问题
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点
示例 1: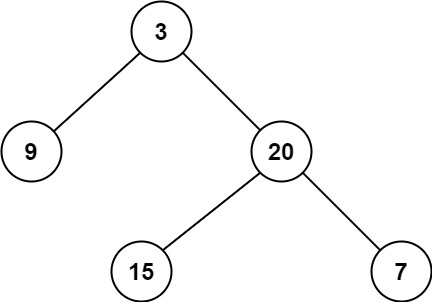
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
思路
在求解树的最大深度和最小深度,直觉上好像是差不多的,其实还是差不少的
最大深度很容易理解,最小深度可有一个误区,如图:
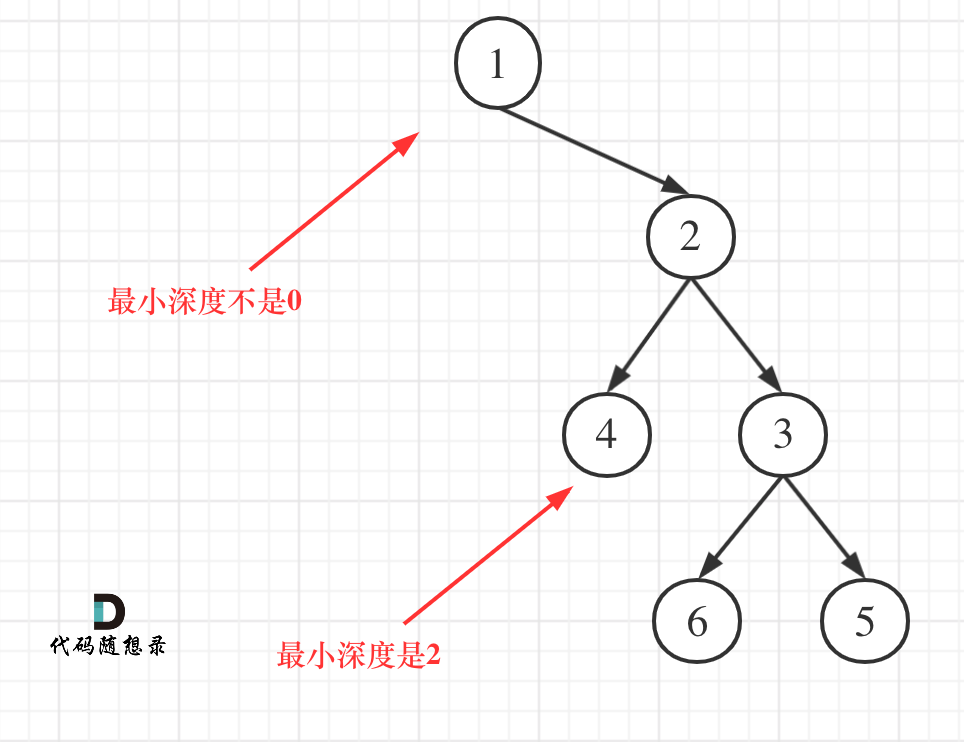
这就重新审题了,题目中说的是:最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。注意是叶子节点
而左右孩子都为空的节点才是叶子节点
解法一:递归法
递归三部曲:
确定递归函数的参数和返回值
- 参数为要传入的二叉树根节点,返回的是int类型的深度。
int getDepth(TreeNode node)
- 参数为要传入的二叉树根节点,返回的是int类型的深度。
确定终止条件
- 终止条件也是遇到空节点返回
0,表示当前节点的高度为0if (node == NULL) return 0;
- 终止条件也是遇到空节点返回
确定单层递归的逻辑
- 这块和求最大深度可就不一样了,一些同学可能会写如下代码:
这个代码就犯了此图中的误区:int leftDepth = getDepth(node.left);int rightDepth = getDepth(node.right);int result = 1 + Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth);return result;
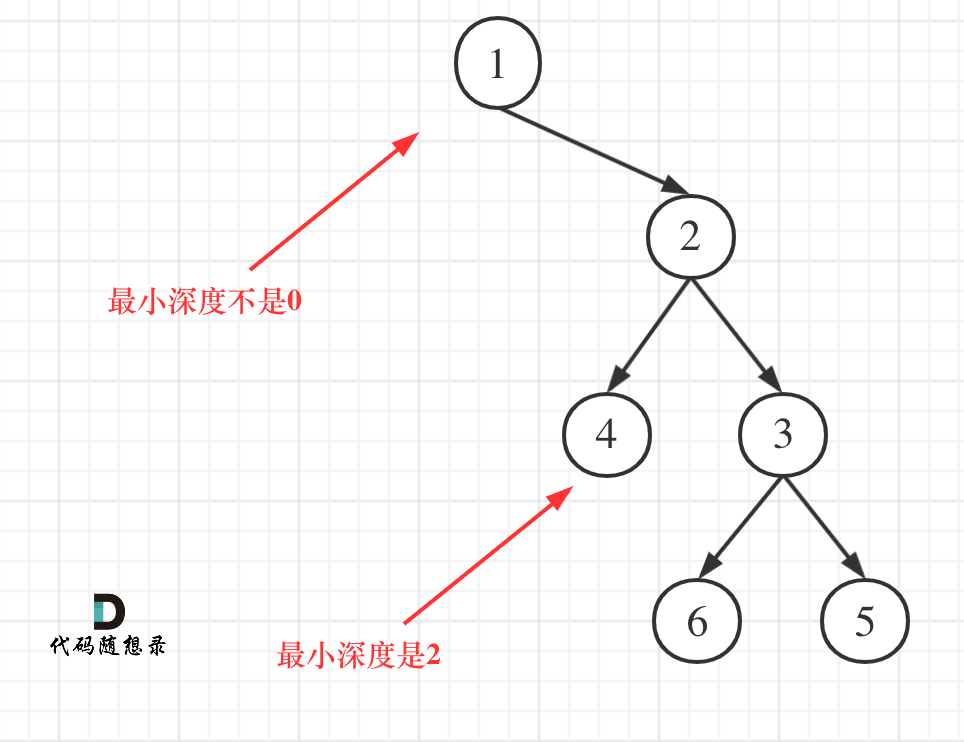
如果这么求的话,没有左孩子的分支会算为最短深度
- 这块和求最大深度可就不一样了,一些同学可能会写如下代码:
所以,如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是
1 + 右子树的深度反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是
1 + 左子树的深度。最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1//官解:分别计算左右子树最小叶子节点的深度class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {return 1;}int min_depth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;if (root.left != null) {min_depth = Math.min(minDepth(root.left), min_depth);}if (root.right != null) {min_depth = Math.min(minDepth(root.right), min_depth);}return min_depth + 1;}}
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {return getDepth(root);}public int getDepth(TreeNode root){if (root == null){return 0;}int leftDepth = getDepth(root.left); // 左int rightDepth = getDepth(root.right); // 右// 中// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点if (root.left == null && root.right != null) {return 1 + rightDepth;}// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点if (root.left != null && root.right == null) {return 1 + leftDepth;}int result = 1 + Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth);return result;}}
解法二:广度优先遍历
//自解class Solution{public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();deque.offer(root);int level = 1;while (!deque.isEmpty()) {int size = deque.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode cur = deque.poll();if (cur.right == null && cur.left == null){return level;}if (cur.left != null){deque.offer(cur.left);}if (cur.right != null){deque.offer(cur.right);}}level++;}return level;}}
//官解class Solution {class QueueNode {TreeNode node;int depth;public QueueNode(TreeNode node, int depth) {this.node = node;this.depth = depth;}}public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}Queue<QueueNode> queue = new LinkedList<QueueNode>();queue.offer(new QueueNode(root, 1));while (!queue.isEmpty()) {QueueNode nodeDepth = queue.poll();TreeNode node = nodeDepth.node;int depth = nodeDepth.depth;if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {return depth;}if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(new QueueNode(node.left, depth + 1));}if (node.right != null) {queue.offer(new QueueNode(node.right, depth + 1));}}return 0;}}作者:LeetCode-Solution链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/solution/er-cha-shu-de-zui-xiao-shen-du-by-leetcode-solutio/来源:力扣(LeetCode)著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
- 时间复杂度:
,其中
N是树的节点数。对每个节点访问一次 - 空间复杂度:
,其中
N是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于队列的开销,队列中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数

