuilder - 3、使用
ByteArrayOutputStreamandinputStream.read - 4、使用
BufferedInputStream和ByteArrayOutputStream - 5、使用
BufferedReader - 6、使用 Stream API 或 parallel Stream API
- 7、使用
StringWriter和IOUtils.copy (Apache Commons) - 8、使用
CharStreams(Google Guava) - 9、JDK原生提供
- 1、使用
- 2、String转化为InputStream
1、InputStream转化为String
1、使用 InputStreamReader 和 StringBuilder (JDK)
public class InputStream2String {public static void main(String[] args) {try {InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("E:/duckAndJava/IO/testFile.txt"); //路径修改为本地文件所在的位置char[] buffer = new char[1024]; //根据需要的数组大小进行自定义StringBuilder out = new StringBuilder();Reader in = new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "UTF-8");for (int numRead; (numRead = in.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) > 0; ) {out.append(buffer, 0, numRead);}String myString = out.toString();System.out.println("myString = " + myString);}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}
2、使用 inputStream.read() and StringBuilder
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (int ch; (ch = inputStream.read()) != -1; ) {sb.append((char) ch);}String myString = sb.toString();
3、使用 ByteArrayOutputStream and inputStream.read
ByteArrayOutputStream result = new ByteArrayOutputStream();byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];for (int length; (length = inputStream.read(buffer)) != -1; ) {result.write(buffer, 0, length);}String myString = result.toString("UTF-8");
ByteArrayOutputStream result = new ByteArrayOutputStream();byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];int length;while ((length = inputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {result.write(buffer, 0, length);}String str = result.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());return str;
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);ByteArrayOutputStream buf = new ByteArrayOutputStream();int result = bis.read();while(result != -1) {buf.write((byte) result);result = bis.read();}String str = buf.toString();return str;
4、使用 BufferedInputStream 和 ByteArrayOutputStream
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);ByteArrayOutputStream buf = new ByteArrayOutputStream();for (int result = bis.read(); result != -1; result = bis.read()) {buf.write((byte) result);}String myString = buf.toString("UTF-8");
5、使用 BufferedReader
String newLine = System.getProperty("line.separator");BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();for (String line; (line = reader.readLine()) != null; ) {if (result.length() > 0) {result.append(newLine);}result.append(line);}String myString = result.toString();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();String line;BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {sb.append(line);}String str = sb.toString();return str;
String result = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)).lines().collect(Collectors.joining(System.lineSeparator()));
String result = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)).lines().parallel().collect(Collectors.joining(System.lineSeparator()));
6、使用 Stream API 或 parallel Stream API
String myString = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)).lines().collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
或
String myString = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)).lines().parallel().collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
7、使用 StringWriter 和IOUtils.copy (Apache Commons)
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();IOUtils.copy(inputStream, writer, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());return writer.toString();
甚至可以直接这样用
String result = IOUtils.toString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
8、使用CharStreams(Google Guava)
String result = CharStreams.toString(new InputStreamReader(inputStream, Charsets.UTF_8));
//方法十二:String str = new String(ByteStreams.toByteArray(inputStream))
分别按照字符串长度来进行测试。
当使用的是一个小字符串(length=175),得到的性能测试结果如下: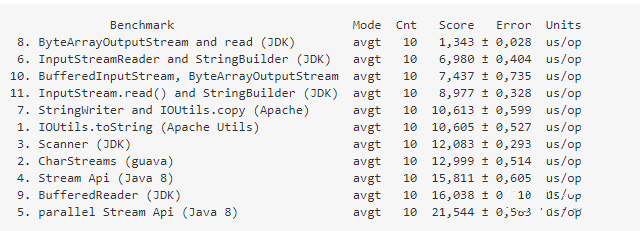
当使用的是一个长字符串(length=50100),得到的性能测试结果如下:
为了更加直观,按照字符串的长度与相应函数消耗的平均时间,做了如下的表格: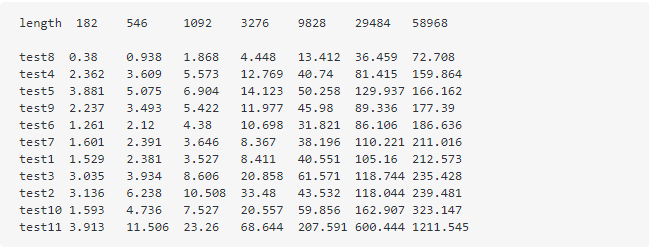
更加直观的表格图,如下: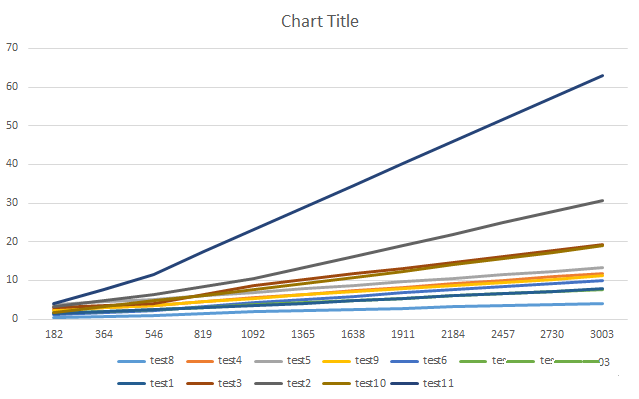
9、JDK原生提供
byte[] bytes = new byte[0];bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];inputStream.read(bytes);String str = new String(bytes);
Scanner s = new Scanner(inputStream).useDelimiter("\\A");String str = s.hasNext() ? s.next() : "";
String resource = new Scanner(inputStream).useDelimiter("\\Z").next();return resource;
2、String转化为InputStream
2.1 JDK原生提供
InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes());
2.2 Apache Common提供
InputStream targetStream = IOUtils.toInputStream(str, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
2.3 Google Guava提供
InputStream targetStream =new ReaderInputStream(CharSource.wrap(str).openStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());

