Java 队列
简单介绍下ArrayBlockingQueue与LinkedBlockingQueue。
对比
| queue | 阻塞与否 | 是否有界 | 线程安全保障 | 适用场景 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayBlockingQueue | 阻塞 | 有界 | 一把全局锁 | 生产消费模型,平衡两边处理速度 | 用于存储队列元素的存储空间是预先分配的,使用过程中内存开销较小(无须动态申请存储空间) |
| LinkedBlockingQueue | 阻塞 | 可配置 | 存取采用2把锁 | 生产消费模型,平衡两边处理速度 | 无界的时候注意内存溢出问题,用于存储队列元素的存储空间是在其使用过程中动态分配的,因此它可能会增加JVM垃圾回收的负担。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedQueue | 非阻塞 | 无界 | CAS | 对全局的集合进行操作的场景 | size() 是要遍历一遍集合,慎用 |
内存方面
ArrayBlockingQueue用于存储队列元素的存储空间是预先分配的,使用过程中内存开销较小(无须动态申请存储空间)LinkedBlockingQueue用于存储队列元素的存储空间是在其使用过程中动态分配的,因此它可能会增加JVM垃圾回收的负担。有界无界
ArrayBlockingQueue有界,适合已知最大存储容量的场景LinkedBlockingQueue可有界可以无界吞吐量
LinkedBlockingQueue在大多数并发的场景下吞吐量比ArrayBlockingQueue,但是性能不稳定。Linked queues typically have higher throughput than array-based queues but less predictable performance in most concurrent applications.
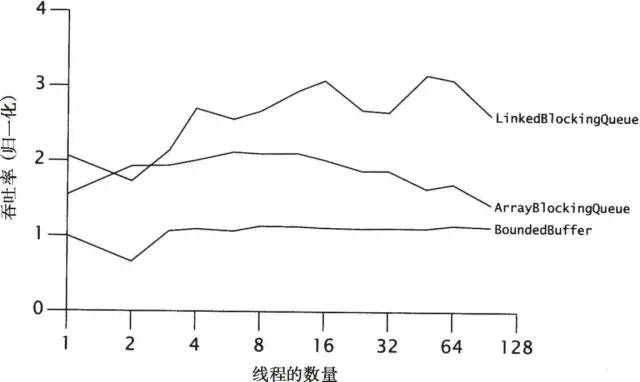
测试结果表明,LinkedBlockingQueue的可伸缩性要高于ArrayBlockingQueue。初看起来,这个结果有些奇怪:链表队列在每次插入元素时,都必须分配一个链表节点对象,这似乎比基于数组的队列执行了更多的工作。然而,虽然它拥有更好的内存分配与GC等开销,但与基于数组的队列相比,链表队列的put和take等方法支持并发性更高的访问,因为一些优化后的链接队列算法能将队列头节点的更新操作与尾节点的更新操作分离开来。由于内存分配操作通常是线程本地的,因此如果算法能通过多执行一些内存分配操作来降低竞争程度,那么这种算法通常具有更高的可伸缩性。
并发方面
ArrayBlockingQueue采用一把锁,两个condition```java /* Main lock guarding all access / final ReentrantLock lock;
/* Condition for waiting takes / private final Condition notEmpty;
/* Condition for waiting puts / private final Condition notFull;
/**
* Inserts element at current put position, advances, and signals.* Call only when holding lock.*/
private void enqueue(E x) { // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; // assert items[putIndex] == null; final Object[] items = this.items; items[putIndex] = x; if (++putIndex == items.length) putIndex = 0; count++; notEmpty.signal(); }
/**
* Extracts element at current take position, advances, and signals.* Call only when holding lock.*/
private E dequeue() { // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; // assert items[takeIndex] != null; final Object[] items = this.items; @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”) E x = (E) items[takeIndex]; items[takeIndex] = null; if (++takeIndex == items.length) takeIndex = 0; count—; if (itrs != null) itrs.elementDequeued(); notFull.signal(); return x; }
此外还支持公平锁```java/*** Creates an {@code ArrayBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed)* capacity and the specified access policy.** @param capacity the capacity of this queue* @param fair if {@code true} then queue accesses for threads blocked* on insertion or removal, are processed in FIFO order;* if {@code false} the access order is unspecified.* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity < 1}*/public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {if (capacity <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();this.items = new Object[capacity];lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);notEmpty = lock.newCondition();notFull = lock.newCondition();}
LinkedBlockingQueue头尾各1把锁 ```java /* Lock held by take, poll, etc / private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
/* Wait queue for waiting takes / private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
/* Lock held by put, offer, etc / private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
/* Wait queue for waiting puts / private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue if it is* possible to do so immediately without exceeding the queue's capacity,* returning {@code true} upon success and {@code false} if this queue* is full.* When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally* preferable to method {@link BlockingQueue#add add}, which can fail to* insert an element only by throwing an exception.** @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == capacity)
return false;
int c = -1;
Node
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { E x = null; int c = -1; long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); final AtomicInteger count = this.count; final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count.get() == 0) { if (nanos <= 0) return null; nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos); } x = dequeue(); c = count.getAndDecrement(); if (c > 1) notEmpty.signal(); } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } if (c == capacity) signalNotFull(); return x; }
<a name="fBnvg"></a>### 应用实例<a name="QBcQh"></a>#### `Executors`用了`LinkedBlockingQueue````javapublic static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());}public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),threadFactory);}public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));}public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),threadFactory));}
使用LinkedBlockingQueue实现logger
public class BungeeLogger extends Logger {private final ColouredWriter writer;private final Formatter formatter = new ConciseFormatter();// private final LogDispatcher dispatcher = new LogDispatcher(this);private final BlockingQueue<LogRecord> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();volatile boolean running = true;Thread recvThread = new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {while (!isInterrupted() && running) {LogRecord record;try {record = queue.take();} catch (InterruptedException ex) {continue;}doLog(record);}for (LogRecord record : queue) {doLog(record);}}};public BungeeLogger() throws IOException {super("BungeeCord", null);this.writer = new ColouredWriter(new ConsoleReader());try {FileHandler handler = new FileHandler("proxy.log", 1 << 24, 8, true);handler.setFormatter(formatter);addHandler(handler);} catch (IOException ex) {System.err.println("Could not register logger!");ex.printStackTrace();}recvThread.start();Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {running = false;}});}@Overridepublic void log(LogRecord record) {if (running) {queue.add(record);}}void doLog(LogRecord record) {super.log(record);writer.print(formatter.format(record));}}

