问题
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点
示例:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
\
5
输出: ["1->2->5", "1->3"]
思路
这道题目要求从根节点到叶子的路径,所以需要前序遍历,这样才方便让父节点指向孩子节点,找到对应的路径
在这道题目中将第一次涉及到回溯,因为我们要把路径记录下来,需要回溯来回退在进入另一个路径
前序遍历以及回溯的过程如图:
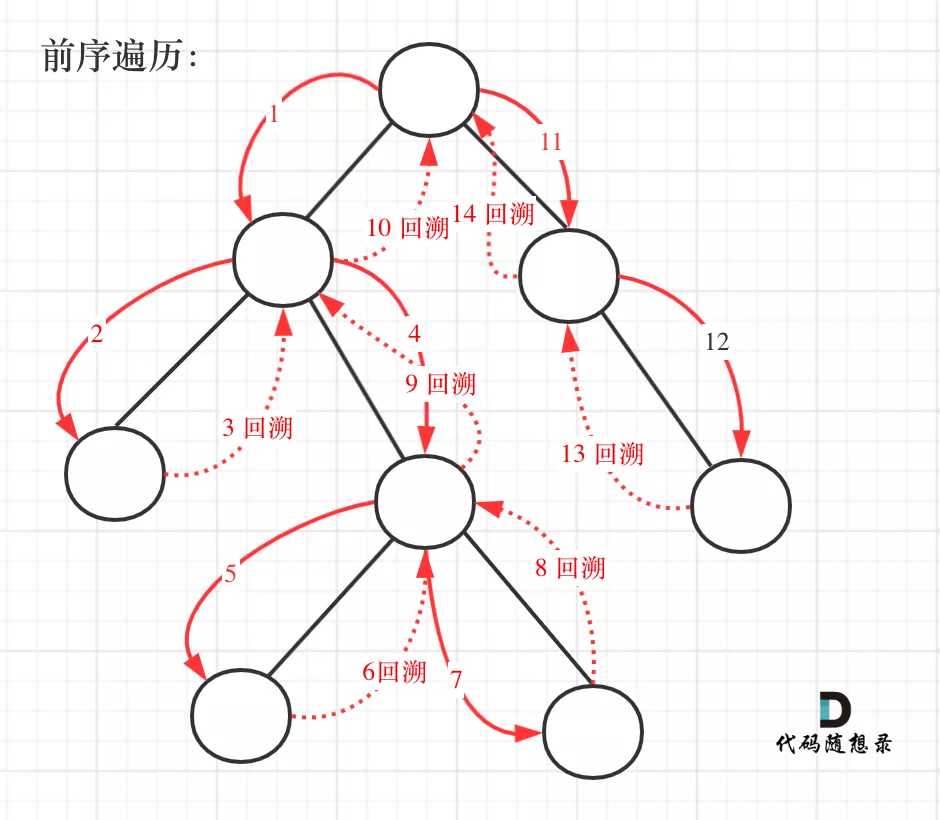
我们先使用递归的方式,来做前序遍历。要知道递归和回溯就是一家的,本题也需要回溯
解法一:递归
- 如果当前节点不是叶子节点,则在当前的路径末尾添加该节点,并继续递归遍历该节点的每一个孩子节点
- 如果当前节点是叶子节点,则在当前路径末尾添加该节点后我们就得到了一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径,将该路径加入到答案即可
- 当对字符串进行修改的时候,需要使用
**StringBuffer**和**StringBuilder**类 ```java //官解 class Solution { public ListbinaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
}List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();constructPaths(root, "", paths);return paths;
//记录每一条路径的 path,存放结果集的 paths
public void constructPaths(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> paths) {
if (root != null) {
StringBuffer pathSB = new StringBuffer(path);
pathSB.append(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { // 当前节点是叶子节点
paths.add(pathSB.toString()); // 把路径加入到答案中
} else {
pathSB.append("->"); // 当前节点不是叶子节点,继续递归遍历
constructPaths(root.left, pathSB.toString(), paths);
constructPaths(root.right, pathSB.toString(), paths);
}
}
}
}
```java
//自解
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
constructPaths(root, "", paths);
return paths;
}
//记录每一条路径的 path,存放结果集的 paths
public void constructPaths(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> paths) {
if (root != null) {
//StringBuffer pathSB = new StringBuffer(path);
path += root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { // 当前节点是叶子节点
paths.add(path); // 把路径加入到答案中
} else {
path += "->"; // 当前节点不是叶子节点,继续递归遍历
constructPaths(root.left, path, paths);
constructPaths(root.right, path, paths);
}
}
}
}
解法二:广度优先遍历
我们维护一个队列,存储节点以及根到该节点的路径。一开始这个队列里只有根节点。在每一步迭代中,我们取出队列中的首节点,如果它是叶子节点,则将它对应的路径加入到答案中。如果它不是叶子节点,则将它的所有孩子节点加入到队列的末尾。当队列为空时广度优先搜索结束,我们即能得到答案
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
if (root == null) {
return paths;
}
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<String> pathQueue = new LinkedList<String>();
nodeQueue.offer(root);
pathQueue.offer(root.val);
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();
String path = pathQueue.poll();
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
paths.add(path);
} else {
if (node.left != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.left);
pathQueue.offer(new StringBuffer(path).append("->").append(node.left.val).toString());
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.right);
pathQueue.offer(new StringBuffer(path).append("->").append(node.right.val).toString());
}
}
}
return paths;
}
}

